TRIPLE ONLY: protein synthesis (DNA and RNA part 2)
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
TRIPLE: the stages of protein synthesis
What is protein synthesis? Where does protein synthesis take place?
The making of proteins
In the cytoplasm
Why can't DNA take the genetic info to the site of protein synthesis?
It is too big
This means that for proteins to be made, the genetic code must be copied and then transferred out of the nucleus by another type of nucleic acid called (full name)
RNA or ribonucleic acid
What are the types of RNA?
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) -- ribosomes are made of RNA and protein
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
What is mRNA?
A single stranded copy of the DNA code and carries this genetic code out of the nucleus and binds to ribosome
What is tRNA?
A molecule found in the cytoplasm of cells that carry the correct amino acids to the ribosome.
There is a complementary base pairing where the codon on the mRNA binds to the anticodon on the tRNA
What are the two stages of protein synthesis?
Transcription and translation
Transcription: where does it take place and what is its role?
It is a stage of protein synthesis that occurs in the nucleus of the cell and its role is to produce a copy of a section of DNA (gene) in the form of a singular strand of mRNA
Describe what happens during transcription
DNA unzips as hydrogen bonds between bases break and template strand is exposed
RNA nucleotides line up alongside the template strand according to the complementary base pairing rules
the building blocks of mRNA are RNA nucleotides
One at a time the RNA nucleotides are linked by RNA polymerase to form a single strand of mRNA
They form bonds between their ribose and phosphate groups to form the sugar-phosphate backbone
When a section of DNA corresponding to a protein (a gene) has been transcribed, the mRNA molecule breaks off and leaves the nucleus through the pores in the nuclear membrane

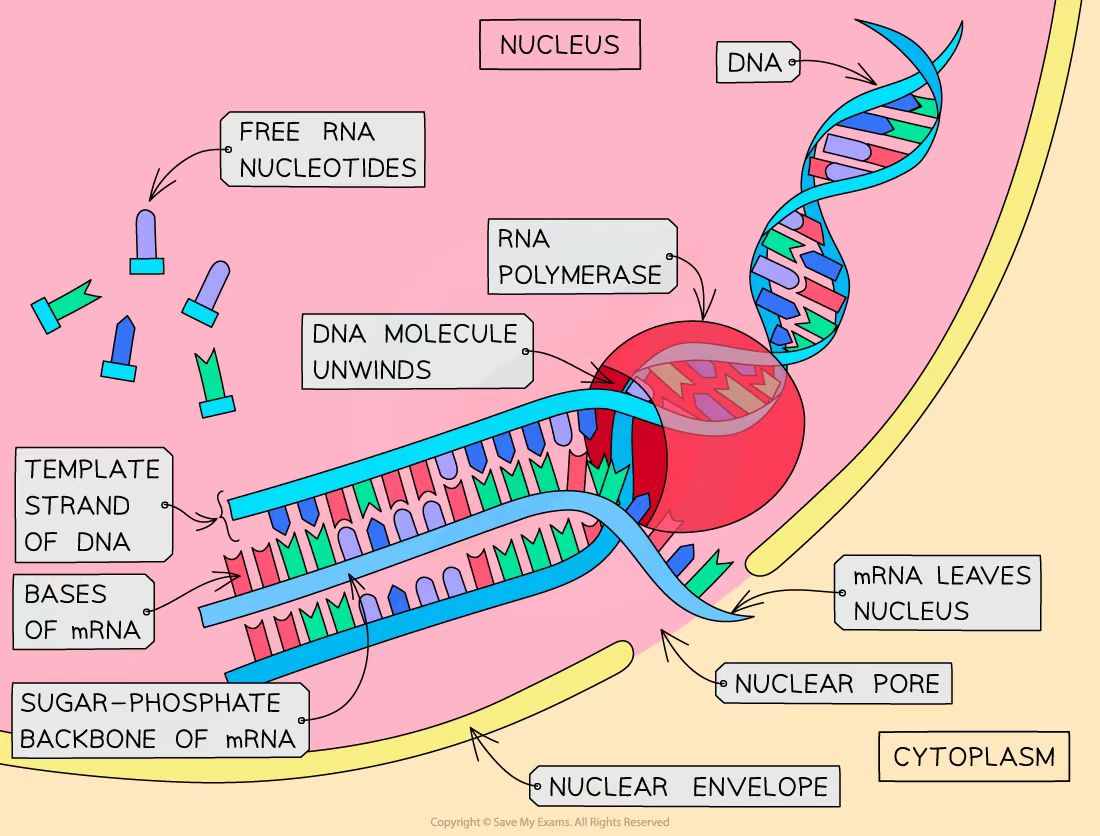
What happens after the mRNA molecule leaves the nucleus?
The DNA helix zips up again
The new strand of mRNA is a _ copy of the DNA code from the original gene
Because of the the triplet code of the DNA is converted into a triplet code in the mRNA
complementary
complementary base pairing
Translation: what is its role and where does it take place?
Occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell and it is when the code in the mRNA is converted into a chain of amino acids that will form a protein
What is the structure of a tRNA molecule?
Anticodon of bases on one end, a site where a specific amino acid can attach on the other end
Image: tRNA molecule with the anticodon UAC carrying the amino acid methionine
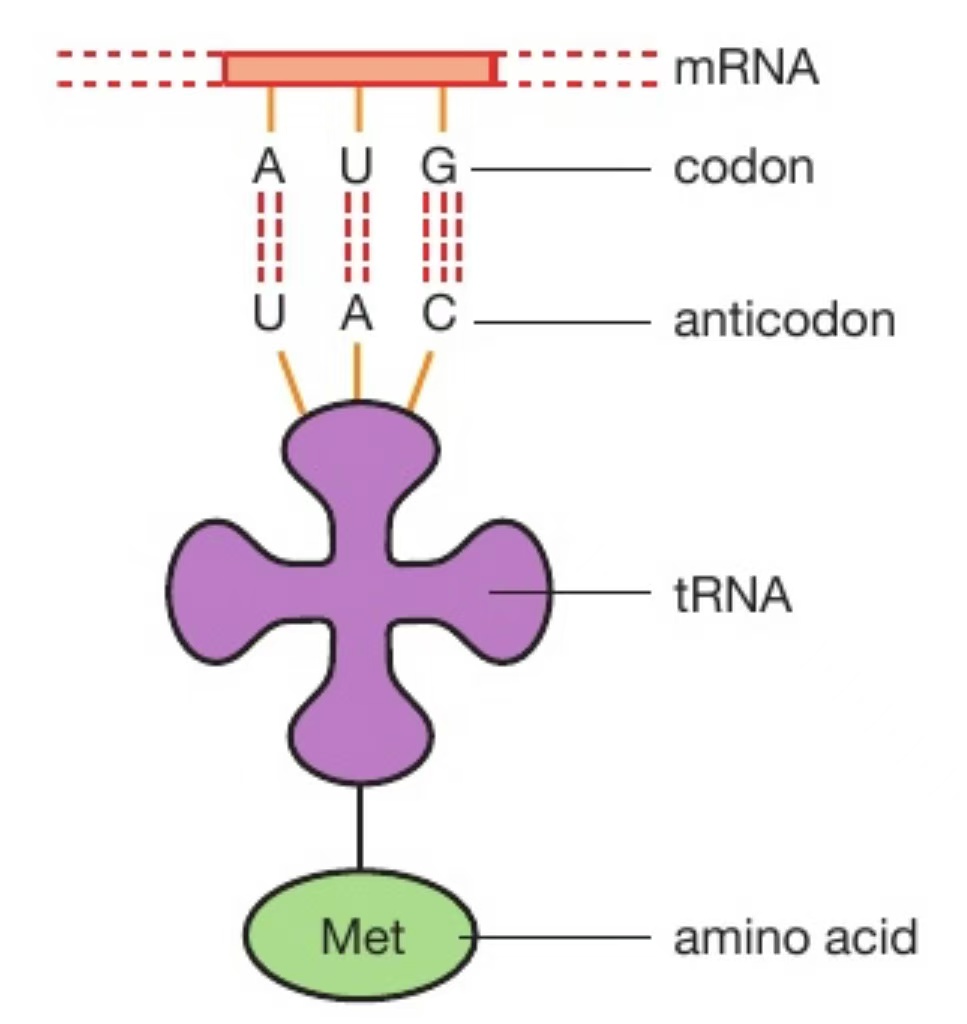
How are enzymes and tRNA similar?
There is a particular tRNA molecule for each type of amino acid
There is a particular enzyme for each substrate
Describe what happens in the translation stage of protein synthesis
mRNA attaches to a ribosome (1)
mRNA has codons / is a template (1)
ribosome moves along mRNA strand (1)/ allow ribosome moves to next codon
mRNA is a chain so not all of it fits inside the ribosome. Cada vez que the codon is finished pairing with anticodon, the mRNA strand will shift to the side so the next codon can be paired
tRNA brings amino acids (to ribosome) (1)
Sometimes it is a separate mark: tRNA binds to mRNA/
anticodon (on tRNA) binds with codon (on mRNA) / allow codon is complementary to anticodon
5.5 not in ms BUT NEED TO KNOW: a second tRNA molecule attaches to its complementary codon on the mRNA and a peptide bond is fromed between the two neighbouring amino acids. The first tRNA molecule is released and goes off but its amino acid stays bonded to the other one
amino acid chain produced / amino acid joined / polypeptide (1) → a protein is a polypeptide
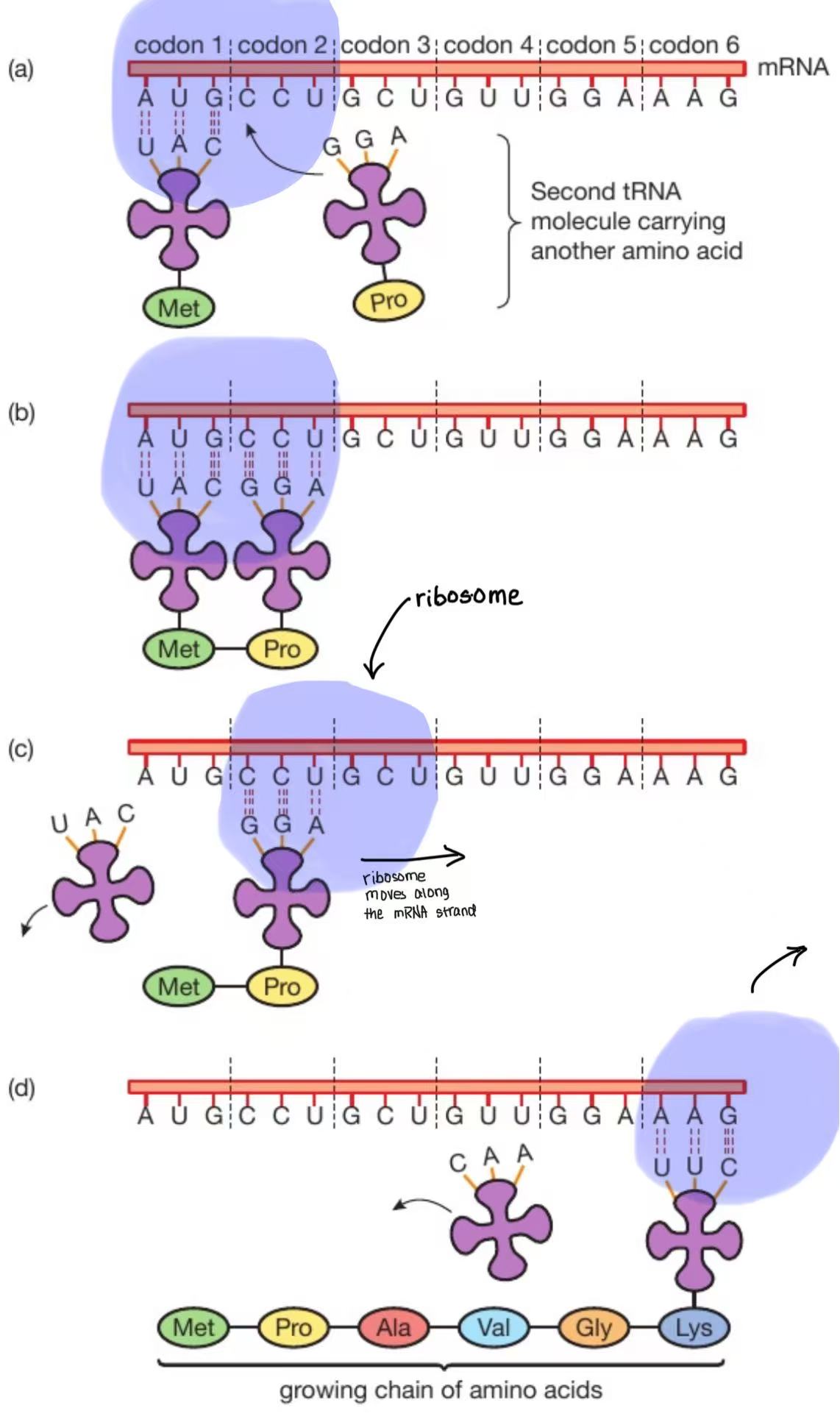
What is the bond between each amino acid?
peptide bond
After a peptide bond forms between each amino acid, what does the tRNA molecule do?
It goes off/detaches (se desvincula del amino acid) to collect another amino acid
When does this process stop?
when a stop codon is reached signalling to the translation to stop as the amino acid coded for by the mRNA molecule is complete and the protein has been formed which is then released
What are codons?
They are a triplet of bases in a mRNA molecule that code for a specific amino acid.
3 bases = one amino acid
CCU = amino acid proline
A student reads that DNA codons are non-overlapping. Suggest what is meant by the term non-overlapping. You should refer to the sequence of bases in your answer (2)
An explanation that makes reference to the following two points:
each triplet / codon codes for one amino acid / eq (1)
codons are discrete / independent of each other / nucleotides / bases are not shared between codons / eq (1)
example of triplet reading frames, e.g. CAT TCA / eq (1)
what are anticodons?
A triplet of bases found on the tRNA molecule. Each anticodon is complementary to one codon on the mRNA.
What are ribosomes?
A structure made of rRNA and proteins found in the cytoplasm of cells that reads the genetic code on mRNA and linking the corresponding amino acids in a chain to form a protein
Describe the differences between the processes of transcription and translation (4). There are two extra ones but not in 2023qp ms but yes in the 2020 ms
2023 qp
Location
transcription in nucleus / eq(1)
or translation takes place in cytoplasm/eq
Producestranscription produces mRNA/ e q (1)
translation produces amino acid chain/polypeptide/protein
Starts withtranscription starts with DNA /eq (1)
translation starts with mRNA
Usesno tRNA in transcription /eq (1)
translation uses tRNA
Extra (but not in this question) if the question is 5 marks and not 4 marks: from 2020 qp
DNA unzips/one strand is copied
anticodons binds to codons
Describe the roles of RNA in protein synthesis (4)
transcription produces mRNA / eq (1)
mRNA copies code of DNA strand / DNA code copied / carried by mRNA / eq (1)
mRNA moves out of nucleus / into cytoplasm / eq (1)
binds with ribosome / eq (1)
tRNA brings amino acids to ribosome /eq (1)
anticodon binds with codons /eq (1)
translation produces polypeptide / protein / amino acid chain (1)
Key point:
When teenagers hit puberty and grow + develop at a fast rate, why do they need to eat more?
Some hormones involved in puberty (pituitary) are proteins and our tissues are made of proteins (grow tissues)
KEY POINT: protein synthesis is a very energy demanding process and uses a lot of the ATP made by the cell
so more glucose intake for more respiration for more release of enrgy ATP
Because protein synthesis is so energy intensive, it uses a lot of the ATP made by the cell that could be used for other cellular functions like:
active transport
muscle contraction
The DNA molecule codes for the amino acids used to make proteins.
There are four different bases in DNA and 20 amino acids used to make proteins.
Use this information to show that a minimum of three bases on the DNA molecule is needed to code for each amino acid (3)
(if read in threes) = 43 or 4 x 4 x 4 (1)
= 64 (1)
(64 is) greater / more than 20 (combinations) required / needed / eq (1)
(if read in twos) = 42 or 4 x 4 = 16 (1)
There are 20 different amino acids so there needs to be at least 20 different codons (and 20 diff anticodons). So why are there 64 codons?
Some amino acids use more than one triplet code.
-e.g th mRNA codons GGU, GGC, GGA, GGG all code for the amino acid glycine