Oxy-Hgb Dissociation Curve
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
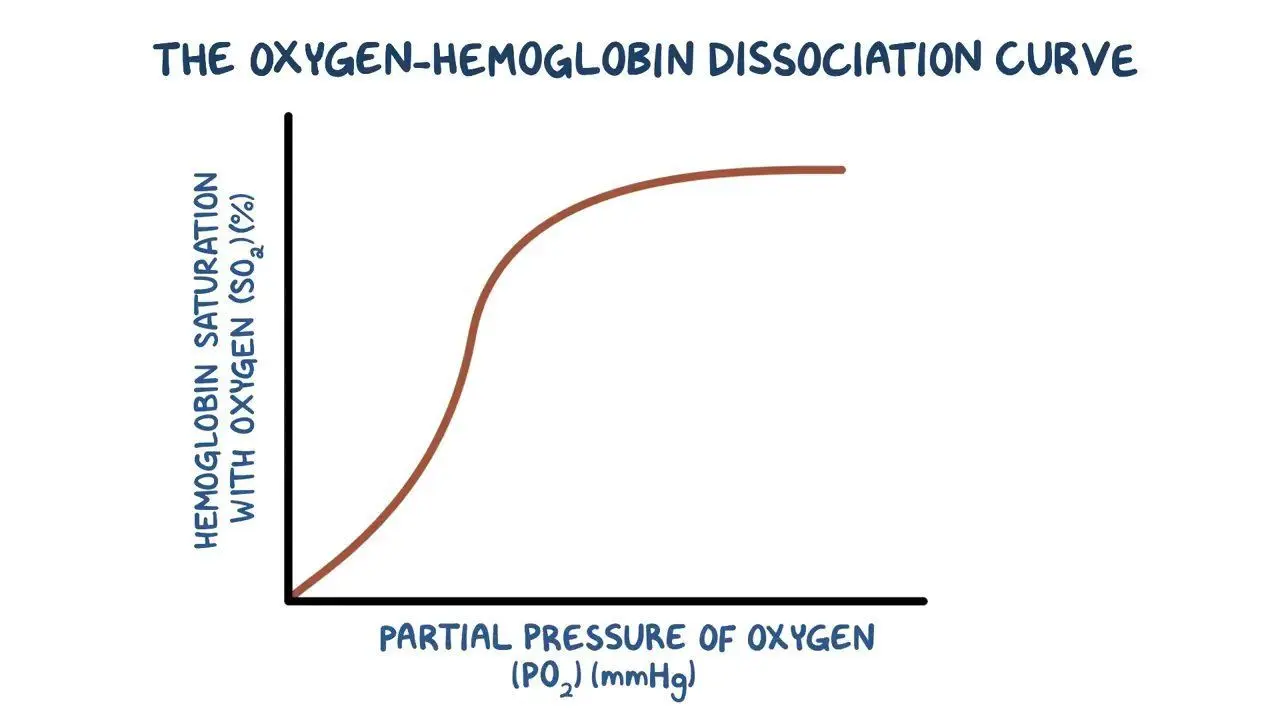
Oxygen-Hemoglobin Dissociation Curve - Summary
The percentage of saturated hemoglobin vs the partial pressure of oxygen, determined by oxygen affinity. Affected by: pH, pCO2, 2-3 DPG, temperature
Oxy-Hgb Axis
Vertical: % saturated hemoglobin
Horizontal: pO2 (mmHg)
Positive Cooperativity
Each O2 molecule bound to Hgb increases Hgb’s affinity for O2
P50
The partial pressure of O2 where 50% of Hgb is saturated
A left shift causes a ___ in p50
decreased
A right shift causes a ___ p50
increased
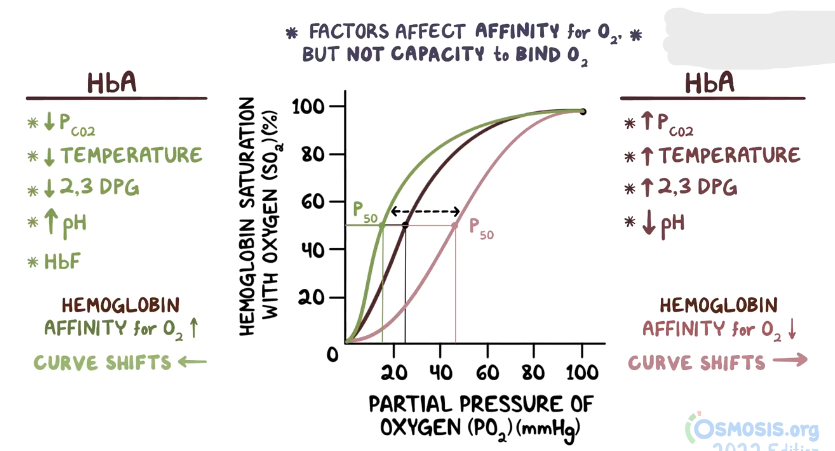
Oxy-Hgb Dissociation Curve Overview
pH change will be the same as O2 affinity (increased pH = increased O2 affinity)
All other factors will be opposite (pCO2; 2,3-DPG; temperature)
Increased pCO2 causes a ___ shift
Right
Decreased pCO2 causes a ___ shift
Left
Increased pH causes a ___ shift
Left
Decreased pH causes a ___ shift
Right
Increased temperature causes a ___ shift
Right
Decreased temperature causes a ___ shift
Left
Increased 2,3-DPG causes a ___ shift
Right
Decreased 2,3-DPG causes a ___ shift
Left
Fetal hemoglobin has a ___ shift compared to maternal hemoglobin
Left
Carbon monoxide causes what to happen to the Oxy-Hgb curve?
Causes a left shift and flattens curve at the % O2 saturation
CO has a 250x ___ affinity for o2
Higher