PSYC 406 Intelligence Test
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:20 PM on 11/22/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
1
New cards
purpose of intelligence/ability testing
provide guidance, asses cognitive strengths/weaknesses, decision-making, diagnosis
2
New cards
Frances Galton
first to try to measure differences in intellectual capacities; intellectual differences were differences in sensation and perception abilities, human abilities have a normal distribution
3
New cards
Albert Binet
created Stanford-Binet test to id kids with special needs; intelligence comprised of complex mental acts (ex. imagination, memory, reasoning, etc.); first practical intelligence test
4
New cards
Stanford-Binet Test
identified tasks: age, school achievement, teacher's perception of ability
goal of test: judge, understand, and reason well
goal of test: judge, understand, and reason well
5
New cards
Binet Test norms
age norms that provide age equivalent score(mental age)
cut-offs: idiot, imbecile, moron, normal
cut-offs: idiot, imbecile, moron, normal
6
New cards
David Weschler
arranged items according to content(subtests); 3 scores(IQ, VIQ, PIQ)
7
New cards
problem with IQ
score did not represent same relative position at one age as another
8
New cards
Wechsler scales of intelligence
preschool and primary scale of intelligence(2-7 years), intelligence scale for children(6-16 years), adult intelligence (16-90 years)
9
New cards
Spearman's Two-Factor Theory
two components: general variation(g-factor) and specific variance (s-factor+ error variance)
10
New cards
fluid intelligence (Gf)(Cattel-Horn)
problem-solving and info processing ability that is largely independent of experience
11
New cards
crystallized intelligence (Gc) (Cattel-Horn)
breadth and depth of general knowledge
12
New cards
other measured abilities in Cattel-Horn
visualization processing, processing speed, short-term memory
13
New cards
Three-stratum theory (hierarchical model) (Carrol)
stratum 1-3
14
New cards
Stratum 3
Broad cognitive ability
15
New cards
Stratum 2
General ability factors
16
New cards
Stratum 1
Narrowly defined cognitive abilities
17
New cards
WISC-V
Individual administration to assess cognitive function of kids 6-16
18
New cards
Picture concepts (fri)
Measure abstract, fluid, categorical reasoning ability
Child presented to two or three of images and asked to match similar ones
Child presented to two or three of images and asked to match similar ones
19
New cards
Letter -number sequencing (WMI)
Repeat letter and numbers in order
20
New cards
Cancellation (psi)
Connect objects that are all the same category (times compared to norm)
21
New cards
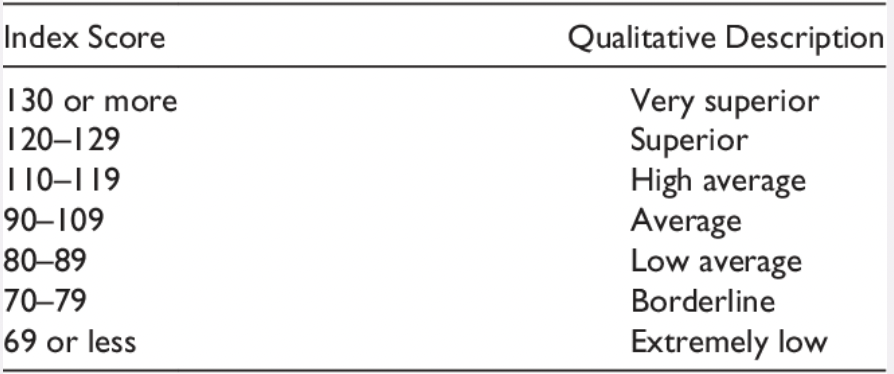
IQ scores meaning
look at picture