business, leadership, decision making (unit 1+2) ✅
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
What is the purpose of a PESTLE analysis
Examines the external macro-environment that a business operates in:
Political
Economic
Social
Technological
Legal
Environmental
What are the main strategic positioning options for a business
Cost leadership - competing on the basis of low prices
Differentiation - offering unique products/services
Focus - targeting a specific market segment
6 key business objectives
Profit
Growth
Cash flow
Survival
Ethical
Social
What acronym describes how business objectives should be
SMART
What does SMART stand for
Specific
Measurable
Achievable
Relevant/Realistic
Timely
5 reasons why businesses set objectives
Provide a clear focus for decision making
Motivates employees
Reduces uncertainty
Provides a target
Provides a criteria for evaluating performance
Hierarchy of objectives
Mission statement
Corporate objectives
Departmental/functional objectives
Total revenue =
Price x Quantity sold
Profit =
Total Revenue - Total Costs
Total costs =
Total Fixed Costs + Total Variable costs
Total Variable costs =
Variable cost per unit x Quantity sold
What is profit
Reward business owners achieve from taking risks and making investments
What is revenue
Achieved from the trading activities of a business, also known as turnover or sales
What are costs
Amounts that a business incurs in order to make goods or produce services
What are variable costs and some examples
Costs that change in relation to output:
Raw materials
Wages
Marketing costs
What are fixed costs and some examples
Costs that do not change in relation to output:
Rent
Rates
Salaries
Advertising
What do unincorporated businesses have
Unlimited liability
Which 2 types of businesses are unincorporated
Sole trader/Sole proprietor
Partnerships
Which 2 types of businesses are incorporated
Private limited companies (Ltds)
Public limited companies (PLCs)
What is unlimited liability
When owners are personally responsible for the debts and liability of the business
Who owns Ltd’s
Shareholders, shares are not traded publicly or on a stock exchange
What is a PLC
A type of limited company where shares may be on a public stock market
What is a public sector company
A company owned and controlled by the government
What is a public sector organisation
Organisation funded by government which provides goods and services operated by public bodies
What is a a non-profit organisation
Business that trade in order to benefit the community
What is a social entreprise
Organisations with the purpose of aiding society or the environment
4 key issues with different business forms
Unlimited and limited liability
Ordinary share capital
Market capitalisation
Dividends
What is ordinary share capital
Money raised by a business through the sale of new shares
What is market capitalisation
The total market value of the issued share capital of a company
What are dividends
Payments made by a company to its shareholders taken from profit made by the company
2 reasons why shareholders invest
Dividends
Increase in share price
How is a share price determined
Through the interaction of supply and demand
4 internal influences on share price
Financial performance
Dividend policy
Relationship with key investors
Management reputation
4 external influences on share price
State of the economy
General market sentiment
Whether the company is a takeover target
Alternative investments in the company’s sector
What are sole traders objectives most likely to be focused on
Survival, since a large proportion of start ups fail in the first few years
What are Ltd’s objectives likely to focus on
Market share
Customer satisfaction
Revenue growth
What are PLC’s objectives likely to focus on
Shareholders want higher dividends and rising share prices to maximise ROI
Objectives are related to profit maximisation
What does the external environment affect
Cost and demand
What is leadership
A relationship through which one person influences the behaviour or actions of others
4 types of management styles
Autocratic
Paternalistic
Democratic
Laissez-faire
3 influences on management styles
Personal value systems
Confidence in subordinates
Pressure
Managers experience
Type of organisation
What does the TannenBaum and Schmidt continuum show
A range of actions related to the:
Degree of authority used by managers
Area of freedom available to non managers
What are the 4 features of the TannenBaum and Schmidt continuum
Tell
Sell
Consults
Joins
Two approaches to decision making
Intuition
Scientific
4 considerations in decision making
Risk
Reward
Uncertainty
Opportunity cost
Decision tree
Used to map out potential choices
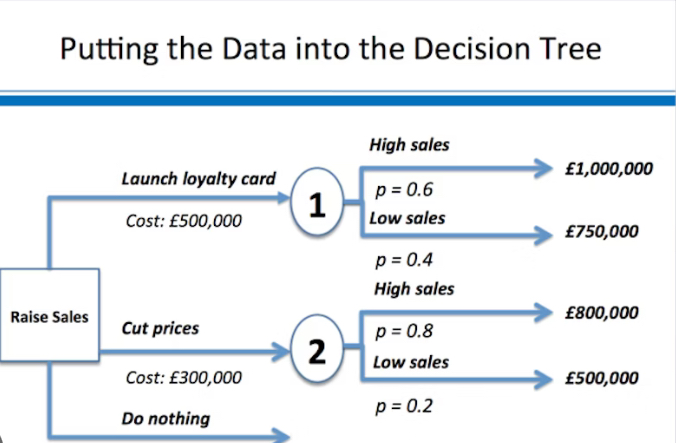
How to calculate expected value from a decision tree
Estimated financial effect x Probability
How to calculate net gain from a decision tree
Total expected value - Cost associated with decision
5 influences on decision making
Mission
Objectives
Ethics
External environment
Resource constraints
Quote from Jack Welch who supported intuitive and gut decision making
“Good business leaders create a vision, articulate the vision, passionately own the vision, and relentlessly drive it to completion
What is Daniel Kahneman’s 3 criteria for trusting your intuition
The situation is regular
You have had lots of practice
Immediate feedback
What is a stakeholder
Any individual who has a vested interest in the activities and decision making of a business
Examples of stakeholders
Shareholders
Business Owners
Managers
Employees
Customers
Suppliers
Banks
Local Community
Government
Stakeholder mapping

What is important for managing the relationship between different stakeholders
Communication and consultation
4 departments of a business
Finance
Marketing
Human Resources
Operations