7.3 - The Kidneys
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
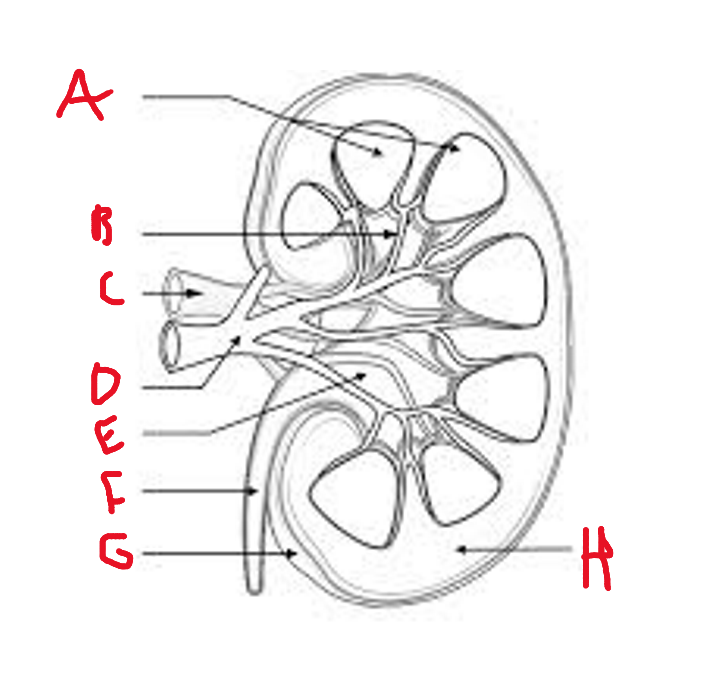
list what these are
A - renal pyramid
B - renal column
C - renal vein
D - renal artery
E - renal pelvis
F - ureter
G - renal capsule
H - renal cortex
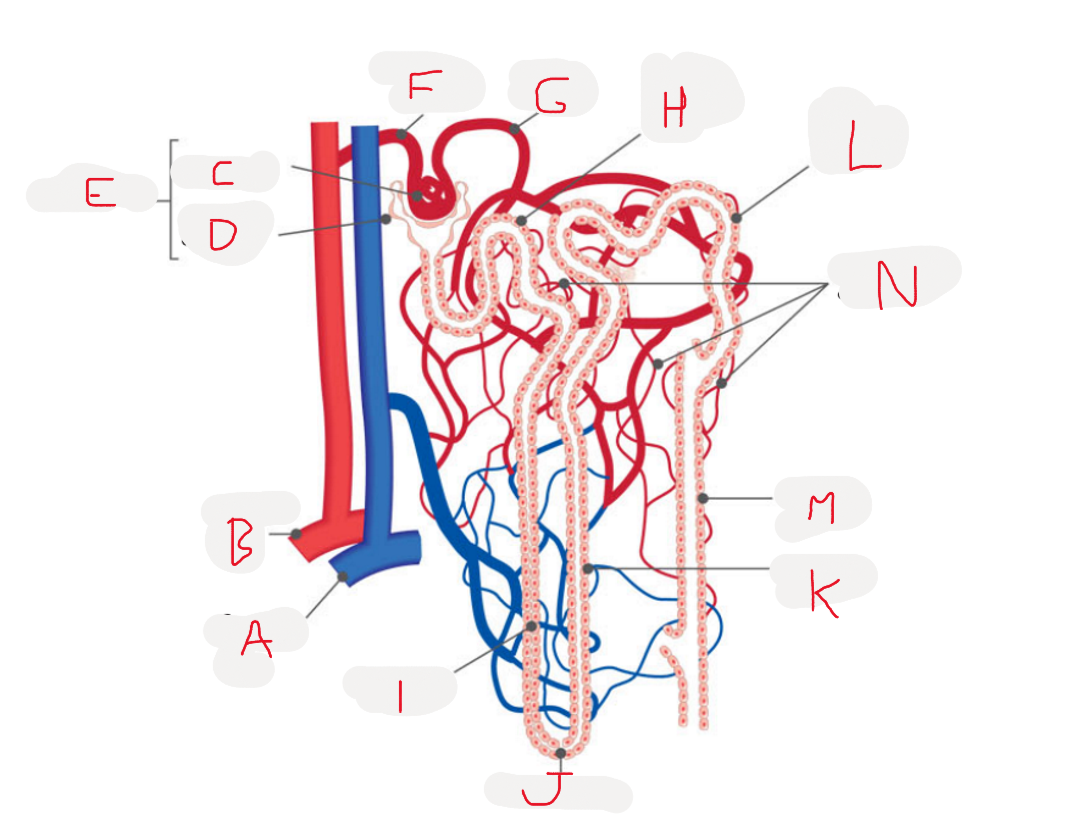
List what these are
A - branch of renal vein
B - branch of renal artery
C - glomerulus
D - glomerular capsule
E - renal capsule
F - afferent arteriole
G - efferent arteriole
H - proximal convoluted tubule
I - descending limb
J - loop of henle
K - ascending limb
L - distal convoluted tubule
M - collections duct
N - peritubular capillaries
what do the nephrons do
remove waste from the blood and regulate blood composition
how does blood enter and travel through the nephrons
enters kidney through renal artery
artery divides into arterioles
afferent arteriole forms glomerulus
efferent arteriole passes out renal capsule
efferent arteriole splits into peritubular capillaries that surround nephron
blood leaves kidneys out of renal vein
what are the three major processes involved in the production of urine
glomerular filtration
selective reabsorption
secretion by tubules
how is high blood pressure maintained in glomerular filtration
afferent arteriole is wider then efferent arteriole
how does the glomerular capsule’s wall help with filtration
it is only one cell thick so pressure forces fluid through semi permeable membrane into capsule
what is leftover after glomerular filtration
filtrate - no red/white blood cells or plasma but does contain
water, salt, amino acids, fatty acids, glucose, urea, uric acid, creatine, and hormones
why isnt all of the plasma filtered out in glomerular filtration
only 20% is filtered because there is continuous bloodflow
why do we need selective reabsorption and where does it occur
some filtered components are useful so selective reabsorption must take place in the cells lining the renal tubule
what are materials reabsorbed in selective reabsorption
water
glucose
amino acids
ions (sodium, potassium ect)
some wastes are partially reabsorbed (urea)
how does selective reabsorption change depending on the body’s needs
the permeability of the membrane can be changed to absorb more or lass water
this is an active process under hormonal control called facilitative reabsorption
what is tubular secretion
adding of materials to filtrate from blood, can be active or passive
what things are tubularly-secreted
penicillin, creatine, potassium, hydrogen ions
what does tubular secretion help maintain
blood pH of 7.4-7.5 be removing hydrogen and ammonium
urine pH
what happens during excretion
substances not reabsorbed drain from collecting ducts into renal pelvis
urine drains into ureters and is pushed by muscles into bladder
urethra carries urine from bladder to exterior of body
how is the formation of urine maximized by the kidney/nephrons (6)
glomerular capsules surround glomerulus to collect fluid filtered out blood capillaries
only two cells for filtrate to pass through
large volume of blood and continual flow maintains concentration gradient
efferent arteriole has smaller diameter to raise blook pressure
each tubule has a large SA due to two sets of convolutions and long loop
each kidney has over a million nephrons
why is a lot of water lost in urine
excreted substances have to be dissolved in a solution so half a liter minimum must be lost daily
how is uric acid produced
the metabolism of purines that come from food and the breakdown of nucleic acids
how is creatine produced
in muscles from breakdown of creatine phosphate
what can we observe from excreted substances
99% of water entering nephrons is reabsorbed
urine doesn’t contain much protein
urine doesn’t contain any glucose
main materials are urea, ions, uric acid, and creatine