CHEM121 CH 9 VOCAB
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
effusion
the process by which a gas escapes from its container through a tiny hole into a region of lower pressure
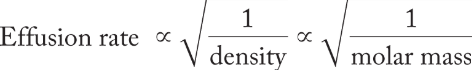
Graham’s law of effusion
the principle that the rate of effusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its molar mass
kinetic molecular theory (KMT)
a model that explains the behavior of gases on the basis of the motion of the particles that make them up
point masses
masses with essentially no volume
elastic
(referring to the collisions of gas molecules) - they result in no net transfer of energy to the walls

root-mean-square-speed (urms)
the square root of the average of the squared speeds of all the particles in a population of gas particles
universal gas constant
the constant R in the ideal gas equation; its value and units depend on the units used for the variables in the equation
diffusion
the spread of a substance (usually a gas or liquid) through another
mean free path
the average distance that a particle can travel through air or any gas before colliding with another particle
barometer
an instrument that measures atmospheric pressure
manometer
an instrument for measuring the pressure exerted by a gas
Boyle’s law
the principle that the volume of a fixed quantity of gas at constant temperature is inversely proportional to its pressure
Charles’s law
the principle that the volume of a fixed quantity of gas at constant pressure is directly proportional to its absolute temperature
Avogadro’s law
the principle that the volume of a gas at constant temperature and pressure is proportional to the quantity (number of moles) of the gas
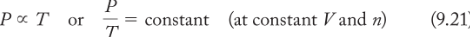
Amontons’s law
(the relationship between P and T, pressure and temperature) the principle that the pressure of a fixed quantity of gas is proportional to its absolute temperature if its volume does not change
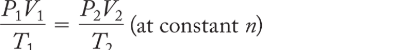
combined gas law
the principle that the ratio PV/T for a given quantity of gas is a constant
ideal gas
a gas whose behavior is predicted by the linear relations defined by the combined gas law
ideal gas equation
the principle relating the pressure, volume, number of moles, and temperature of an ideal gas, expressed by the equation PV = nRT, where R is the universal gas constant
standard temperature and pressure (STP)
0 degree C and 1 bar as defined by IUPAC, or 1 atm (pressure) in the US
partial pressure
the contribution to the total pressure made by a component in a mixture of gases
Dalton’s law of partial pressures
the principle that the total pressure of a mixture of gases is the sum of the partial pressures of all the gases in the mixture
mole fraction (xi)