Stage 2 - Homeostasis
1/40
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Homeostasis
The maintenance of a relatively constant internal environment to ensure the body can function.
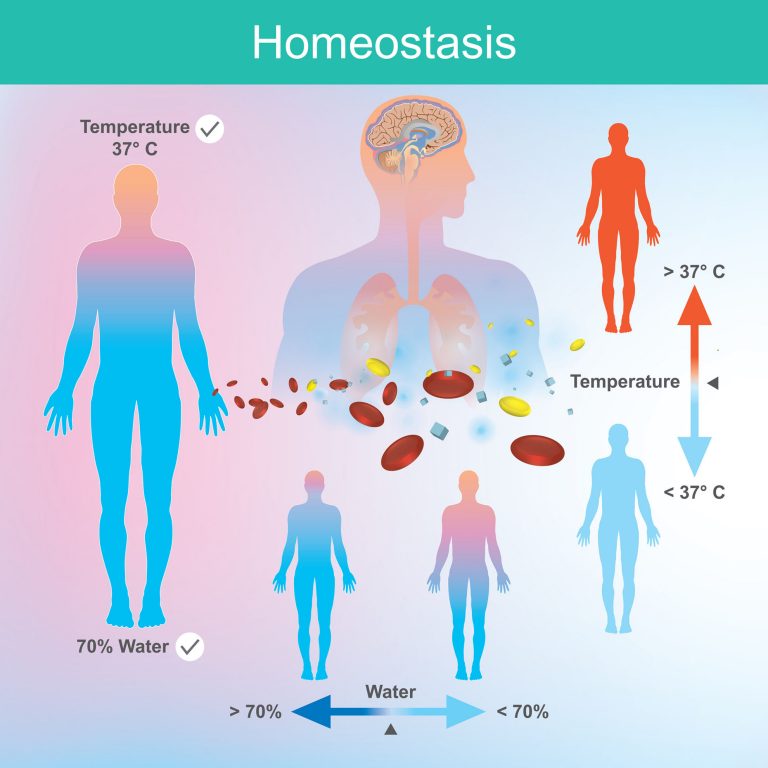
What factors have tolerance limits (4 points)?
Body temperature
Water availability
CO2 concentration in the blood and tissues
Blood glucose levels
Stimuli
Detectable changes in the internal and external environment.
What is the stimulus-response model used for?
To describe what happens when stimuli is detected, which involves different components and mechanisms.
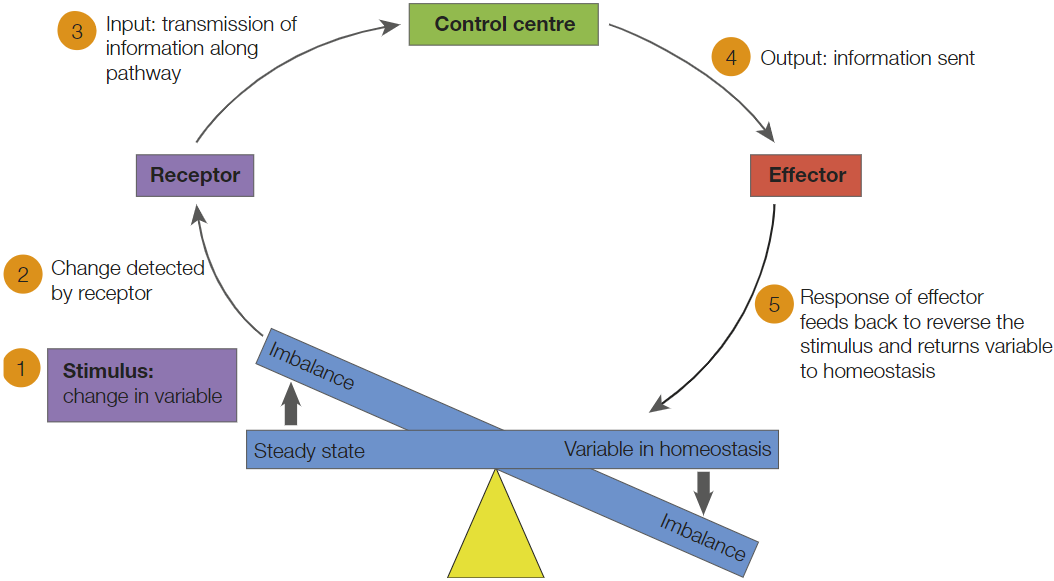
What is the difference between receptor and effector?
Receptors are cells or tissues that can detect stimuli whereas effectors are glands or muscles that initiates a response after receiving the information (which is the stimuli) from the control centre.
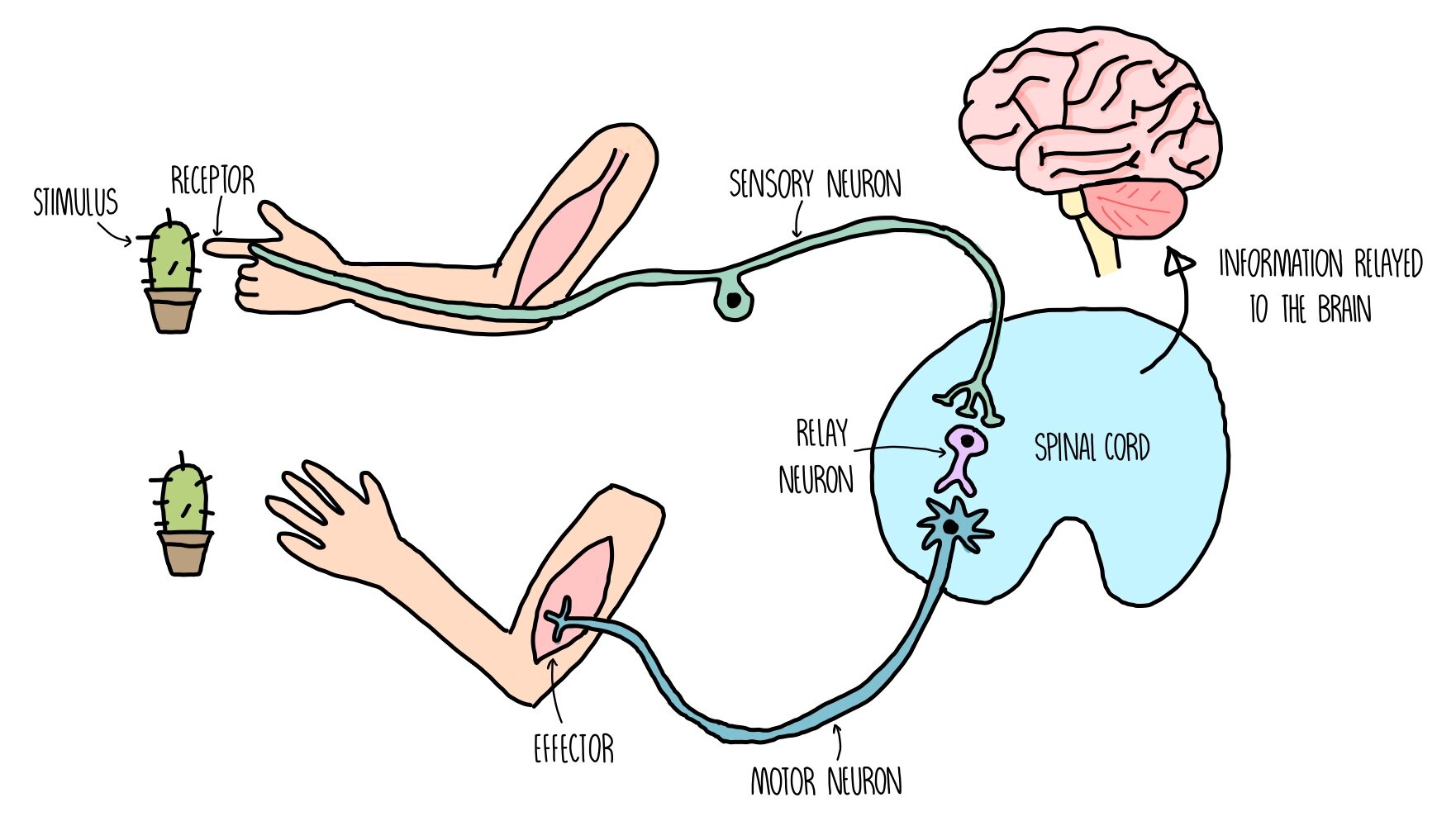
Transmission
A relay of information via nerves and/or hormones to an effector.
How is response and feedback related?
Response is the action that occurs due to the initial stimulus and feedback is the impact of that response (either positive or negative).
What is the difference between negative and positive feedback?
Negative feedback is the counter-response to stimuli whereas positive feedback amplifies stimuli.
Nervous System
One of the body systems that plays an important role in controlling almost everything we do.
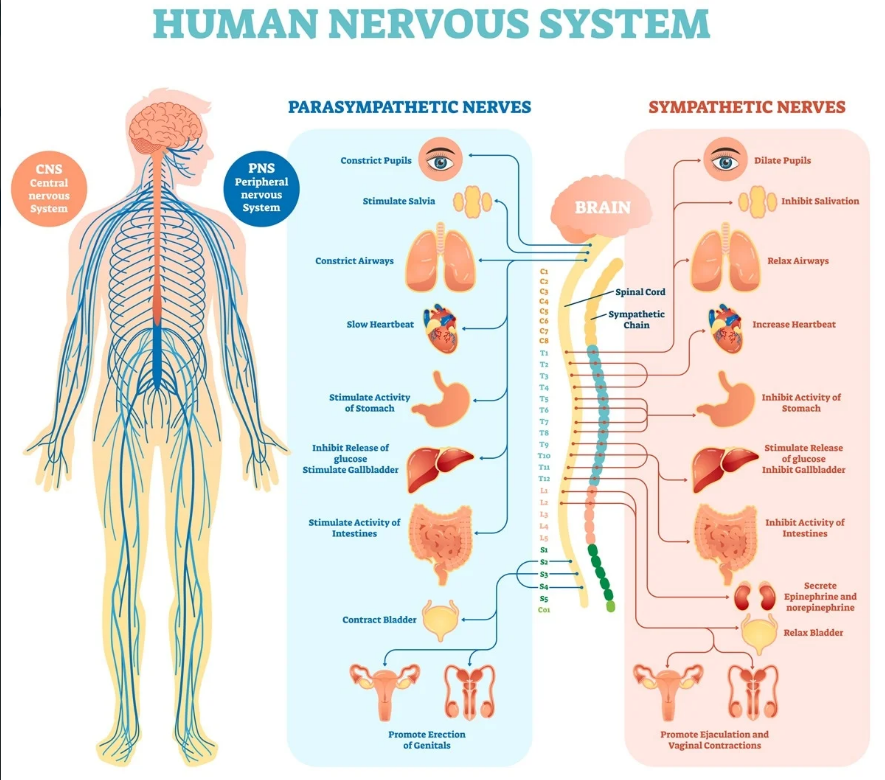
Neurons
Nerve cells that play an important role in receiving stimuli from receptors and transmit a response to effectors.
What are the three types of neurons?
Sensory Neuron
Interneuron (relay)
Motor Neuron
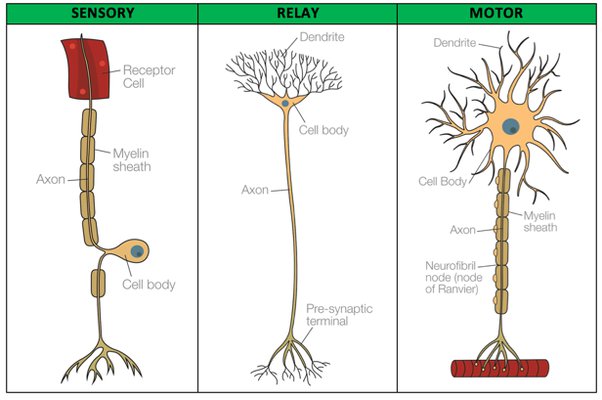
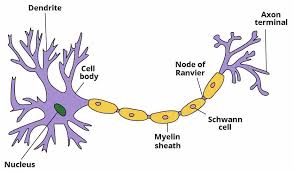
What are the three main components of most neurons?
Axon
Cell Body
Dendrites
Myelin sheath (some neurons)
Synapses
The gap between neurons or receptors/effectors
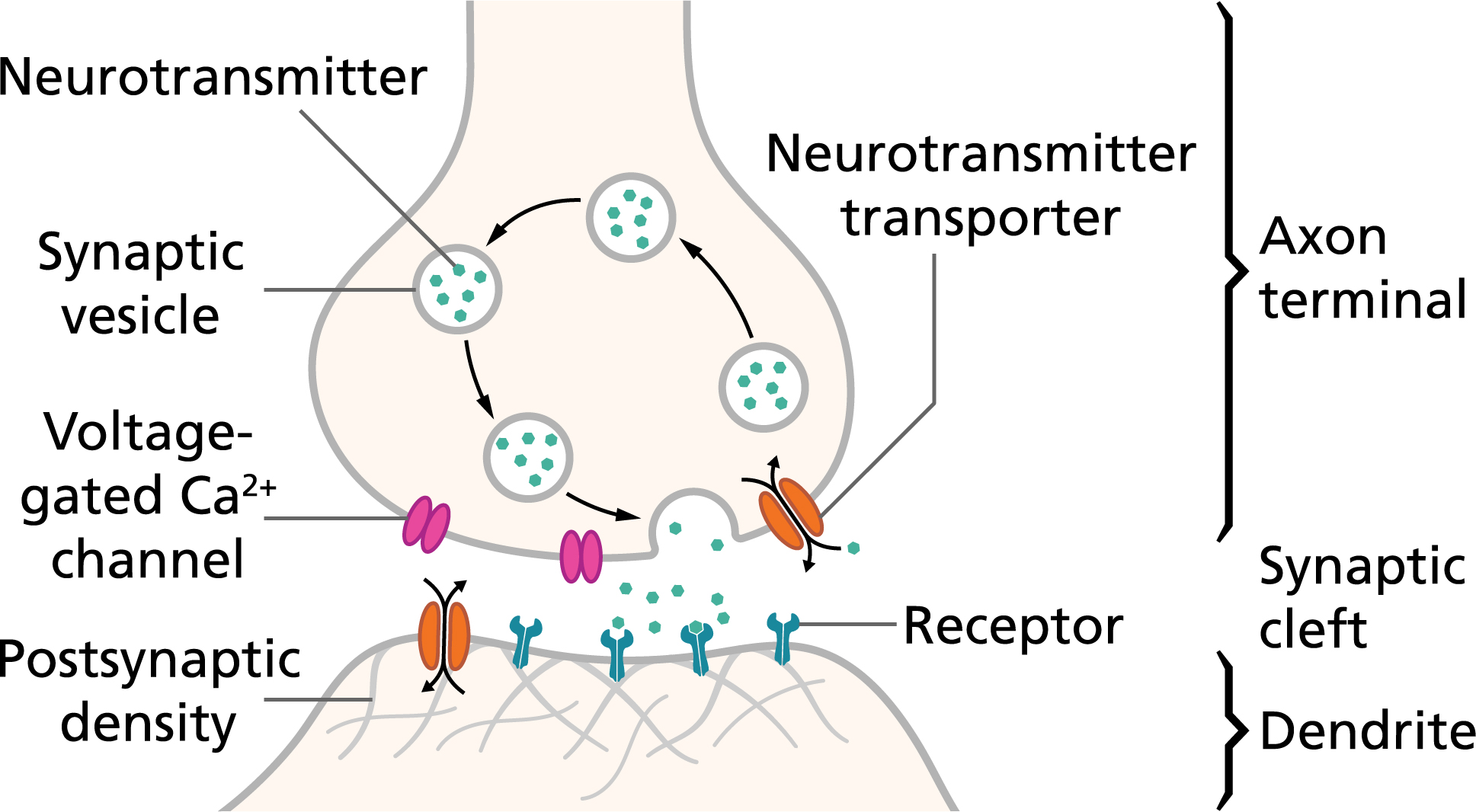
Neurotransmitters
Chemicals released from nerve impulses that bind to receptors to further transmit nerve impulses.
Reflex Arc
An automatic and rapid response to stimulus.
Why are blood pH levels important to maintain?
If blood pH levels aren’t maintained, it could lead to death or coma
What regulates blood pH levels?
Exhaling Carbon Dioxide
Endocrine System
One of the body systems that consists of a group of glands which secrete hormones.
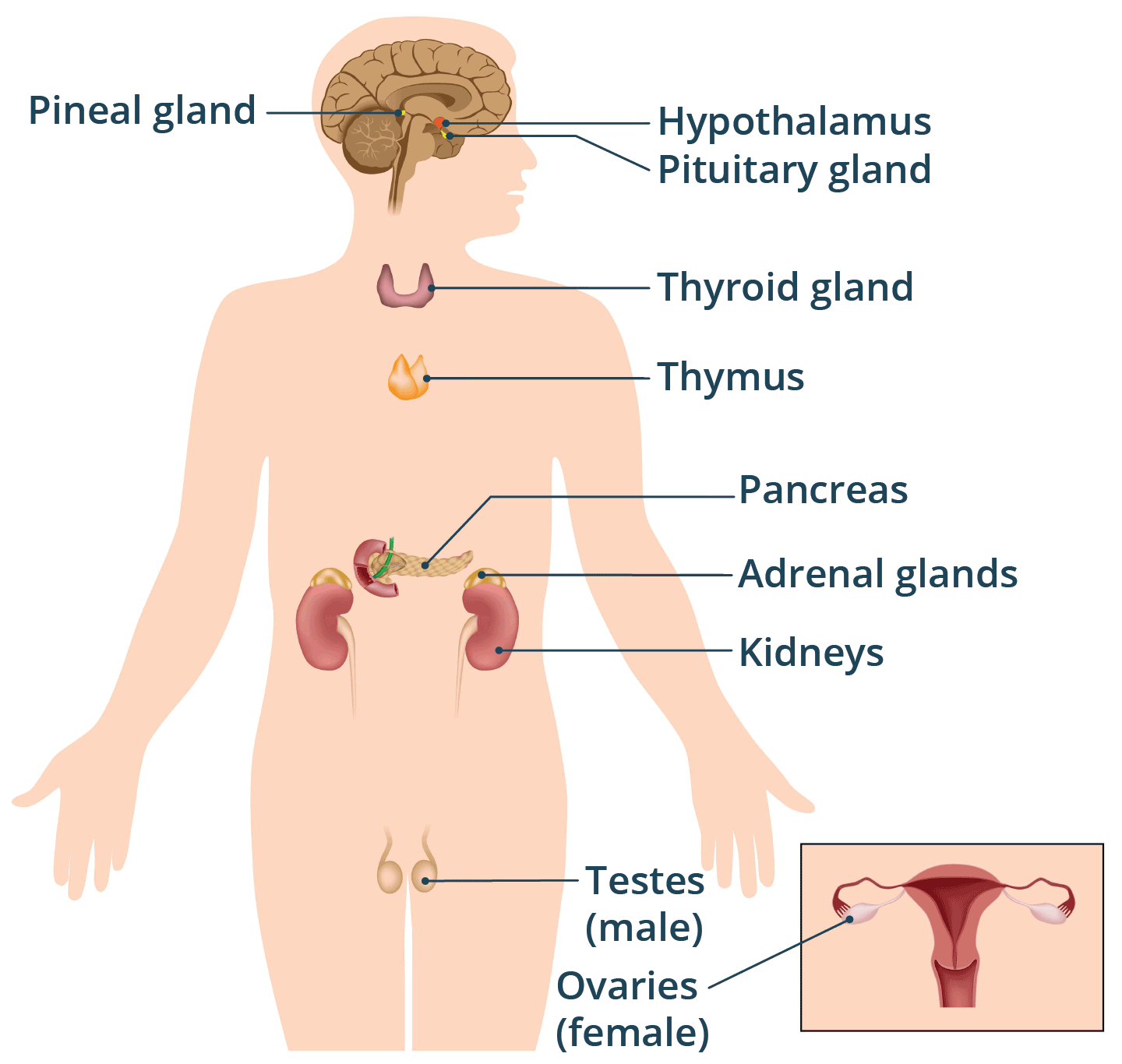
Hormones
Small chemicals which causes a response in another region of the body.
What are three types of hormones?
Peptide Hormone
Protein Hormone
Steroid Hormone
Which hormones are water-soluble, and which one is lipid-soluble?
Peptide and protein hormones are both water-soluble whereas steroid hormone is lipid-soluble.
Why should blood glucose levels be maintained?
To avoid the risk of diabetes and any other health risks.
What do glycogen and insulin do differently to regulate blood glucose levels?
Glycogen increases blood glucose levels when it’s too low whereas insulin decreases blood glucose levels when it’s too high.
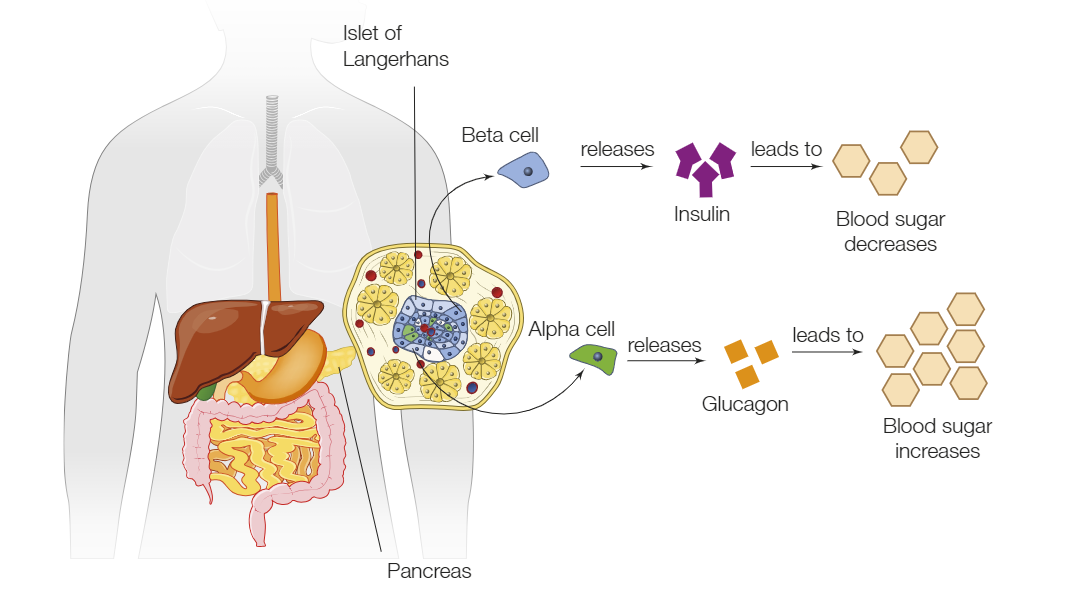
What is the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes is the result of decreased production of insulin whereas Type 2 diabetes is the result of body cells developing resistance against insulin.
When someone’s blood glucose levels are higher than normal, they are experiencing…
Hyperglycaemia
To increase metabolic rate and heat production, what hormone gets released?
Thyroxine
Osmoregulation
The control of body fluids in order to maintain water and solute balance.
To increase reabsorption of water, what hormone gets released?
Anti-diuretic hormone
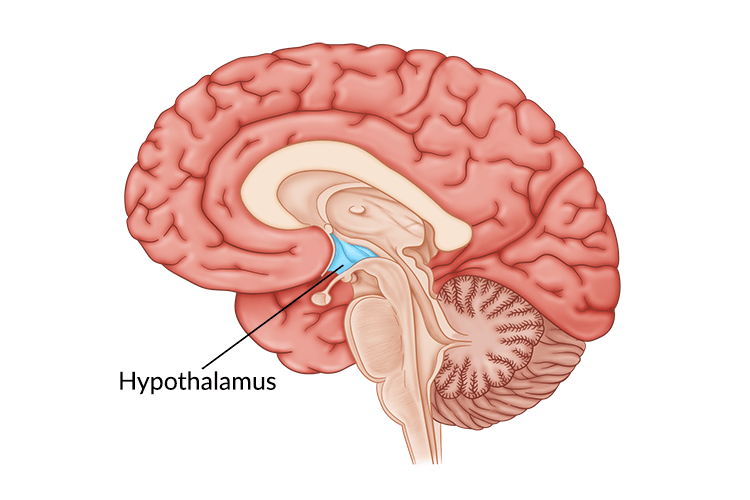
What structure of the brain detects most stimuli?
Hypothalamus
What gland is responsible for secreting various hormones?
Pituitary Gland
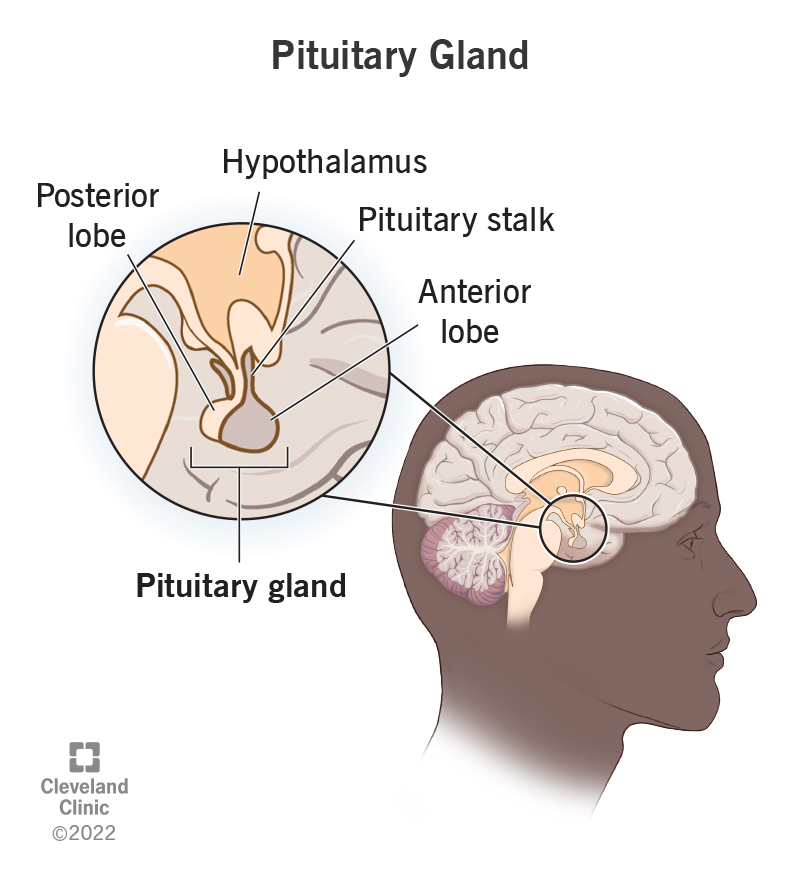
What is the difference between anterior and posterior pituitary gland?
Anterior regulates most hormones whereas posterior regulates oxytocin and ADH (vasopressin)
Thermoregulation
The control of internal body temperature.
What is the difference between blood pressure and blood volume?
Although both are affected by osmoregulation, blood volume is the total amount of blood in the circulatory system whereas blood pressure is the pressure of blood being pumped through blood vessels.
Flight-Or-Fight Response
A physiological response that occurs when a threat or stressful situation arises.
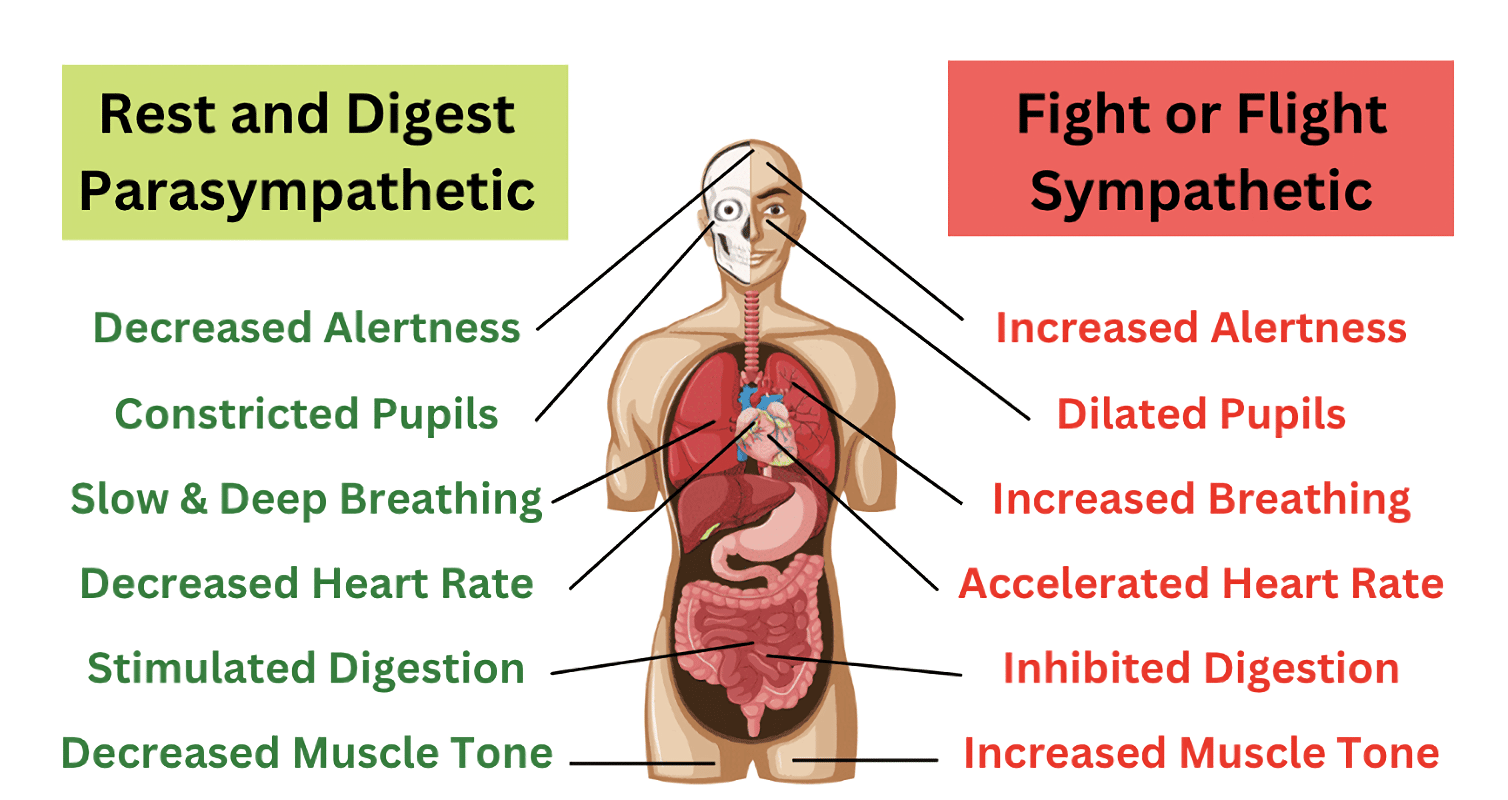
What hormone is involved in the fight-or-flight response?
Adrenaline
What is the difference between autoregulation and extrinsic regulation?
Although both are homeostatic regulations, autoregulation happens at a local level whereas extrinsic involves the nervous or endocrine system, which affects various areas of the body.
To decrease blood pressure, what must happen?
The heart decreases cardiac output, meaning volume of blood the heart pumps.
What receptors are involved in regulating blood pressure levels?
Baroreceptors in the heart and carotid sinuses.
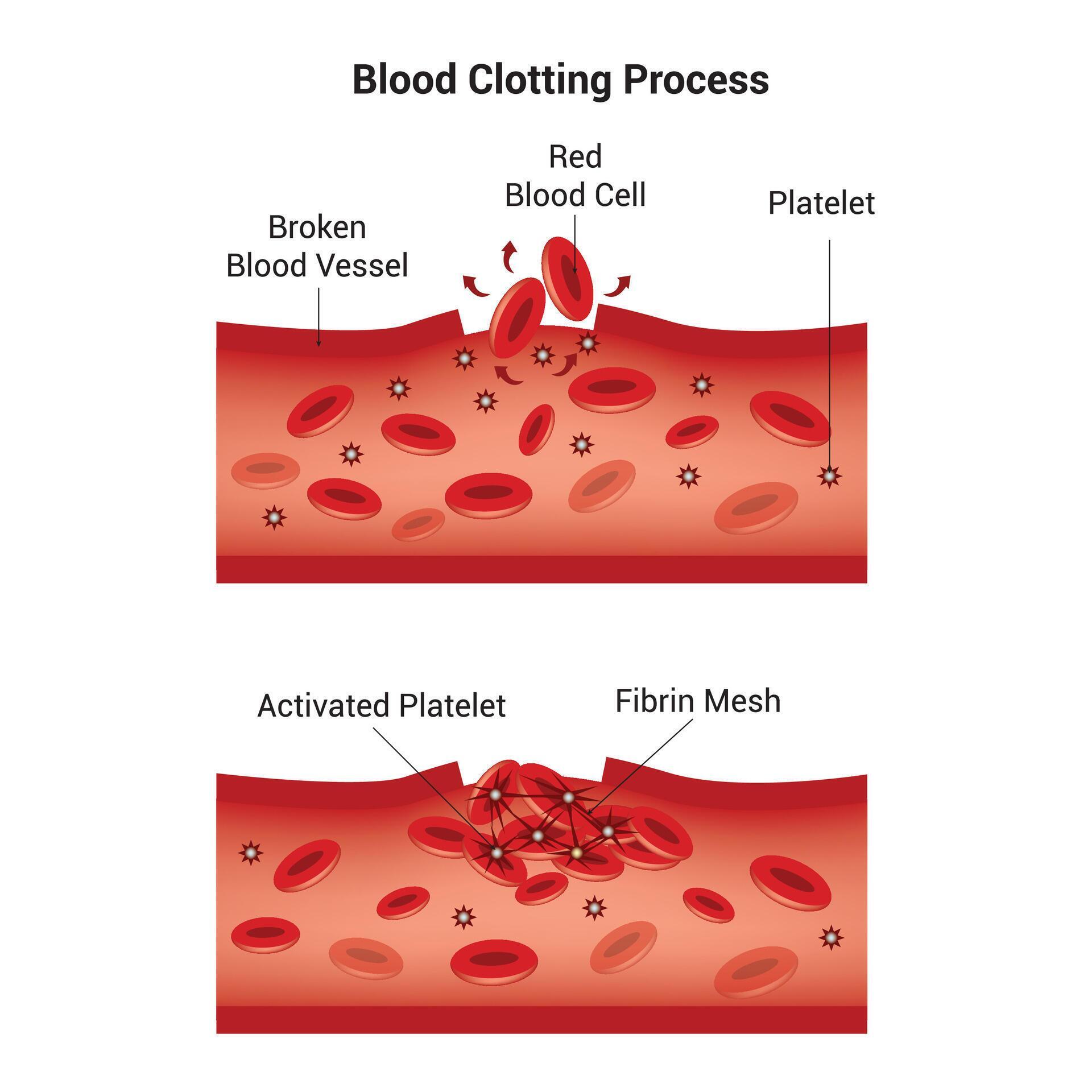
What are two common examples of positive feedback?
Blood clotting and labour contractions.
How do blood clots form?
Platelets (Cell fragments) are triggered from chemicals nearby the site of injury, where it will build up to form a blood clot to stop bleeding.
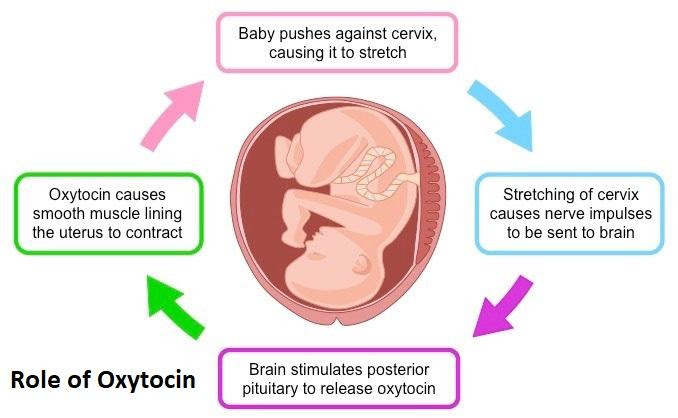
How does labour contractions work?
Contractions are sent to the hypothalamus, where a signal is sent to the posterior pituitary gland to secrete oxytocin to stimulate stronger labour contractions of the uterus. Prostaglandin is also triggered to assist in labour contractions.