Unit 10 - Biology
1/58
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
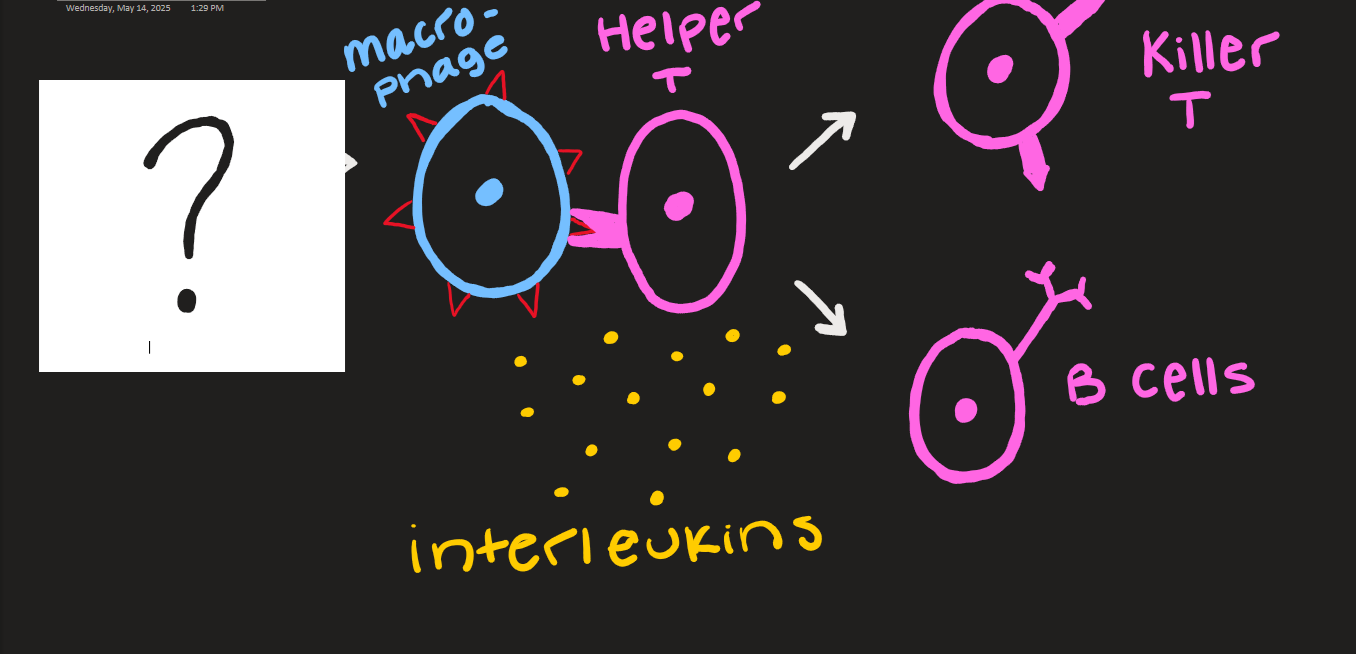
what goes here?
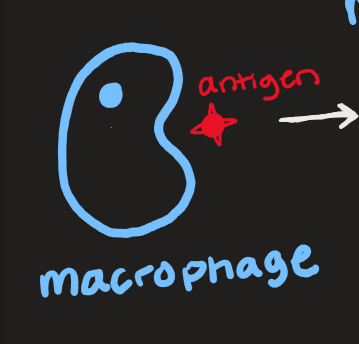
macrophage and antigen
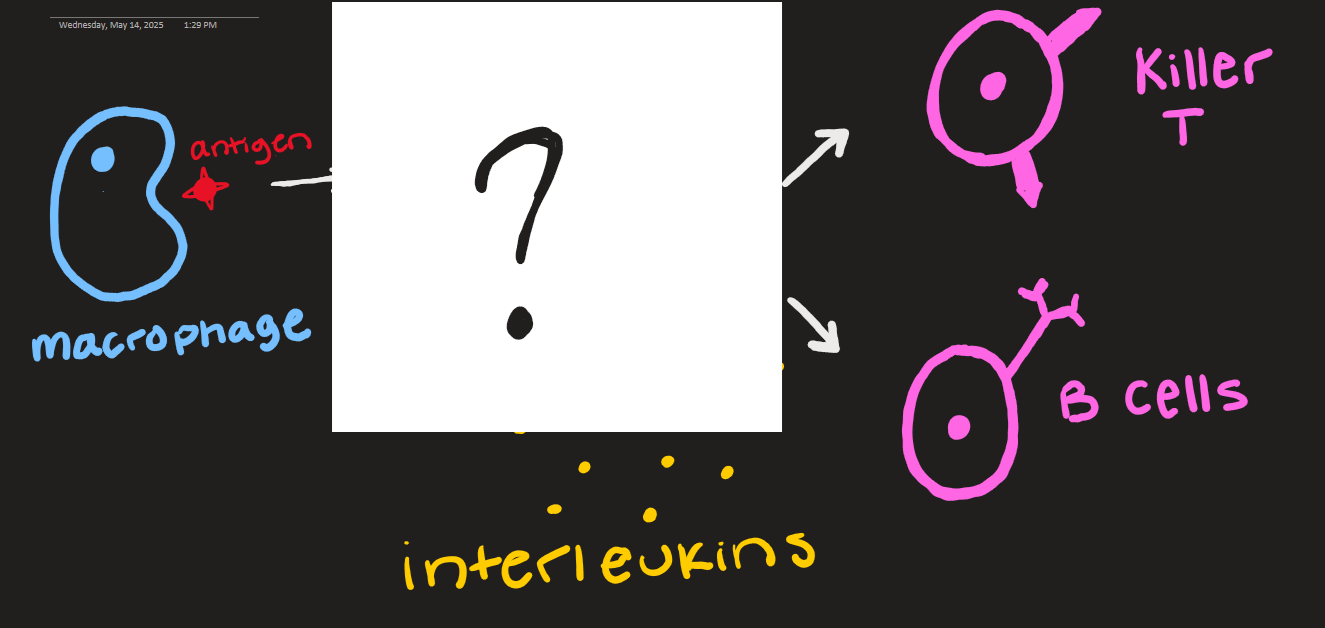
what goes here?
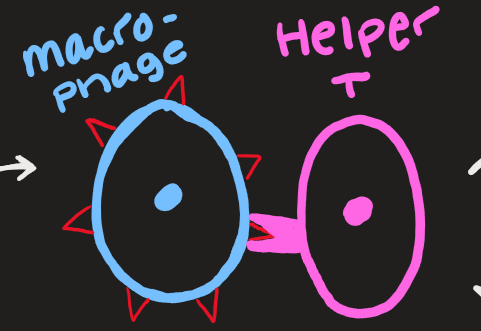
macrophage and helper T
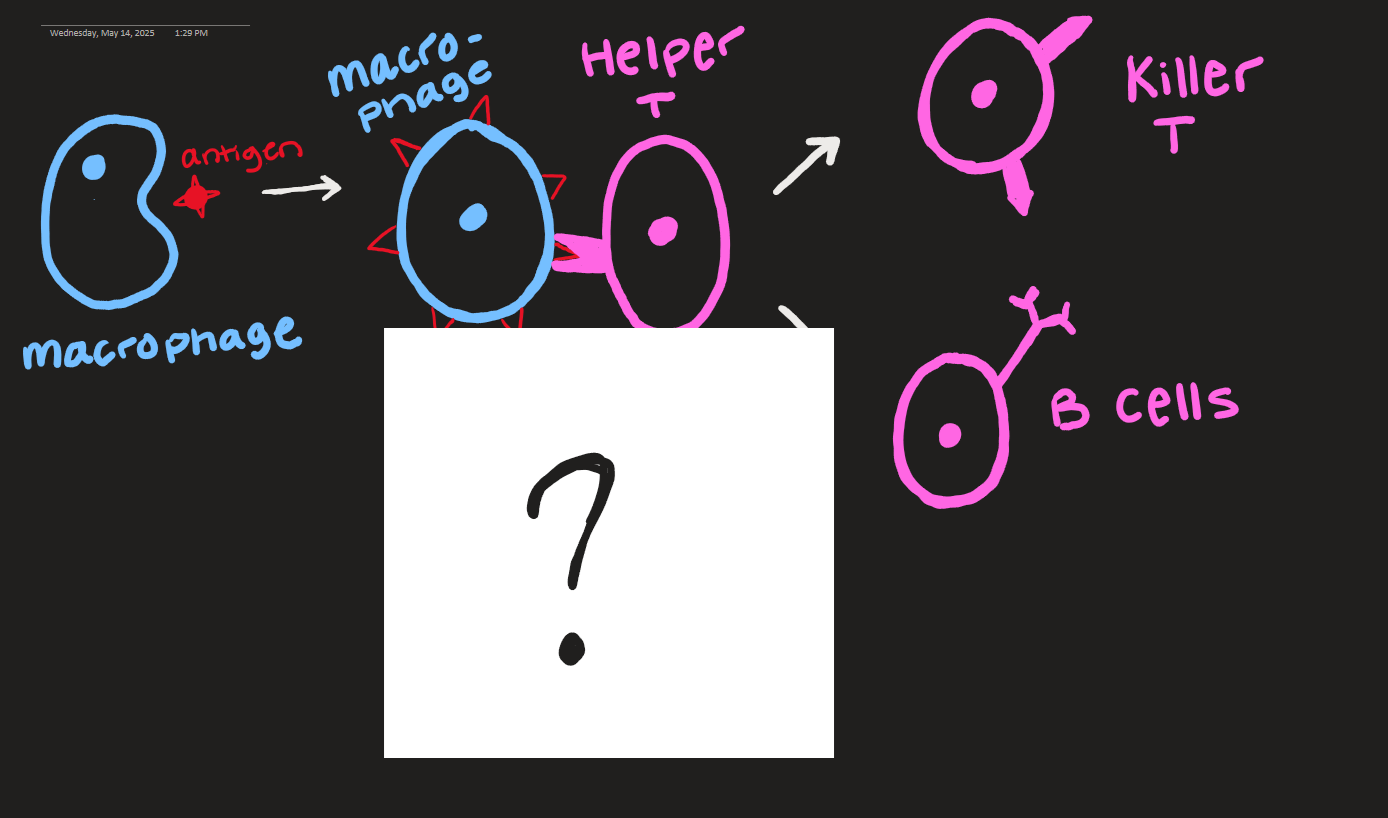
what goes here?
interleukins

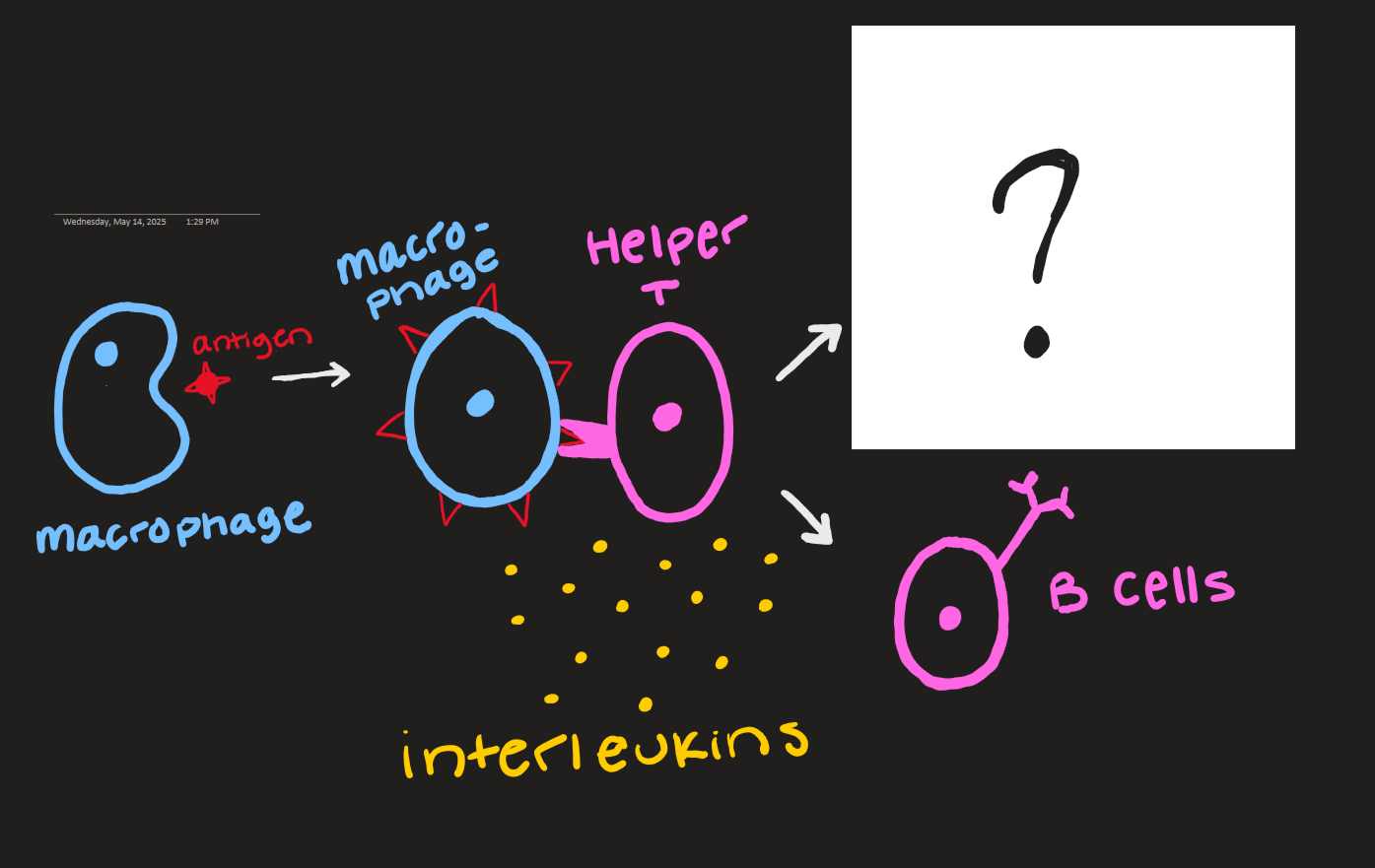
what goes here?
killer T

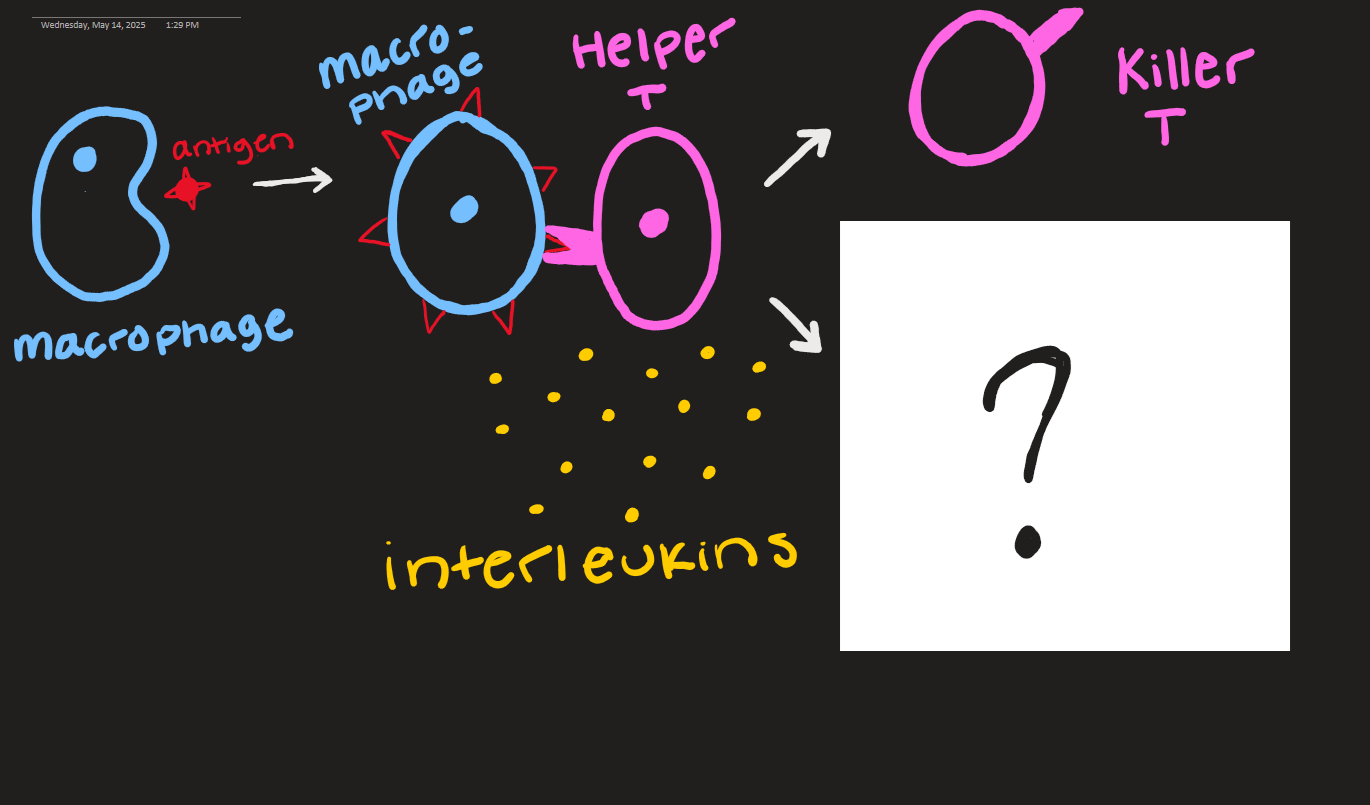
what goes here?
B cells

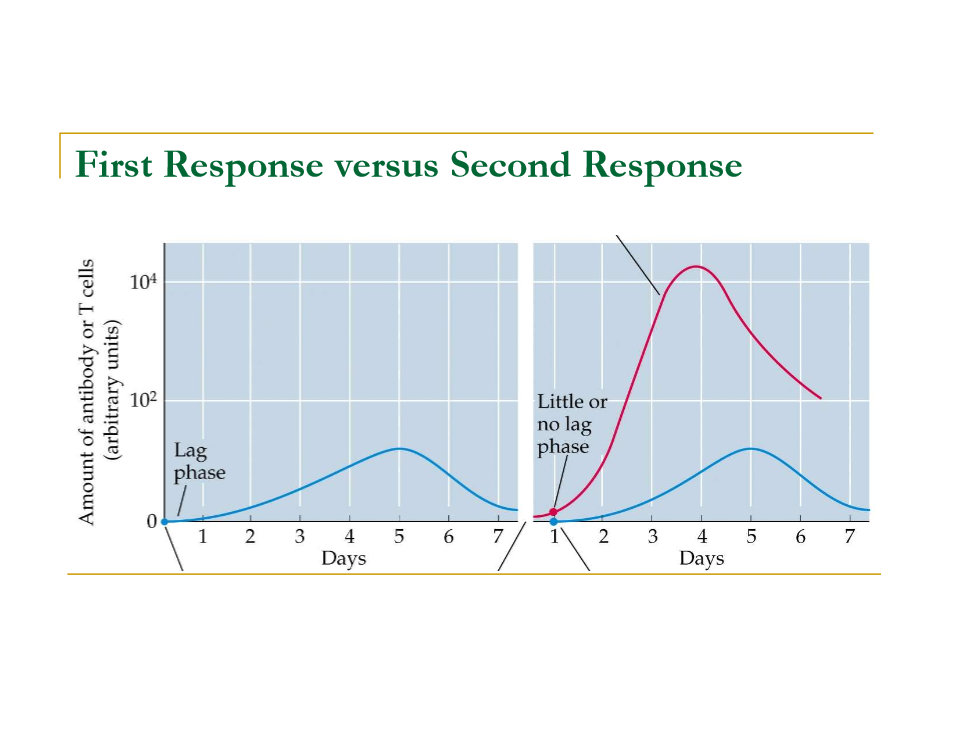
what goes on the Y-axis in the 1st response vs. 2nd response?
amount of antibody or T cells
what goes on the X-axis in the 1st response vs. 2nd response?
days
what would you title the graph of the first response vs. the second response?
Number of T cells & Antibodies Produced During First & Second Exposure to Pathogen
draw the graphs of the First Response vs. Second Response
what are the 2 major parts of viruses?
-Genetic material
-Protein coat
what are the 2 different cycles viruses reproduce in?
Lytic Cycle
Lysogenic Cycle
what are the steps of the Lytic Cycle?
virus attaches to host cell because host is fooled by protein coat
virus inserts DNA into host cell
cell reads viral DNA, which tells it to make virus parts
virus parts are assembled
viruses break free from cell to infect more cells, to repeat the cycle
what are the steps of the Lysogenic Cycle?
viruses insert DNA or RNA
DNA becomes incorporated into host cells DNA
cells containing viral DNA are then replicated
what does it mean if a virus reproduces in the Lytic Cycle?
the virus reproduces immediately
what does it mean if a virus reproduces in the Lysogenic Cycle?
the viruses lay dormant for periods of time
what is an example of a Lytic Virus?
the flu
what is an example of a Lysogenic Virus?
herpes
Which virus is worse? Lytic or Lysogenic?
a Lysogenic Cycle turns Lytic many cells start with the infection, therefore causing more damage.
when do Infectious Diseases occur?
when microorganisms, called pathogens, disrupt normal body functions
what is a pathogen? (include examples)
a disease causing agent.
examples: bacteria, viruses, fungi
what are some common ways diseases can be transmitted?
air-borne, food or water-borne. body fluids.
what happens when a disease is caused by toxins?
-blocks enzyme functions
-can damage nervous, reproductive, and digestive systems
-may delay mental and physical development
how does your body protect you from illness?
three lines of defense
what are the 3 lines of defense?
Nonspecific External
Nonspecific Internal
Specific
what happens in the first line of defense?
-physical and chemical barriers
-eternal (keeps things out of your cells)
what happens in the second line of defense?
-includes inflammatory response & fever
-initiates when foreign antigens are identified in the body
what is the Inflammatory Response?
when pathogen makes it past first lube if defense, specialized mast cells release chemical signal called histamine into the blood
what does Histamine cause?
-blood vessels to expand and become leaky, causing inflammation
-specialized white blood cells called phagocytes are released into infected area
when is a fever included?
if it is necessary to kill microorganisms
what is step 1 of the specific defense system?
proteins (MHC) on all your cells to help you recognize “self” from “non-self”
- if immune systems finds a cell without your unique MHC, it starts the attack
what is step 2 of the Specific Defense System (SDS)?
it finds cells specifically designed to fight invader and attack invader.
what are the 2 different responses? (for step 2 of SDS)
Cell-Mediated Immune Response (uses T cells), Humoral Immune Response (uses B cells and antibodies)
what happens with the cell-mediated response?
-Helper T finds correct cytotoxic T cells and clones them
-cytotoxic T cells work then to find the infected body cells and inject toxin into them
-this causes infected body cells to rupture and die
what happens with the humoral response?
-correct B cells are found and cloned
-B cells can then turn into plasma cells or memory B cells
-then plasma cells make antibodies
what is step 3 of the Specific Defense System (SDS)?
-after the invader is eliminated, memory B and T cells remain
-if body sees same antigen again, it immediately will release interleukins and make antibodies
what is HIV?
Human Immunodeficiency Virus
- Targets human Helper T cells as hosts
- Retrovirus
what are the steps of the HIV life cycle?
binding
reverse transcription
integration
transcriptions and translation
assembly
why is HIV so hard to fight?
-cells other than helper T cells can be infected, therefore the virus can colonize many tissues of the body
-clones quickly
how do vaccines work?
a weak or dead form of the germ is introduced
this sparks your immune response to develop antibodies that remember the germ
the antibodies fight off the germ if it invades again
what is herd immunity?
immunity that occurs when the vaccination of a significant portion of a population (or herd) provides a measure of protection for individuals who have not developed immunity.
when do allergies occur?
when your body makes the wrong type of antibodies.
what are some antibody functions?
bind to and inactivate foreign pathogens
mark invaders for destruction
help activate immune response
what are some types of antibodies?
ImmunoglobulinG (IgG)
ImmunoglobulinD (IgD)
ImmunoglobulinM (IgM)
ImmunoglobulunE (IgE)
which lines of defense are external and which are internal?
1st line is external, 2nd and 3rd line are internal
which lines of defense are non-specific and which are specific?
1st and 2nd line are nonspecific, and the 3rd line is specific
list some examples of external structures that are part of the first line of defense
mucus, nasal hairs, skin, tears, saliva… etc
describe what happens in the second line of defense
pathogen enters body through break in skin
antigen is detected so mast cells secrete histamine causing inflammation
the blood vessels dilate and become leaky
white blood cells called macrophage come to the area and inspect pathogen
what chemical messenger is used to trigger B and T cells to clone?
interleukins
how is a memory of a pathogen kept by the immune system?
memory B and T patrol body so if same antigen is encountered a second time, antibodies produced immediately and pathogen killed before it can replicate
know how to draw the lytic and lysogenic virus life cycle
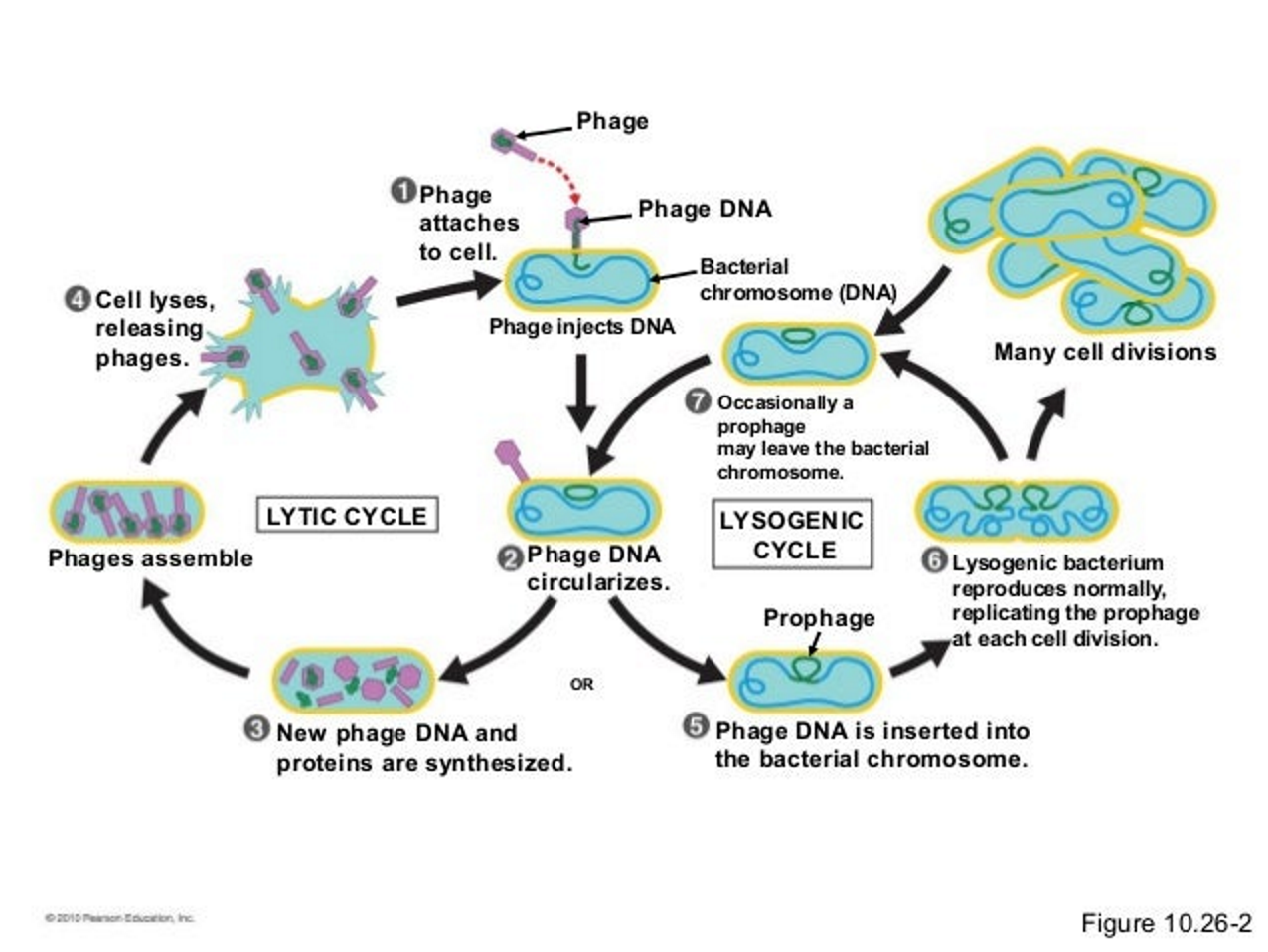
what are the major differences of lytic and lysogenic life cycles and which virus has the potential to do more damage?
lytic cycle reproduces immediately, lysogenic stays doormat for periods of time.
- lysogenic has potential to do more harm because more cells start with viral DNA
how do vaccinations work and why do they protect you from viruses you have not been directly exposed to?
expose you to the antigen so your body has an immune response which creates a memory of the antigen
how does herd immunity stop outbreaks of illness?
when enough people in a population have been vaccinated or are immune they protect those who aren’t or cant be vaccinated because they cant catch it or spread it
describe the structure of an HIV virus
-small spherical virus (RNA + plus enzymes enclosed in many layers to protect it)
-proteins on surface allow them to sneak into helper T
briefly explain the steps of the HIV life cycle
-enters Th
-RNA is turned into DNA by reverse transpiration
-DNA incorporated into host cell by interphase
-new HIV virus made, goes off to infect more
what were the two hypotheses for why certain indivuduals apppeared to have immunity to the HIV virus? WHich hypothesis was supported by the data?
super helper T cells & supper killer/cytotoxic T cells
- super helper T cells was supported by the data
which antibodies are used in allergic reactions?
IgE → attack parasites normally
what is an allergy?
how are allergies activated?
what is the difference between the first and second exposer to an allergen?
incorrect identification of antigen
mast cells have IgE antibodies attached to them, they explode with histamine when allergen encountered
2nd encounter moves because they have attached to mast cells and know the antigen
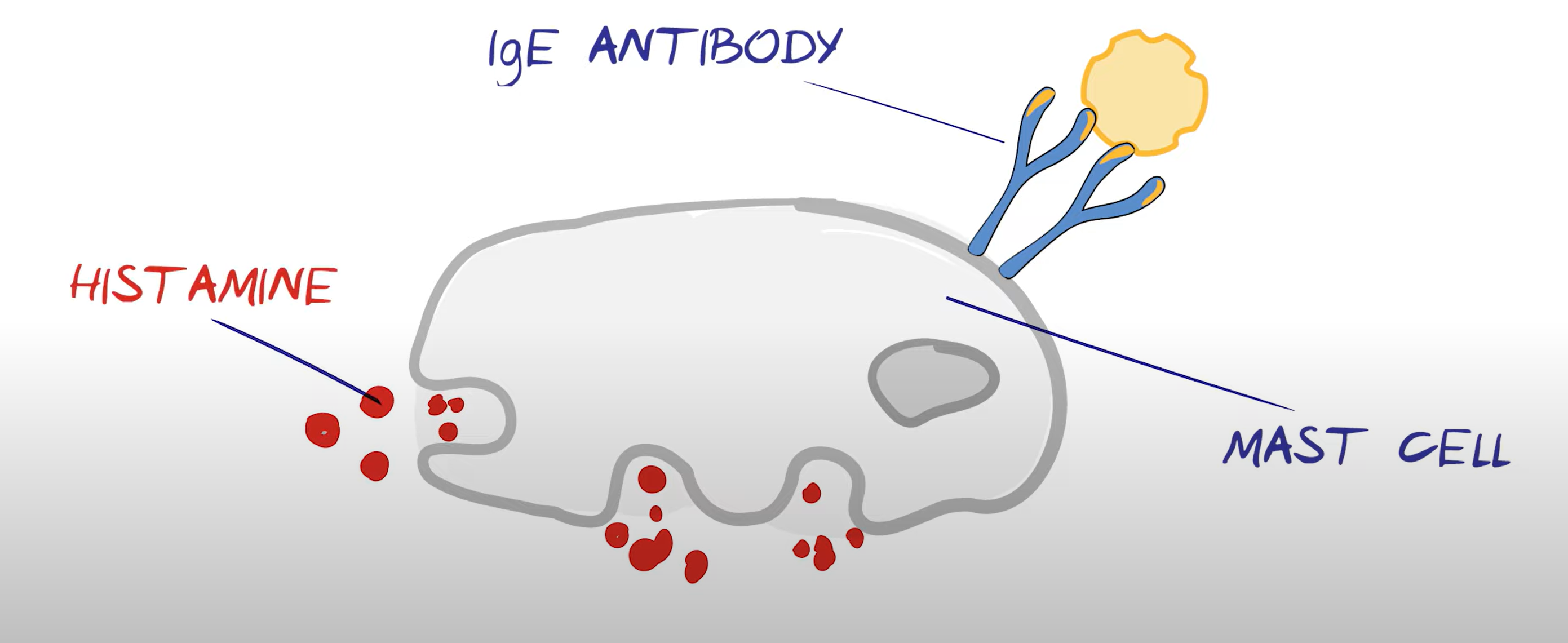
describe the symptoms of anaphylactic shock
low blood pressure
swelling of throat
lungs release mucus/ difficulty breathing
tears
hives
abdominal pain