Human Muscular Structure, Diseases, and Actions
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/53
Last updated 4:04 PM on 12/12/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
1
New cards
Posterior
towards the back (Dorsal)
2
New cards
Anterior
towards the front (Ventral)
3
New cards
Medial
towards the middle
4
New cards
Lateral
away from the midline
5
New cards
Superior
towards the head (Cranial)
6
New cards
Inferior
towards the feet (Caudal)
7
New cards
Transverse Plane
a plane that divides human anatomy into superior and inferior portions
8
New cards
Sagittal Plane
a plane that divides human anatomy into medial and lateral portions
9
New cards
Frontal Plane
a plane that divides human anatomy into anterior and posterior portions
10
New cards
Origin of Muscle
where bone and muscle attach, but do NOT move during contraction
11
New cards
Insertion of Muscle
where bone and muscle attach and MOVE during contraction
12
New cards
Function of Skeletal Muscle:
Enables the human body to move and perform all daily tasks
13
New cards
Flexion
Bending bones, bringing them closer together
14
New cards
Extension
Straightening a bone
15
New cards
Adduction
Movement of a limb towards the body
16
New cards
Abduction
Movement of a limb away from the body
17
New cards
Supination
Rotation of the arm so palm paces up
18
New cards
Pronation
Rotation of the arm so the palm faces down
19
New cards
Rotation
Turning a bone around it's own axis
20
New cards
Circumduction
Moving a limb so it's in a cone shape
Ex. Arm Circles
Ex. Arm Circles
21
New cards
Masseter
Origin: Zygomatic Arch
Insertion: Ramus of Mandible
Action: Elevates mandible
Insertion: Ramus of Mandible
Action: Elevates mandible
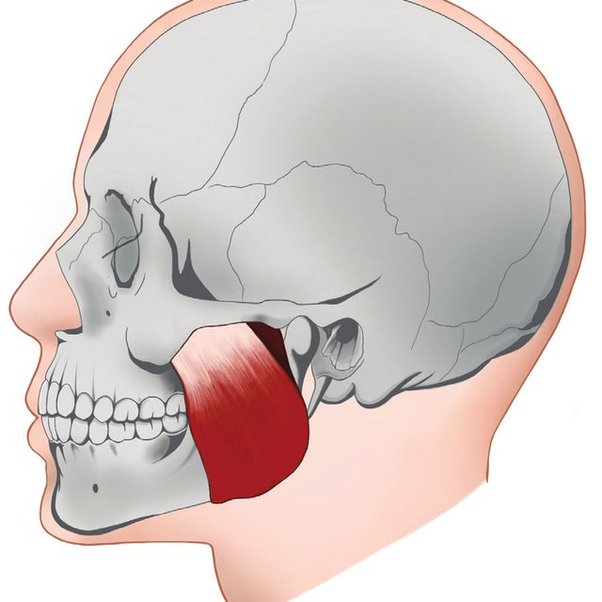
22
New cards
Temporalis
Origin: Temporal Fossa
Insertion: Coronoid Process of Mandible
Action: Move mandible up, back, and side to side
Insertion: Coronoid Process of Mandible
Action: Move mandible up, back, and side to side
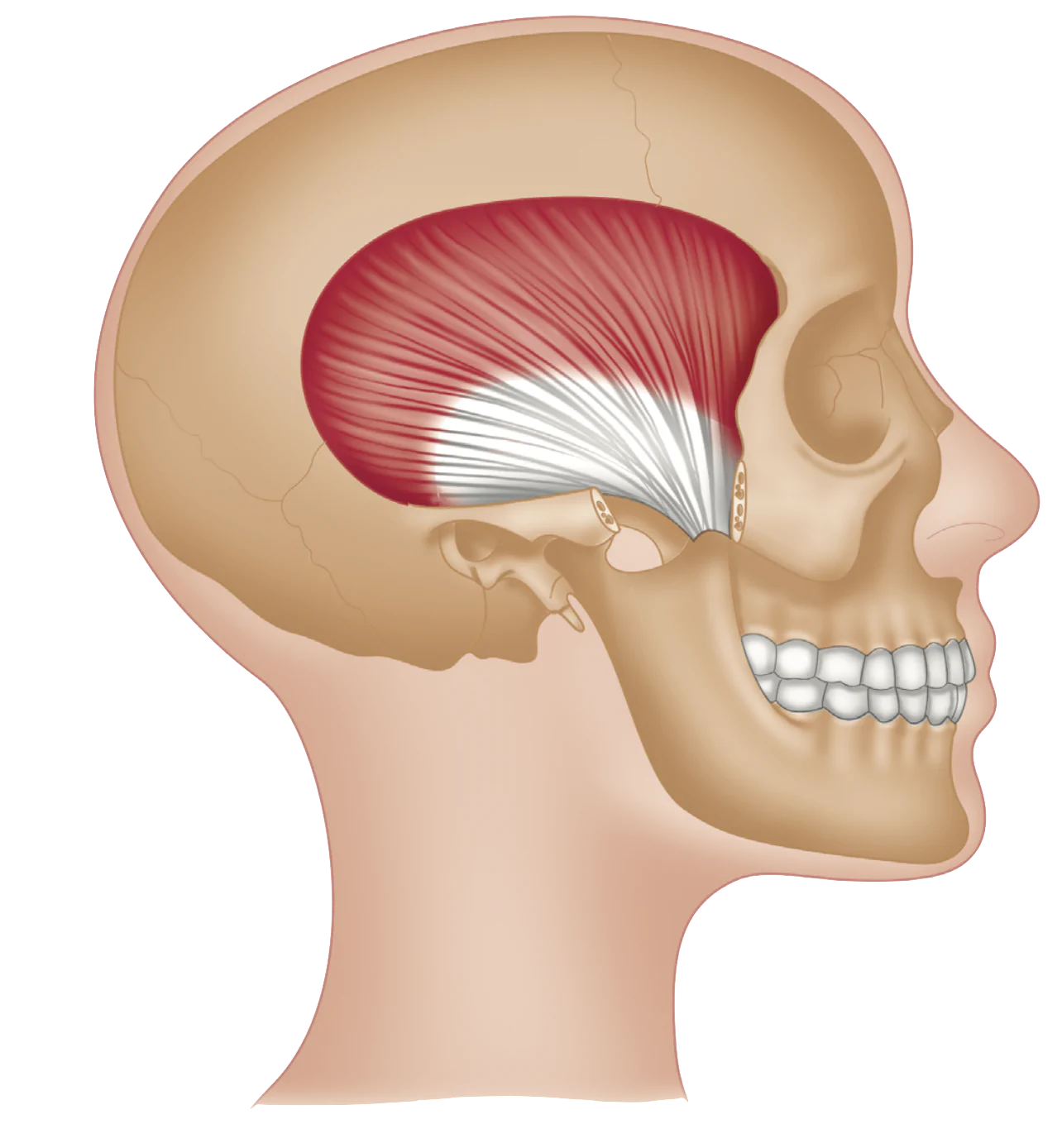
23
New cards
Digastric
Origin: Anterior = digastric fossa of mandible
Posterior = mastoid notch on temporal bone
Insertion: Hyoid Bone
Action: Depresses mandible and elevates hyoid bone during chewing and swallowing
Posterior = mastoid notch on temporal bone
Insertion: Hyoid Bone
Action: Depresses mandible and elevates hyoid bone during chewing and swallowing
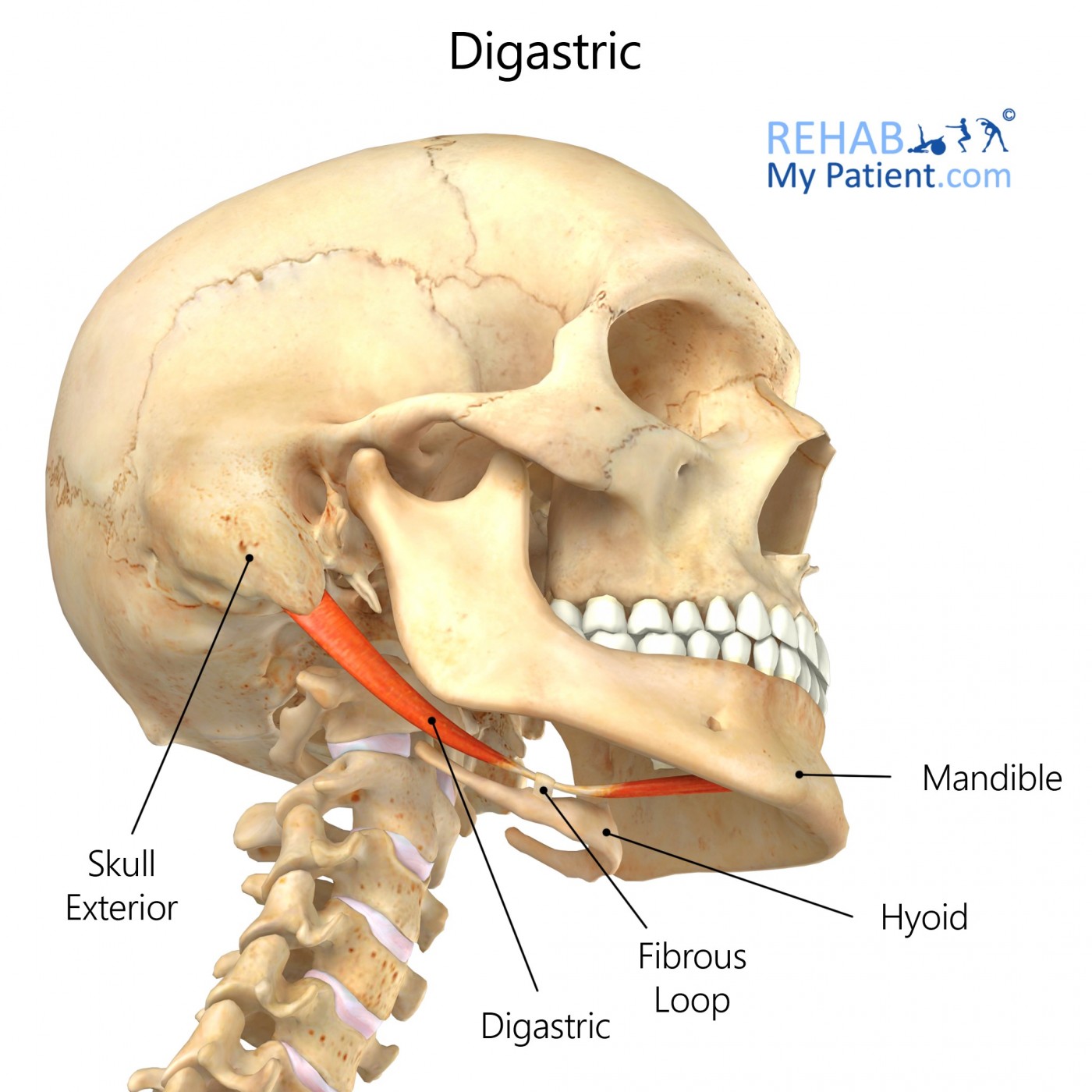
24
New cards
Sternocleidomastoid
Origin: Manubrium of Sternum and Medial Clavicle
Insertion: Mastoid Process
Action: Rotation of the head and flexion of the neck
Insertion: Mastoid Process
Action: Rotation of the head and flexion of the neck
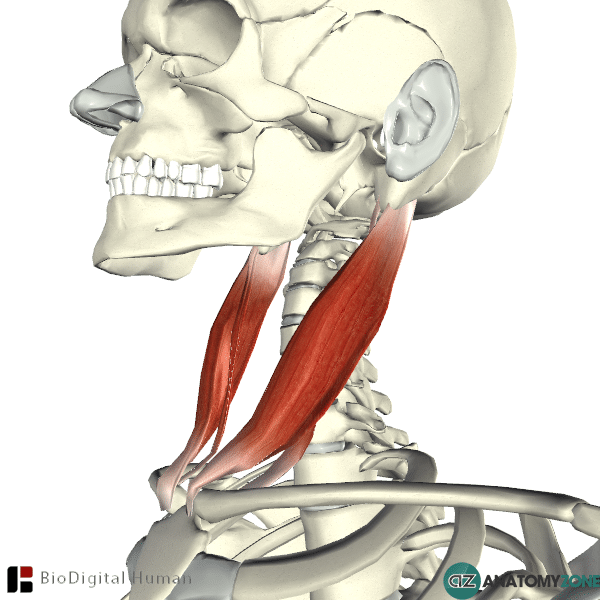
25
New cards
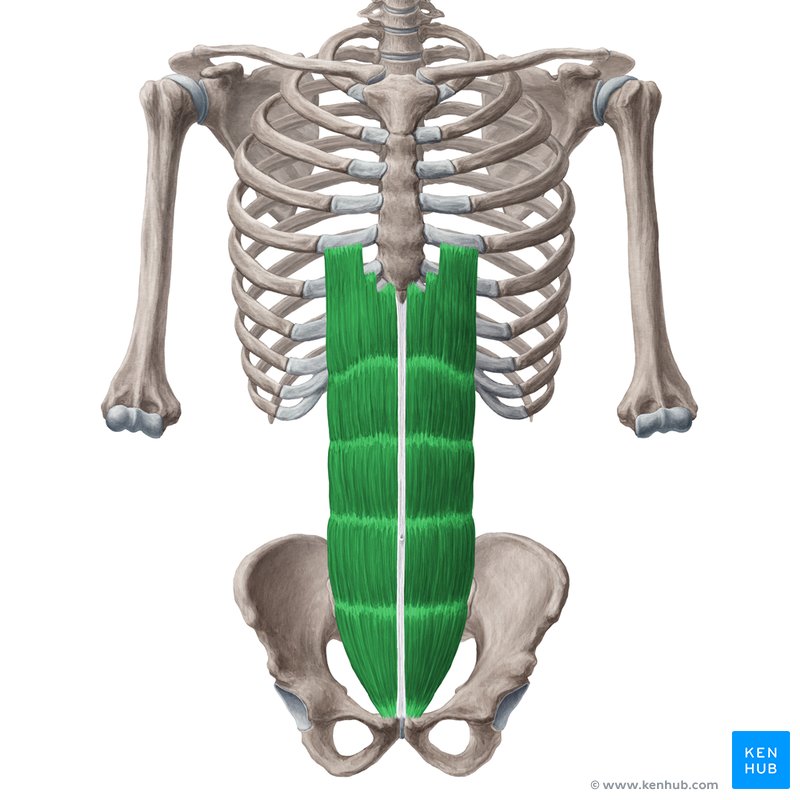
Rectus Abdominus
Origin: Pubic bone
Insertion: Xiphoid process and costal cartilage
Action: Flexion of trunk
Insertion: Xiphoid process and costal cartilage
Action: Flexion of trunk
26
New cards
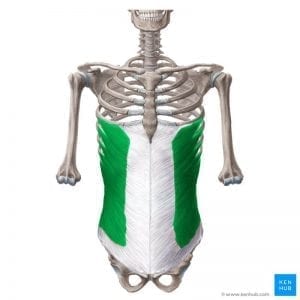
External Oblique
Origin: External surface of ribs 5-12
Insertion: Ilium
Action: Flexes and rotates trunk
Insertion: Ilium
Action: Flexes and rotates trunk
27
New cards
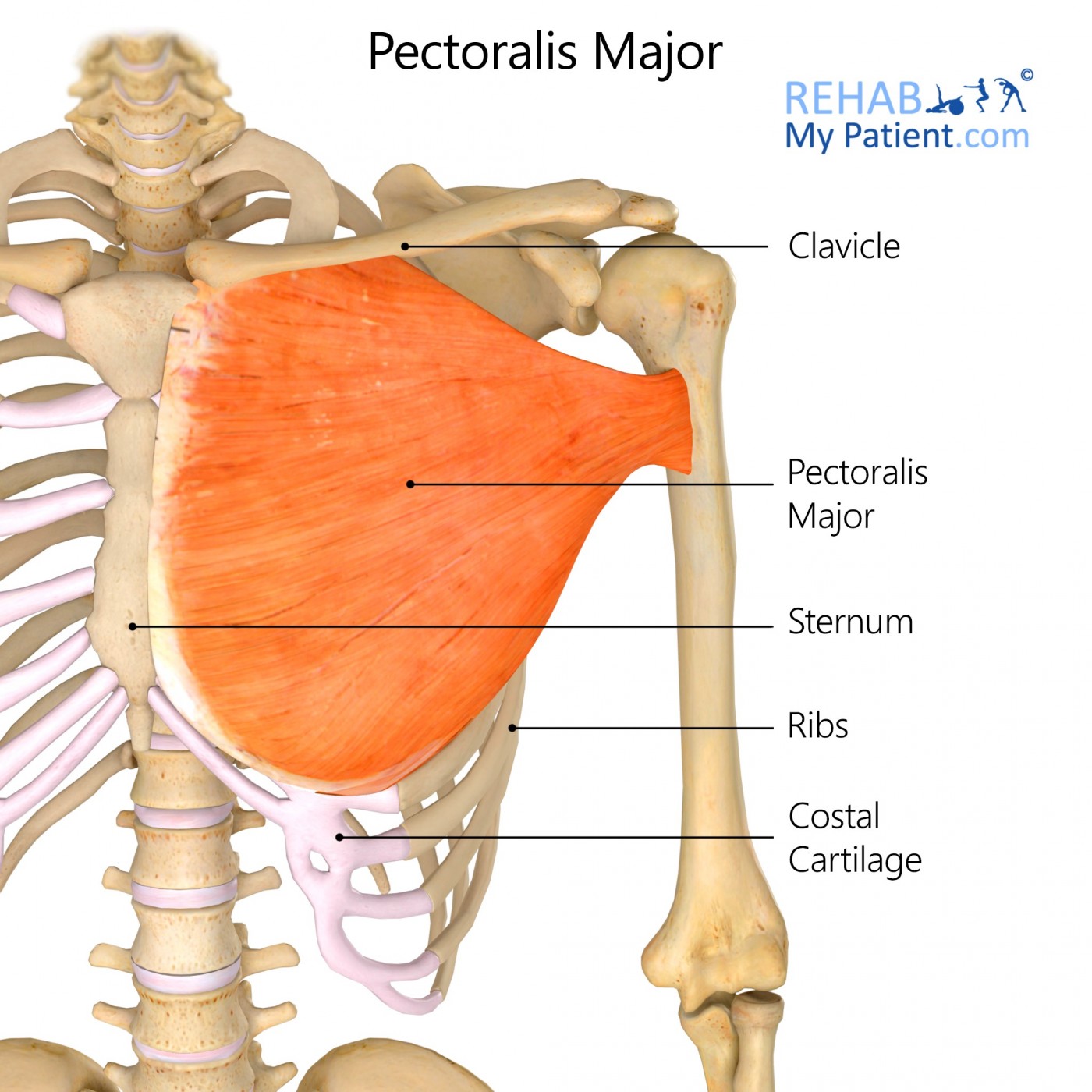
Pectoralis Major
Origin: Medial part of clavicle, sternum, costal cartilage (ribs 1-6), and rectus sheath
Insertion: Crest of greater tubercle of humerus
Action: Adductor, and rotates humerus at the shoulder joint
Insertion: Crest of greater tubercle of humerus
Action: Adductor, and rotates humerus at the shoulder joint
28
New cards
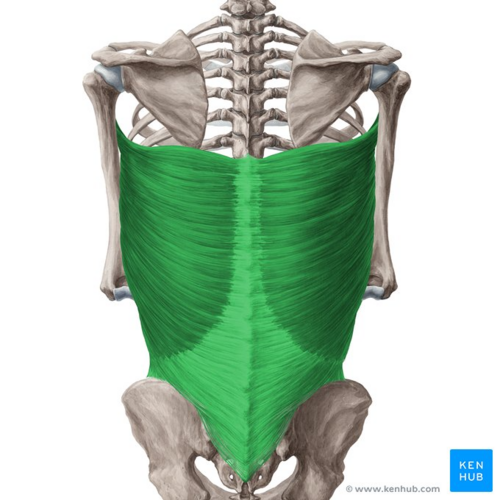
Latissimus Dorsi
Origin: Vertebrae 7-12, Crest of Ilium, Ribs 9-12, Inferior angle of Scapula
Insertion: Humerus
Action: Arm adduction and extension
Insertion: Humerus
Action: Arm adduction and extension
29
New cards
Supraspinatus
Part of ROTATOR CUFF
Origin: Supraspinous fossa of Scapula
Insertion: Greater tubercle of Humerus
Action: Abduction of arm
Origin: Supraspinous fossa of Scapula
Insertion: Greater tubercle of Humerus
Action: Abduction of arm
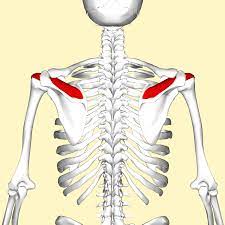
30
New cards
Infraspinatus
Part of ROTATOR CUFF
Origin: Infraspinous fossa of Scapula
Insertion: Greater tubercle of Humerus
Action: External Rotation of arm
Origin: Infraspinous fossa of Scapula
Insertion: Greater tubercle of Humerus
Action: External Rotation of arm
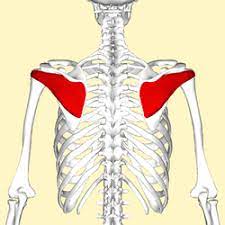
31
New cards
Subscapularis
Part of ROTATOR CUFF
Origin: Subscapular fossa of Scapula
Insertion: Lesser tubercle of Humerus
Action: Internal Rotation of arm
Origin: Subscapular fossa of Scapula
Insertion: Lesser tubercle of Humerus
Action: Internal Rotation of arm
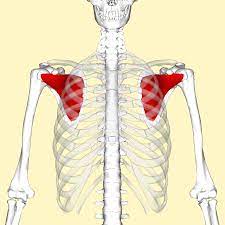
32
New cards
Biceps Brachii
FRONT OF ARM
Origin: Scapula (coracoid process and supraglenoid tubercle)
Insertion: Radial tuberosity of Radius
Action: Flexion of elbow
Origin: Scapula (coracoid process and supraglenoid tubercle)
Insertion: Radial tuberosity of Radius
Action: Flexion of elbow
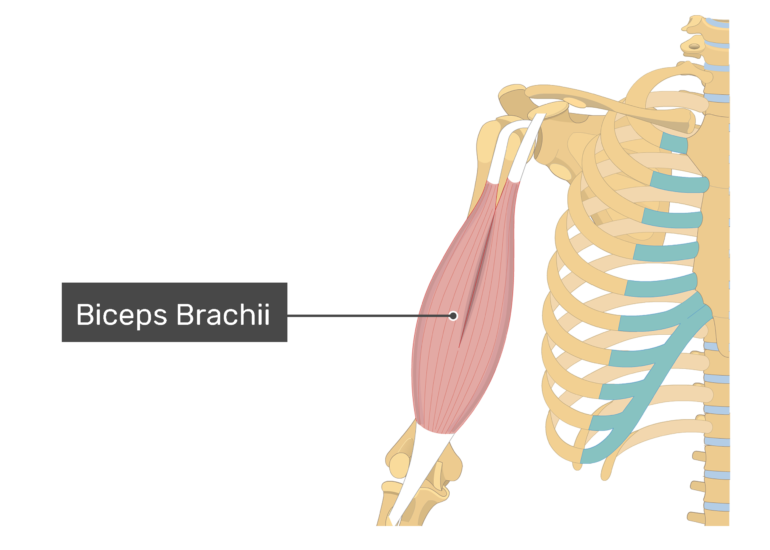
33
New cards
Triceps Brachii
BACK OF ARM
Origin: Scapula and Humerus
Insertion: Olecranon of Ulna
Action: Extension of elbow
Origin: Scapula and Humerus
Insertion: Olecranon of Ulna
Action: Extension of elbow
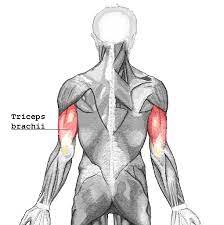
34
New cards
Flexor Digitorum Superficialis
Origin: Humerus and radial head
Insertion: Sides of phalanges (2-5)
Action: Flexion of fingers, hand, and wrist
Insertion: Sides of phalanges (2-5)
Action: Flexion of fingers, hand, and wrist
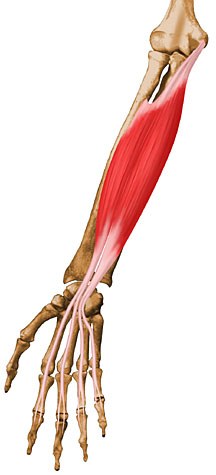
35
New cards
Trapezius
Origin: Occipital bone, spinous process of vertebrae T1-T12
Insertion: Clavicle, acromion, and spine of scapula
Action: Retracts scapula
Insertion: Clavicle, acromion, and spine of scapula
Action: Retracts scapula
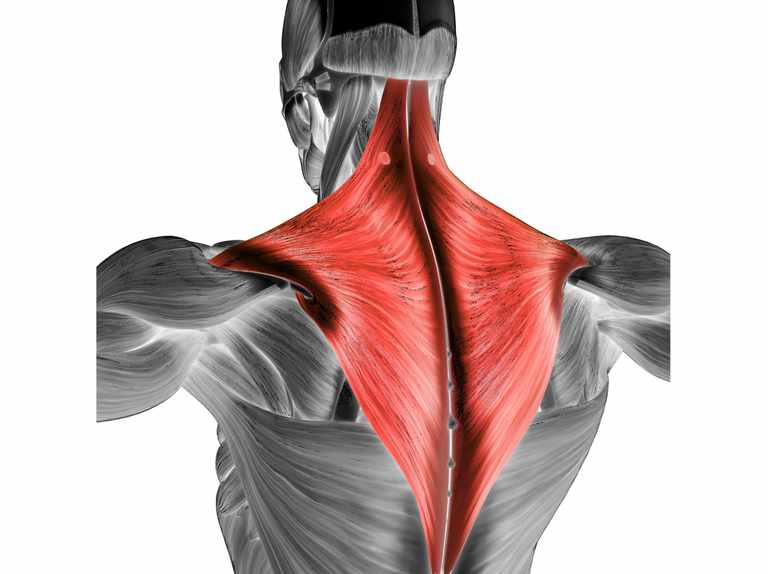
36
New cards
Gluteus Maximus
Origin: Sacrum, Coccyx, Ilium
Insertion: Femur
Action: Abduction and adduction of thigh
Insertion: Femur
Action: Abduction and adduction of thigh
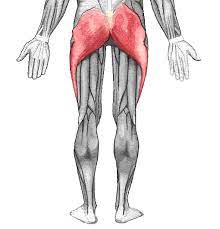
37
New cards
Biceps Femoris
HAMSTRINGS POSTERIOR LATERAL Origin: Ischial tuberosity and femur
Insertion: Head of fibula
Action: Hip and Knee Joint( thigh extension, external rotation, leg flexion and external rotation )
Insertion: Head of fibula
Action: Hip and Knee Joint( thigh extension, external rotation, leg flexion and external rotation )
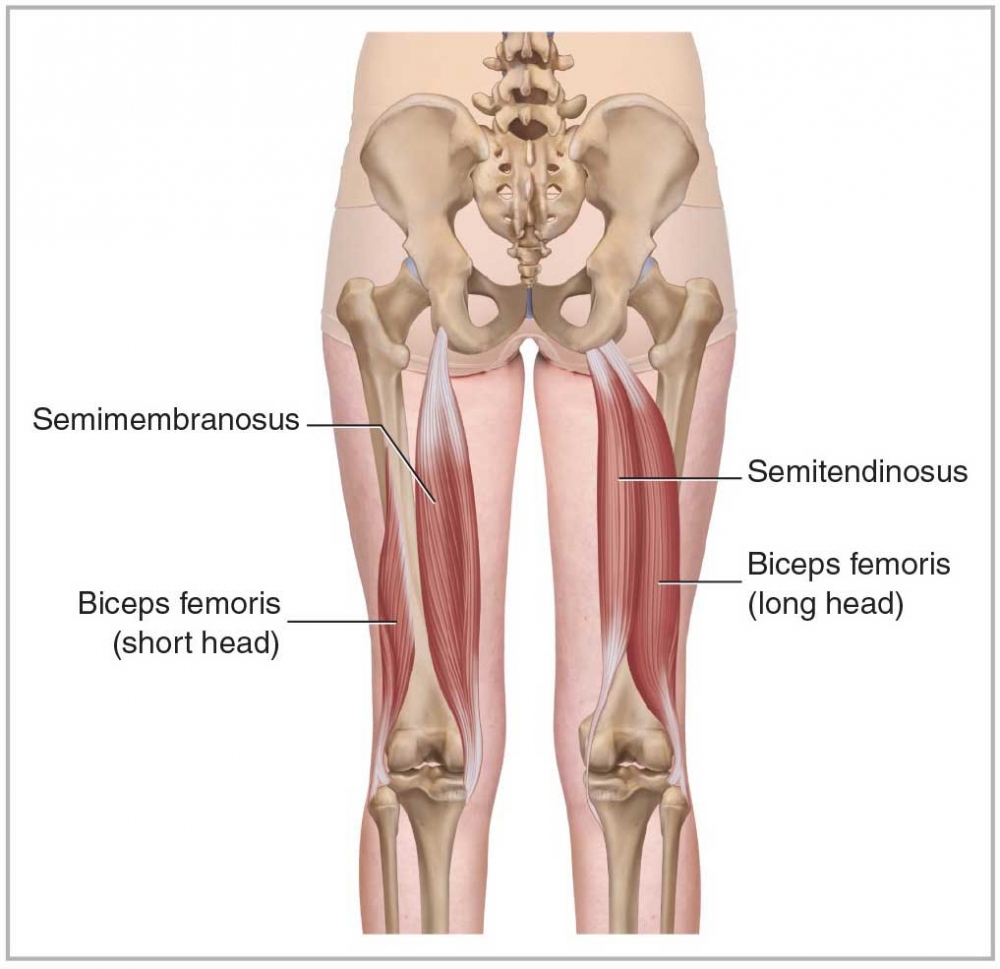
38
New cards
Semitendinosus
HAMSTRINGS
POSTERIOR MEDIAL
Origin: Ischial Tuberosity
Insertion: Tibia (proximal end)
Action: Thigh Extension and internal rotation, leg flexion and internal rotation
POSTERIOR MEDIAL
Origin: Ischial Tuberosity
Insertion: Tibia (proximal end)
Action: Thigh Extension and internal rotation, leg flexion and internal rotation
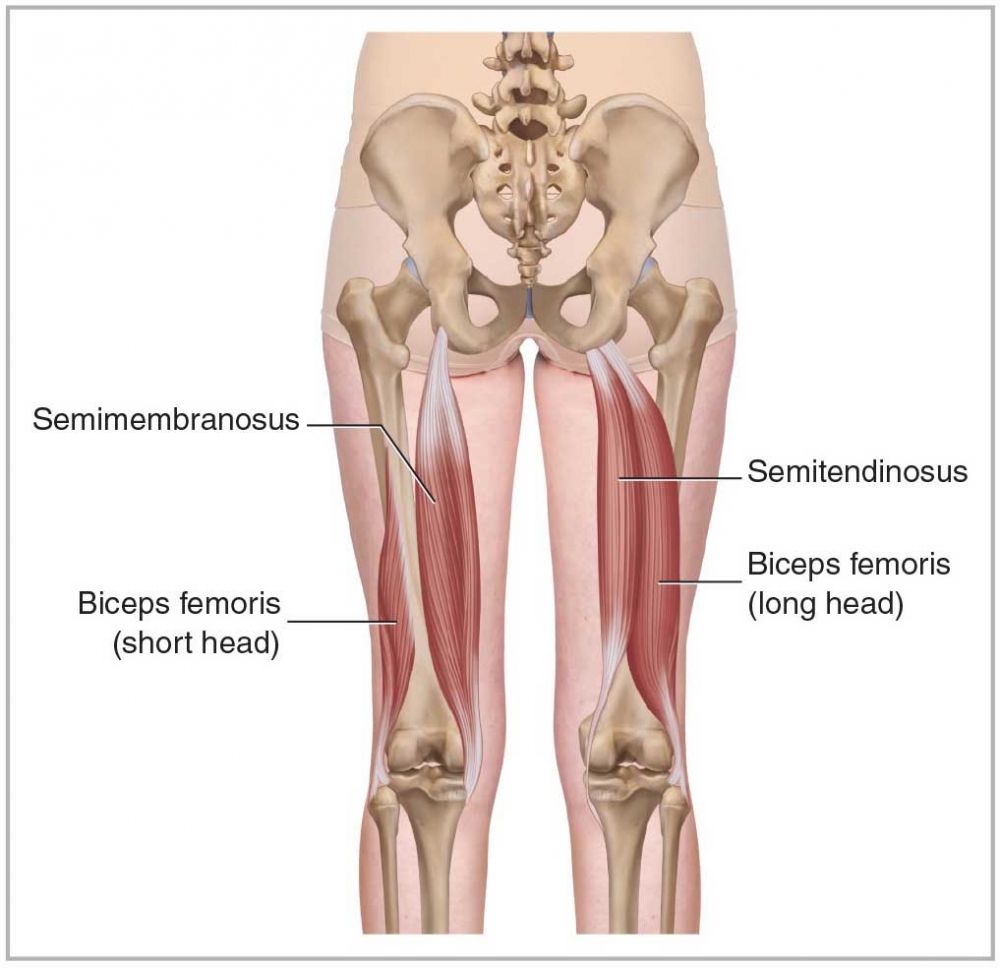
39
New cards
Rectus Femoris
QUADRISEPS
Origin: Iliac spine
Insertion: Tibial tuberosity and patella
Action: Thigh flexion and leg extension
Origin: Iliac spine
Insertion: Tibial tuberosity and patella
Action: Thigh flexion and leg extension
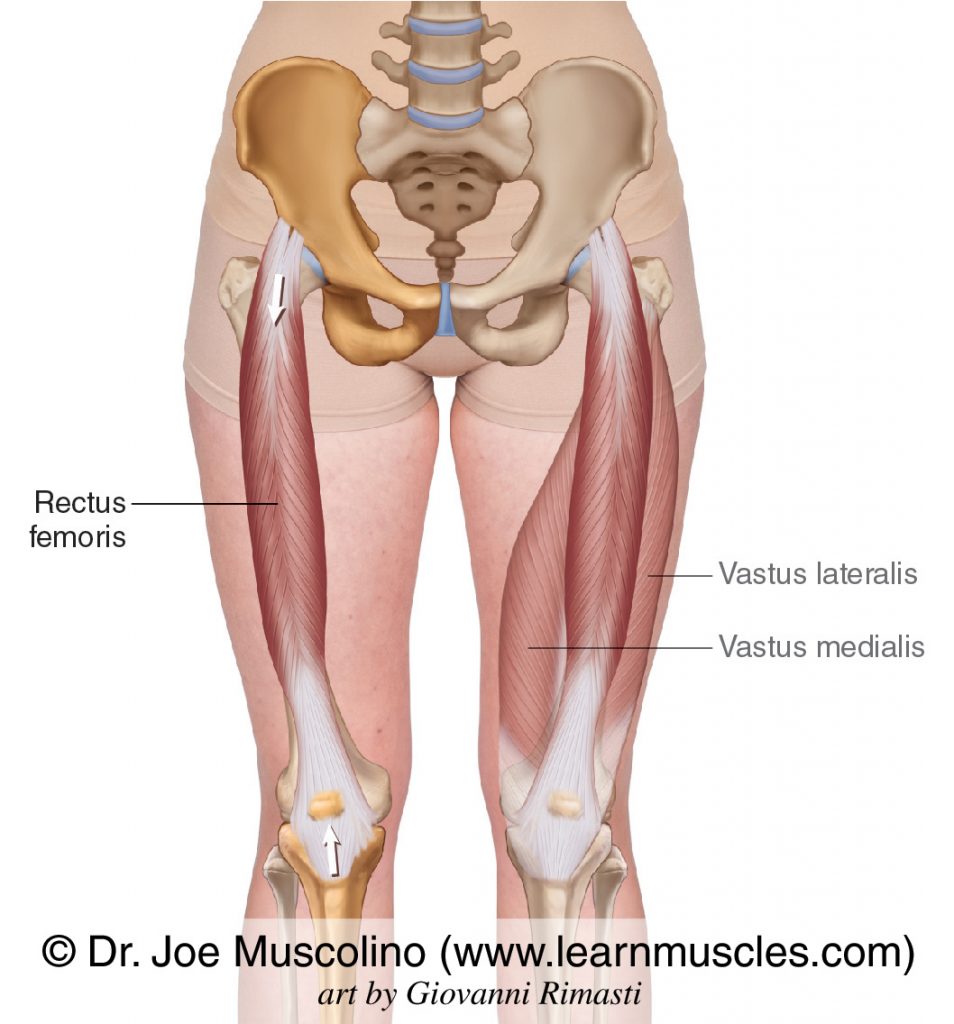
40
New cards
Vastus Lateralis
QUADRISEPS
Origin: Femur
Insertion: Tibial tuberosity and patella
Action: Leg extension (knee joint)
Origin: Femur
Insertion: Tibial tuberosity and patella
Action: Leg extension (knee joint)
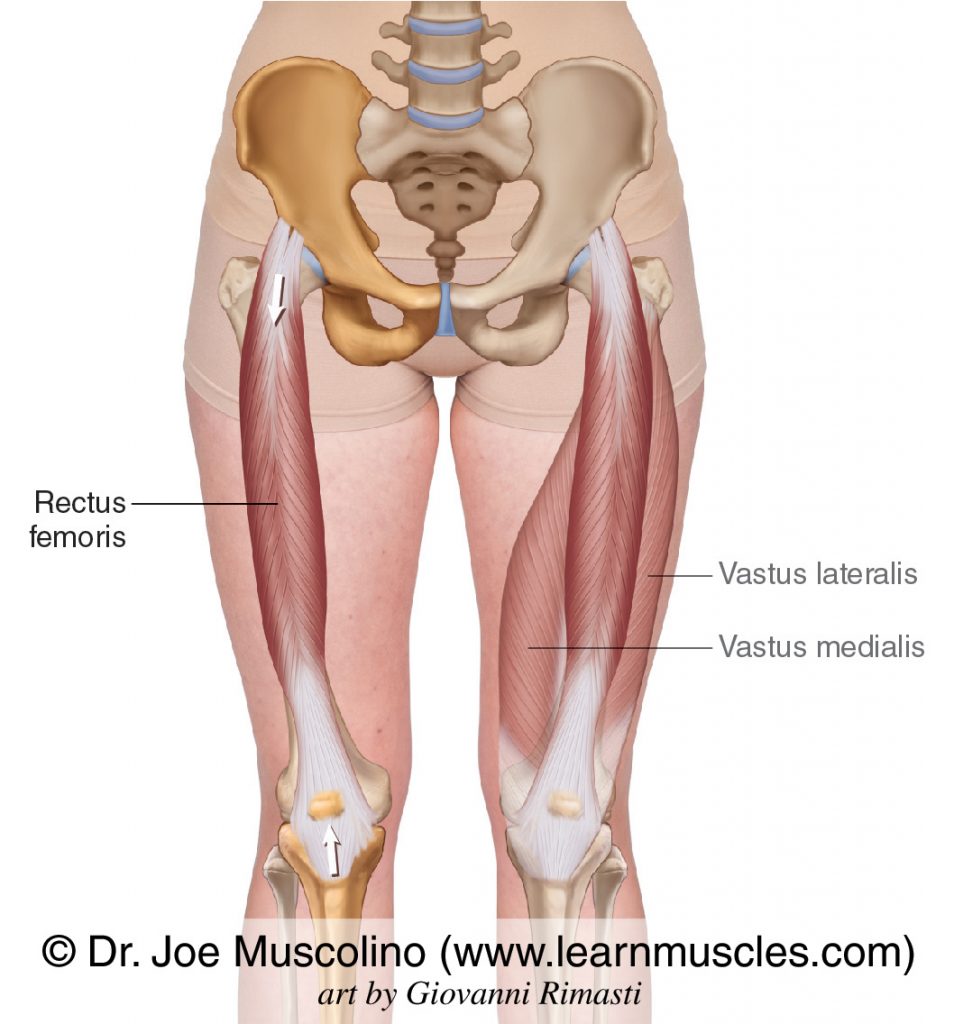
41
New cards
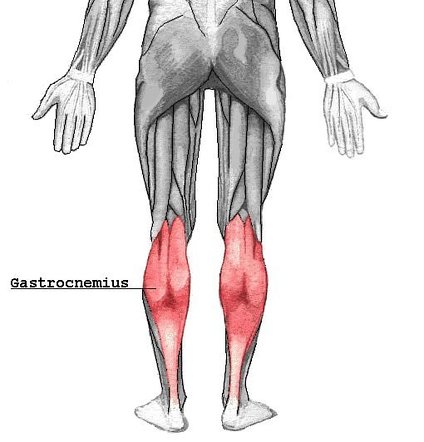
Gastrocnemius
Origin: Lateral condyle of femur
Insertion: Calcaneus
Action: Foot flexion and leg flexion (leg joint)
Insertion: Calcaneus
Action: Foot flexion and leg flexion (leg joint)
42
New cards
Muscular Dystrophy
Inherited disease (affects males)
- Weakness and wasting away of muscle tissue
-9 types (focus on 2)
1. Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD)
Onset: Ages 2-6
Symptoms:
- Weakness in muscles - Eventually involves all muscle
- Survival beyond 20 is rare
2. Becker Muscular Dystrophy
Onset: teen-adult
Symptoms:
- Same as DMD (just less severe)
Survival is into your middle age
- Weakness and wasting away of muscle tissue
-9 types (focus on 2)
1. Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD)
Onset: Ages 2-6
Symptoms:
- Weakness in muscles - Eventually involves all muscle
- Survival beyond 20 is rare
2. Becker Muscular Dystrophy
Onset: teen-adult
Symptoms:
- Same as DMD (just less severe)
Survival is into your middle age
43
New cards
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
ALSO CALLED: Lou Gehrigs Disease & Motor Neuron Disease
Inherited disease (SLIGHTLY more common in men)
- Motor neuron loss; disease hat affects the nervous system that controls voluntary muscle movement
Onset: Middle age- young adult
Signs and Symptoms:
- Weak/tight muscles - Muscles eventually become paralyzed
(Involuntary muscles and senses aren't affected)
Inherited disease (SLIGHTLY more common in men)
- Motor neuron loss; disease hat affects the nervous system that controls voluntary muscle movement
Onset: Middle age- young adult
Signs and Symptoms:
- Weak/tight muscles - Muscles eventually become paralyzed
(Involuntary muscles and senses aren't affected)
44
New cards
Tetanus
ALSO CALLED: Lockjaw
Infectious BACTERIAL disease
- Affects nervous system
Causes:
(feces, soil, dust, etc.)
Spores of bacteria grow and create a chemical called TETANOSPASMIN
Signs and Symptoms:
- Spasms/Stiffness in Jaw and Neck - Difficult swallowing
Infectious BACTERIAL disease
- Affects nervous system
Causes:
(feces, soil, dust, etc.)
Spores of bacteria grow and create a chemical called TETANOSPASMIN
Signs and Symptoms:
- Spasms/Stiffness in Jaw and Neck - Difficult swallowing
45
New cards
Motor Neuron
controls muscle cells
* apart of the peripheral nervous system
* comes from brain/spinal cord
* apart of the peripheral nervous system
* comes from brain/spinal cord
46
New cards
What is the connection between a muscle fiber and axon of a motor neuron called?
Synapse
47
New cards
How does the nervous system control muscle contraction?
Chemical reactions
48
New cards
Neurotransmitter
A chemical in control of something
49
New cards
Neuromuscular Junction
where a motor neuron connects to muscle fiber
(where muscle fibers are specialized and form a motor end plate)
(where muscle fibers are specialized and form a motor end plate)
50
New cards
Acetylcholine
makes muscle fibers contract (stored in DISTAL END OF AXON)
51
New cards
Steps for a bone to move
1. ACh diffuses across synapse
2. ACh binds to muscle fiber membrane (making NA enter the cell)
3. Entry of NA into the muscle cell stimulates a muscle impulse (action potential)
52
New cards
What is calcium?
The key to muscle contraction
(must be in sarcomere)
(must be in sarcomere)
53
New cards
Calcium in the sarcomere causes…
Actin and Myosin to grab ahold of each other
54
New cards
Muscle Relaxation Steps
1. ACh is destroyed by enzyme acetylcholinesterase
2. No ACh, so calcium is transported back to sarcoplasmic reticulum