Costs of production
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Fixed costs - definition
Costs that do not vary with the level of production or sales, in the short run they remain constant no matter the output
What are fixed costs, some examples?
Associated with the basic operations of a business, also known as overheads
How do fixed costs correlate to output required?
The higher the level of fixed costs, the higher the output needed to break even.
Variable costs - definition
Costs that change based on short run level of production changes, increase as output increases.
How are variable costs linked to marginal costs?
Variable costs are determined by the marginal cost of extra units of output as more variable inputs are hired.
Examples of variable costs
Bonuses, raw materials, part time wages, energy costs
Average cost equation
Total cost/ quantity
Average variable cost equation
Total variable cost/ quantity
Average fixed cost equation
Total fixed costs/quantity
Average total cost equation
Average variable cost + average fixed costs
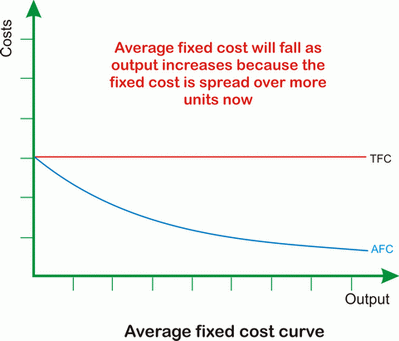
Graph for average and total fixed costs + explanation
Total fixed costs - constant no matter the output (short run)
Average fixed costs - decrease as cost spread over a larger output
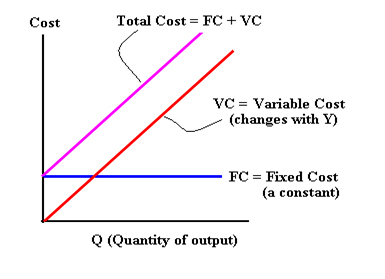
Total cost, variable cost and fixed cost graph
(straight line)
When variable costs = 0, Total cost = fixed cost
Average costs graph
Marginal cost - definition
The cost added by producing one more unit of a good/service.
Marginal cost equation
Change in total cost/ change in output
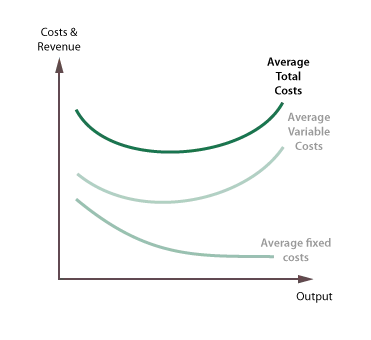
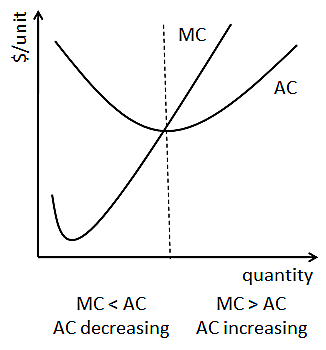
Marginal Costs and Average total cost graph
If MC<AC, last unit produced costs less than the average good, so average total cost falls
IF MC = AC, average cost remain constant, as the cost of the last unit produced is the same as that of the average good
IF MC>AC, last unit produced costs more than the average good, so average total cost rises
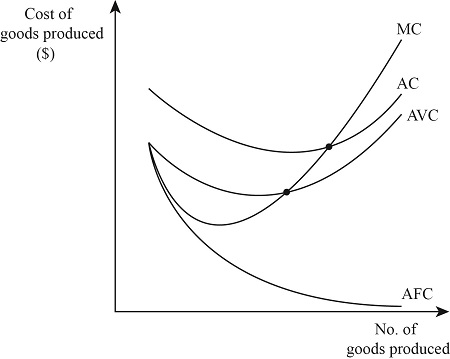
Marginal cost & total, variable, fixed average cost graph
Difference between average cost and average variable cost lines = average fixed costs
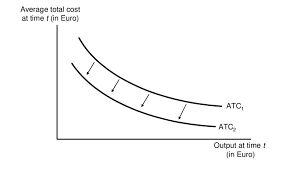
What effect does a change in fixed cost have?
Causes average cost curve to shift
Variable and marginal costs unaffected.
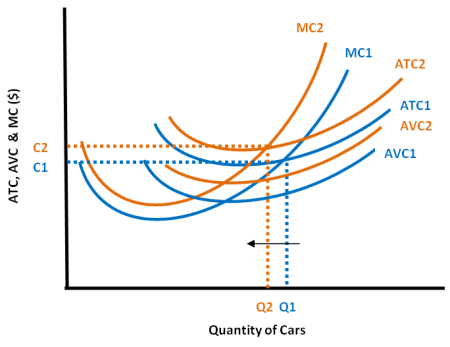
What affect does a change in variable cost have?
Increases both total avg cost and marginal cost.
Causing an upward shift in both curves.
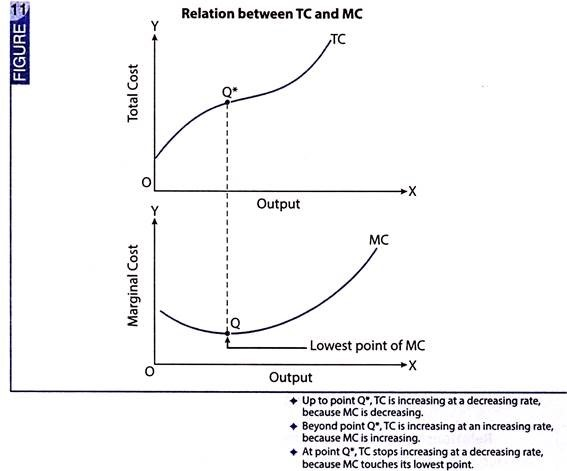
How does marginal cost link to total cost?
Total cost is always increasing with output.
TC rises at a diminishing rate as MC falls, each extra output is adding less and less to TC.
Then TC rises at increasing rate as MC rises.