zoo final
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
describe blood flow through mammal circulatory system
deoxy blood into right atrium then right ventricle, out to lungs to be oxy, the oxy blood returns to left atrium then left ventricle, then fully oxy blood out to heart
what ensures rhythmic heart beat in mammals?
Sinoatrial node in right atrium
what derived trait in mammals allow each cell to contain more hemoglobin?
mammal red blood cells do not have nucleus, a derived trait not in any other vertebrates
defining characteristics of mammals?
Hair
Mammary glands
Sebaceous skin
Jaw bones and muscles
Specialized nasal bones
Specialized teeth
Ear structure
Specialized kidney
Cerebral cortex
True gestational pregnancy
what are the benefits of fur/hair in mammals?
Made of keratin protein
2 types of hair
Under hair: dense, soft, insulation to retain body temp
Guard hair: coarse, longer, protection and coloration
Vibrissae (whiskers/bristles) attach to nerves and provide sensory info
communication
what are the 2 types of hair in mammals?
Under hair: dense, soft, insulation to retain body temp
Guard hair: coarse, longer, protection and coloration
what is fur/hair made of?
keratin protein
what is vibrissae?
whiskers/bristles that attach to nerves and provide sensory info
what are mammary glands?
Secrete milk
Ductal system surrounded by milk producing cells, secreted through nipples
Glands vary from 2-20
Grow late in pregnancy in response to hormones
Lactation means offspring do not forage on own, mother supplies nutrients
what are sebaceous glands?
Excrete sebum lipids to keep skin/hair soft and pliable, helps waterproof skin
what are eccrine glands?
Secrete watery fluid
Allows temp regulation (perspiration)
Not all animals have, found in hairless areas of body, most primates (and horses) have them scattered through body
what glands allow perspiration?
eccrine glands
what are apocrine glands?
Secrete milky odorous fluid, scent gland, used for communication
Develop during sexual maturity
Location dependent on species
Skunks can discharge secretions 6-10 ft
how did olfaction impact mammals brain?
Have highly developed sense of vision, hearing, taste, and smell
Sense of smell especially well developed and linked to skin glands used extensively in communication
Olfactory receptors distributed in nasal cavity and connected to olfactory bulb in brain
Some have vomeronasal organ (Jacobson’s organ)
Info processed by cerebral cortex, outermost layer of gray matter which receives all sensory info and controls voluntary muscle movement, memory, judgement…
what is the kidneys with loops of henle function?
Able to concentrate urine to maintain osmoregulation
Urine has high concentration of solutes, up to 4x concentration of blood
Urinary bladder
what is the pulmonary systems function?
Inhale air through nasal cavity, turbinate bones in nasal cavity warms air and adds moisture
Air flows through pharynx and larynx and into trachea which funnels inhaled air into lungs and exhaled air out of lungs
Trachea divides into 2 major branches, called primary bronchi
All bronchi tubes are lined w smooth muscle (can contract to push air out of lungs-cough) and hyaline cartilage
Inside each tube are goblet cells to produce mucus and ciliated cells to remove particles in air
Each primary bronchus branches into secondary branches into secondary bronchi which branch into tertiary bronchi which branches into bronchioles, each bifurcation (or branch) leads to a smaller passage
what are the parts of the trachea?
Trachea divides into 2 major branches, called primary bronchi
All bronchi tubes are lined w smooth muscle (can contract to push air out of lungs-cough) and hyaline cartilage
inside each tube are goblet cells to produce mucus and ciliated cells to remove particles in air
Each primary bronchus branches into secondary branches into secondary bronchi which branch into tertiary bronchi which branches into bronchioles, each bifurcation (or branch) leads to a smaller passage
what are the benefits of mammals external ears?
Greater surface area to receive soundwaves and dissipate heat
what are flight adaptations?
Wings
Modified hand/paw w membrane skin extending to back limbs
True flight (bats)
Patagium
Skin that extends from sides of body to front and back limbs
Gliding flight (flying squirrels)
what is echolocation and who uses it?
Bats produce short, high frequency pulses from their mouth
Cetaceans (whales, dolphins, porpoises) produce clicks in nasal passage and then focused in their melon
How are horns and antlers different?
True horns occur in Bovidae family (sheep, cattle, antelopes)
Have bone core extending from skull w epidermal layer covering bone and keratin layer covering epidermal
Not shed
Don’t branch
Grow continuously in both sexes
Antlers occur in Cervidae family (deer)
Grow in spring, shed in fall after breeding ssn
Solid bone covered in velvet
Are shed
Do branch
Grow for limited time in males only (caribou/reindeer females are exception)

what are true horns and what family/species do they occur in?
True horns occur in Bovidae family (sheep, cattle, antelopes)
Have bone core extending from skull w epidermal layer covering bone and keratin layer covering epidermal
Not shed
Don’t branch
Grow continuously in both sexes
what are antlers and what family/species do they occur in?
Antlers occur in Cervidae family (deer)
Grow in spring, shed in fall after breeding ssn
Solid bone covered in velvet
Are shed
Do branch
Grow for limited time in males only (caribou/reindeer females are exception)
how are mammals mouth musculature and teeth different than other animals?
lower jaw comprised of 1 bone called dentary hinged to temporal bone of skull
Abductor muscle closes jaw, temporalis, and masseter allowing up/down and side/side movement
Specialized heterodont teeth w diff teeth for diff functions
Other vertebrates are homodonts
Diphyodonts
Mammals have “baby” teeth and adult teeth wherease most other vertebrates can replace teeth through their life

what are diphyodonts?
Mammals have “baby” teeth and adult teeth wherease most other vertebrates can replace teeth through their life
what are mammals different feeding specializations?
insectivores
herbivores
carnivores
omivores
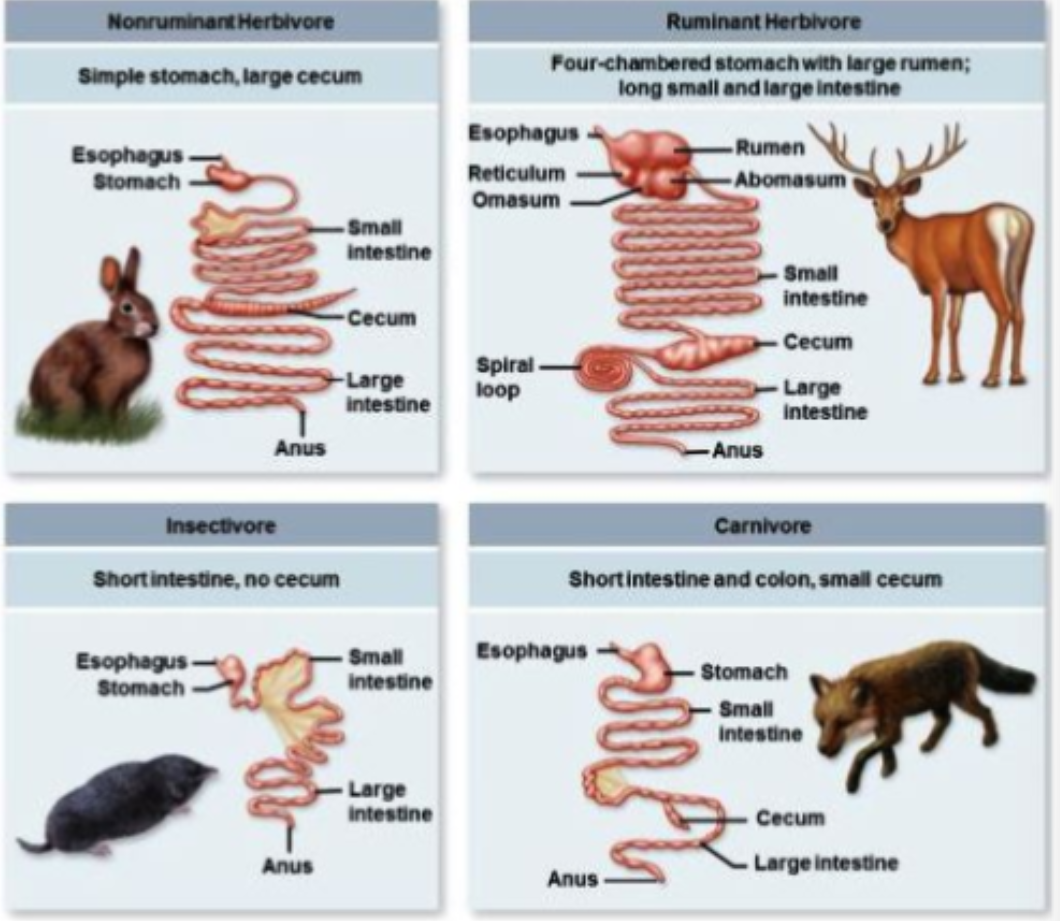
what are insectivores?
Eat insects and other inverts
No food requiring prolonged fermentation due to short intestinal tracts
Specialized teeth to crush exoskeleton
Shrews, moles, bats, anteaters…
what are herbivores?
Feed on grass and other veg
No canine teeth, premolars/molars for grinding
Digesting cellulose requires specific anaerobic bacteria that produce cellulase
Very long digestive tract
Non ruminants: fermentation occurs in colon or cecum (elephants, horses)
Remnants: fermentation occurs in 4 chambered stomach (bison, antelope, giraffes)
eat continuously
what are non ruminants vs ruminants in herbivores?
Non ruminants: fermentation occurs in colon or cecum (elephants, horses)
Remnants: fermentation occurs in 4 chambered stomach (bison, antelope, giraffes)
what are carnivores?
Feed on other vertebrates, aquatic mollusks, crustaceans
Large canines, pre molars/molars to shear muscle away from bones
Protein easier to digest than cellulose, they have short digestive tract
Eat in large discrete meals
Very intelligent
what are omnivores?
Feed on both plant and animal
Versatile teeth w round molars for crushing
Pigs, bears, primates
how do mammals reproduce?
Most have defined mating ssn in winter or spring
Females coming into estrus defines mating ssn
Monoestrous: 1 estrus cycle per breeding ssn (fox, wolves, bats)
Polyestrous: recurrent estrus cycles per breeding ssn (most mammals)
Fall into 1 of 3 reproductive patterns
monotremes
marsupials
placentals (eutherians)
monoestrous vs polyestrpus?
Monoestrous: 1 estrus cycle per breeding ssn (fox, wolves, bats)
Polyestrous: recurrent estrus cycles per breeding ssn (most mammals)
what are the 3 reproductive patterns?
Monotremes
Platypus, echidnas
1 breeding ssn/year
eggs hatch relatively underdeveloped
Thin, leathery shell secreted around embryo
Platypus: eggs laid in burrow, brooded by mother
Echidnas: eggs brooded in abdominal pouch
Have mammary glands but no nipples
Marsupials
Kangaroos, opossums, tasmanian devils, koalas
Pouched viviparous
Short placental gestation, embryos born anatomically and physiologically underdeveloped
Once born embryo crawls to pouch and attaches to nipple to complete development
Female kangaroos have unique reproduction, embryonic diapause, where embryo is attached to nipple in pouch the female can get pregnant again
This embryos development stops while “joey” in pouch continues to grow, and once joey leaves the diapaused embryo continues to develop and is born ~33 days later
Placentals (eutherians)
Viviparous placental w prolonged gestation that increases w body size
Placenta connects to mothers uterus where gas, waste, and nutrient exchange occur
Once born young are either
Altricial: blind, sometimes hairless, helpless
Precocial: fur, open eyes, able to move around
Mother produces milk for young to nurse and teaches young to be an adult
what are monotremes?
Platypus, echidnas
1 breeding ssn/year
eggs , typically 2, fertilized in oviduct and develop in uterus 10-12 days, hatch elatively underdeveloped
Thin, leathery shell secreted around embryo
Platypus: eggs laid in burrow, brooded by mother
Echidnas: eggs brooded in abdominal pouch
Have mammary glands but no nipples
what are marsupials?
Kangaroos, opossums, tasmanian devils, koalas
Pouched viviparous
Short placental gestation, embryos born anatomically and physiologically underdeveloped
Once born embryo crawls to pouch and attaches to nipple to complete development
Female kangaroos have unique reproduction, embryonic diapause, where embryo is attached to nipple in pouch the female can get pregnant again
This embryos development stops while “joey” in pouch continues to grow, and once joey leaves the diapaused embryo continues to develop and is born ~33 days later
what are placentals (eutherians)?
Viviparous placental w prolonged gestation that increases w body size
mice=21 days
wolves=63 days
horses=330 days
elephant=22 months
Placenta connects to mothers uterus where gas, waste, and nutrient exchange occur
Once born young are either
Altricial: blind, sometimes hairless, helpless
Precocial: fur, open eyes, able to move around
Mother produces milk for young to nurse and teaches young to be an adult
What is the primary function of hair in mammals?
To trap a layer of air to maintain body temperature
Which gland is responsible for producing sebum, providing water resistance and lubrication for hair in mammals?
Sebaceous gland
Which group of muscles allows mammals to perform chewing movements?
Adductor muscles
What is the term for mammals having different types and shapes of teeth, including incisors, canines, premolars, and molars?
heterodont
What is the specialized group of cardiac cells located in the walls of the right atrium, determining the heart rate in mammals?
sinoatrial node
What distinguishes mammalian erythrocytes (red blood cells) from those of other vertebrates?
Lack of nuclei in erythrocytes
What distinguishes monotremes (prototheria) from other mammals?
egg laying
What is unique about the gestational period of marsupials (metatheria)?
It is only about a month long.
What feature distinguishes placental (eutheria) mammals from monotremes and marsupials?
Chorioallantoic placenta
Which of the following lead to the great diversity of mammal species?
feeding specialization
What are the differences between Ultimate versus Proximate Causations?
Ultimate (why)
Evolutionary
What led to this behavior?
How does this behavior increase relative fitness
Ultimate causations are dependent on proximate causations
Ex. why do zebras group in herds?
Proximate (how)
Physiological
What mechanism led to this behavior?
Nervous, endocrine
Proximate causations lead to ultimate causations
Ex. what pushes them to group in herds
what is ultimate causation?
Ultimate (why)
Evolutionary
What led to this behavior?
How does this behavior increase relative fitness
Ultimate causations are dependent on proximate causations
Ex. why do zebras group in herds?
what is proximate causation?
Proximate (how)
Physiological
What mechanism led to this behavior?
Nervous, endocrine
Proximate causations lead to ultimate causations
Ex. what pushes them to group in herds
Kinesis versus Taxis?
2 diff types of movement
Kinesis is undirected movement in response to stimulus
Taxis is directed movement towards or away from stimulus
what is kinesis?
undirected movement in response to stimulus
what is taxis?
directed movement towards or away from stimulus
what are innate behaviors?
Instinctual
genetic
Independent of enviro influence
Occur naturally in response to specific stimulus
Ex. spider spinning web, suckling behavior
what is a fixed action pattern?
Movement elicited in response to stimulus, movement continues when stimulus is changed or removed
Ex. Male sickleback attacking anything with red on its underside
Ex. Geese retrieving eggs that have rolled from their nest using head tucking movements
what is migration?
Long range seasonal movement
Response to change in source availability
Innate, but pattern and destination learned
Ex. birds migrating to warmer weather
what is foraging?
Movement to search for food/water
Optimal patterns maximize energy gain and minimize energy loss
what is group living?
Living in group requires innate behaviors
Even solitary animals must interact w others to mate
3 general characteristics of innate behaviors involved in animal interactions
Communication
Altruistic behavior
Mating rituals
What are the different ways animals can communicate?
Communication
Chemical (pheromones)
Ex. wolf peeing on trees to mark territory
Visual (courtship and aggressive displays)
Aural (sound)
Tactile (touch)
Mating rituals
Altruistic behavior
Lower fitness of individuals exhibiting behavior and increase fitness of another
Ex. mutual grooming, beggar bats, wolves bringing food back from hunt
What is the difference between interspecific and intraspecific mate selection?
Intersexual selection
Individuals of 1 sex choose mates of the other sex based on visual, aural, tactile, and chemical cues
Ex. female peacocks choose mates w brightest plumage
Intrasexual selection
Competition for mates within same sex, involving displays and aggressive rituals
Ex. male giraffes head butt to determine dominance and access to females
what is intersexual selection?
Individuals of 1 sex choose mates of the other sex based on visual, aural, tactile, and chemical cues
Ex. female peacocks choose mates w brightest plumage
what is intrasexual selection?
Competition for mates within same sex, involving displays and aggressive rituals
Ex. male giraffes head butt to determine dominance and access to females
What are the three main mating types?
Monogamous: 1 male and 1 female pair for atleast 1 breeding ssn
Gray wolves, female gets parental care from father
Polygynous: 1 male mates w multiple females
Elephant seal, mae can mate with many females and females are protected
Polyandrous: 1 female mates w many males
Sea horses, males don’t have to look for mate and females can mate with many males
monogamous?
1 male and 1 female pair for atleast 1 breeding ssn
Gray wolves, female gets parental care from father
polygynous?
1 male mates w multiple females
Elephant seal, male can mate with many females and females are protected
polyandrous?
1 female mates w many males
Sea horses, males don’t have to look for mate and females can mate with many males
what are learned behaviors?
Flexible and can be modified
Occur as result of experience
Able to adapt to changes in enviro
Ex. young animals playing, gorilla using tools
2 main types of simple learned behaviors
Habituation
imprinting
what is habituation?
Simple form of learning in which animal stops responding to stimulus after repeated exposure
Exposure can be positive or associated w no harm
what is imprinting?
Seen in many newly born/hatched animals
Ex. hatchling ducks recognize and bond w first big animal they see, typically their mother
What is the main difference between taxis and kinesis?
Taxis is directed movement, while kinesis is undirected movement
Which of the following best describes a fixed action pattern?
Series of movements elicited by a stimulus, continuing after its removal.
What is the purpose of migration in animals?
Long-range seasonal movement in response to resource availability
What is optimal foraging behavior, and why is it favored by natural selection?
Feeding behaviors maximizing energy gain and minimizing energy expenditure
What are the different types of signals used by animals for communication within a species?
Chemical, aural, visual, and tactile.
Explain the overall role of pheromones in animal communication?
Pheromones elicit specific behaviors.
What is the concept of altruistic behaviors?
Altruistic behaviors benefit others at a cost to the individual exhibiting the behavior.
Which type of selection involves individuals of one sex choosing mates of the other sex based on visual, aural, tactile, and chemical cues?
Intersexual selection
What is a characteristic feature of polyandrous mating systems
One female mates with many males
What is the significance of imprinting in the maturation process of young animals?
It fosters a bond with the first adult seen, promoting protection and survival.