BCH 401G In class Quiz Questions
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Nitrogenous base
A nucleotide contains which of the following?
A. 6-carbon sugar
B. At least 3 phosphate groups
C. Nitrogenous sugar
D. 4-carbon sugar
E. nitrogenous base
C. The action of CPS2 to create Carbamoyl Phosphate
The first committed step in pyrimidine biosynthesis is:
A. The action of CPS2 to create Inosine 5’ Monophosphate (IMP)
B. The action of ribonucleotide reductase to create dTTP
C. The action of CPS2 to create Carbamoyl Phosphate
D. The action of Glutamine:PRPP Aminotransferase to create OMP
B. Phosphodiester bond
Nucletides are joined together in a polymer chain via a:
A. Glycosidic Bond
B. Phosphodiester bond
C. DNA Ligation
D. Hydrogen bond
E. Nucleophilic reaction
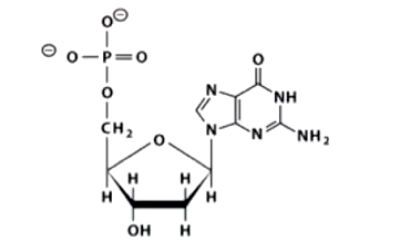
B. 2’-deoxyguanosine 5’ monophosphate (dGMP)
What is the name of this structure?
A. 2’-deoxythymidine 5’ triphosphate (dTTP)
B. 2’-deoxyguanosine 5’ monophosphate (dGMP)
C. Adenosine 5’-monophosphate (ADP)
D. 2’-deoxycytidine 5’-monophosphate (CMP)
B. Can use mono, di, and triphosphate nucleotides in synthesis
Which is FALSE about DNA polymerase III?
A. Requires a template strand for synthesis
B. Can use mono, di, and triphosphate nucleotides in synthesis
C. Has polymerase and exonuclease activity
D. Requires a primer-can only add nucleotides to a growing chain
E. Uses magnesium to stabilize its active site
C. The nucleotide triphosphate is attached to the 3’-hydroxyl of the new strand
What best describes chain elongation during replication?
A. The nucleotide diphosphate is attached to the 5’-hydroxyl of the new strand
B. The nucleotide monophosphate is attached to the 5’-hydroxyl of the new strand
C. The nucleotide triphosphate is attached to the 3’-hydroxyl of the new strand
D. The nucleotide monophosphate is attached to the 5’-hydroxyl of the template strand
C. Initially, the leading strand is continuous while the lagging strand is composed on disconnected fragments
What’s the difference between the leading and lagging strands?
A. The leading strand is synthesized 5’ to 3’ while the lagging strand is synthesized 3’ to 5’
B. The leading strand is made of DNA only but the lagging strand is DNA and RNA
C. Initially, the leading strand is continuous while the lagging strand is composed on disconnected fragments
D. The leading strand is synthesized only by DNA polymerase and lagging only by DNA polymerase I
B. Eukaryotic replication occurs only in S phase of the cell cycle while bacteria continuously replicate their DNA
How does DNA replication in eukaryotes and prokaryotes differ?
A. Eukaryotic DNA replication is not bi-directional
B. Eukaryotic replication occurs only in S phase of the cell cycle while bacteria continuously replicate their DNA
C. Replication forks in eukaryotes move more slowly
D. There are fewer DNA polymerases in eukaryotes
E. There are fewer replication origins in eukaryotes
B. Mismatch
What is the most common source of mutation in DNA?
A. Chemical mutagens
B. Mismatch
C. Replication slippage
D. Gamma Irradiation
E. Base insertion
D. Crosslinking between strands blocks replication
Why would an alkylating agent cause cell death?
A. Uracil is incorporated into the DNA
B. Resulting thymine dimers block replication
C. Causes guanine to pair with adenine
D. Crosslinking between strands blocks replication
D. Base methylation is present on the parental DNA that is not yet added to the daughter strand
The MutS/MutL/MutH mismatch repair system in E. coli can distinguish daughter strand DNA from parent DNA by:
A. An altered conformation of the daughter DNA due to recent replication
B. Histones have not yet been added to daughter strand DNA
C. Differential incorporation of heavy and light nitrogen
D. Base methylation is present on the parental DNA that is not yet added to the daughter strand
E. All of these play a role
Which of the following does not play a role in base-excision repair?
A. DNA polymerase
B. DNA ligase
C. Deoxyribose phopshodiesterase
D. AP Endonuclease
E. All of these play a role
C. Uses ribose triphosphate when growing the chain
Which of the following is specific to transcription compared to DNA replication?
A. synthesis proceeds 5’ to 3’ only
B. 3’ OH of growing chain attacks phosphate of incoming triphosphate
C. Uses ribose triphosphates when growing the chain
D. Synthesis driven by pyrophosphate hydrolysis
C. The termination signal is coded in the DNA
Which of these is true for both intrinsic and protein-dependent termination?
A. Requires a protein called rho (p)
B. Contains a G-C rich sequence followed by a stretch of U’s
C. The termination signal is coded in the DNA
D. Forms a hairpin structure
E. ATPase activity allows a protein to pull down on the newly formed RNA
C. Glucose levels are high
The lac operon does NOT transcribe downstream genes when..
A. allolactose binds to the repressor
B. B-galactosidase binds to the Lac promoter
C. Glucose levels are high
D. Lactose levels are high
E. CAP with cAMP binds to operon
A. Estradiol binding to the NHR induces a conformational change in the NHR
How are coactivators recruited to enhance transcription at Estrogen Response Elements?
A. Estradiol binding to the NHR induces a conformational change in the NHR
B. NHR with coactivators binds to the DNA-binding domain
C. Chromatin opens due to addition of acetyl groups by HATs
B. Decreased rate of degradation and increased ability to be transcribed
Which of the following would you expect for mRNAs that have a 5’ cap versus those that do not?
A. Decreased rate of degradation and decreased ability to be transcribed
B. Decreased rate of degradation and increased ability to be transcribed
C. Increased rate of degradation and decreased ability to be transcribed
D. Increased rate of degradation and increased ability to be transcribed
D. splicing
What process requires the presence of the sequence 5’-AAUAAA-3’ in the eukaryotic mRNA transcript?
A. Capping
B. Editing
C. Polyadenylation
D. splicing
E. tRNA base modification
A. intron
The branch point A residue involved in lariat formation is part of the….
A. intron
B. exon
C. 5’ cap
D. 3’polyA tail
A. GU
The 5’ end of the intron is marked by ____, where splicing factors bind
A. GU
B. GG
C. A
D. GT
E. AG
C. three
How many reading frames are in a 6 nucleotide stretch of mRNA 5’-AUACAC-3’
A. one
B. two
C. three
D. four
E. five
D. 4
Within the reading frame of the first start codon (AUG), how many amino acids are in this peptide? 5’-UCAUGCAUGCAUGCG-3’
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
D. anti-codon
Inosine can be within which part of the tRNA?
A. acceptor stem
B. Hydrogen bonds
C. CCA 3’ end
D. anti-codon
C. GTP bound to the amino acid
Which does NOT contribute to the specific binding of an amino acid into the aminoacyl tRNA synthase binding pocket?
A. size of the amino acid
B. charge of the amino acid
C. GTP bound to the amino acid
D. hydrophobicity of the amino acid
C. Shine-Delgarno sequence
What sequence on the prokaryotic mRNA correctly positions mRNA in the ribosome for translation?
A. mRNA cap
B. polyA tail
C. Shine-Delgarno sequence
D. Initiation Factor 3 (IF3)
B. P site
fMet is loaded onto which site in the ribosome to initiate translation?
A. A site
B. P site
C. E site
D. Z site
C. inhibit fMethionine-tRNAf binding at the ribosome
Antibiotics like streptomycin are able to target bacteria and not eukaryotic cells because they
A. inhibit methionine-tRNAi binding at the ribosome
B. block the function of initiation factors
C. inhibit fMethionine-tRNAf binding at the ribosome
D. stop translation of uncapped mRNA