Peter Test 1
1/156
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
157 Terms
- Extreme temperatures
- Injury
- Chemical irritation
Pain triggers
the physiological process of detecting/transmitting noxious stimuli to the CNS
Nociception
- Transduction
- Conduction
- Transmission
- Modulation
- Perception
Nociception Steps
ascending pathways
transmission
descending pain pathway (attenuates pain through endogenous opioids)
modulation
<30 days
Acute pain
Months to years
chronic pain
0-2
mild pain
4-6
moderate pain
8-10
severe pain
Soft tissues and musculoskeletal structures
somatic
Internal organs
visceral
feels like it's coming from a nearby somatic structure
Referred pain is visceral, but
- nociceptive
- neuropathic
- nociplastic
Non-cancer pain
Tissue damage
Nociceptive
CNS/PNS damage
Neuropathic
- central sensitization
- CNS becomes hypersensitive and amplifies pain signals
- example is fibromyalgia
Nociplastic
- Nerve and bone pain
- Inflammation and chemotherapy (treatment-related)
cancer pain
Abnormally increased pain
Hyperalgesia
Pain from stimulus that doesn't usually cause pain
Allodynia
Inability to feel pain
Analgesia
Reduce prostaglandin synthesis by inhibiting COX enzymes
NSAIDS MOA
maintains GI epithelium
COX 1
is overexpressed in inflammatory diseases
COX 2
-anti-inflammatory
- analgesic
- antipyretic
NSAIDS effects
- Inhibit chemotaxis (directed movement of cells in response to a chemical gradient)
- Decrease IL-1
- Produce Reactive Oxygen Species
anti-inflammatory
Reverse peripheral sensitization
analgesic
Suppress PGE2 production
antipyretic
- Irreversible COX inhibitor
- Antiplatelet effects last 7-10 days
Asprin
- Reduces platelet aggregation
- primary use
Low dose aspirin (<325 mg)
Antipyretic and analgesic effects
Intermediate dose aspirin (325-2,400 mg)
Anti-inflammatory effects
High dose aspirin (2,400-4,000 mg)
Reye's syndrome when used for viral infections and fever
Asprin has an increased risk of _____ in children
GI bleeding (except for aspirin)
NSAIDS BBW
An increased risk for nephrotoxicity and AKI
NSAIDS AE
- celecoxib
- increased risk for CV events (MI, stroke, HF)
- decreased risk for GI events
COX-2 selective NSAIDS
- diclofenac
- meloxicam
- increased affinity for COX-2 but still retain activity for COX-1
- caution in patients with increased CV risk
partially selective NSAIDS
- ibuprofen
- naproxen
- aspirin
- decreased risk for CV events
- aspirin is cardio protective at low doses
- increased risk for GI events
nonselective NSAIDS
Take aspirin 1 hour before or 8 hours after
Ibuprofen special considerations
- One of the safest NSAIDs
- Has a long t1/2
Naproxen special considerations
- Has many dosage forms
- Oral
- Topical
- Ophthalmic
- Patch
- Injection
- Has increased risk of bleeding and CV events after an MI
Diclofenac special considerations
- Strong GI effects
- Pancreatitis
- Headache
- Effective for acute inflammation
indomethacin special considerations
Also inhibits LOX enzymes
- ketoprofen special considerations
Affects TNF-alpha and nitric oxide synthase (NOS)
flurbiprofen special considerations
- very High GI bleeding risk
- very Potent
- PO
- IV
- IM
ketorolac special considerations
- Dosed QD, but high doses are needed
- Has a low risk of GI damage
nabumetone special consideration
Useful in gout (since it is uricosuric)
oxaprozin special consideration
- Inhibits neutrophil migration and lymphocyte function, and decreases ROS formation at high doses
- Has a high risk of peptic ulcers and bleeding
piroxicam special consideration
- Useful in RA and OA
- Has a high risk of MI and thrombosis
meloxicam special consideration
- Renal toxicity
- Rashes
- HTN
- Thrombotic events
celecoxib special consideration
- Inhibits COX-3
- Has minimal effects on COX-1 or COX-2
acetaminophen MOA
- Analgesic and antipyretic effects
- No anti-inflammatory effects
acetaminophen has
4g/day
acetaminophen max dose
Severe hepatotoxicity
acetaminophen AE
N-acetylcysteine
________ is the antidote for acetaminophen overdoses
antipyretic
anilides have _____ effects
- Methemoglobinemia
- Jaundice
anailides toxicities
iron in hemoglobin is oxidized to a ferric state, which prevents it from carrying oxygen effectively
Methemoglobinemia
- Carboxylic acid is necessary, and must be adjacent to a hydroxyl group
- Presence of di-fluoro groups increase lipophilicity and acidity
salicylates
Optimal separation of carboxylic acid from the aromatic ring is one methylene unit
Aryl acetic acids
- Optimal separation of carboxylic acid from the aromatic ring is one methylene unit
- Alpha-substitution with a branched alkyl group is detrimental
- Highest level of anti-inflammatory activity occurs with the S-(+) isomer
Aryl propanoic acids
Display different pharmacophores
Oxicams
CYP2C9 metabolism by oxidation of pyridine
Piroxicam
CYP2C9 metabolism by thiazole methyl group
Meloxicam
Carboxylic acid group is replaced with sulfonamide
Selective COX-2 inhibitors
- Most opioids act on the mu-opioid receptors
- Directly inhibit neurons to lead to the activation of descending inhibitory neurons (inhibit an inhibitory, or GABAergic, neuron)
Opioid MOA
- Close presynaptic voltage-gated Ca2+ channels (VGCCs).
- Open postsynaptic K+ channels
opioids cellular effects
- Analgesia
- Addiction (“reward pathway”)
- Euphoria
- Dysphoria
- Sedation
- Opioid-induced hyperalgesia
- Respiratory depression (Cause of overdose/death)
- Cough suppression
- N/V
- Temperature fluctuations
- Neuroendocrine effects
- Miosis (pupil constriction)
opioids CNS effects
- miosis
- constipation
Patients will not develop tolerance to
- Constipation
- Urinary retention
- Immune system modulation
- Vasodilation
- Pruritus
- Bronchoconstriction
opioids peripheral effects
- Addiction, abuse, and misuse that can lead to OD and death
- Respiratory depression (that can be fatal)
- Increased risk of death when combined with other CNS depressants (benzodiazepines, alcohol, etc)
- Accidental ingestion in children can be fatal
- Crushing, dissolving, or chewing long-acting products can deliver a fatal dose
- Life-threatening neonatal withdrawal with prolonged use during pregnancy
opioids BBW
- Oral doses need to be much higher than IV doses due to the first pass effect
- Renally excreted
opioids PK
CYP3A4
fentanyl is metabolized by
CYP2D6
Codeine (a prodrug), oxycodone, and hydrocodone are metabolized by
Involves reduced clinical efficacy after using (higher doses are needed to achieve the same effects)
opioid tolerance
- Receptor down-regulation
- Anti-opiate chemicals
- Can be avoided with "opioid rotation"
opioid tolerance occurs due to
- psychological
- physical
opioids dependance can be
Desire/compulsion to take the drug despite harm
Psychological
Withdrawal symptoms occur with cessation of drug exposure
Physical
- Codeine
- loperamide
- Diphenoxylate/atropine
- methadone
- buprenorphine
- fentanyl
- meperidine
opioid agonist drugs
- analgesia
- Cough
- Diarrhea
- opioid use disorder
- anesthesia adjuvant
- post-anesthetic shivering
opioid agonists treat/cause
codeine
cough
- loperamide
- Diphenoxylate/atropine
diarrhea
- Methadone
- Buprenorphine
opioid use disorder
fentanyl
anesthesia adjuvant
Meperidine
Post-anesthetic shivering
- Naloxone
- Naltrexone
- Methylnaltrexone
- Naloxegol
- Naldemedine
opioid antagonist drugs
- opioid overdose
- OUD
- opioid-induced constiptaion (OIC)
opioid antagonists treat/cause
Naloxone
opioid overdose
Naltrexone
OUD
- Methylnaltrexone
- Naloxegol
- Naldemedine
opioid-induced constipation (OIC)
Oxymorphone
Hydromorphone
Levorphanol
Morphine
Oxycodone
Hydrocodone
Dihydrocodeine
Codeine
- old heads love mouthing off (go) home dirty clown
order of potency (most to least)
- morphine
- hydromorphone
- oxymorphone
- methadone
- fentanyl
- sufentanil
- alfentanil
- remifentanil
- meperidine
- levorphanol
strong agonists
- codeine
- oxycodone
- dihydrocodeine
- hydrocodone
- diphenoxylate
- loperamide
mild/moderate agonists
- buprenorphine
- butorphanol
- nalbuphine
- pentazocine
mixed receptor actions
- tramadol
- tapentadol
other CNS analgesics
- Naturally occurring
- Benzene ring
- Piperidine ring (N17)
- Phenol (C3)
- Secondary alcohol (C6)
- Alkene (C7-C8)
morphine
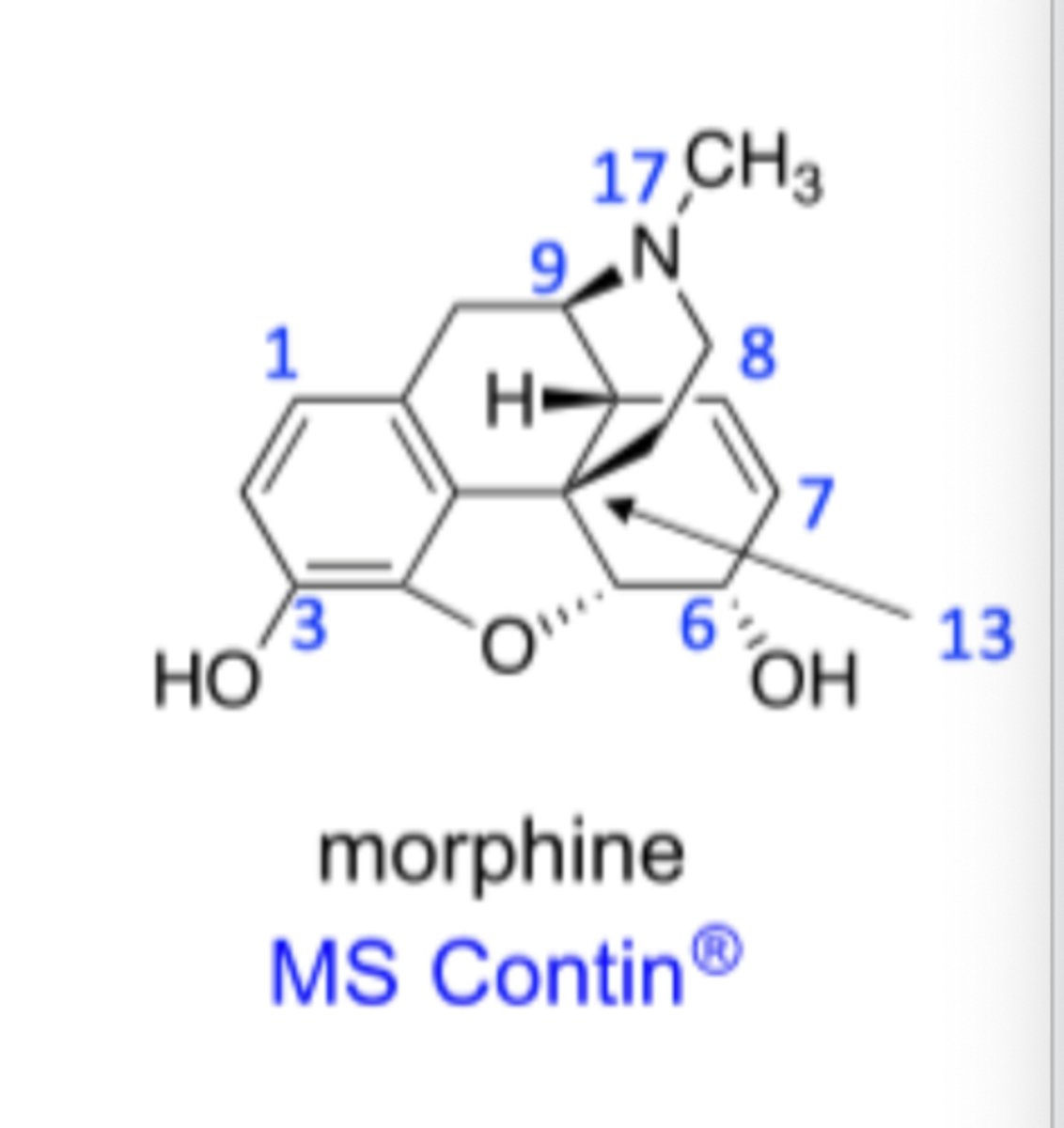
- Tertiary basic amine (N17)
- Central carbon (C13) with no hydrogens
- Phenyl ring attached to the central carbon (C13)
- Two carbons between the central carbon (C13)
in morphine there must be
agonist/antagonist activity
N17 substituent determines
activity
Phenol at C3 affects