medsurge GI
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
Bonus lab question for best practice: what is the last thing you should do before putting on sterile gloves?
Hand hygiene: set up sterile field, clean/prep site, open sterile gloves, hand hygiene, put on sterile gloves
What is a fecal occult blood test?
test stool for blood, parasites, bacteria, DNA changes (cancer, note: fecal occult means detecting nonvisible blood
What is good patient education for a fecal occult blood test?
no anticoagulants/nsaids for 7 days prior, 3 samples on different days, three repeats of + = GI bleed, guaiac card can be mailed
What is an endoscopy?
direct visualization inside body under moderate sedation through natural openings: used to diagnose GI disorders: cancer GI bleed etc. (only uses natural openings)
What is a colonoscopy?
visualize rectum and colon with endoscope, client must complete bowel prep to remove stool: only clear liquids (no blue green orange red), no anticoagulants preprocedural
What is an EGD?
visualize the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum going through the mouth
What is an ERCP?
endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography combines x ray and an endoscope to diagnose and treat issues with the pancreas and gallbladder, bile ducts, and liver
What is a capsule endoscope?
swallow a capsule with a camera for video of small bowel (capsule leaves via stool)
What are pre procedure endoscopy nursing notes?
NPO, no anticoagulants, patient positioning
What are post procedure nursing notes?
vitals, no liquid until gag reflex returns, watch for complications, lozenges for sore throat, no driving for 18 hours
What are complications of an endoscopy?
oversedation, hemorrhage, aspiration, perforation of bowel
What is a hydrogen breath test?
Identifies malabsorption, impaired digestion, overgrowth of bacteria: exhale into the hydrogen analyzer before and after ingesting test sugar. Positive indicate excess hydrogen in bloodstream
What are enteral feedings?
nutrition through the GI tract but bypasses mouth (for inability to swallow: feedings can be done via push, pump, or gravity, continuously or intermittent
What are the types of tube (enteral) feeds?
NG nose to stomach, ND nose to small intestine, NJ nose to small intestine, PEG percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy abdomen to stomach, PEJ abdomen to small intestine
What are complications for enteral feedings (and nursing cares to help)?
over feeding (residual volume checks, check rate), diarrhea (slow rate, check temp, test cdiff, skin protection), constipation (add water flushes, switch to fiber formula, increase physical activity), aspiration pneumonia (tube could be displaced, confirm placement, keep HOB>30, refeeding syndrome (assess for seizures, confusion, shallow respiration, muscle weakness, electrolyte labs), tube clogged (use water first to unclog, flush per shift, and before/after feeding and meds, limit residual checks
What is TPN?
total parental nutrition, used for GI tract disfunction but not preferred over enteral, administered through a central line
What is a hypertonic in relation to TPN?
more solute, contains complete nutrition when a client cannot utilize the digestive system
What is a PPN?
less hypertonic TPN that can be given peripherally (central line TPN more common though)
What is good TPN nursing management?
regular lab checks for electrolytes, glucose, etc. gradually increase rate, daily weights, follow sterile procedure, change tubing/bag every 24 hours even if not empty, no not add anything to solution bag, filter on the end of it
What are good central line notes for TPN?
done shower, 10ml syringes no smaller, change dressing every 7 days or more if needed, dedicated TPN feeding
What are complications of TPN (and nursing cares)?
Metabolic (frequent labs, monitor glucose), Air embolism (Watch for signs – dyspnea, chest pain, hypoxia, anxiety
What are preventions for GERD?
What is fundoplication?
fundus of stomach is wrapped around and behind the esophagus to create a barrier
What is a paracentesis? What are ascites?
fluid removal via needle or catheter form the abdominal cavity, indicated by respiratory distress: ascites are abnormal accumulations of protein – rich fluid in the abdominal cavity usually caused by cirrhosis of the liver
What is good nursing management for a paracentesis preprocedural?
consent, vitals, measure abdominal girth, weight, client should void prior to procedure
What is good nursing management for paracentesis post procedure?
hold pressure to insertion site and then apply dressing, measure drainage (usually 4 to 6 liters), VS, weight, measure abdomen girth again, administer albumin and diuretics to help restore fluid balance, monitor blood albumin, protein, glucose, electrolytes, BUN, creatine
What are complications of paracentesis?
hypovolemia, low albumin levels, infection
What is a nasogastric decompression?
NG tube is inserted w/ suction applies to relieve abdominal distension
What is an ostomy (3 kinds)?
surgical opening in from inside to outside: stoma (can be from the small or large intestine bypassing everything else down the line
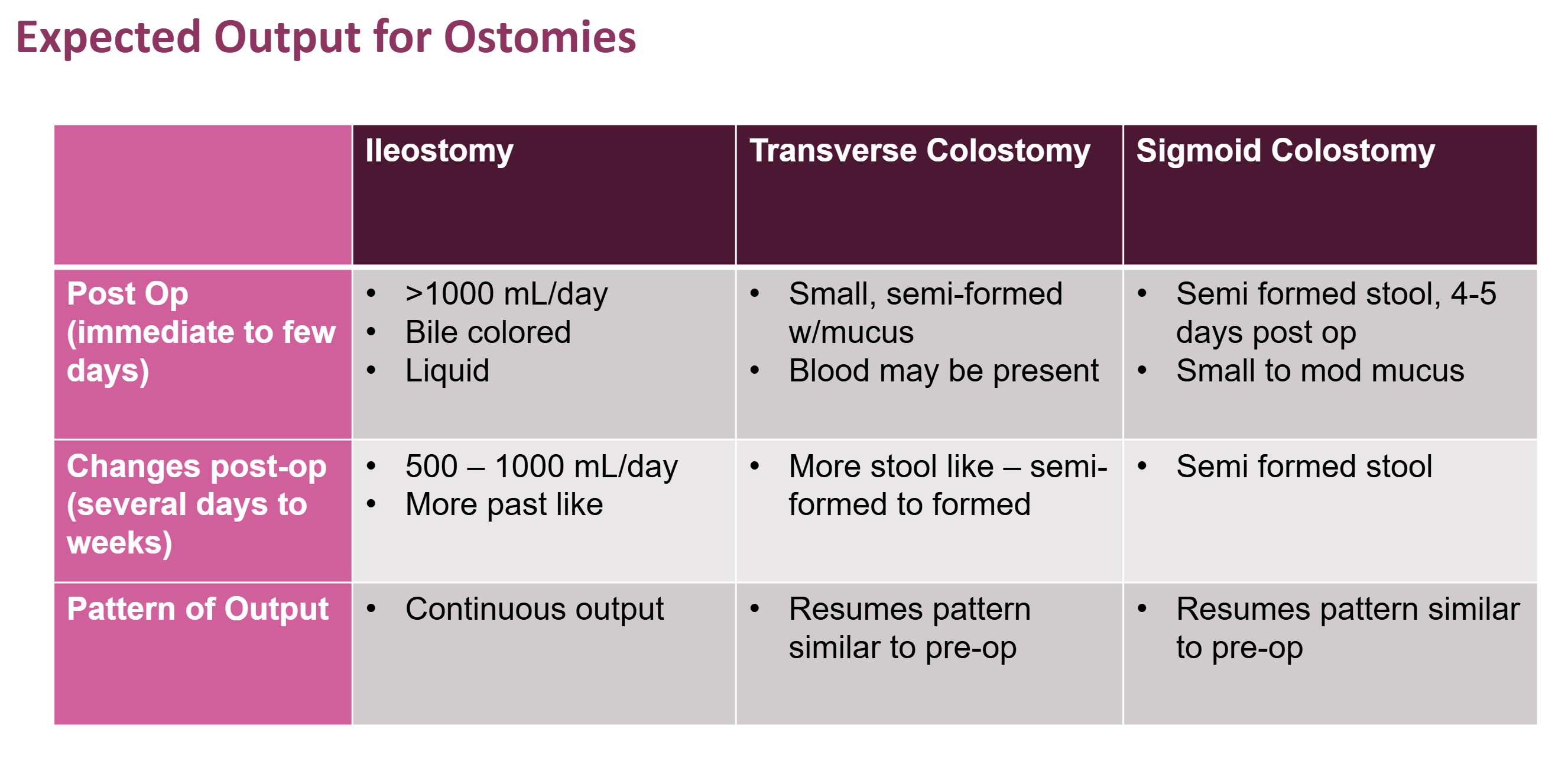
What is expected output for ostomies?
see slide 17
What is good nursing management for ostomies?
assess peristomal skin and stoma appearance, output change PRN/per order, watch for complications (color or bowel sound changes for example)
What is good client education for ostomies?
reduce foods that can cause odor and flatulence, teaching bag change/drain, discuss feelings/concerns, ostomy support groups
What is GERD?
back flow into the esophagus due to incompetent sphincter
What are findings for GERD?
dyspepsia (indigestion), pain, pyrosis (burning sensation), throat irritation, increased flatus and burping, cavities, chest congestion/wheezing w/ aspiration
What is a hiatal hernia?
protrusion of the stomach above the diaphragm into the thoracic cavity
What are findings for hiatal hernias?
heartburn, reflux, chest pain, dysphagia, belching, fullness after eating, worsening symptoms when supine, sense of suffocation
What are meds and therapeutic procedures for hiatal hernias?
PPIs and antiacids—EGD, CT w/ contrast, barium swallow (same as gerd), fundoplication
What are health promotion strategies for hiatal hernias?
similar to gerd: limit caffeine, carbonated drinks, citrus, healthy weight, HOB etc.
What are esophageal varices?
swollen/fragile blood vessels in the submucosa of the esophagus
What are risk factors for esophageal varices?
portal hypertension (high vein BP, alcoholic cirrhosis, viral hepatitis, age
What are findings for esophageal varices?
possibly no findings until bleeding begins, vomiting coffee/frank blood, melena stool
What are diagnostics/procedures for esophageal varices?
LFTs, hemoglobin/hematocrit, elevated blood ammonia, endoscopy
What is good nursing care for esophageal varices?
BBs, vasoconstrictors, monitor bleeding, infection and aspiration
What are therapeutic procedures for esophageal varices?
focused on fixing the liver
What is PUD?
Peptic ulcer disease: erosion of the mucosal lining of the stomach, esophagus or duodenum hat can lead to bleeding and perforation – mostly caused by H. pylori bacteria
What causes stress ulcers?
acute stress events such a s burns sepsis and organ trauma
What are PUD findings?
dyspnea, heartburn, bloating, nausea, uncomfortable fullness or hunger
What are diagnostics for PUD?
EGD, urea breath test, stool samples, hemoglobin and hematocrit
What is good nursing care for PUD?
note that antibiotics are the unique part of the list
What are therapeutic procedures for PUD?
EGD, surgical interventions (ex: pyloroplasty—enlarging whole between stomach and small intestine to increase gastric emptying rate)
What are complications of PUD?
perforation/hemorrhage, pernicious anemia, pyloric obstruction, dumping syndrome
What is dumping syndrome and client education for it?
rapid release of metabolic peptides following ingestion of food: law down after meals, small frequent meals, no liquids with meals, limit milk sugar and fiber
What is gastritis?
stomach lining inflammation (nonerosive, erosive, acute, chronic, extensive)
What are symptoms of gastritis?
nausea, vomiting, bloating, pain, indigestion, burning feeling in stomach, loss of appetite etc.
What are diagnostics for gastritis?
CBC, H. pylori test, EGD
What are complications of gastritis?
GI bleed/obstruction, dehydration, pernicious anemia
What is good nursing management for gastritis?
histamine antagonists, antacids, PPI, small frequent meals, avoid GI irritation foods, watch for signs of bleeding/anemia
What is an EGD?
medical procedure that uses a long, flexible tube with a camera and light to examine the lining of the esophagus, stomach, and the first part of the small intestine (duodenum)
What is pernicious anemia?
Pernicious anemia, one of the causes of vitamin B12 deficiency, is an autoimmune condition that prevents your body from absorbing vitamin B12.
What are risk factors for hernia?
male, age, increased intraabdominal pressure due to pregnancy, obesity, genetics
What are findings for hernia?
protrusion or lump and groin, umbilicus, incision scar and when strangulated can cut off food and supply to bowel leading to necrosis
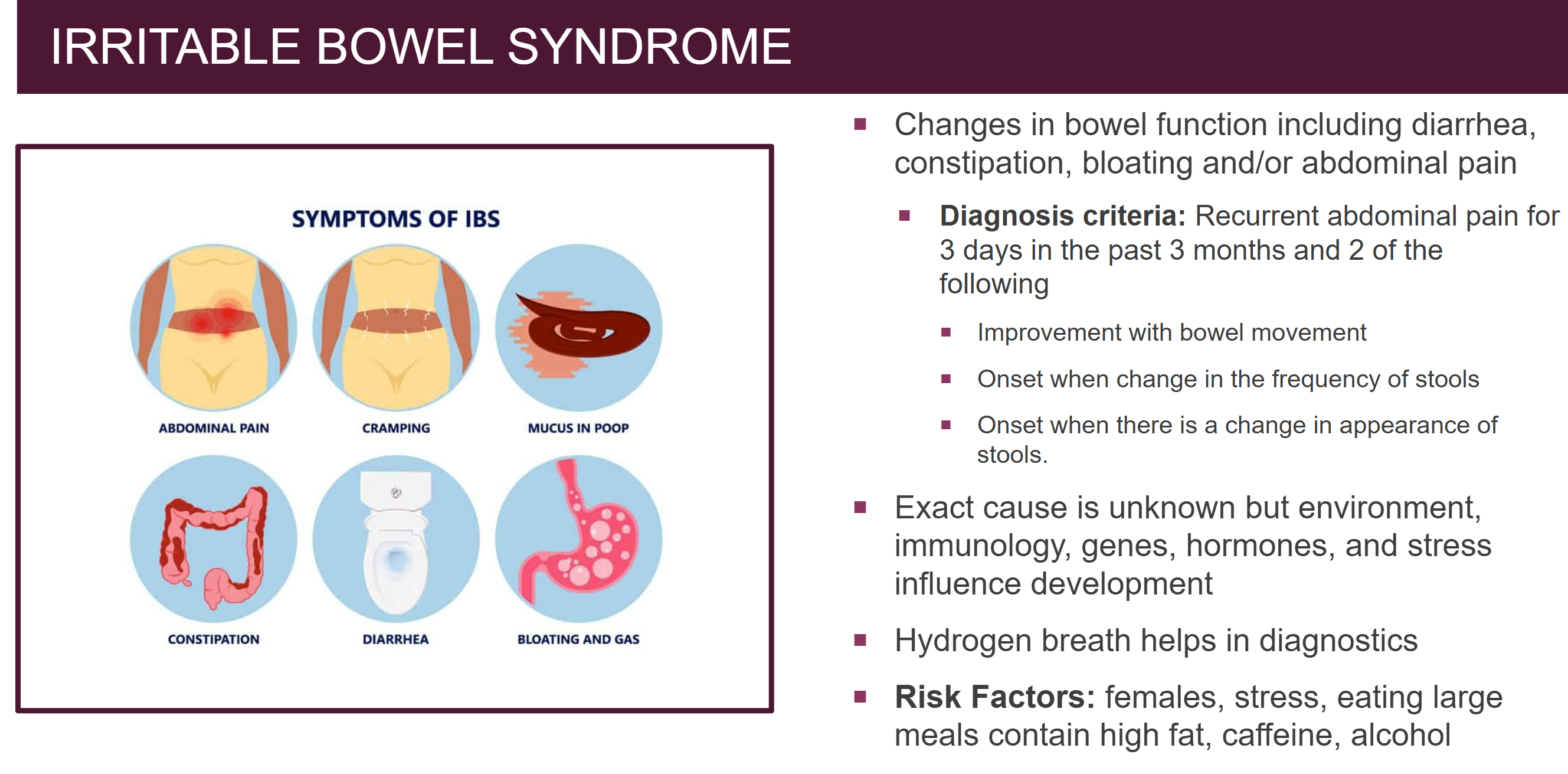
What is IBS/irritable bowel syndrome?
see slide 36
What is good nursing management for IBS?
reduce stress, poop meds, diet changes
What is Celiac Disease?
ingestion of gluten causes body to attack villi of small intestine
What are signs and symptoms of celiacs disease?
abdominal pain, bloating, chronic diarrhea, constipation, gas, lactose intolerance, weight loss, etc.
What is good nursing management for celiacs disease?
avoid gluten
What are the 3 main acute inflammatory bowel diseases?
Appendicitis, peritonitis, gastroenteritis
How is gastroenteritis spread?
contact, not washing hands (24 hour flu – don’t use that term), relate to nora and rota etc. virus
What is chronic inflammatory ulcerative colitis?
edema and inflammation primarily in the colon usually towards the end but can affect it all
What are risk factors for chronic inflammatory ulcerative colitis?
genetrics, Caucasian, Jewish, adolescents and young adults (female), older adulthood (male)
What are findings for ulcerative colitis?
abdominal pain (lower left), distention, tenderness, firmness—weight loss, high pitches bowel sounds, rectal bleeding, low HCT/Hg B12 and electrolytes, increased WBC and ESR
What are diagnostics for ulcerative colitis?
colonoscopy, barium enema, colectomy—treat with anti inflammatory meds, corticosteroids, electrolyte replacement
What is Crohn’s disease?
sporadic inflammation and ulceration of the GI trat often at the distal ilium
What are the main diagnostics/labs for Crohn’s disease?
abdominal pain (right lower), anorexia, weight loss, fever, diarrhea, high pitched bowel sounds
What are therapeutic procedures for Crohn’s disease?
NG tube w/ vent, surgical intervention, laparotomy
What is nursing management for ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease?
assess bowel sounds, colonoscopy, weight, IV fluids, pain management
What is diverticulitis?
chronic or acute, inflammation AND infection of the bowel trapped in the diverticula of the intestinal wall w/ ridged board like abdomen
What are risk factors and findings for diverticulitis?
African American, older adults, male gender
What are complications of chronic GI issues like diverticulitis, Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis?
peritonitis (life threatening inflammation), board like abdomen, fever, tachycardia
What are nursing actions for diverticulitis?
semi fowlers, NPO, IV fluids, antibiotics, promote ABCs
What are the four main complications of ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease, and diverticulitis?
bleeding (black and tarry), fluid/electrolyte imbalances, abscess and fistula formation, toxic megacolon
What is an mechanical intestinal obstruction (w/ risk factors)?
something inside or outside the intestine (tumors, endometriosis, Crohn’s disease, radiation, diverticulitis, fecal impaction, hernia, volvulus (twisting), intussusception (telescoping))
What is a nonmechanical intestinal obstruction (w/ risk factors)?
diminished peristalsis within the bowel (spinal fracture, post surgery, hypokalemia, peritonitis, sepsis)
Review intestinal obstruction findings
see slide 50
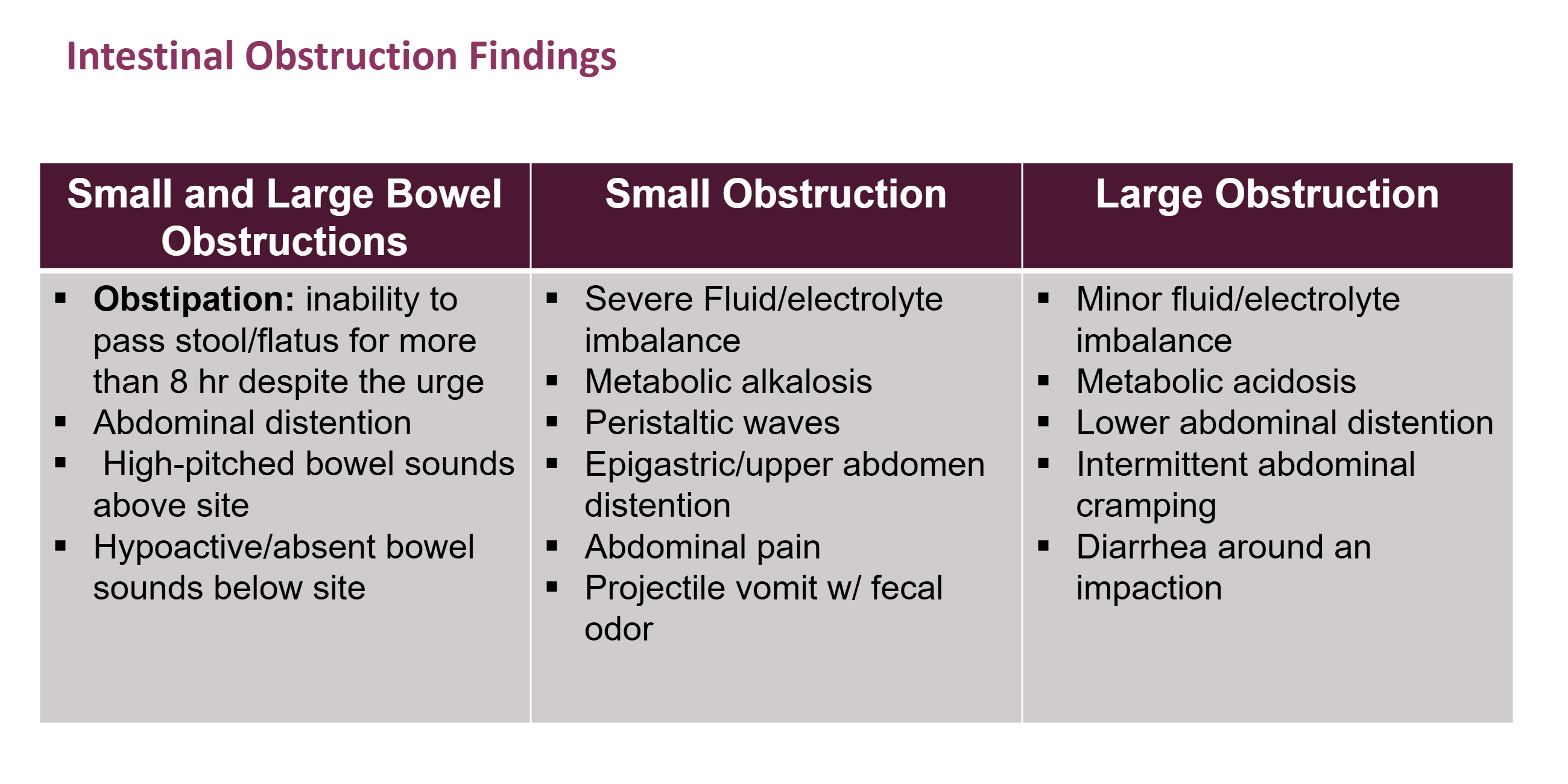
What is obstipation?
inability to BM/fart for more than 8 hours despite having the urge to do so for 8 hours
What are complications for bowel obstructions?
metabolic alkalosis in small bowel and acidosis in large bowel + fluid imbalance
What is good nursing management for bowel obstructions?
NPO, assess bowel sounds, IV fluids, pain management, semi fowlers
What are diagnostics for bowel obstructions?
x ray, endoscopy, CT, Labs (elevated HG/Hct, BUN, creatinine, WBC – decreased Na, K)
What is general nursing care for GI disorders?
monitor for malabsorption, I/Os, electrolytes, complications, bleeding, anemia—reduce stress, educate on foods and monitoring for complications
poop color for upper vs lower gi bleed, puke color for upper vs lower gi bleed
black, red, red, black
What is the hallmark sign of peritonitis?
rigid board like abdomen, will need antibiotics