Excretion
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
Excretion
-removal of metabolic waste from the body.
metabolic
reactions in cell
Examples of excretion in the body
-lungs excrete CO2
-kidneys produce urine containing urea.
Metabolic waste examples
-CO2
-nitrogenous waste (e.g., ammonia, urea)
-bile pigments
Danger of waste accumulation
-changes cytoplasm and body fluid pH
-causing enzymes to work less efficiently
Effect of CO2 accumulation
-blood pH falls
-leading to acidosis.
Effect of ammonia accumulation
-increases cytoplasm pH
-interferes with metabolic processes and receptors in the brain
Effect of urea accumulation
-diffuses into cells
-decreases their water potential
-leading to osmotic pressure that can cause cell bursting
Effect of uric acid accumulation
forms crystals in joints; causing gout.
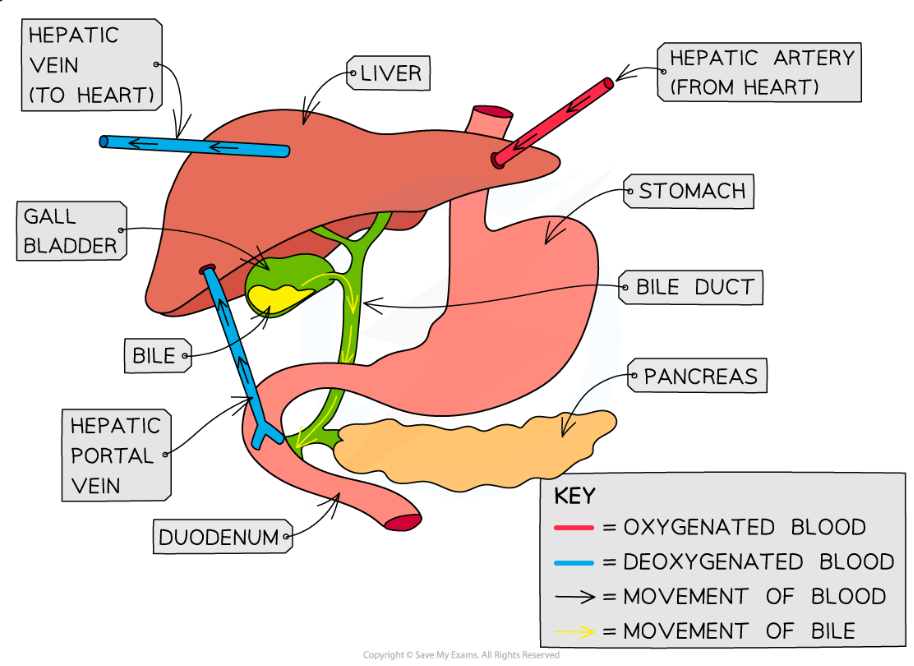
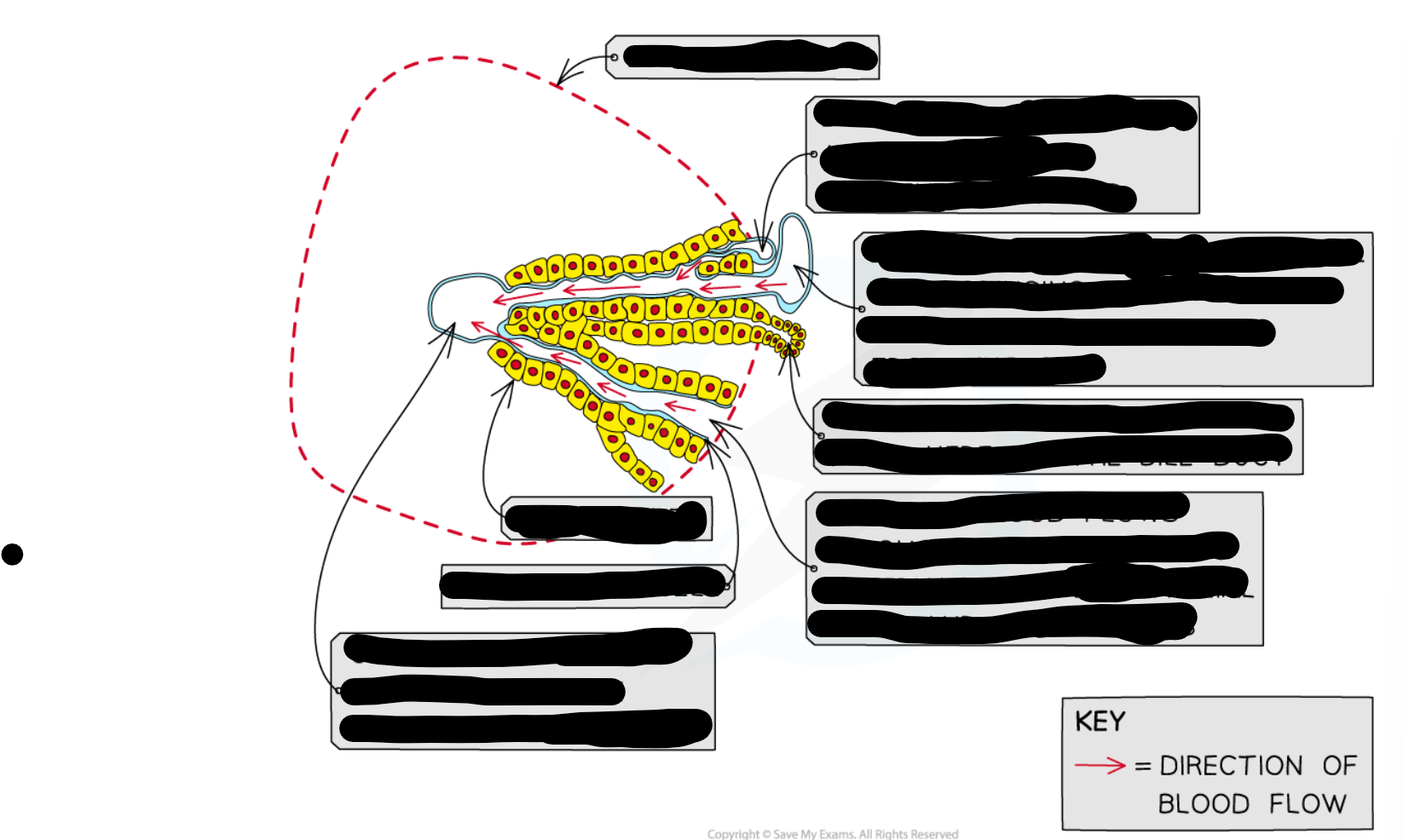
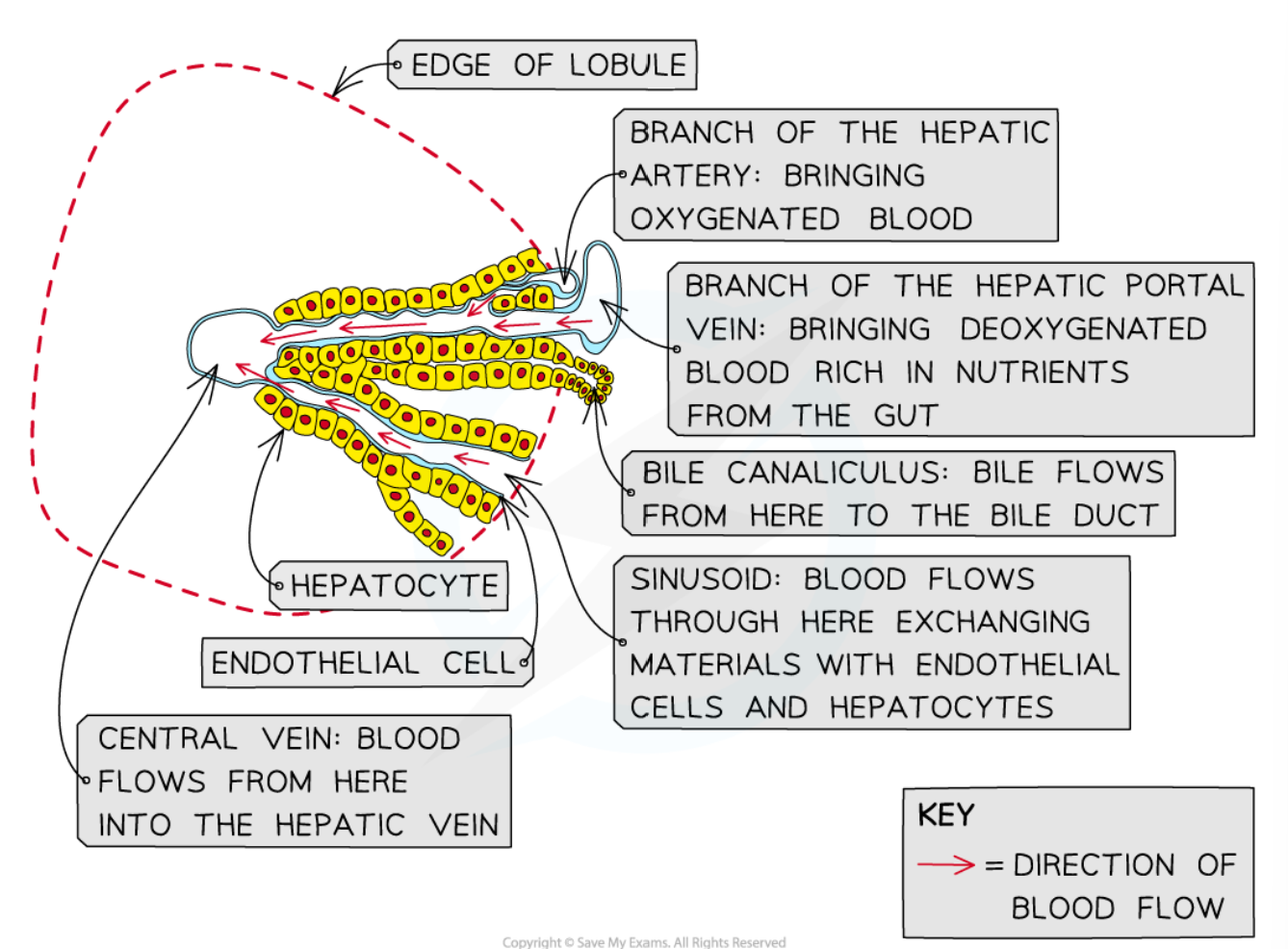
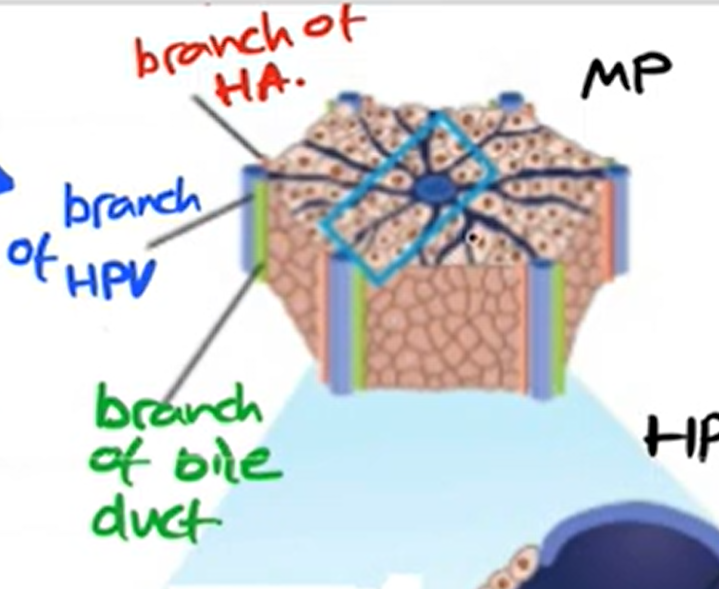
blood supply to and from liver
-hepatic portal vein
-hepatic artery
-hepatic vein
hepatic artery
-provides oxy blood
-thicker wall
-smaller lumen
hepatic vein
-deoxygenated blood exits
-regulated level of nutrients
-in the centre
hepatic portal vein
-brings blood from intestine to liver
-rich in nutrients (glucose, amino acids)
-which are by products of digestion
-have been absorbed into blood supply by the small intestine
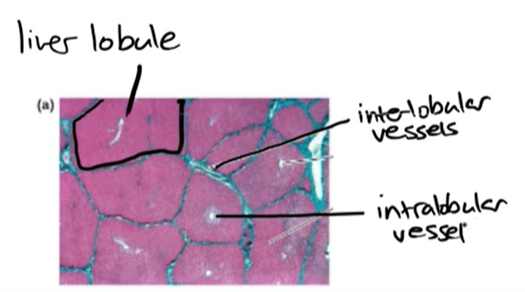
inter lobular vessel
-vessels that between the lobules
intra lobular vessel
-in centre of lobule
-all fluids drain into it
Function of the liver
-absorbs and metabolizes nutrients from the digestive system
-regulates conc of nutrients and toxin molecules
Structure connecting liver and gall bladder
Bile duct.
Sinusoid
-Wide capillaries carrying blood from the hepatic artery and hepatic portal vein
-blood from HA & HPV mix
-inc O content
bile cannaliculus
-drains toxic waste products to bile duct
bile duct
-drains waste product into gall bladder
kupffer cells
-modified macrophages(wbc)
-immune response for liver function
-mainly process dead rbc
-covert haemoglobin into bilirubin which is put into bile canaliculi
Cells lining sinusoids
Endothelial cells.
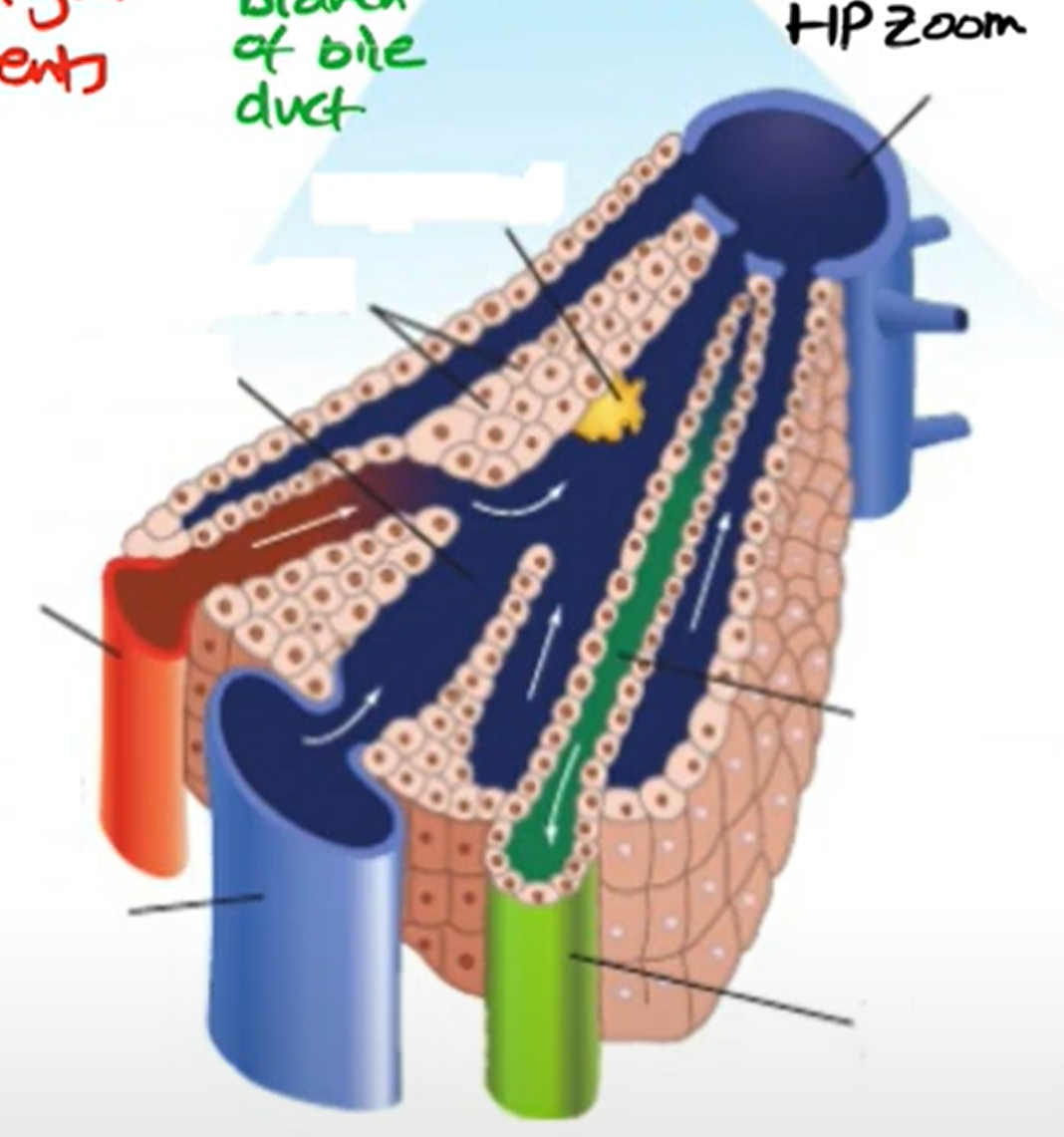
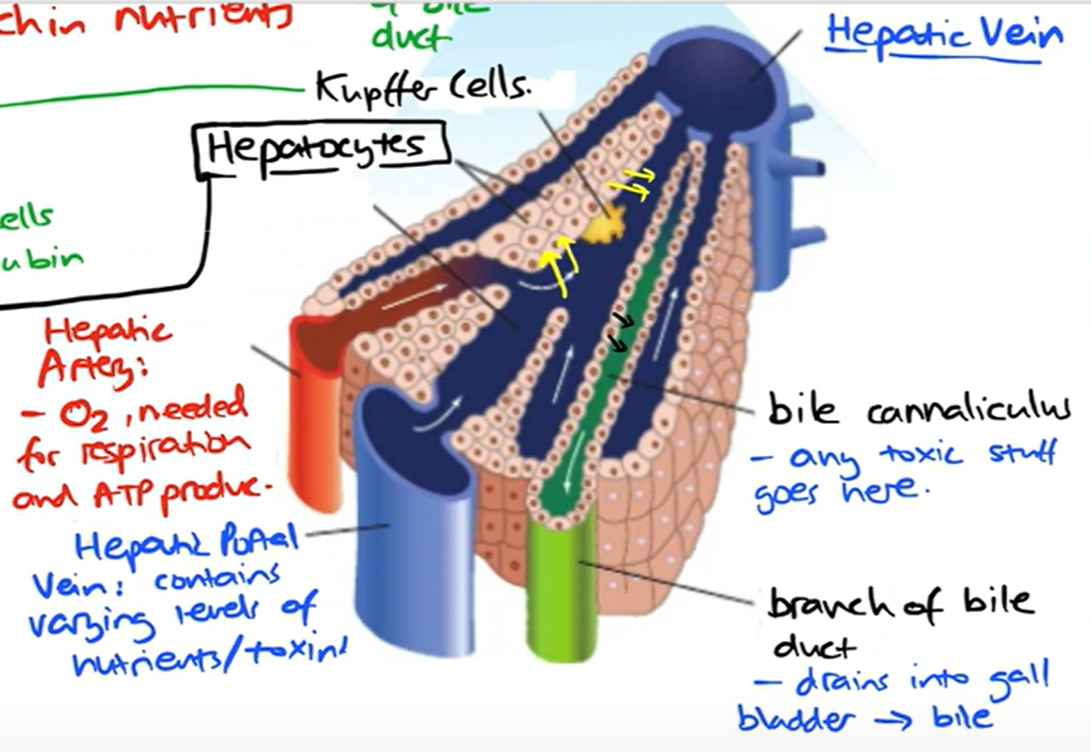
hepatocytes
-liver cells
-cuboid shape
-many mito; metabolically active
-have microvilli on surface
-lots of organelles
-taken in chemicals and process them and put out other chemicals
-need O for this
-output waste products into bile canaliculi
hepatocyte function
-control blood glucose, amino acid and lipid levels
-synthesis of plasma proteins & cholesterol and RBC in fetus
-detoxification of alcohol + toxins
-break down of hormones
-synthesis of urea
Why hepatocytes have microvilli
-inc SA
-good at absorbing nutrients from blood
-maximize the exchange of substances
Glycogenesis
-liver converts excess glucose in blood to glycogen
-glycogen stored as granules in liver cell until needed
how hepatocyte control blood glucose
-respond to insulin to convert glucose to glycogen
-respond to glucagon to convert glycogen to glucose and relase itno blood stream
-hpv carries glucose to sinusoide
-insulin/glucagon can be transported thru HA from pancreas to sinusoid
synthesis of urea
-cannot store excess amino acids
-broken down into keto acid(respired) + ammonia(toxic)
-ammonia and CO2 fed into ornithine cycle to break it down and make urea
-2NH3 + CO2 → CO(NH2)2 + H2
What happens to excess amino acids
They are deaminated.
How ammonia is made less toxic
It is converted to urea.
Components combining to form urea
Ammonia and CO2.
what happens to urea when produced
-released in blood travels kidney to be removed
Respiratory acidosis
Condition where H ions lower blood pH; detected by the respiratory center.
Detoxification
-Breaking down substances in the liver that are not needed or are toxic.
-alcohol, drugs, medicines
Substances commonly detoxified by the liver
Lactate, alcohol, hormones, medicinal drugs.
Excess lactate in the body
-Absorbed by hepatocytes and metabolized to pyruvate
Conversion of lactate in the liver
Converted to pyruvate.
Alcohol detoxification in the liver
Ethanol to ethanal to ethanoic acid to ethanoate (acetate) then to acetyl coenzyme A.
Metabolism of hormones
Protein and peptide hormones are hydrolysed into amino acids and converted to urea.
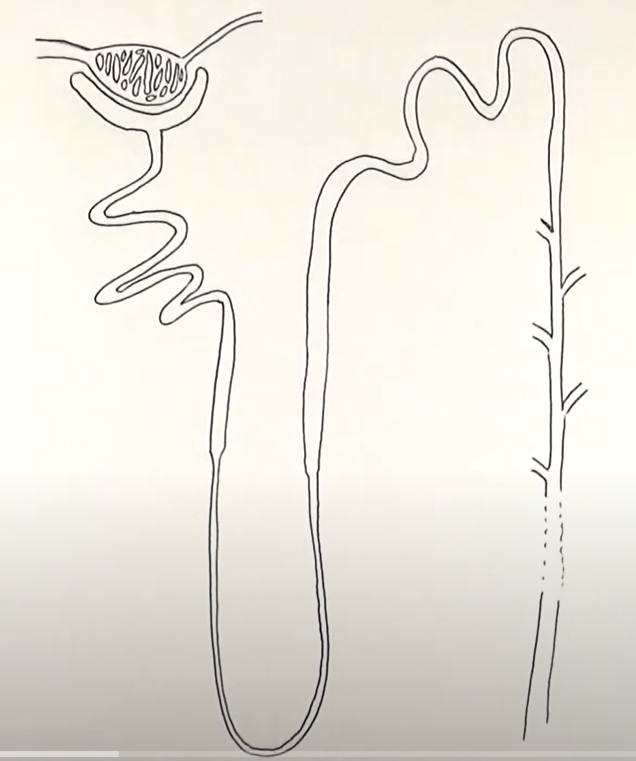
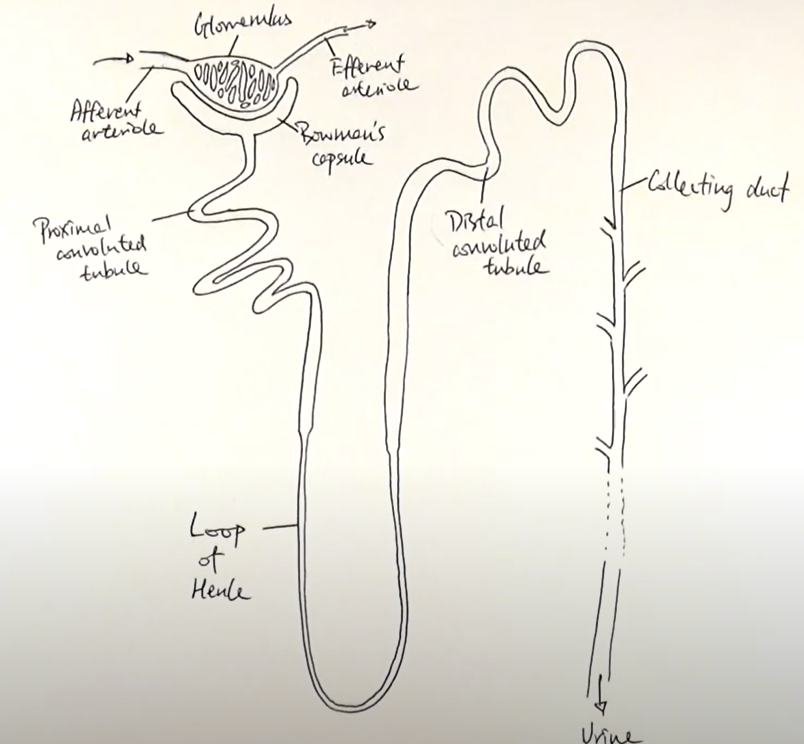
nephron
role of kidney
-osmoregulation
-excretion of nitrogenous waste
osmoregulation
-process of controlling water potential in blood
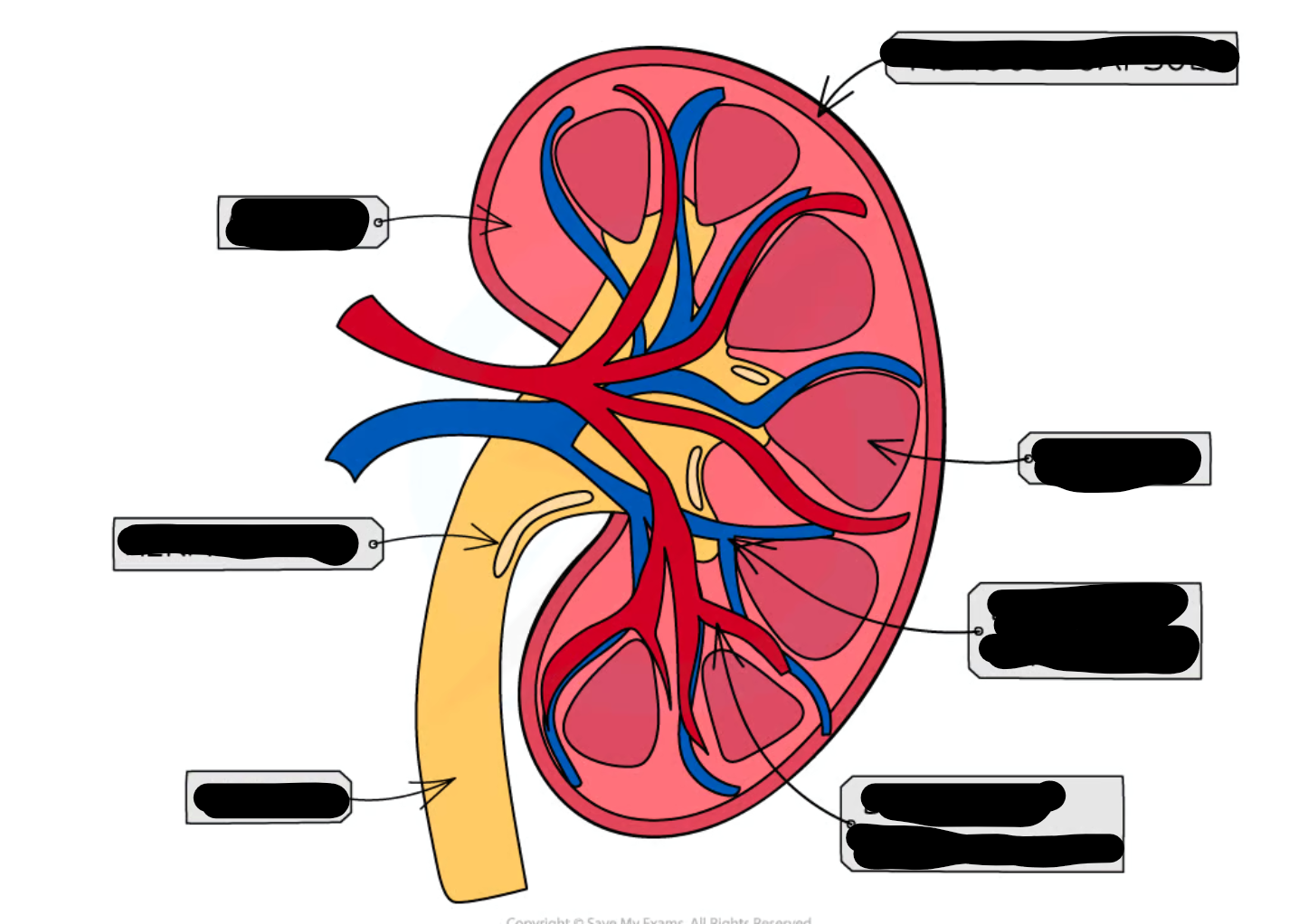
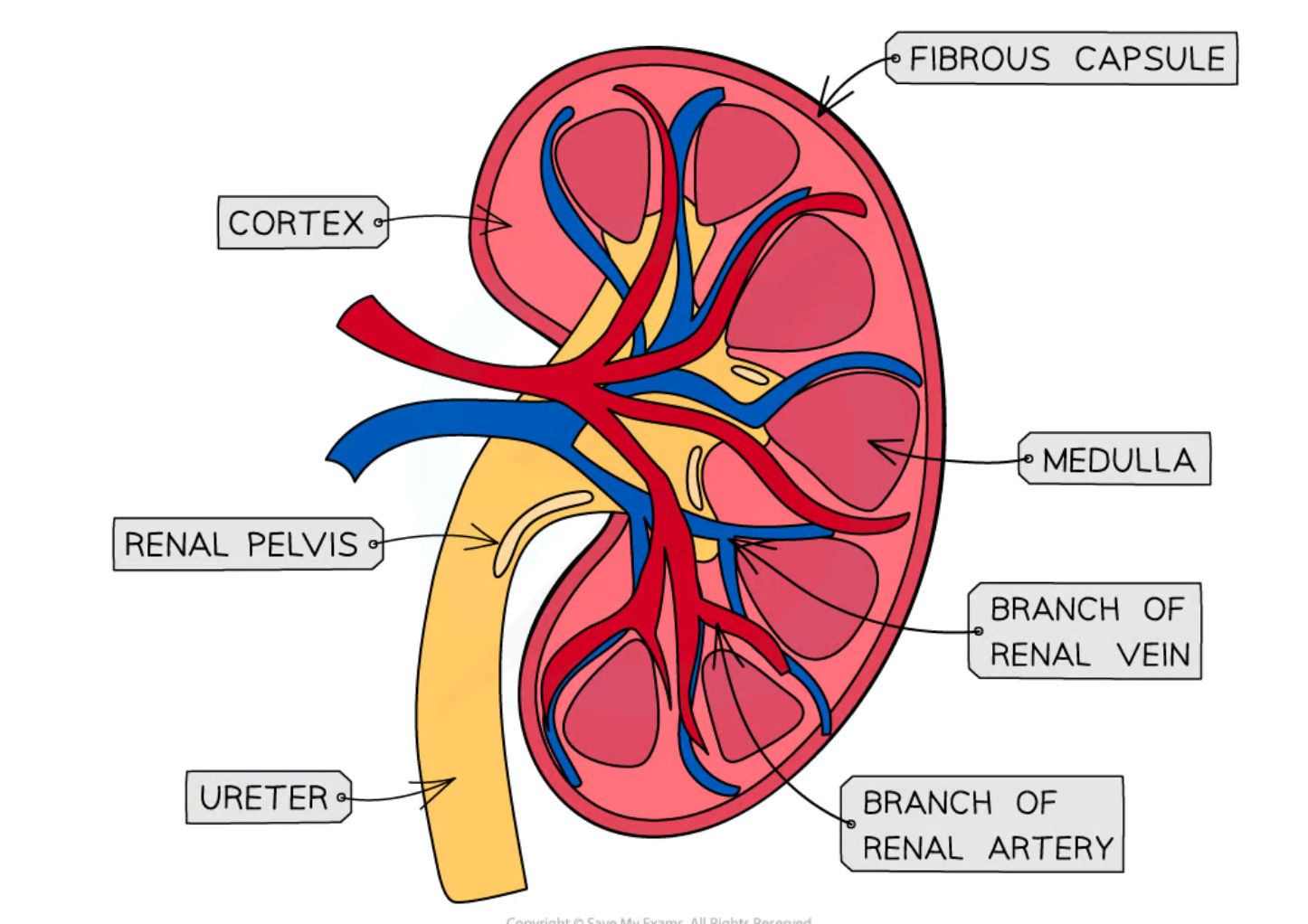
what vessel supplied kidney with blood
renal artery
what vessel carried filtered blood away from kidney
renal vein
3 layers of kidney
-cortex
-medulla
-pelvis
describe cortex of kidney
dark outer layer
describe medulla of kidney
contains nephrons
describe the pelvis of the kidney
-urine collects
-before leaving the kidney and travelling to the ureter
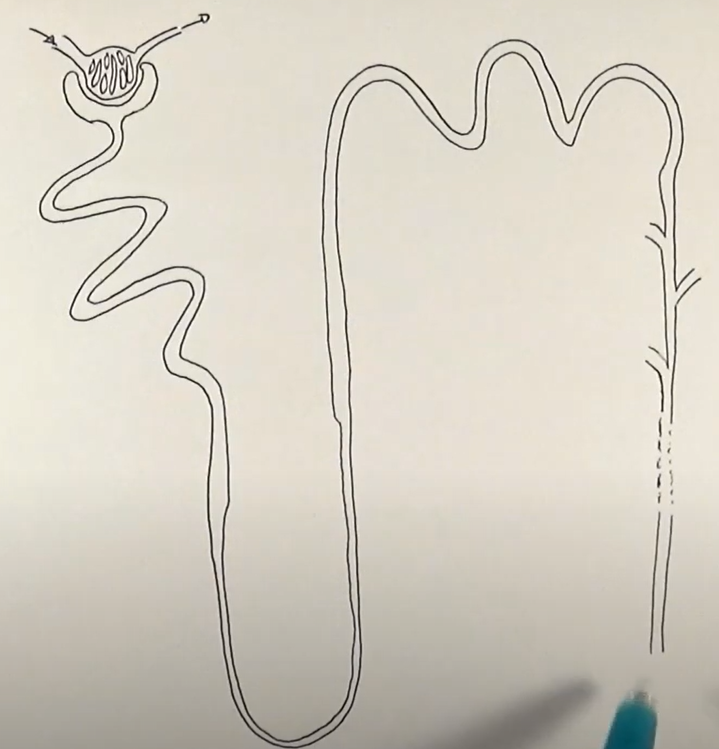
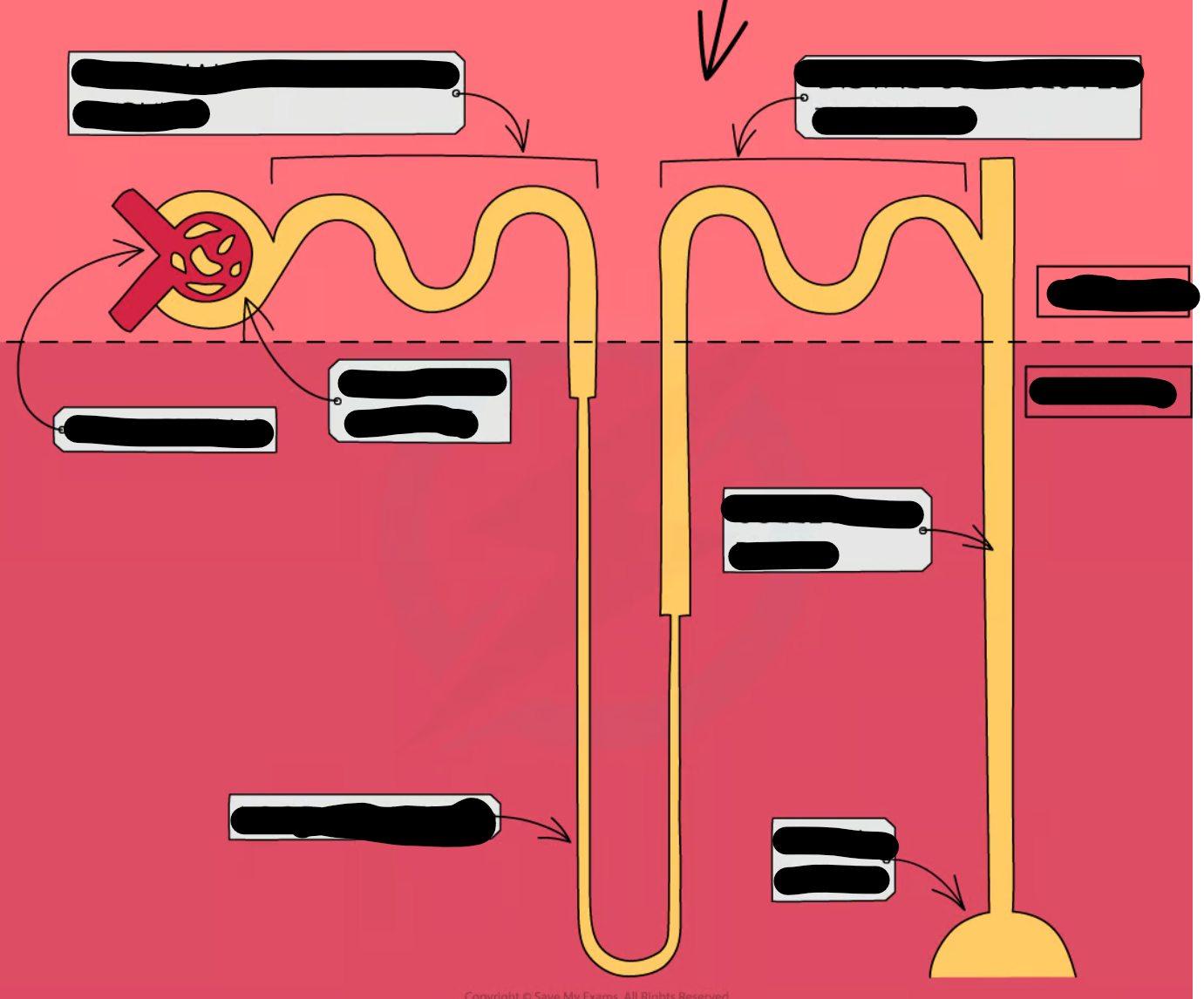
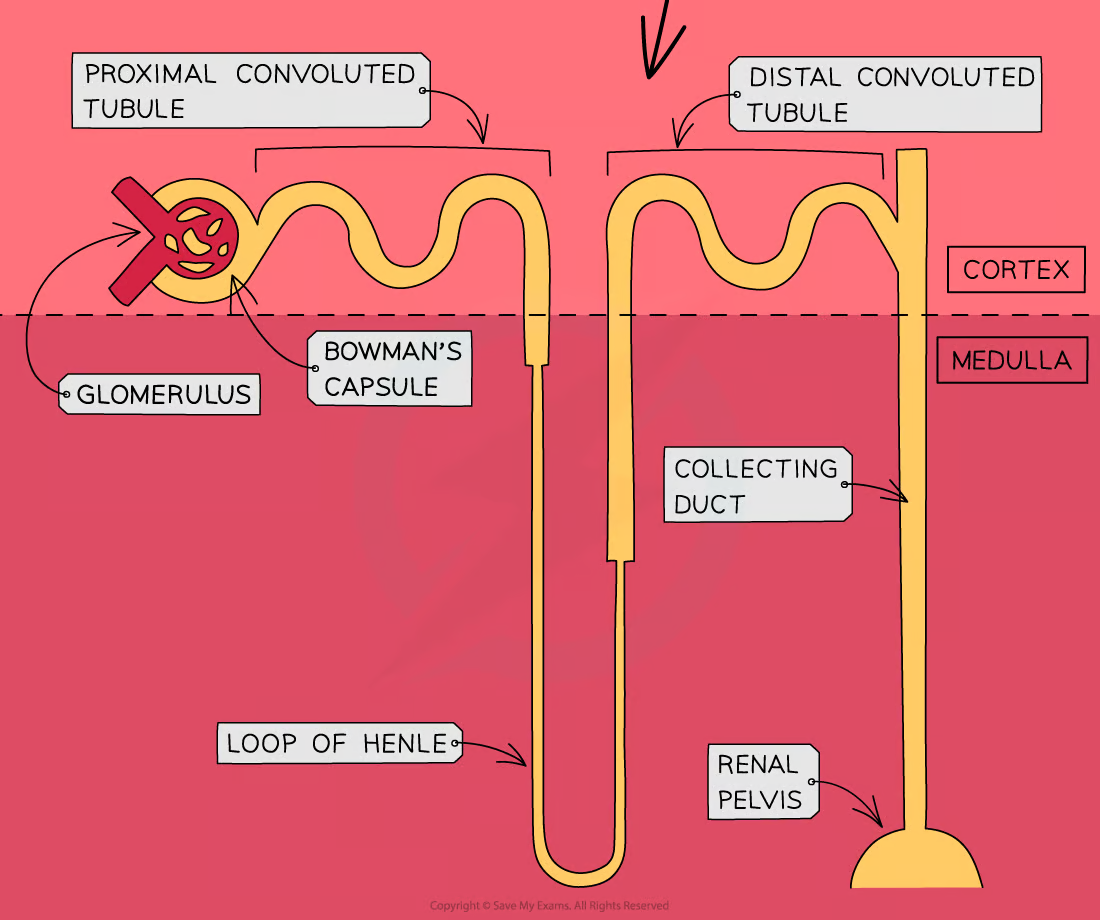
what does the glomerulus do?
filters small solutes from the blood
what does proximal convuluted tubule do?
reabsorbs ions, water and nutrients
what does the descending loop of henle do?
aquaporins allow water to pass from the filtrate into the interstitial fluid
what does the ascdending loop of henle do?
reabsorbs sodium and chloride from the filtrate into interstatial fluid
what does the distal convoluted tubule do?
-selectively secretes and reabsorbs different ions
-maintain blood PH and electrolyte balance
what does the collecting duct do?
reabsorbs solutes and water from the filtrate
where are nephrons found in the kidney?
cortex and medulla
what happens in nephrons
blood is filtered and useful substances are reabsorbed into the blood.
why do animals in dry climate have longer loope of henle
-as this is where reabsorption occurs
-so filtrate spends more time travelling thru
-more water and salt reabsorbed
mineralocorticoids
-hormones which are produced using metabolic processes from cholesterol
-steroid based
-have an effect on transitional factors
-switch on or off genes
-helps control Na/K conc in blood
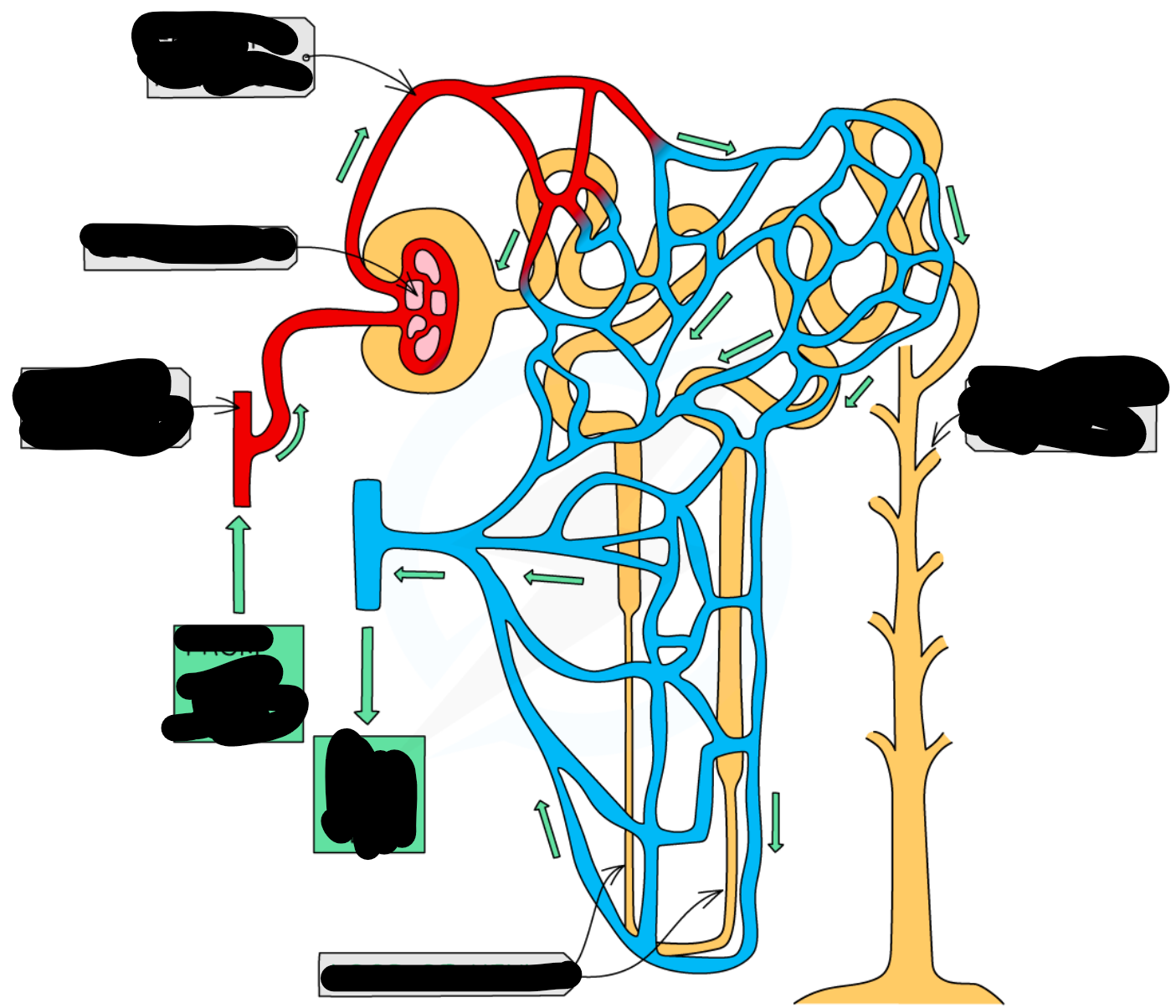
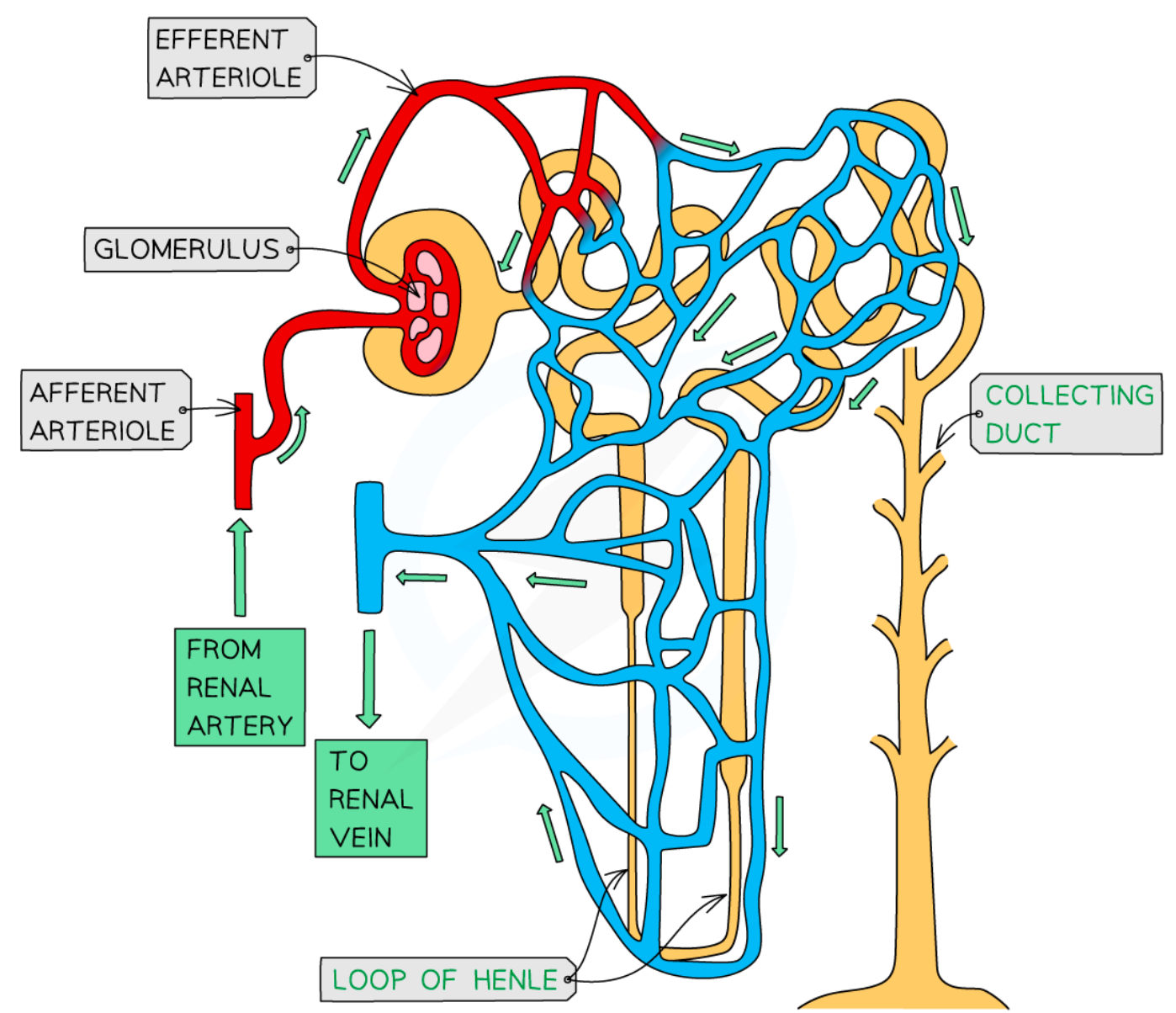
ultrafiltration process
-blood enters through afferent arterioles which split into many capillaries which make up the glomerulus and some leaves thru efferent arteriole
-afferent has larger lumen the efferent to create filtration pressure in glomerulus
-endothelium layer on capillary wall and basement membrane has gaps in it; acts as 1st filter
-stops RBC, WBC, plasma proteins
-forces water and other small molecules out of capillaries
-this forms glomerulus filtrate and goes to bowman’s capsule
-before they enter bowman’s capsule lumen they pass thru wall of capsule which have podocytes (2nd filter) have extensions called pedicels which form slits
-podocytes wrap around capillaries
-substances that stayed in the blood exit thru efferent arteriole
why is there a high hydrostatic pressure of blood when it enters the glomerulus?
it has gone from travelling through the afferent arteriole which has a relatively larger lumen compared to the capillary, hence this high pressure change
podocytes
reabsorbs solutes and water from the filtrate
what podocytes do
special cells that act as additional filter
selective reabsorption
-after filtrate enters bowman’s capsule travels thru proximal convoluted tubule
-amino acids, vitamins active transported out
-glucose co-transported out
-blood surrounding descending limb came from efferent so has low wp so water moves out via osmosis
-filtrate moves to loop of henle
-descending limb is permeable wall lining to water where water leaves thru osmosis
-through AT Na and Cl is moved out in ascending limb of loop of henle
-ascending limb is impermeable to water
-as we move down ion conc of filtrate inc as water is leaving filtrate
-once it reaches bottom; filtrate reaches hypertonic point
-therefor salt moves out thru diffusion
-water conc in filtrate stays same until it reaches collecting duct; AT Cl and Na ions out
-at distal convoluted tubule; reabsorption depends on body needs; balance water and salt level
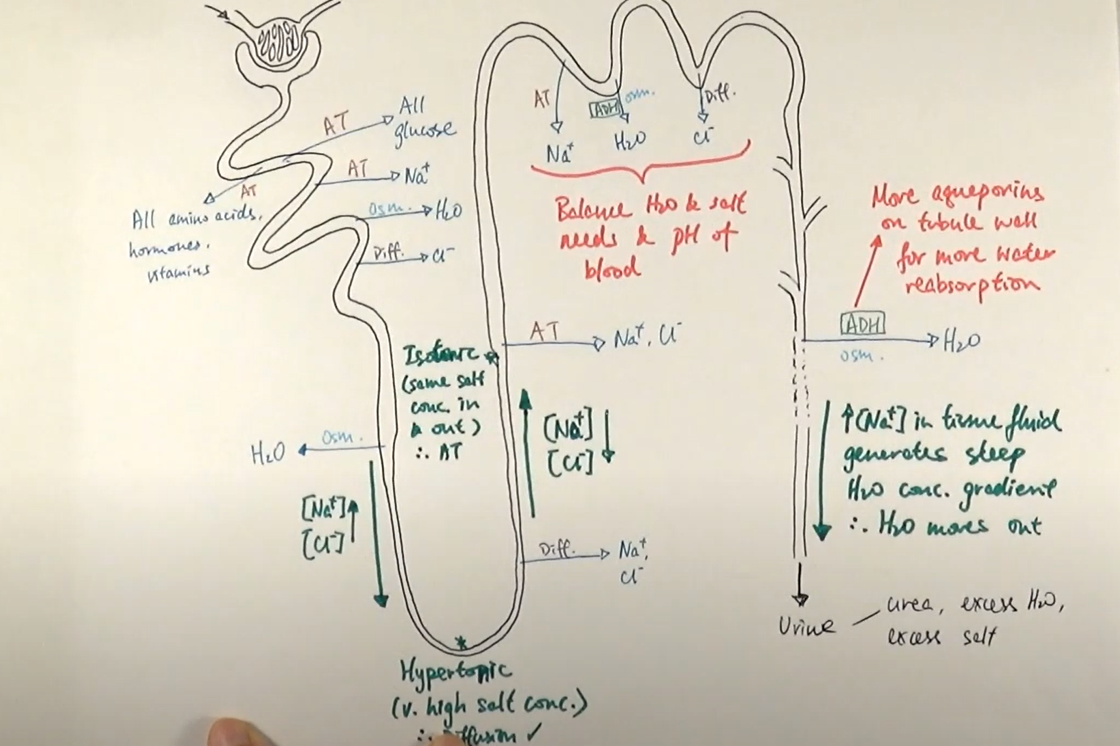
what does isotonic mean?
both solutions have an equal concentration
what is the hypertonic point?
conc of salts/ions in loop of henle is much higher than outside
osmoregulation
process of controlling the water potential of the blood
osmoregulation process if less water in blood
-osmoregulatory which are sensory receptors in hypothalamus detect osmotic pressure when the osmoreceptors shrink when they loose water to blood as wp of blood lessens
-which sends signal to neurosecretory cells in pituitary gland in brain
-ADH and aldosterone(adrenal gland) made in hypothalamus and stored in pituitary gland and released from there
-ADH binds to cells of collecting duct
-aldesterone binds to duct cell causing Na and Cl to at out
-vesicles w/ aquaporins fuse with plasma membrane
-inc permeability of collecting duct wall
-more water moved down wp gradient into cells
what happens to urine when blood water level is too high
-less water reabsorbed back into body
-more water stays in filtrate
-urine is less conc
-higher vol of urine
-paler colour
lumen of collecting duct
how ADH works
-binds to receptor on surface of collecting duct
-coverts ATP to cyclic AMP (acts as secondary messenger)
-tells vesicle containing aquaporins to move towards plasma membrane of inner wall of collecting duct
-helps water move across into blood
what happen if kidney fails
-urea, water, salts and various toxins retained not excreted
-less blood filtered by glomerulus; glomerulus filtration rate decrease
-leads to build up of toxins in blood
-electrolyte imbalance
what happens when excess K ions
-abdominal cramps
-tiredness
-muscle weakness
-paralysis
-freq of impulses from sinoatrial node in heart may decrease; arrhythmia & cardiac arrest
-build up causes disorientation
Na imbalance in body
-kidney may conserve or secrete
-Na needed in:
—neuromuscular function
—fluid balance
--acid/base balance
-excess Na causes:
—disorientation
—muscle spasm
—high bp
—general weakness
kidney failure treatment
-kidney transplant
-renal dialysis
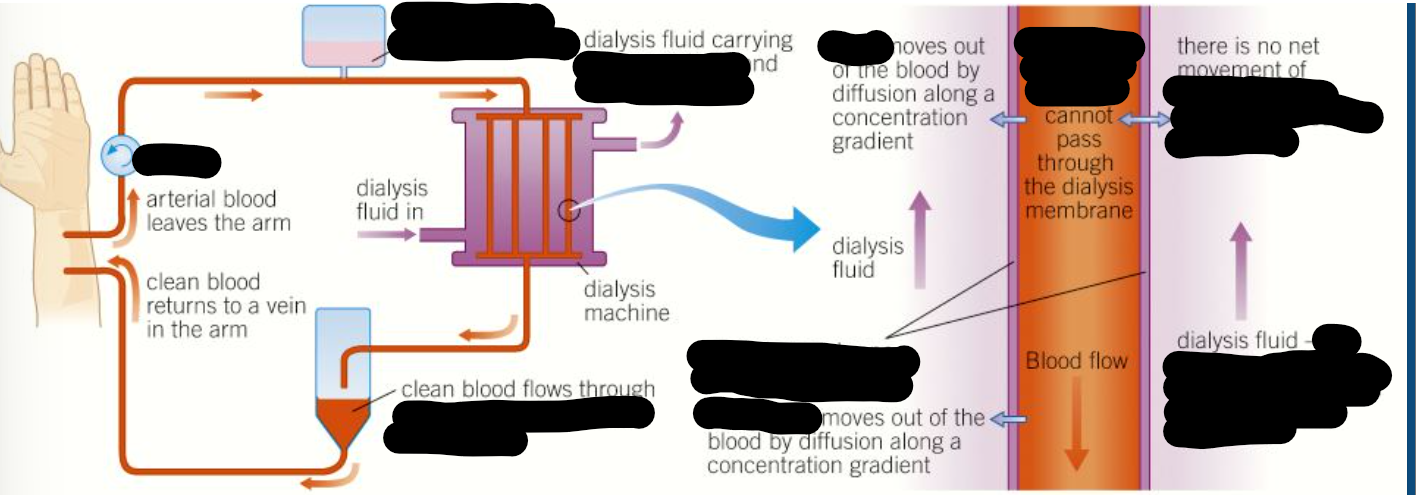
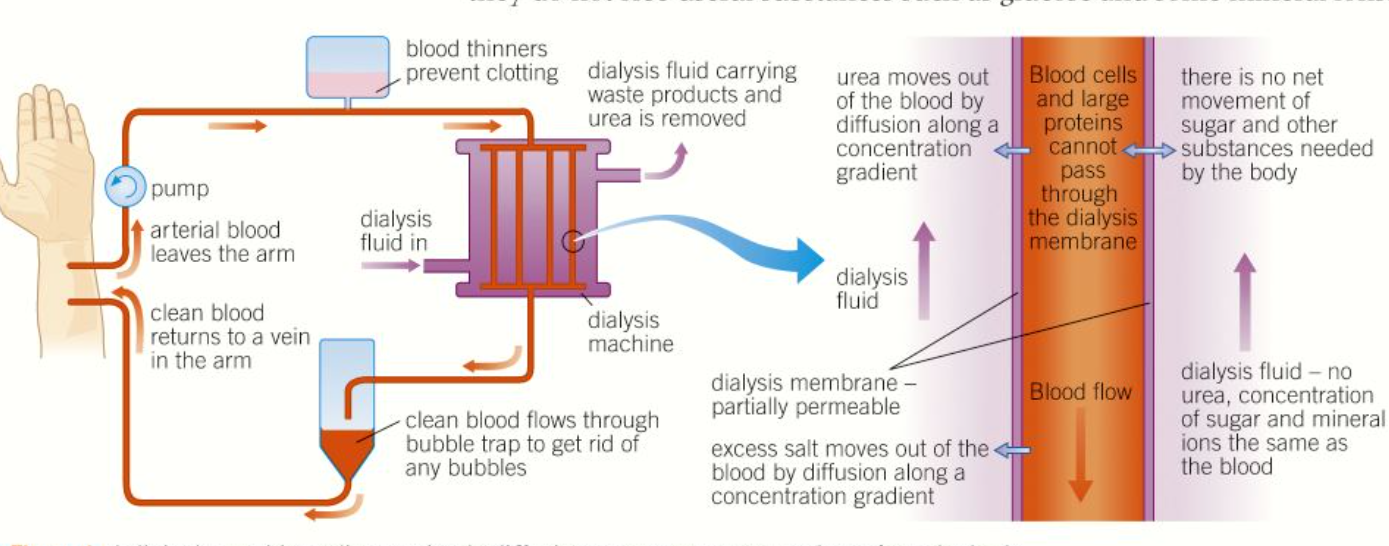
dialysis
-separation of small & large molecules
-using partially permeable membrane
renal dialysis
-patient req regular treatment in hospital or at home using hemodialyzer
-blood leaves patients body form artery and flows into machine
-flows between partially permeable dialysis membrane
-they mimic basement membrane of bowmans capsule
-on other side of membrane there is dialysis fluid
-dialysis fluid and blood flow in oppo direction
-maintain counter current exchange
-max exchange occurs
dialysis fluid
-contains normal plasma levels of glucose; no net movement of glucose out of blood
-normal plasma levels of mineral ions; excess mineral ions in blood diffuse out into dialysis fluid
-contains no urea; steep conc gradient; urea diffuses out
kidney transplant
-better long term sol to kidney failure
-1 kidney req
-donor has compatible blood group
-patient must take med to stop immune system from rejecting donated kidney as it has dif tissue type
how kidney transplant done
-blood vessels joined
-ureter of new kidney inserted into bladder
kidney transplant benefit
-patient has more freedom
-less restrictive diet
-dialysis only works for limited time
kidney transplant disadvantage
-donor doesn’t have same antigen on cell surface; immune response (risk of rejection)
-suppressed by taking immunosuppressant drug for rest of life; patient vulnerable to infection
-not enough donor for demand
why preg test tests for hCG
-6 days after conception; site of developing placenta produce human chorionic gonadotrophin
-found in blood and urine
monoclonal antibody
-antibody from a single clone of cell that are prod to target particular cells or chemical in body
how monoclonal antibody made
-mouse injected w/ hCG
-makes the appropriate antibody
-B-cells that make req antibody removed from spleen of mouse
-fused w/ myeloma (type of cancer cell that divides rapidly)
-millions of living factories make monoclonal antibody
-collected and purified
how preg test works
-wick soaked in first urine passed in morning(highest level hCG)
-test contains mobile monoclonal antibody; have small coloured bead attached to them
-hCG binds to complementary mobile antibodies
-antibody complex moves along test stick w/ urine
-reach line of immobilised monoclonal antibodies only bind with hCG/antibody complex
-anitbody complex binds only w/ immobolised monoclonal antibodies specific to them
-binding of antibody with immobilised anti-antibody produces coloured line
-another like immobilsed monoclonal antibody which bind regardless if mobile antibody is bound to hCG (control)
-if preg; 2 lines
how to test for anabolic steroid in urine
-anabolic steroid excreted in urine
-tested using gas chromatography and mass spec