IOS_1 RESPIRATORY_HISTOLOGY_CONDUCTING_PATHWAYS
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
What are the types of epithelium that we can find?
. Stratified squamous epithelium (keratinized and non-keratinized)
. Olfactory epithelium (in the nasal cavity. Contains serous glands and nerves)
. Respiratory epithelium (general epithelium found along the respiratory tract)
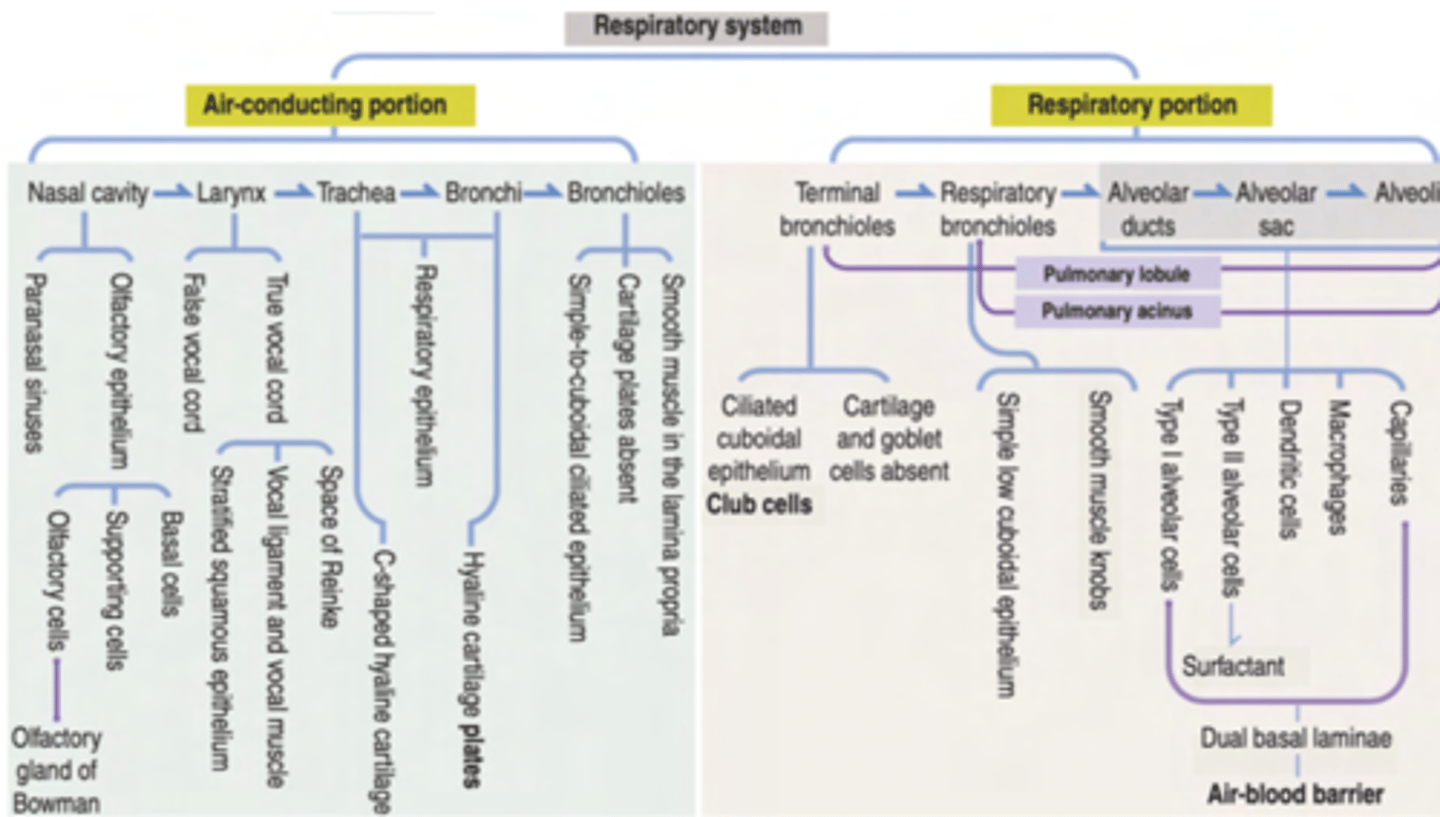
EPITHELIUM COVERS THE RESPIRATORY TRACT
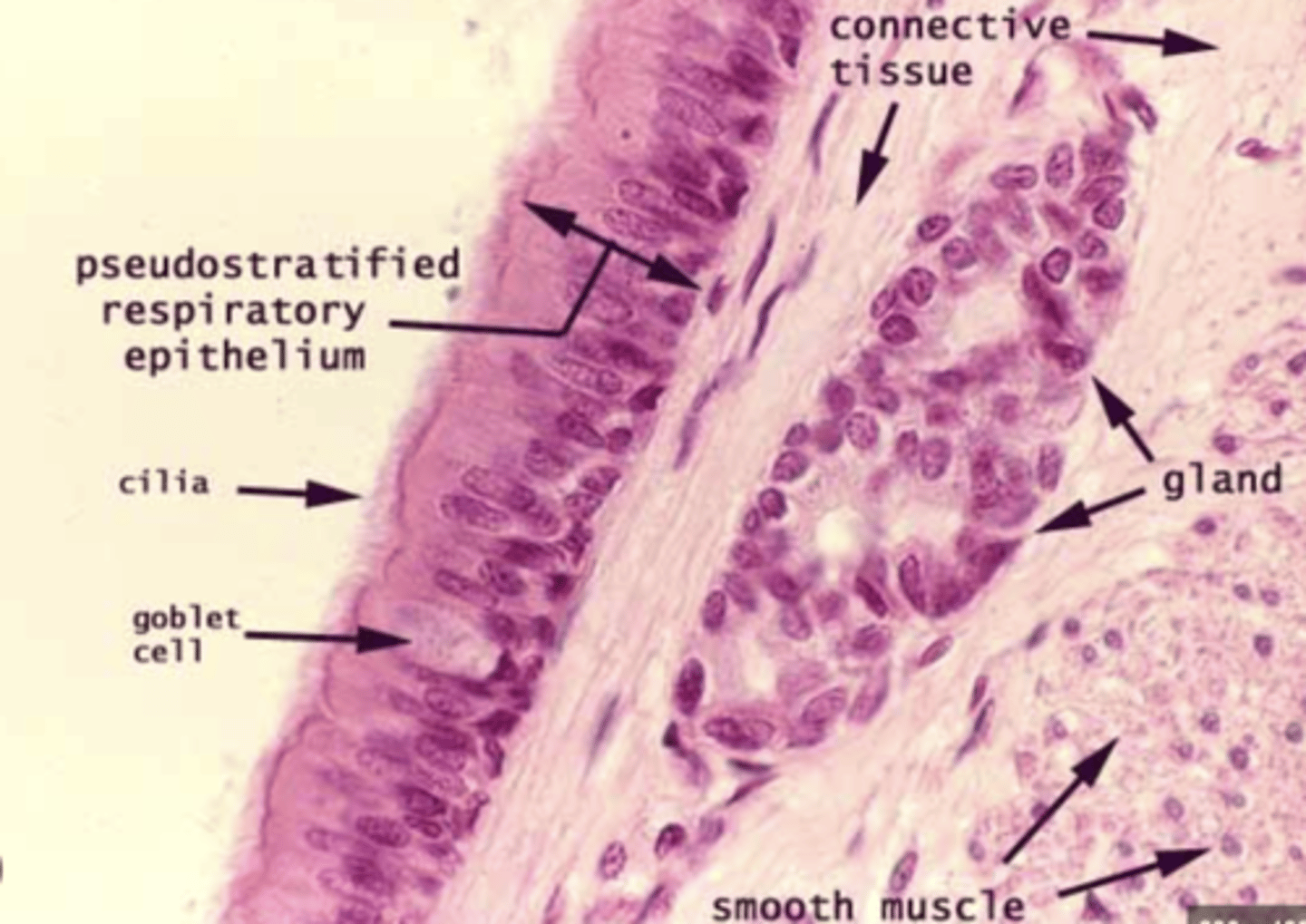
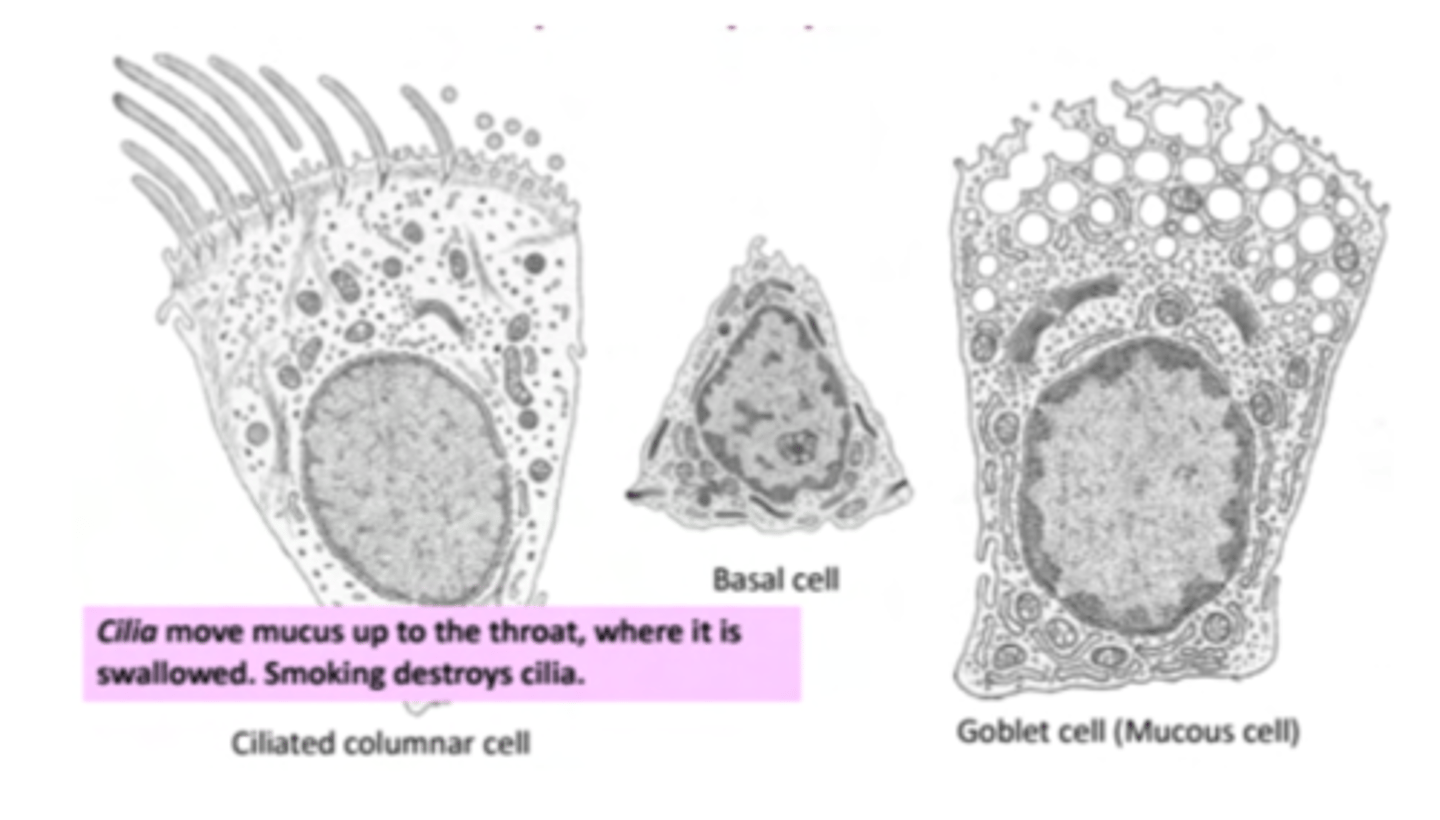
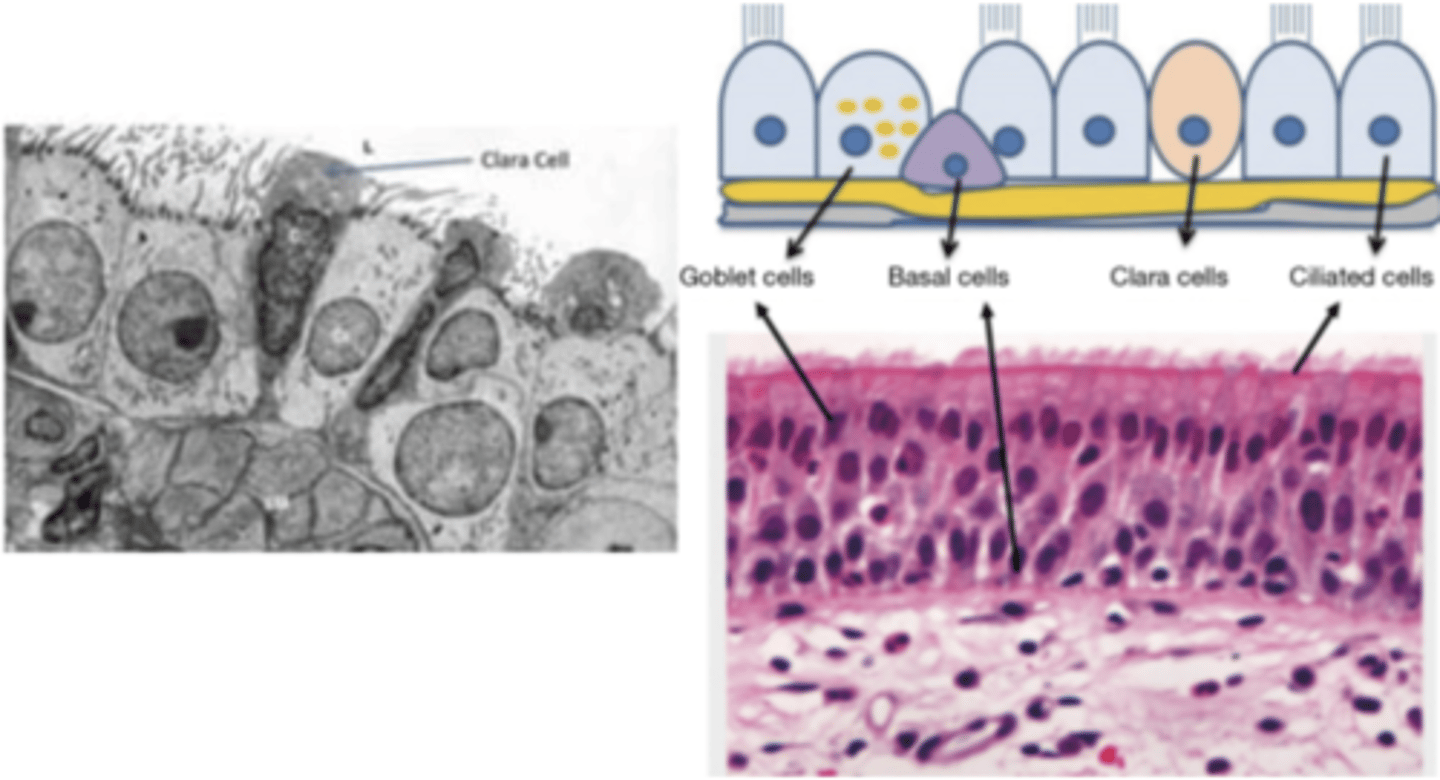
What are the main cell types in the respiratory epithelium?
. Ciliated cells: their function is to move mucus to remove
foreign particles
.Goblet cells: their function is to secrete mucus
. Basal cells: involved in the regeneration of upper epithelial
cell layers
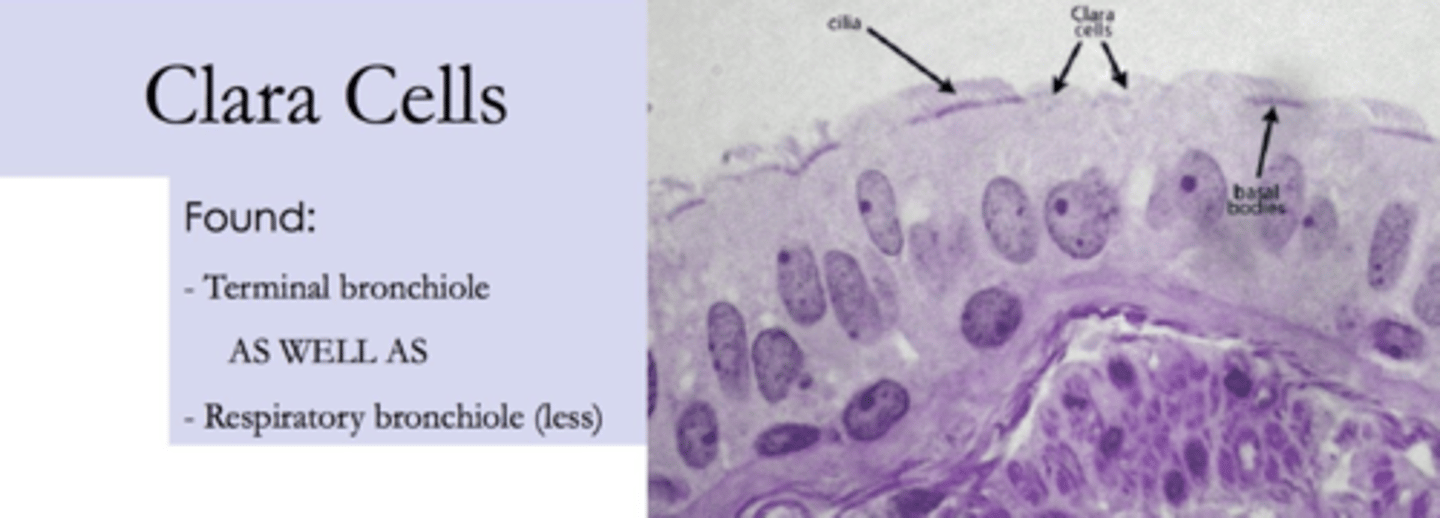
What is the purpose of the clara cells?
secrete a fatty substance, surfactant.
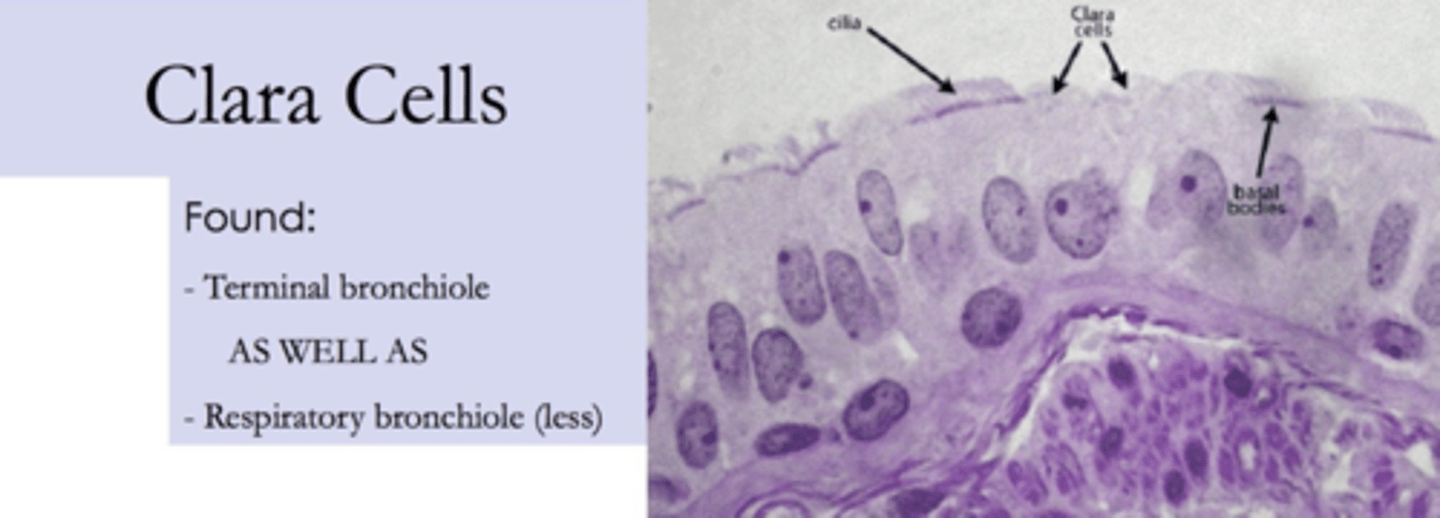
Where are clara cells located?
mainly in trachea and bronchi
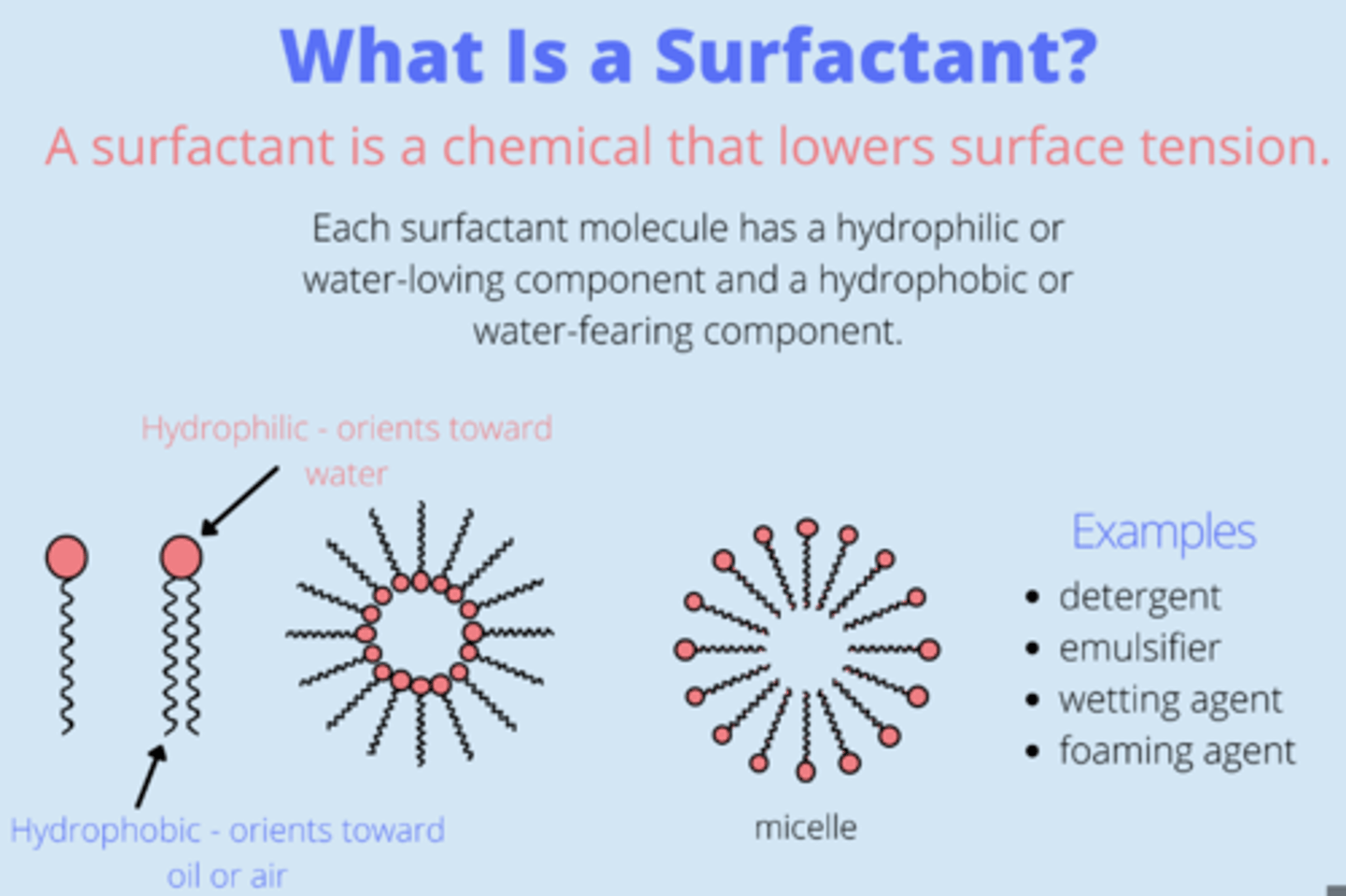
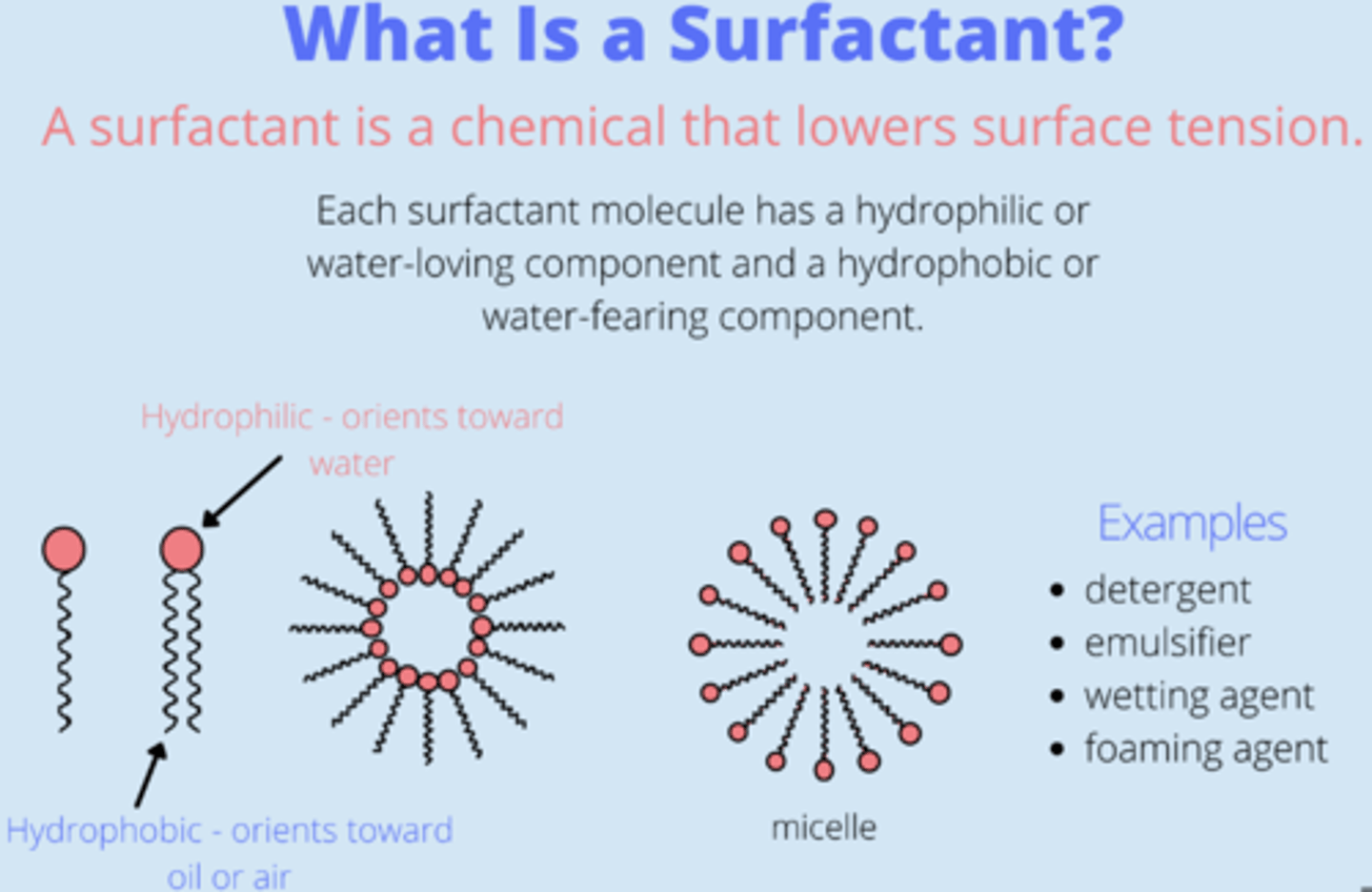
What's the purpose of surfactant?
lowers surface tension of liquids, therefore increasing its
spreading properties = enables the cavities which lack cartilaginous rings to remain open, and not collapse. Helps keep alveoli inflated between inspirations
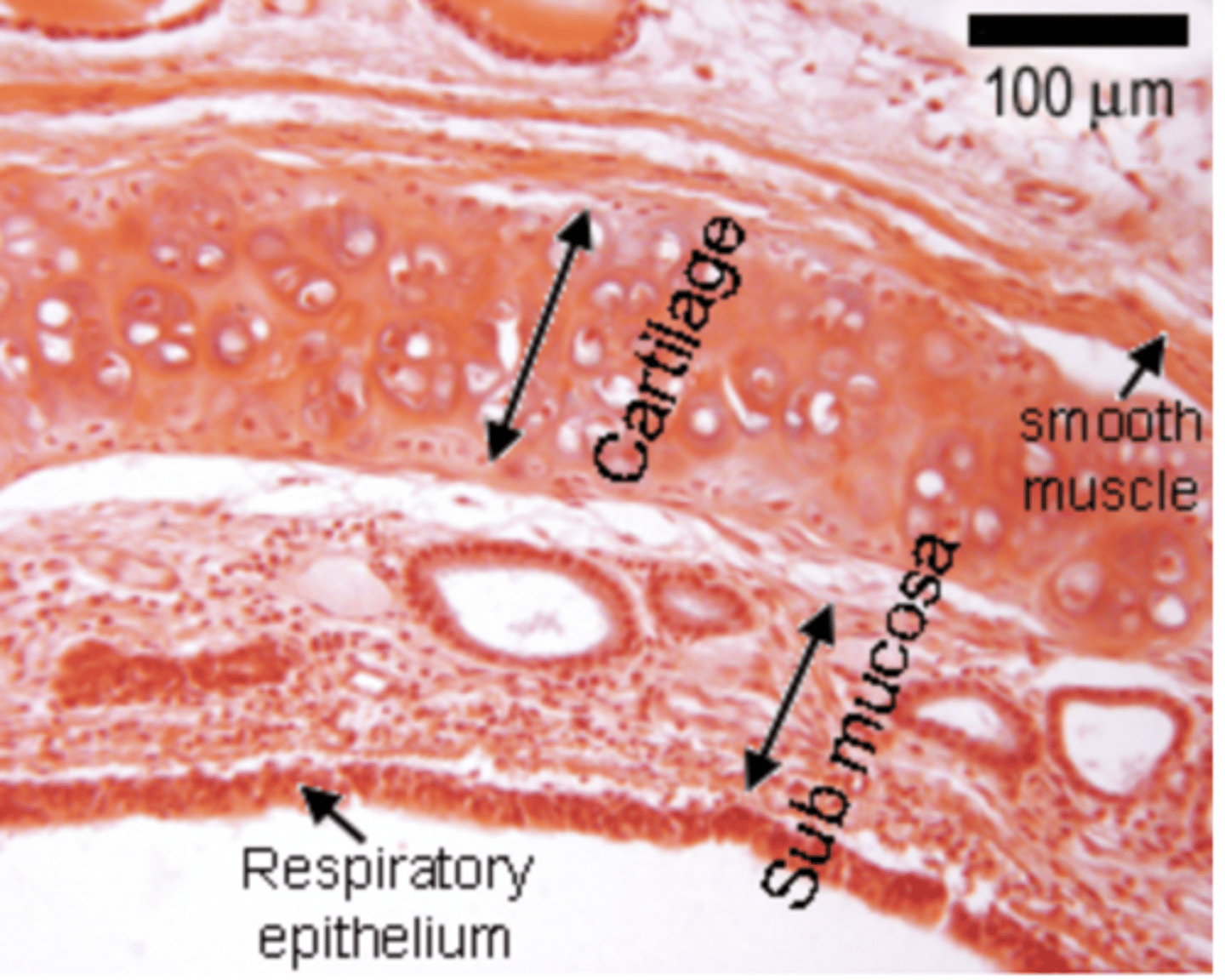
What is the structural organization of layers in the respiratory tract?
1. MUCOSA
2. SUBMUCOSA,
3. MUSCULARIS EXTERNA
4. ADVENTITIA or SEROSA.
INTERNAL layer TO EXTERNAL layer order
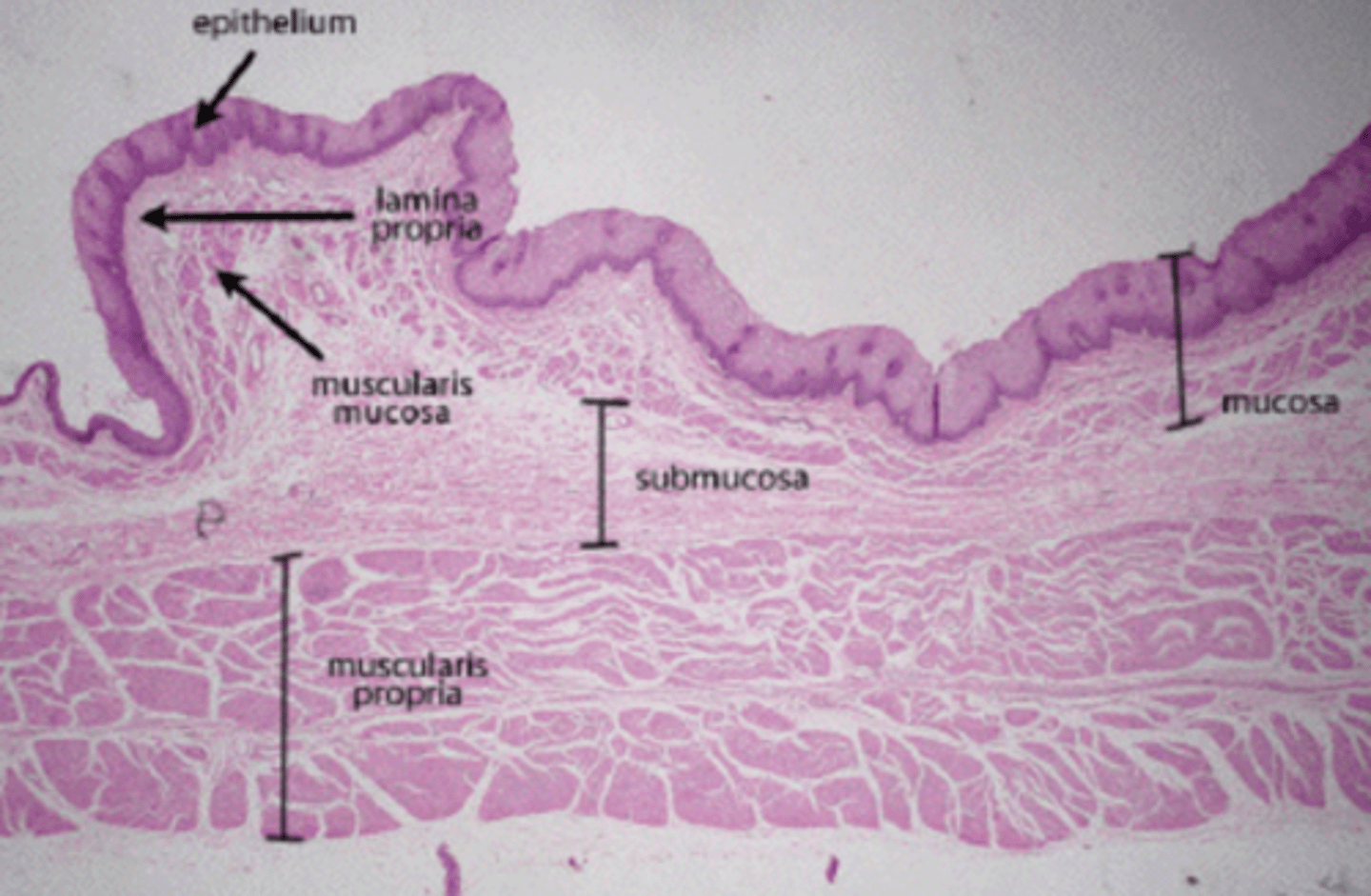
What are the main components of the mucosa?
Epithelium
Lamina propria
What are the two types of epithelium?
Respiratory epithelium: Found in most parts of the respiratory tract, consisting of pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium with goblet cells for mucociliary clearance.
Olfactory epithelium: Specialized epithelium in the nasal cavity for detecting odors.
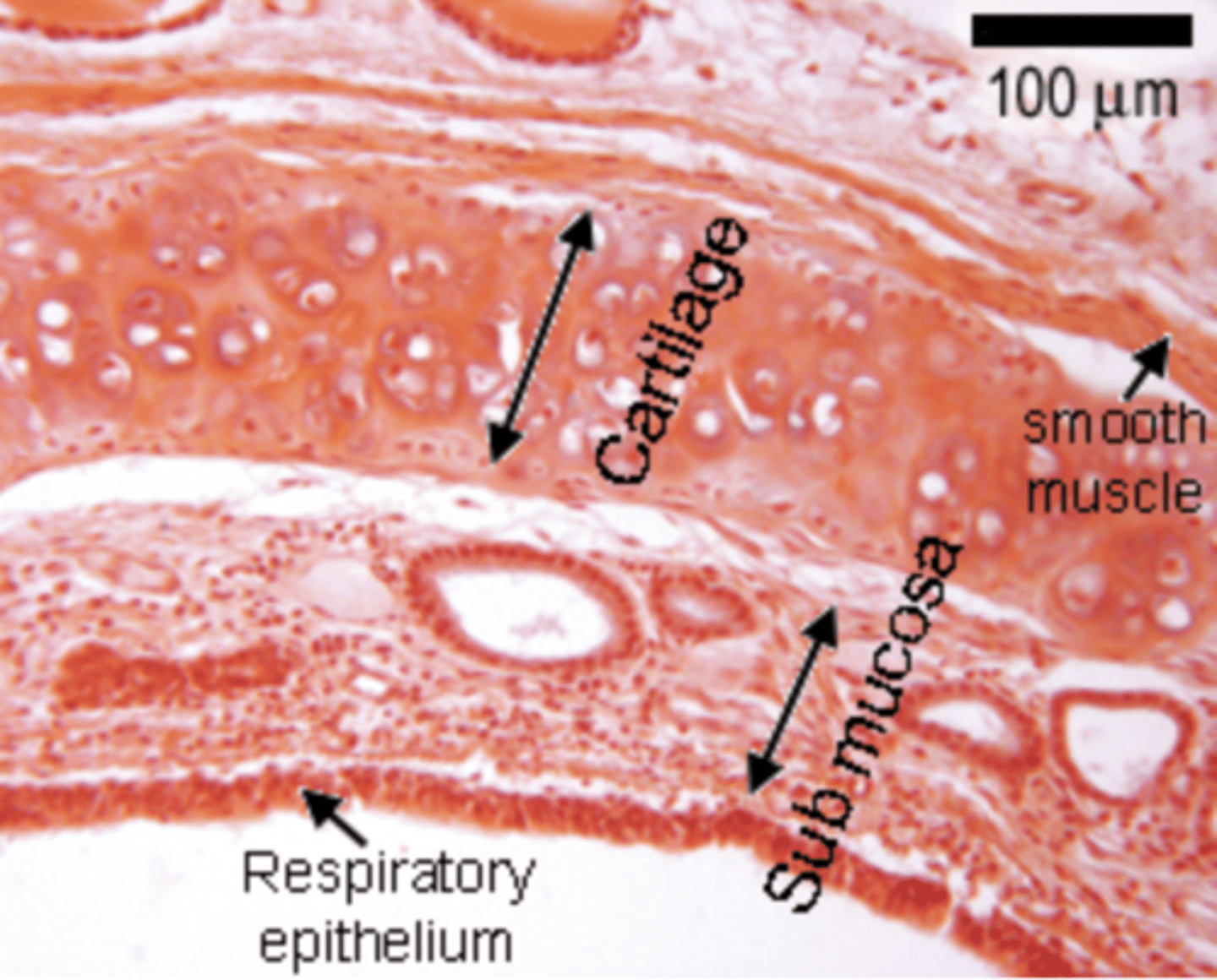
What is the lamina propria?
A layer of loose fibroelastic connective tissue (FECT) beneath the epithelium, containing blood vessels, nerves, and immune cells.
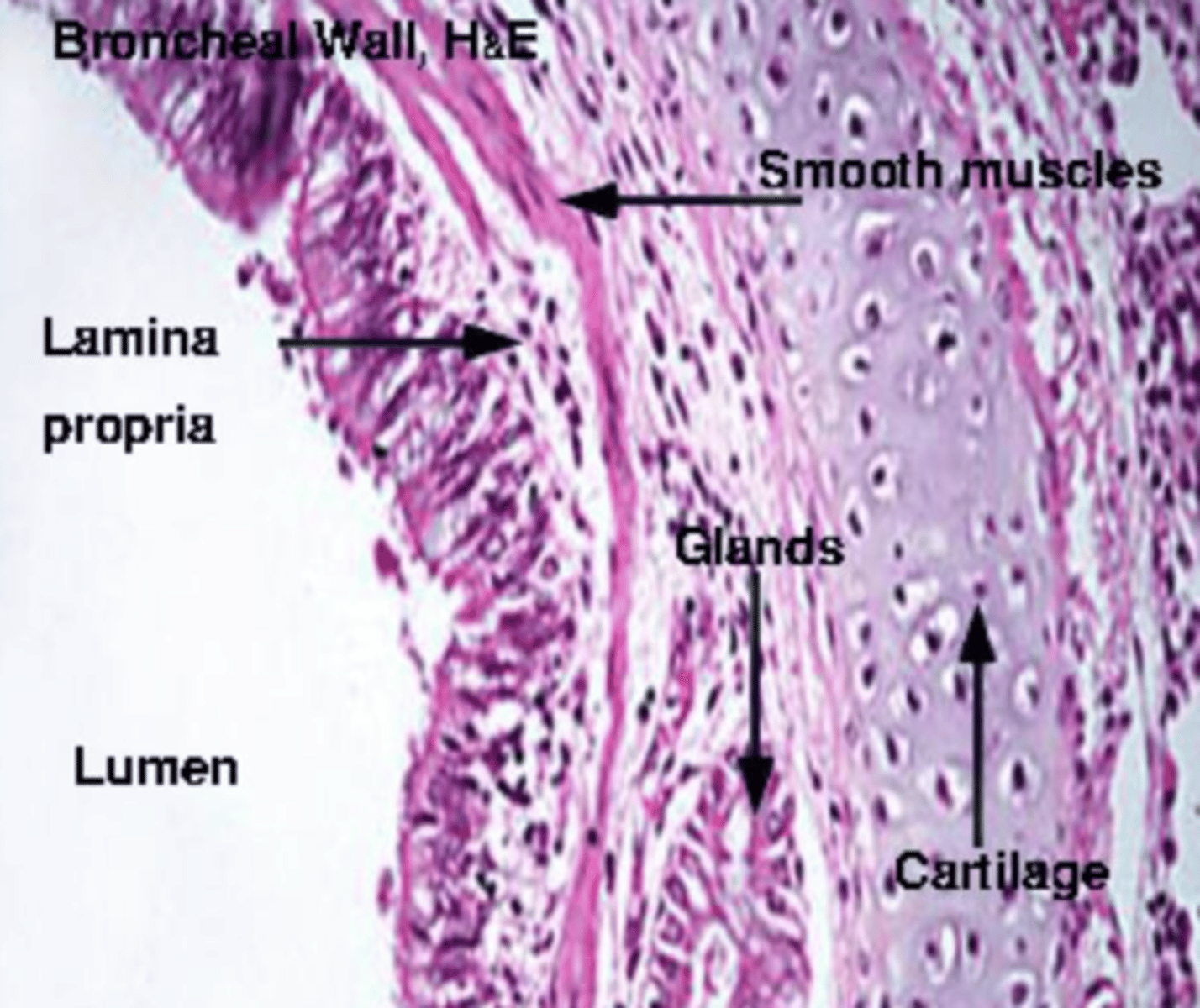
What are the main characteristics of the submucosa?
contains connective tissue and accessory structures.
and may contain serous glands that secrete fluids to keep the respiratory epithelium moist and protect against pathogens.In some regions, the submucosa is absent or indistinct, merging with the lamina propria.
SM : Submucosa. (Trachea)
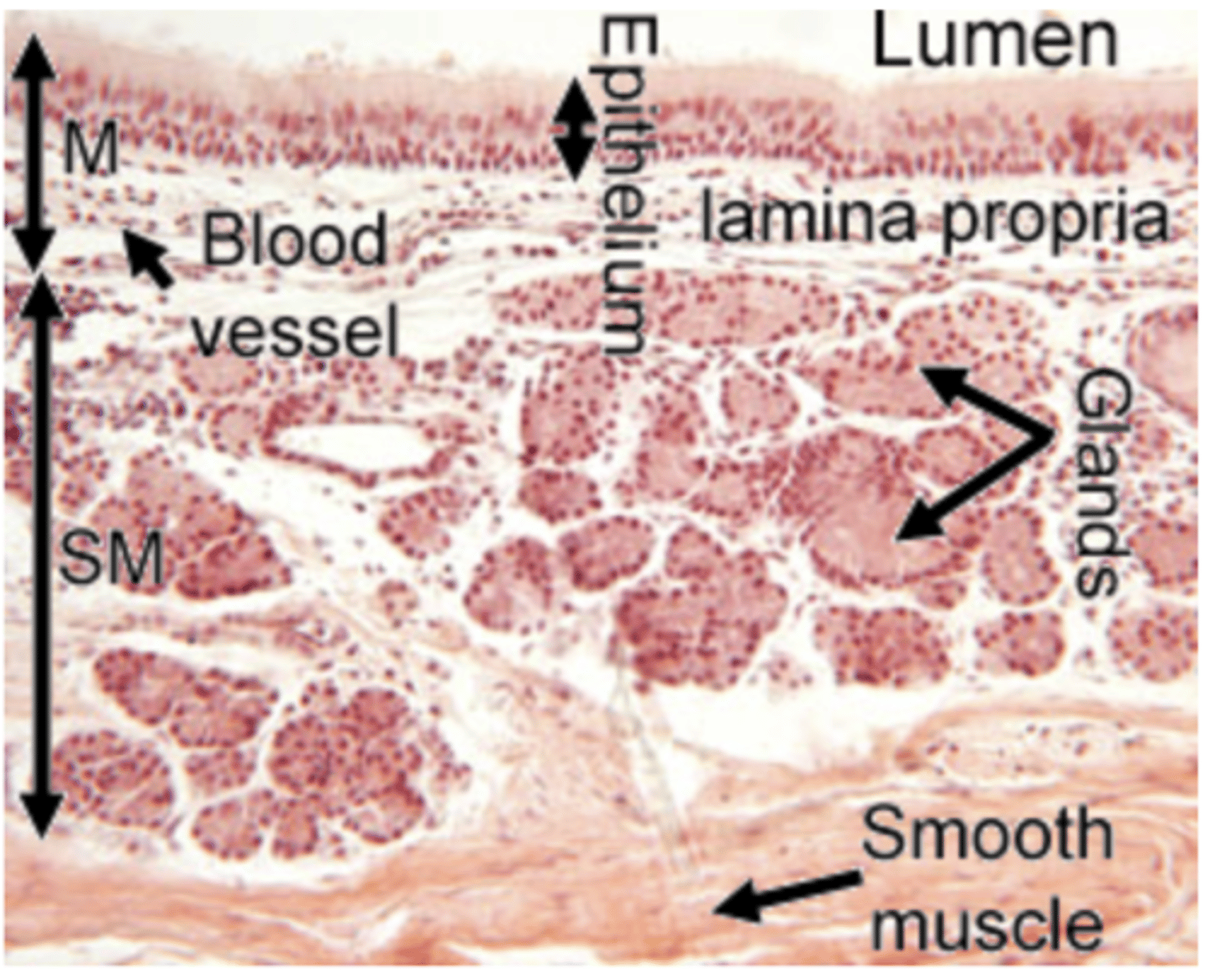
What are the main characteristics of the muscularis externa?
Responsible for structural support has 3 main components
Smooth muscle: Found in smaller airways (e.g., bronchioles), regulates airflow by contraction or relaxation
Cartilage: Found in larger airways (e.g., trachea and bronchi), maintains airway patency and prevents collapse during inhalation.
Bone: Found in regions like the nasal cavity, provides rigid structural support.
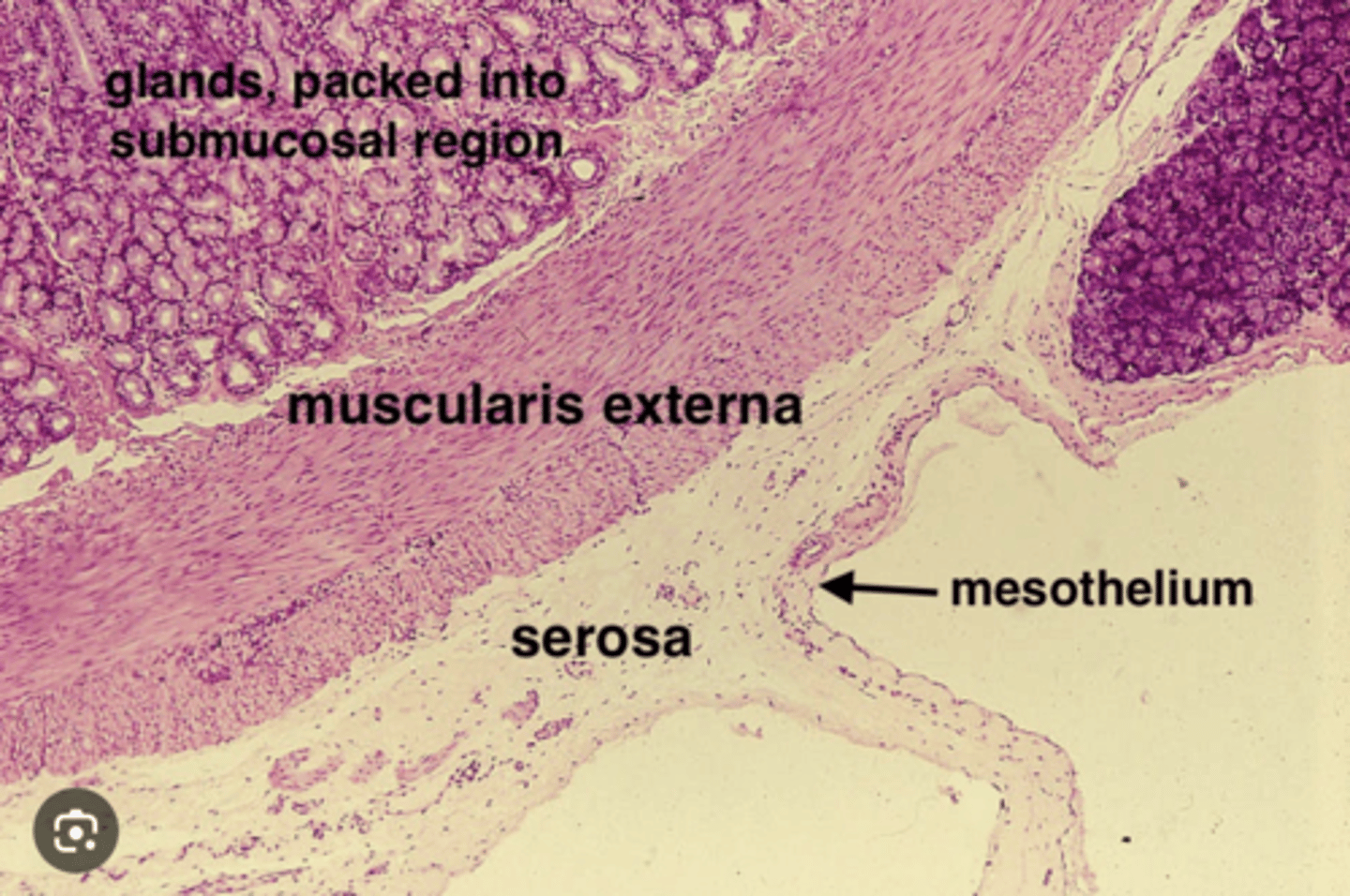
What are the main differences between adventitia and serosa layers?
Adventitia anchors to surrounding tissues (ie trachea to other organs) while serosa encloses and reduces friction (ie pleural)
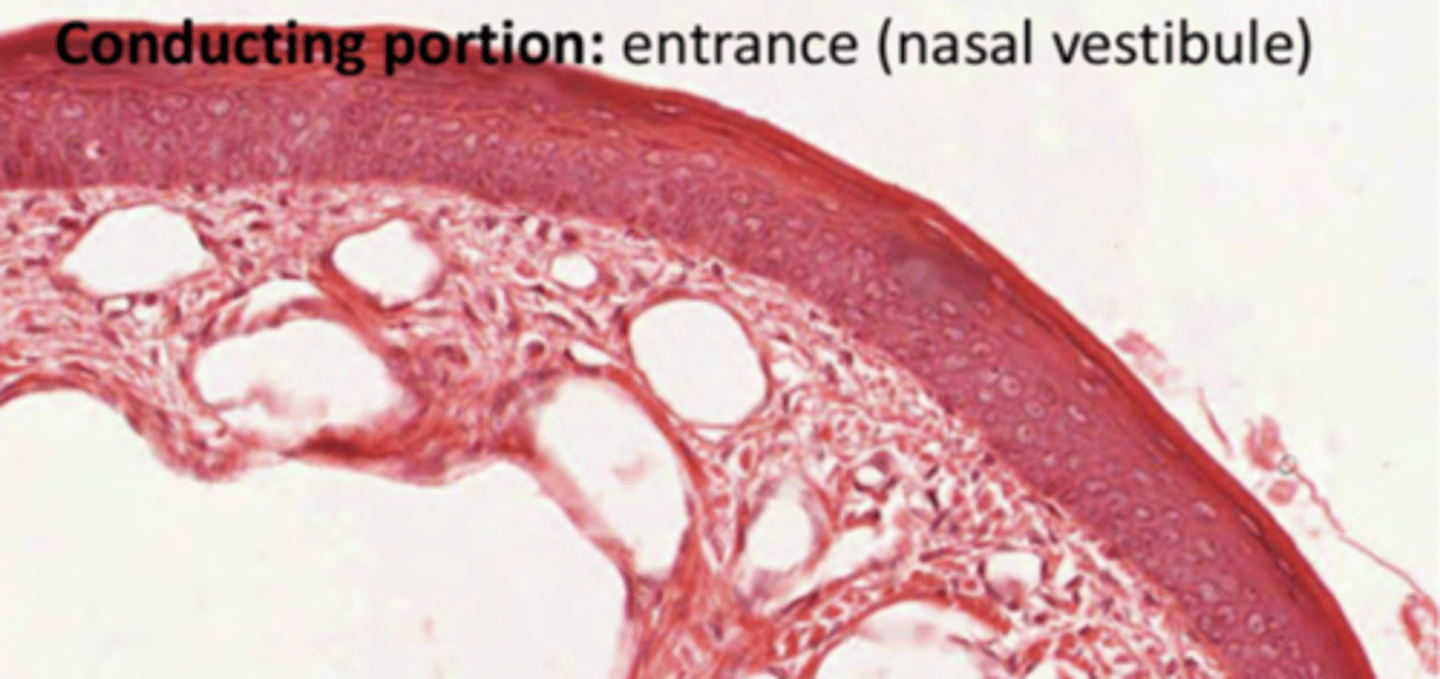
How are the cells of the nasal cavity?
Stratified keratinized squamous epithelium, recovering the entrance.
As we enter the cavity, the epithelium loses keratin, transitioning into stratified non-keratinized squamous epithelium. In deeper portions it will turn into pseudostratified ciliated epithelium (olfactory or respiratory, depending on the region of the nasal cavity).
Nasal cavity structure
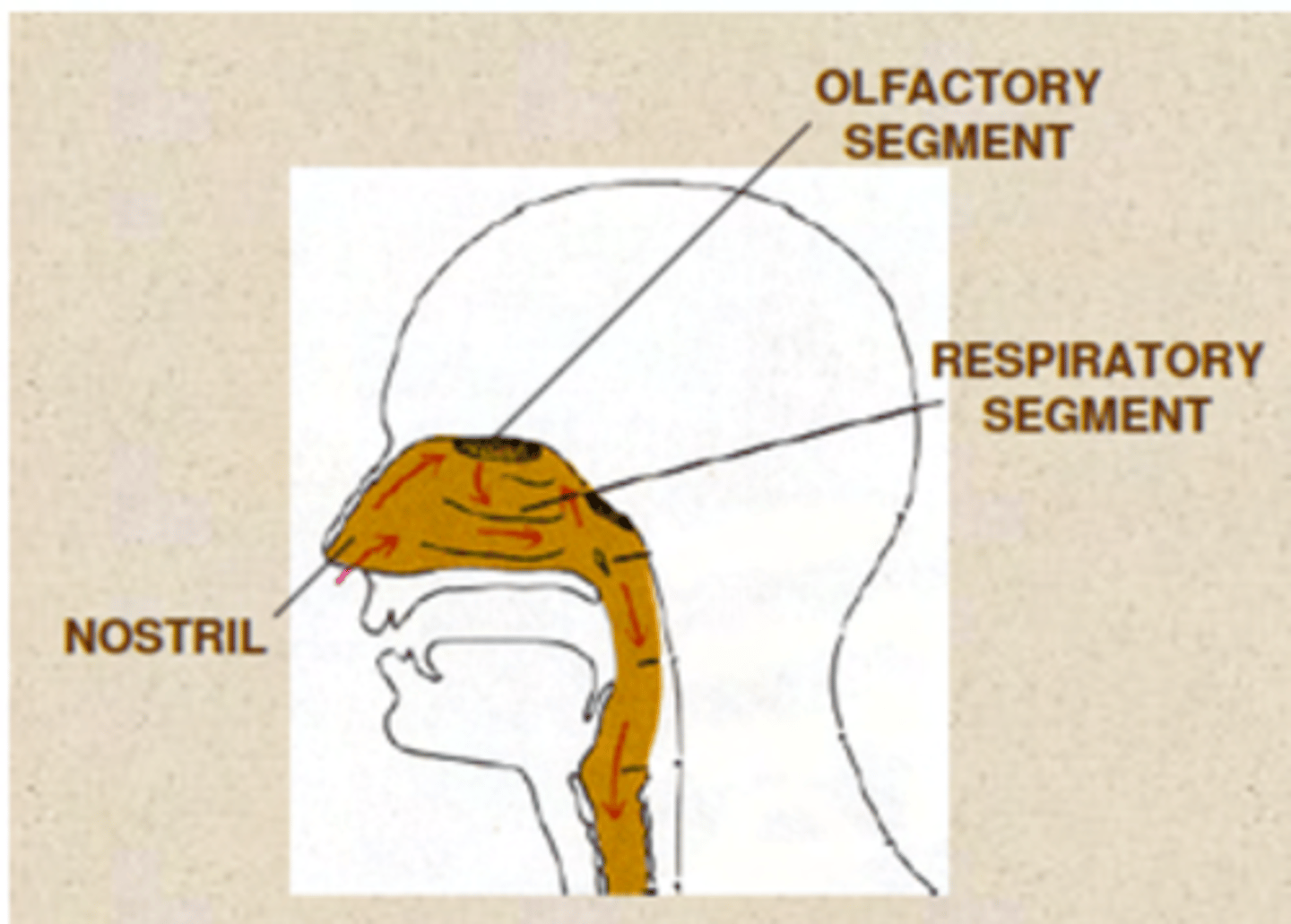
What segments do we have in the nasal cavity?
. Respiratory segment (respiratory epithelium)
. Olfactory segment (olfactory epithelium)
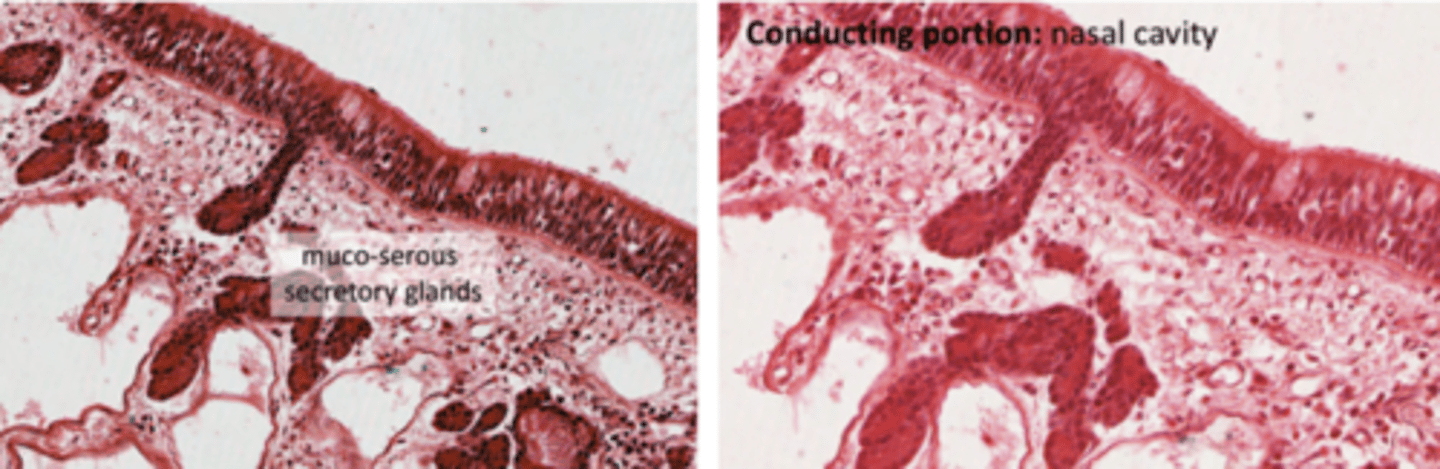
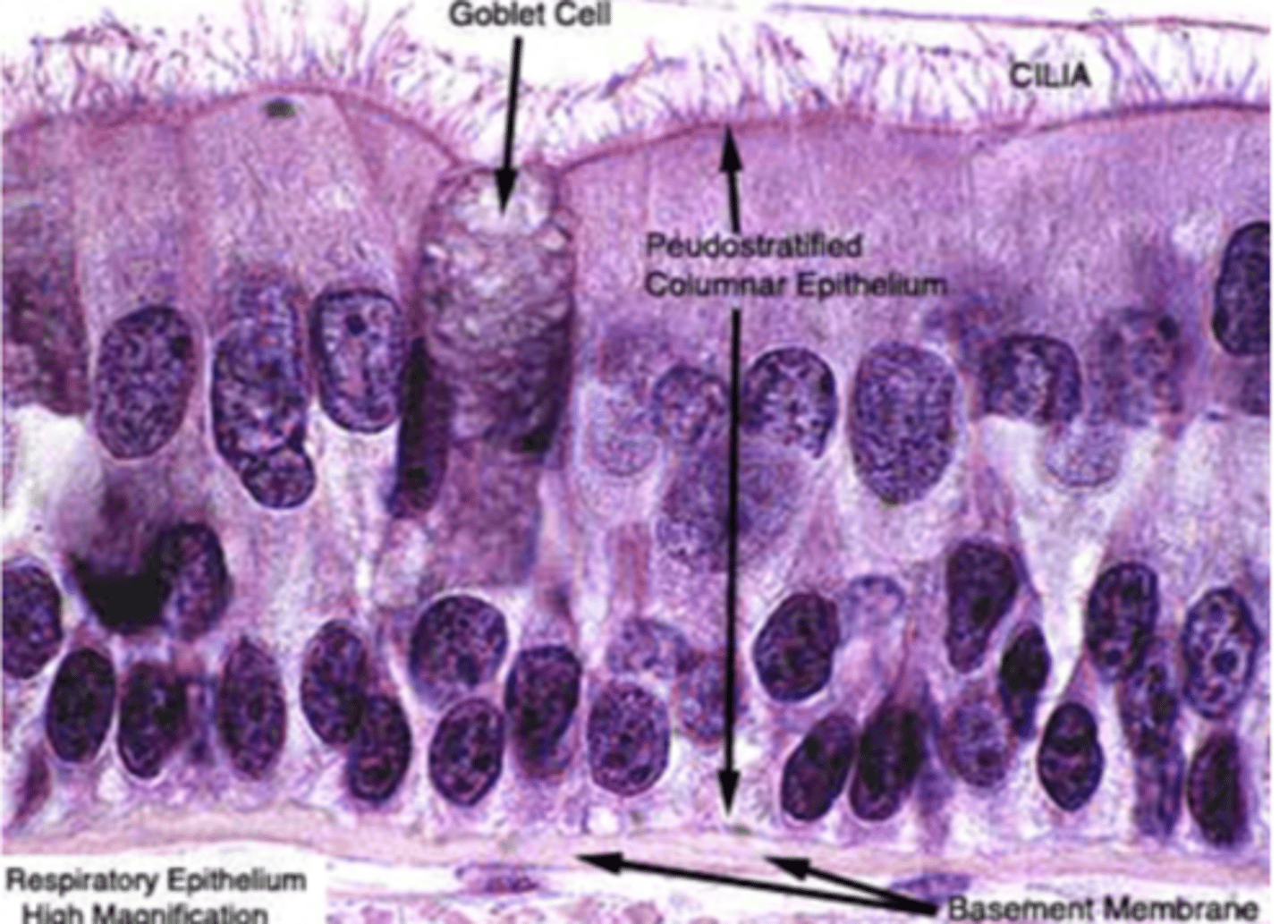
What is the structure of the respiratory respiratory epithelium?
. Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium = mucosal layer
.Goblet cells in the submucosa, secreting mucus
. May also contain mixed muco-serous glands
. Basement membrane, with basal cells (like all epithelia)
. No nerve endings
Where is secreted the surfactant?
Respiratory epithelium, in lower portions of the
respiratory tract which lack cartilage to maintain its structure and prevent them from collapsing.
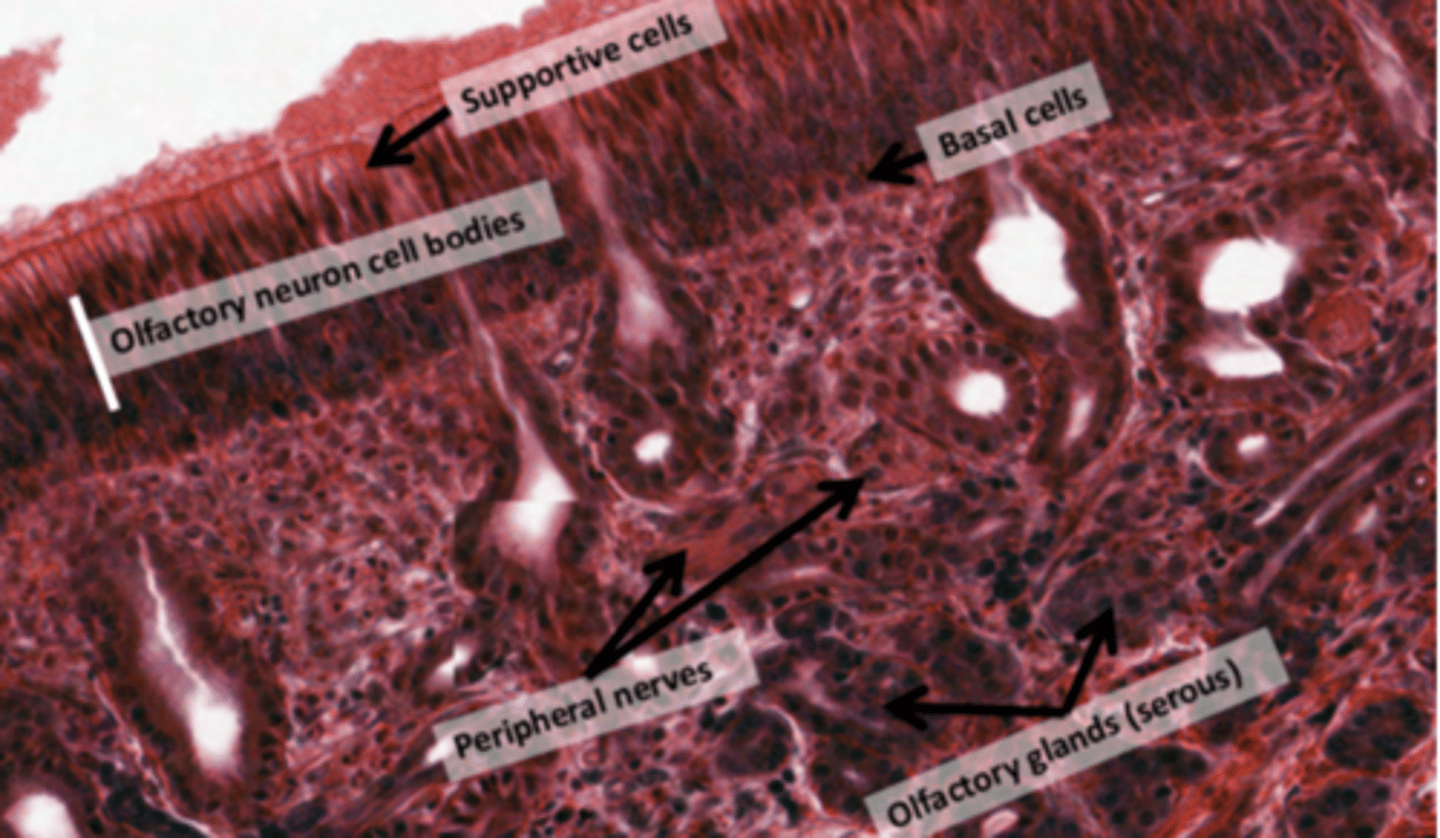
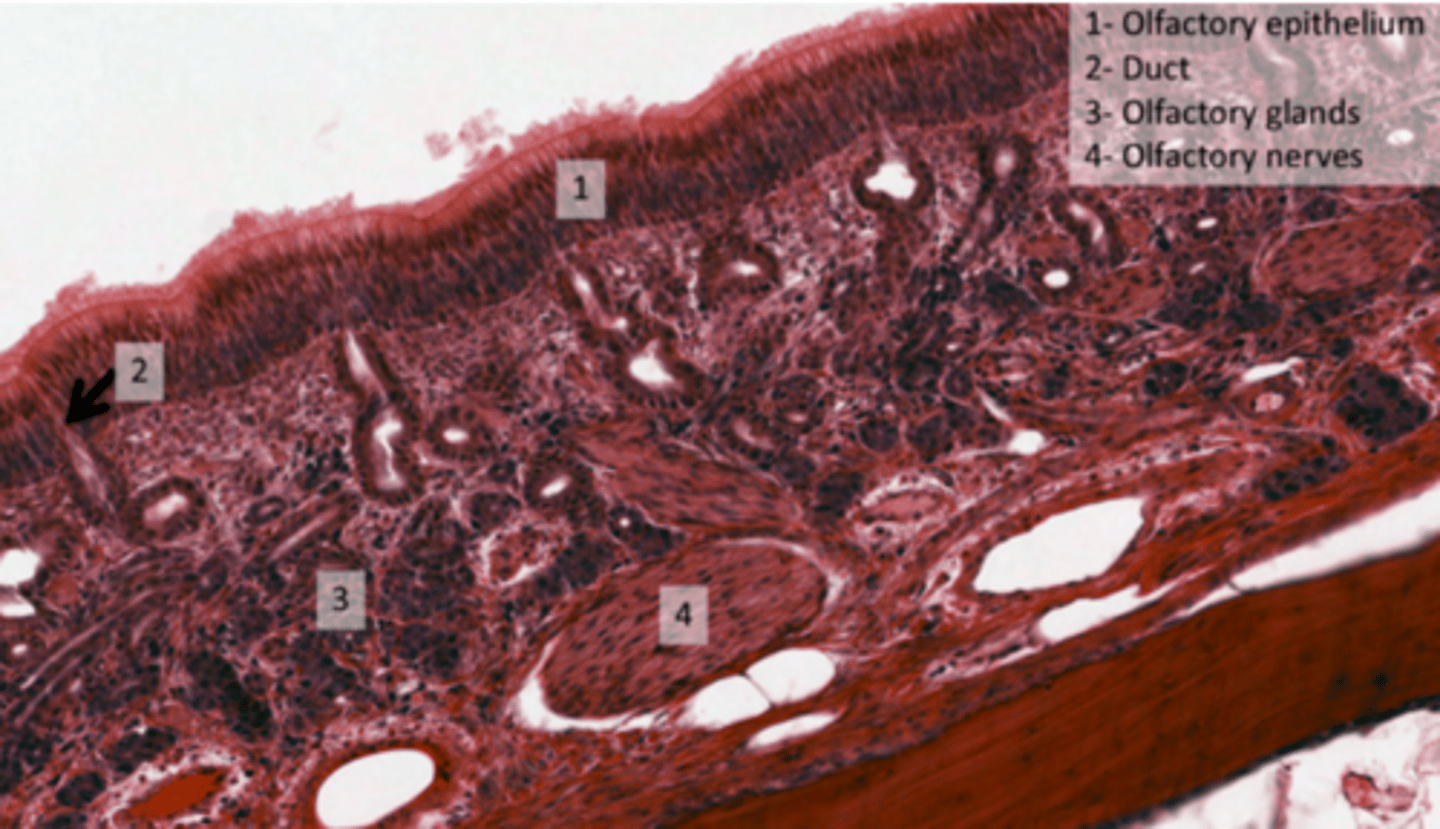
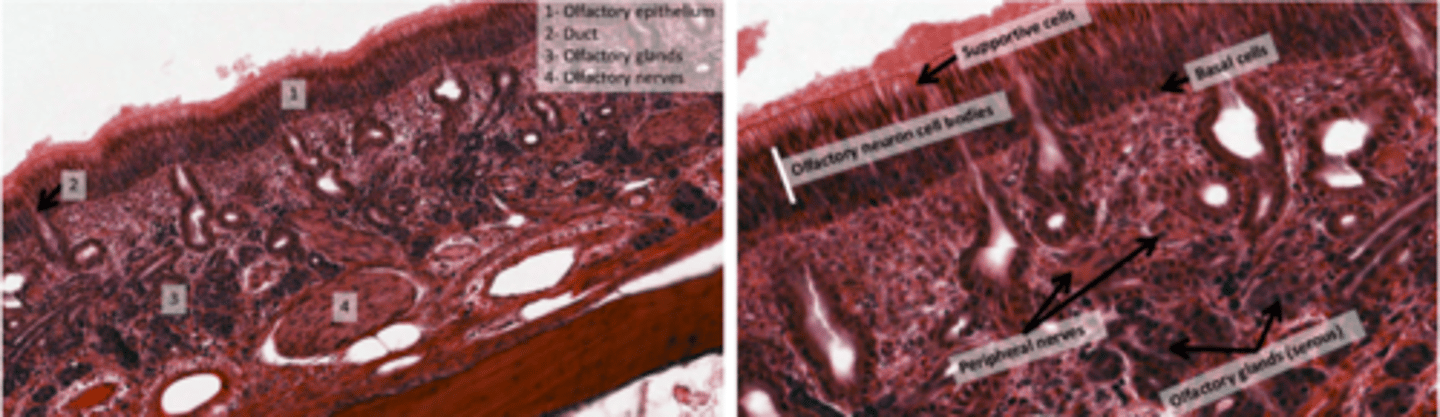
What forms the olfactory epithelium?
. pseudostratified cells
. Olfactory nerve endings
. Specialized olfactory glands (Bowman's glands)
. NO goblet cells, olfactory epithelium LACKS Goblet Cells
Why there are no goblet cells in olfactory epithelium?
To ensure a clear path for odorant molecules to interact with sensory receptors without obstruction from mucus.
What is the nerve endings in the olfactory epithelium?
(Cranial Nerve I): Embedded between the epithelial cells. These specialized sensory neurons detect odorant molecules and send signals to the brain.
The nerve fibers pass through tiny openings in the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone (foramina cribrosa) to connect with the olfactory bulb.
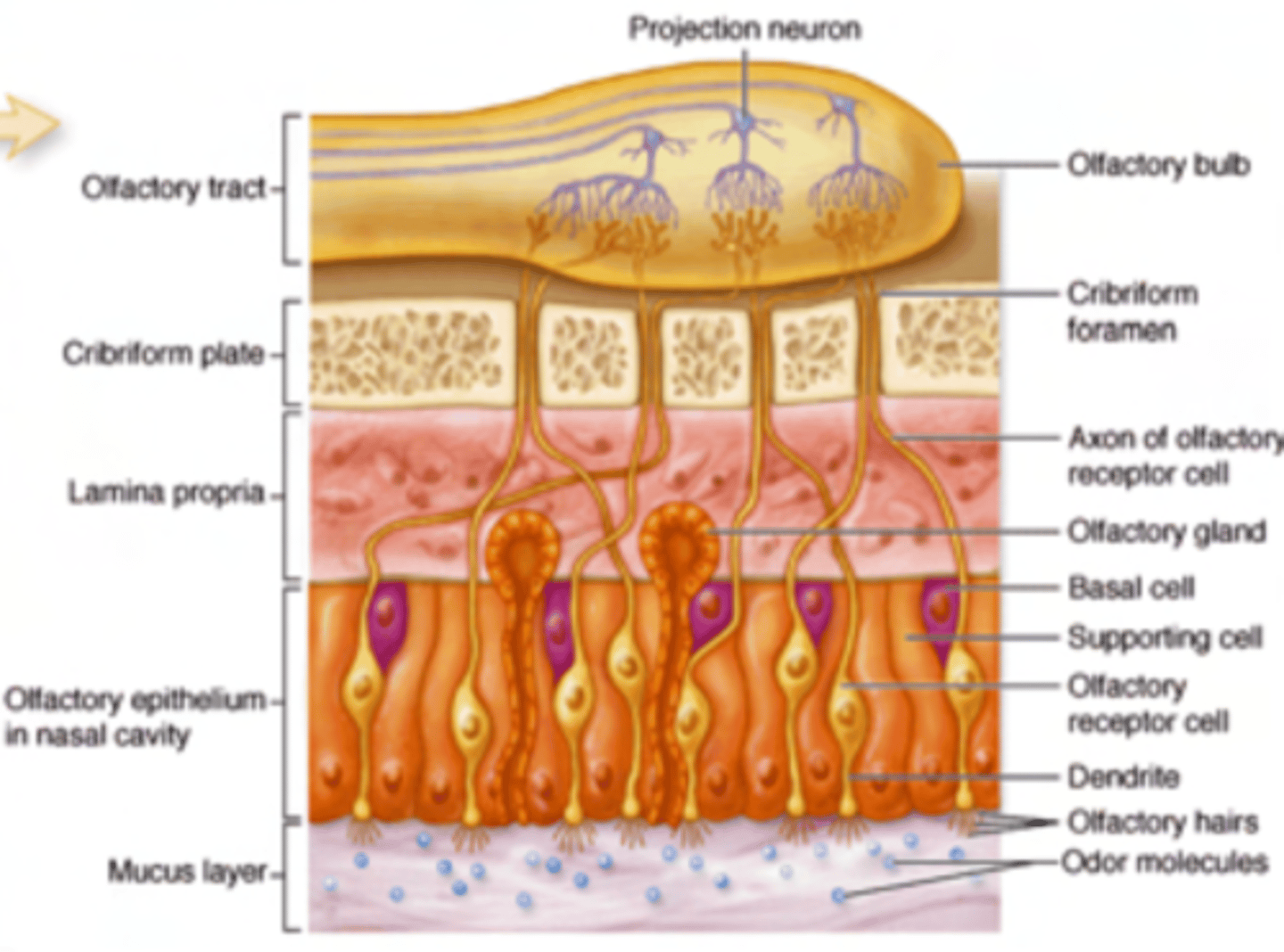
What is the pathway of the nerves in the olfactory epithelium?
pass through tiny openings in the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone (foramina cribrosa) to connect with the olfactory bulb.
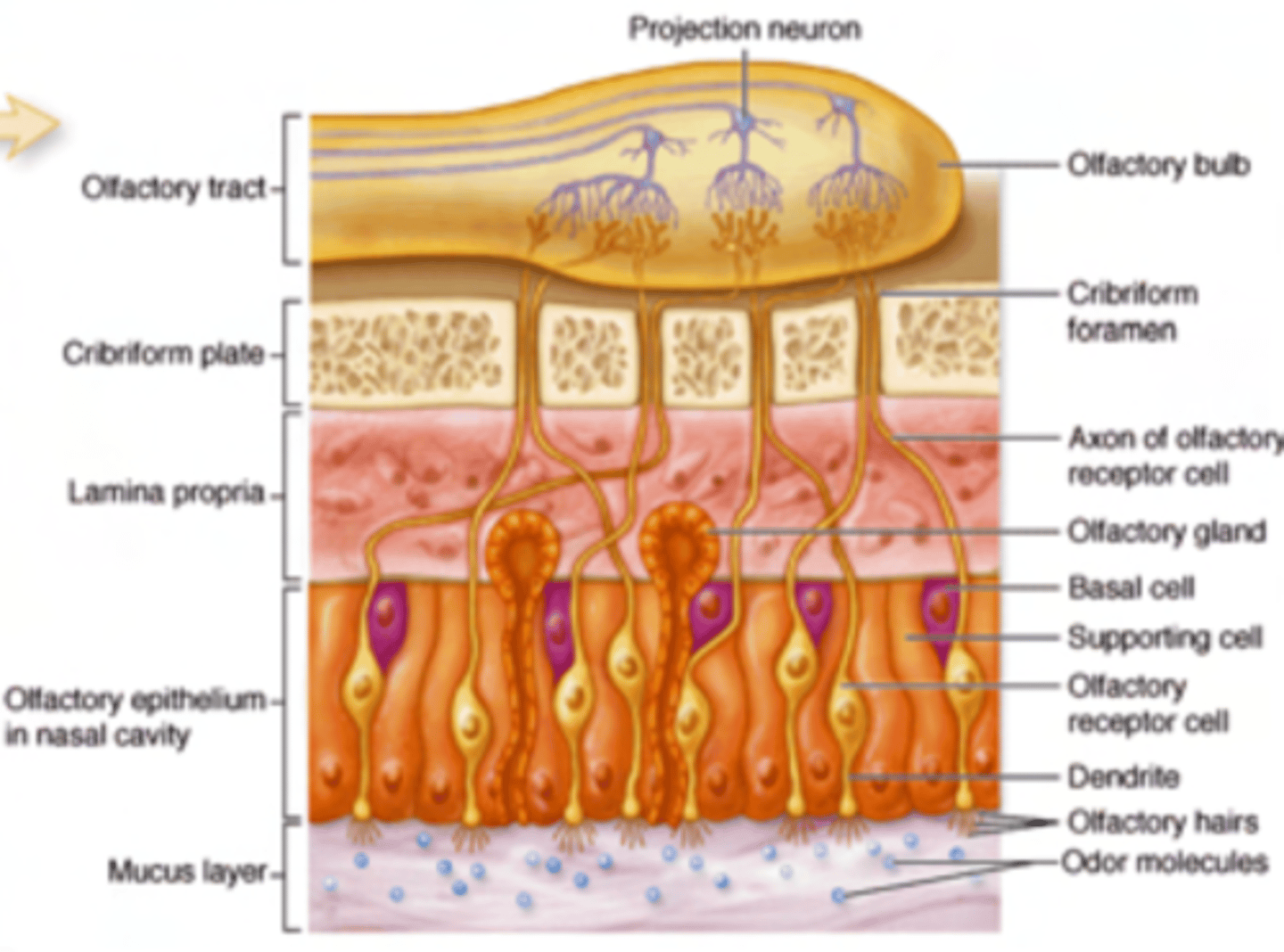
What are Bowman's glands?
Serous glands located in the submucosal layer.
Produce watery secretions to dissolve odorant molecules for detection by sensory receptors. Wash away the molecules after detection, preparing the receptors for new smells.
What is the name of separation between both nasal cavities?
Septum
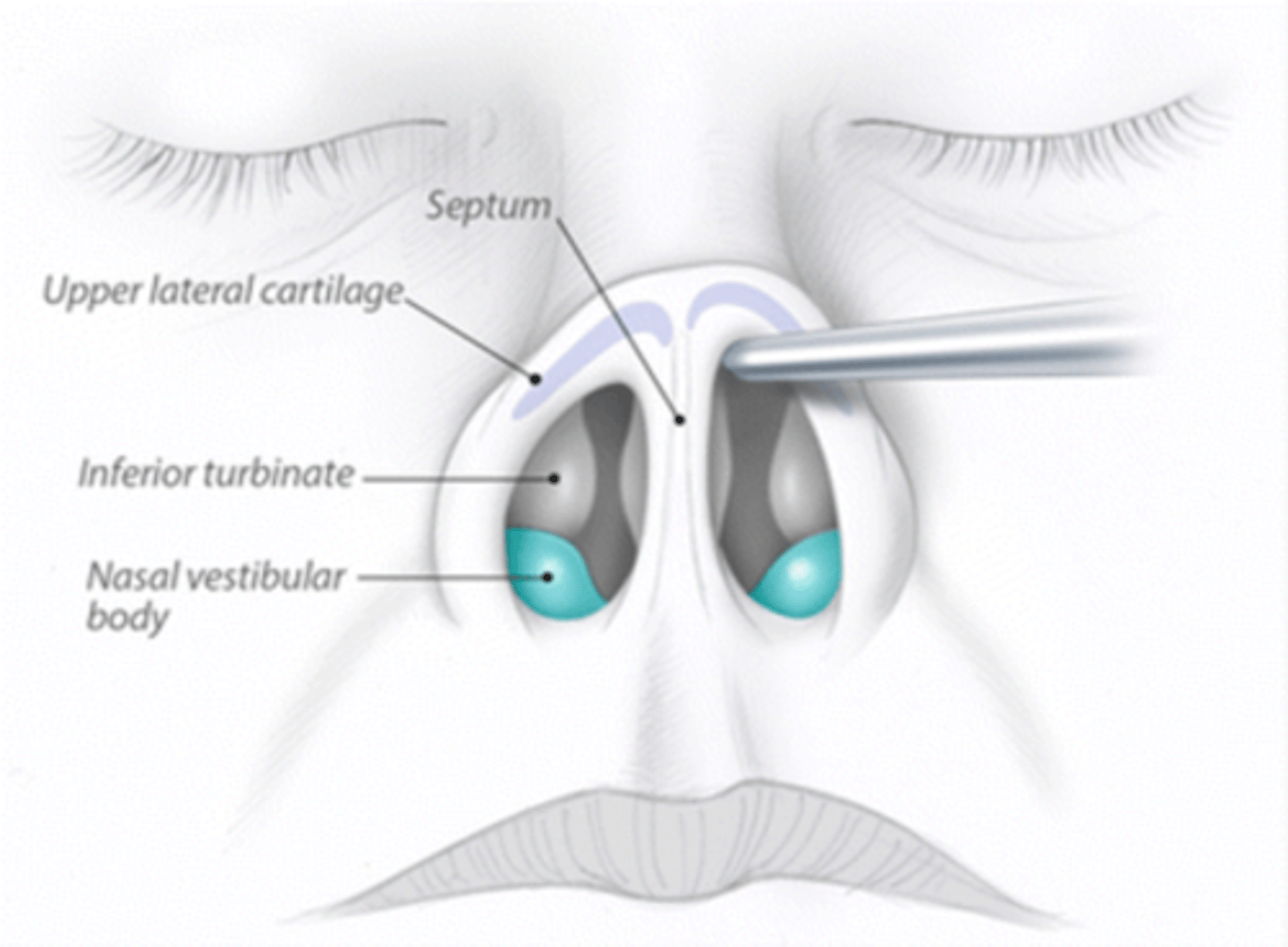
What forms the septum?
hyaline cartilague
OBSERVE THERE ARE MANY SPACES. THEY ARE VASCULAR SPACES. Their function is to warm up the
incoming air so it more or less resembles body temperature.
* Their function is to warm up the
incoming air so it more or less resembles body temperature.
* We find Goblet cells along the whole respiratory epithelium, down til the point where they
begin to be replaced by Clara cells, EXCEPT in olfactory epithelium. Serous glands = more
probable to be found in the nasal cavity
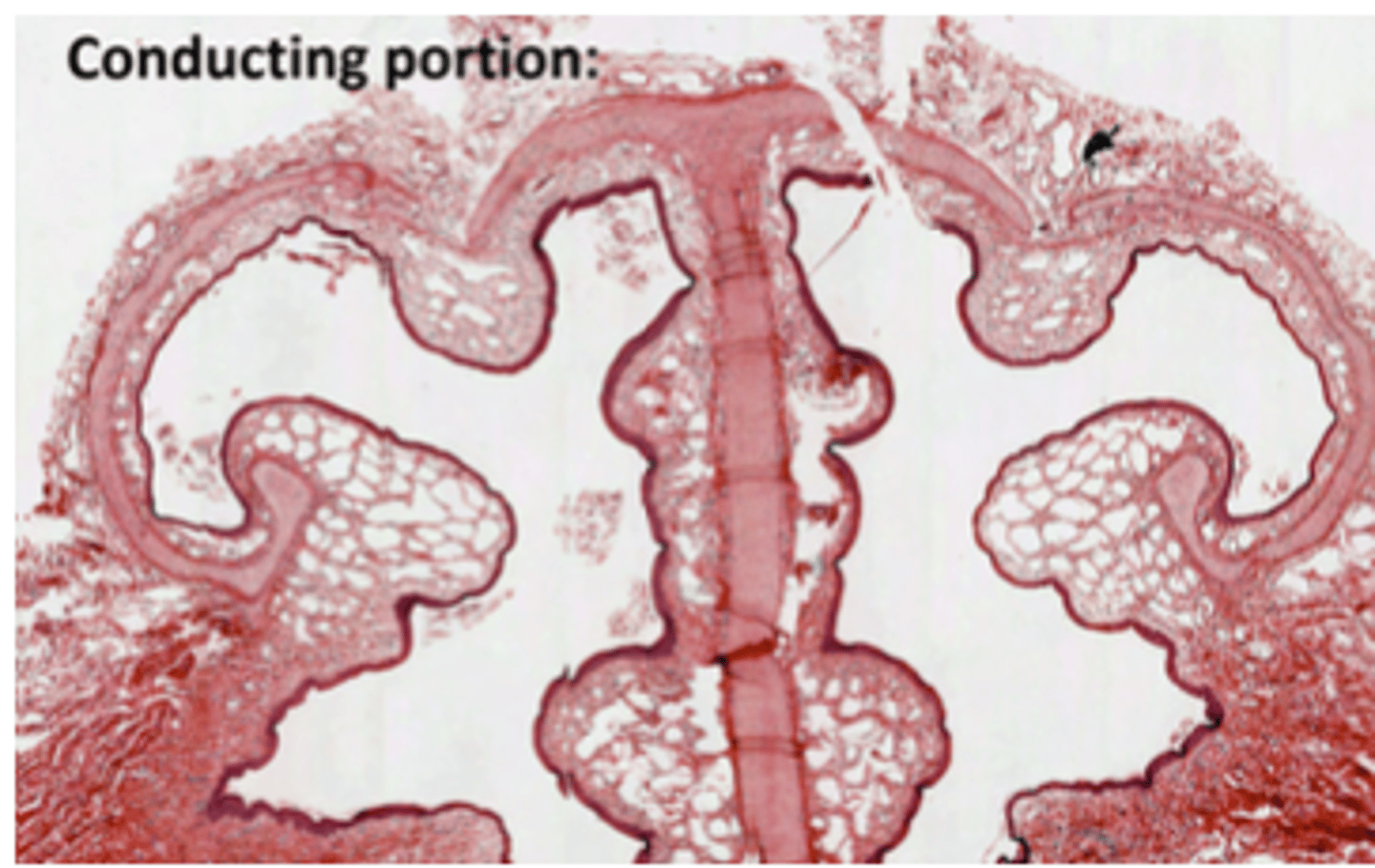
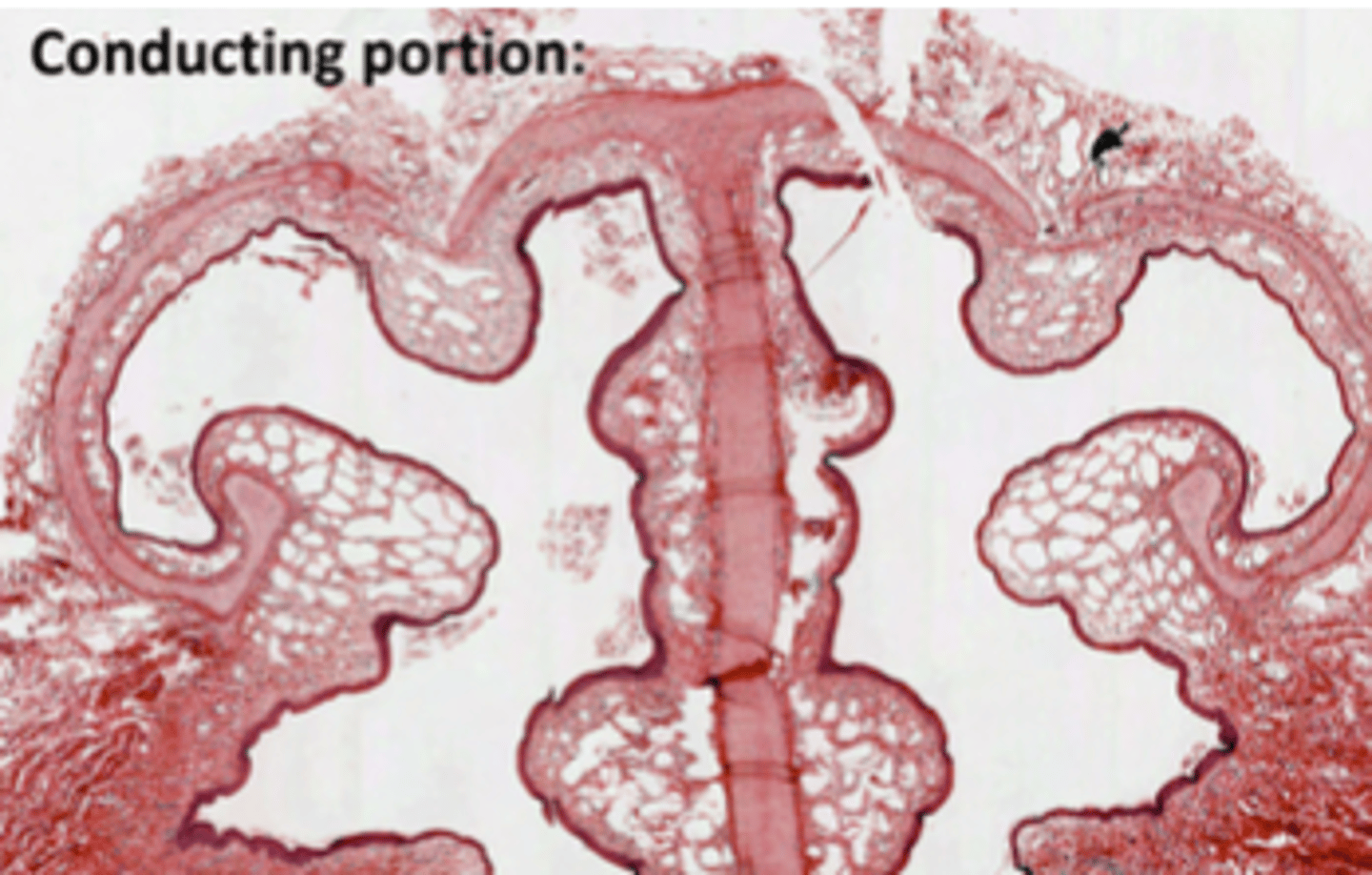
Where do we find Goblet cells?
Along the whole respiratory epithelium, down til the point where they begin to be replaced by Clara cells, EXCEPT in olfactory epithelium.
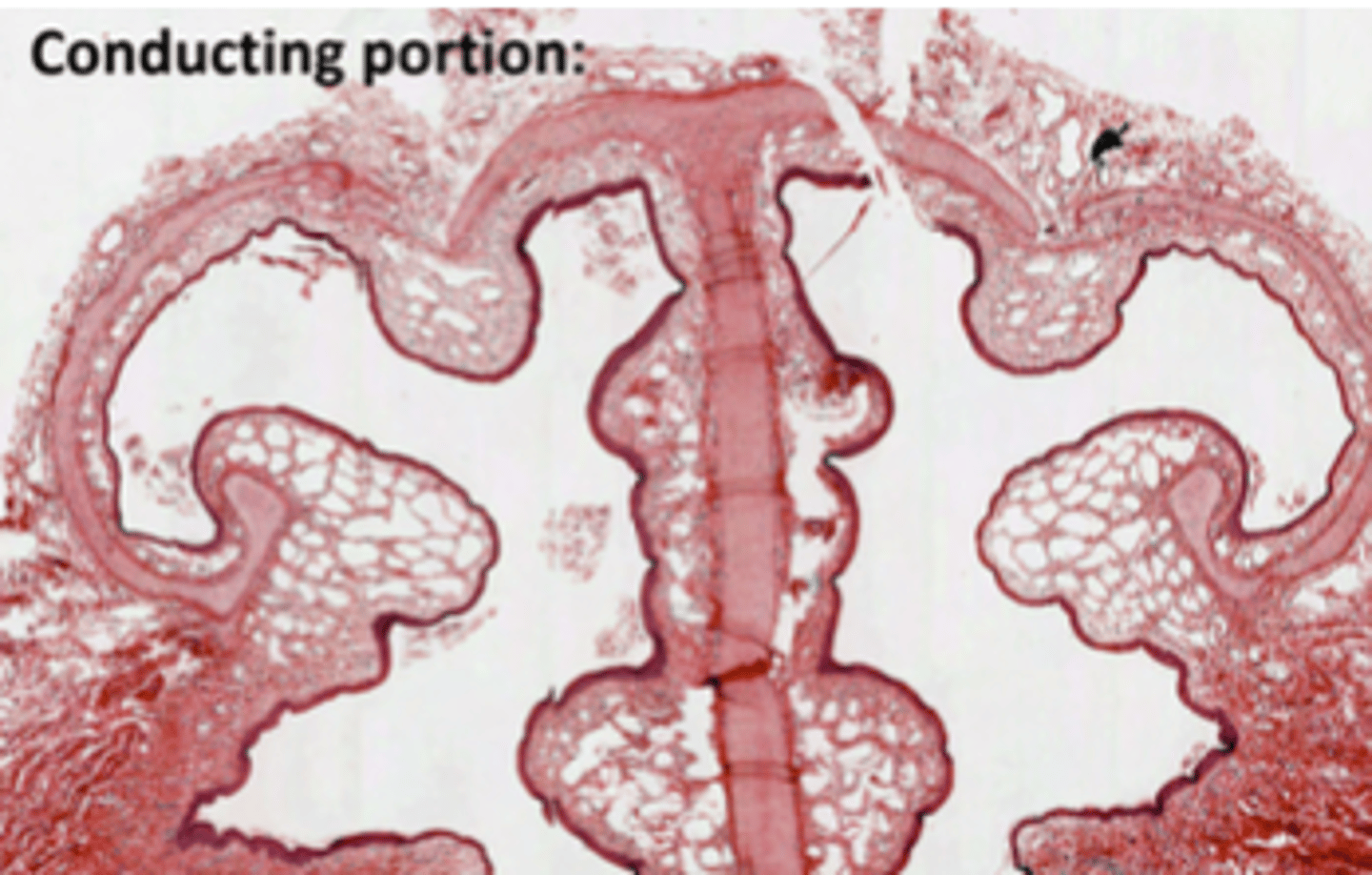
Where is most probable to find serous glands?
In the nasal cavity
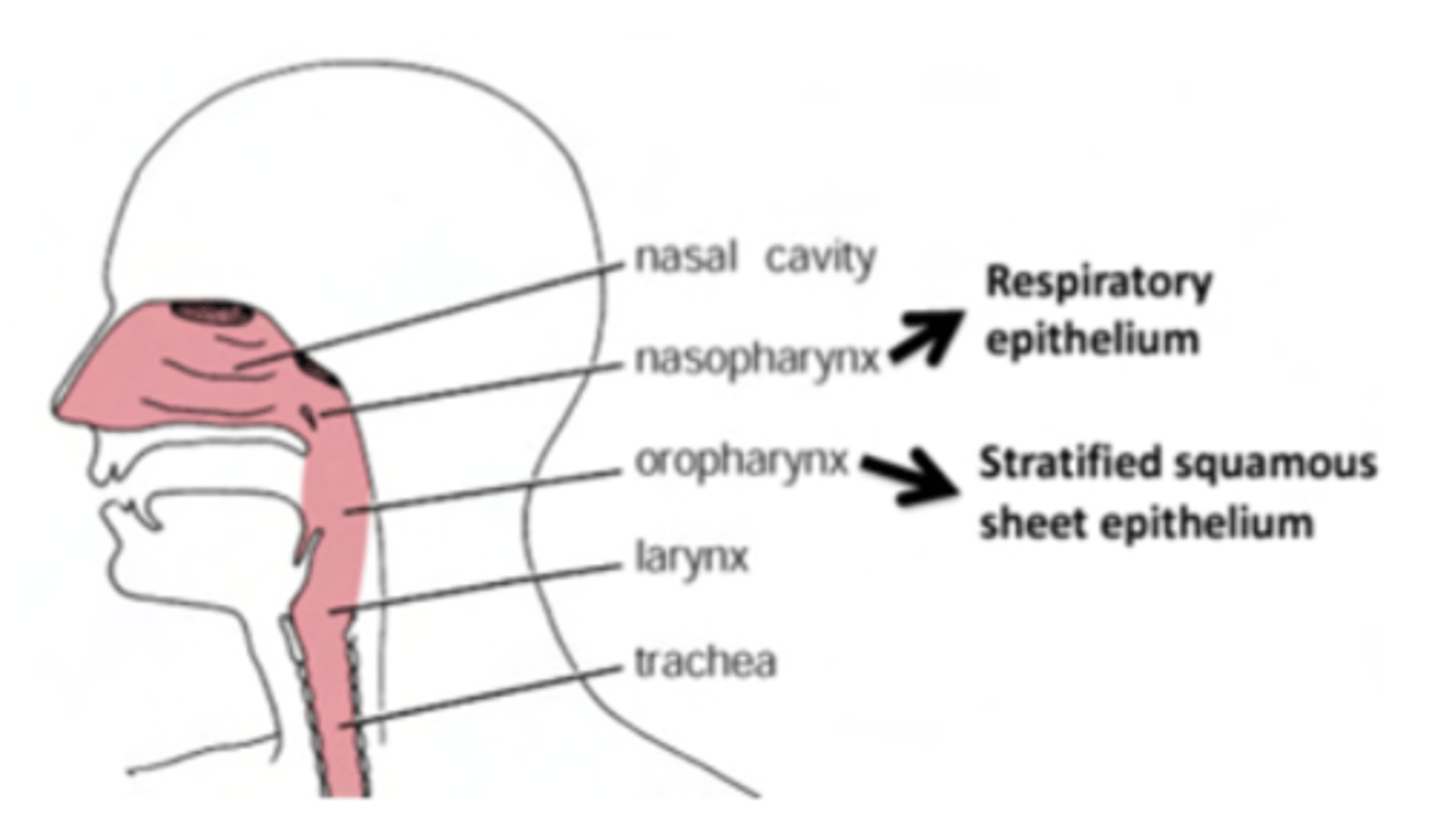
What cells does pharynx contains?
Contains respiratory epithelium in the nasopharynx and stratified squamous epithelium (non-keratinized) in the oropharynx.
Olfactory epithelium is restricted to the nasal cavity.
What is the structure found in the trachea?
Respiratory epithelium
containis cilia and some goblet cells.
cartilaginous rings which maintain its structure.
Smooth muscle cells surround the airways from the trachea down to the alveolar ducts.
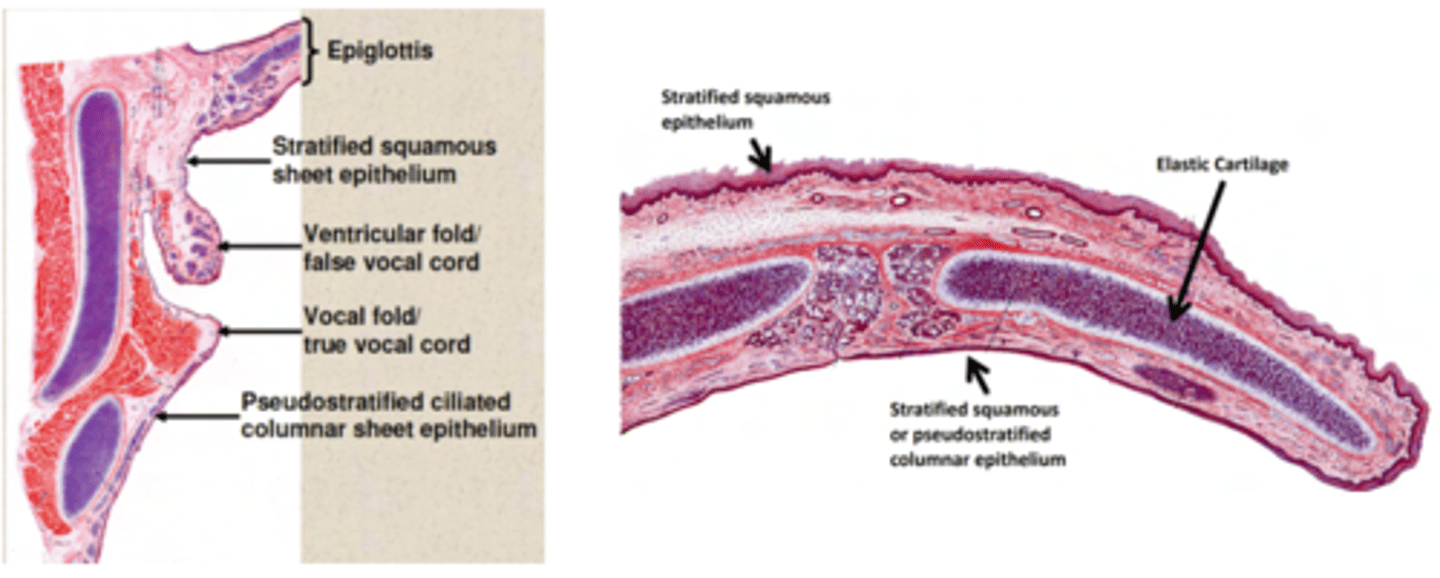
What cells does larynx contains?
. Stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium
. Respiratory epithelium: pseudostratified respiratory epithelium.
Underneath the epithelial layers, lies a layer of smooth muscle.
The larynx contains a cartilaginous structure, the epiglottis, which shuts to prevent foreign objects from crossing into the respiratory tract. Behind it, the esophagus descends.
What is ASMA?
Bronchoconstriction in the smooth muscle due to chemical irritants, smoke or inflammatory mediatiors as histamine
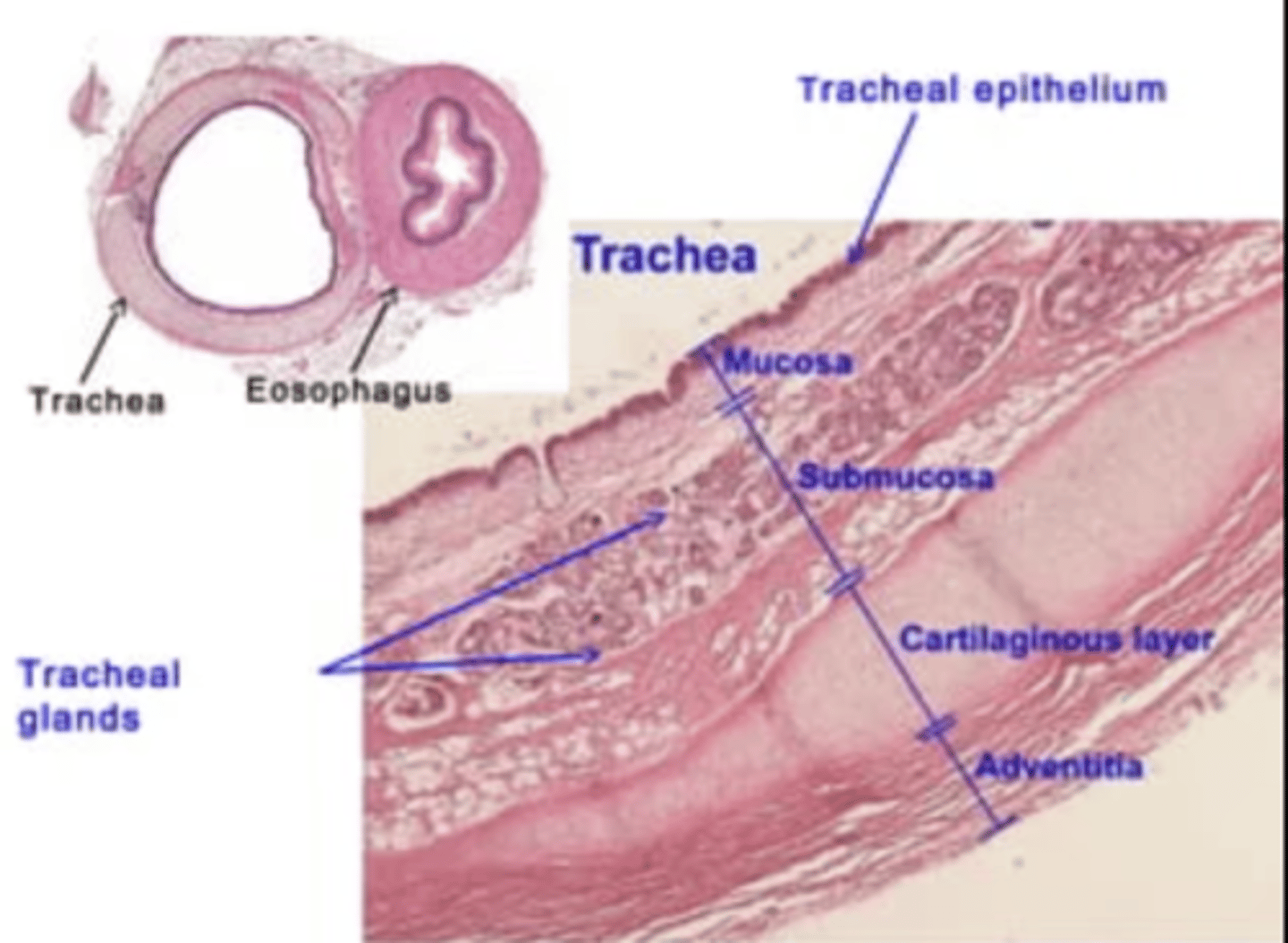
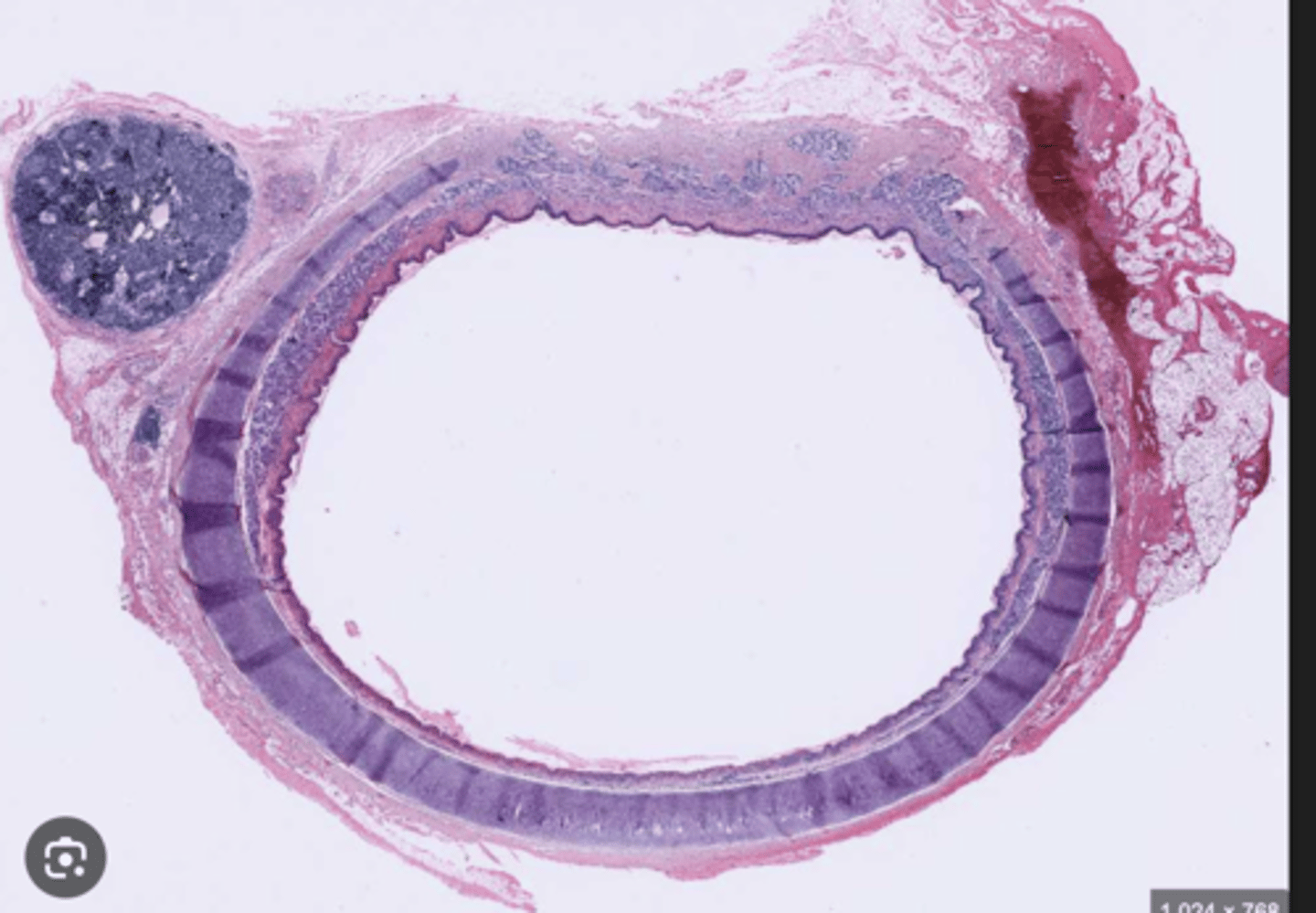
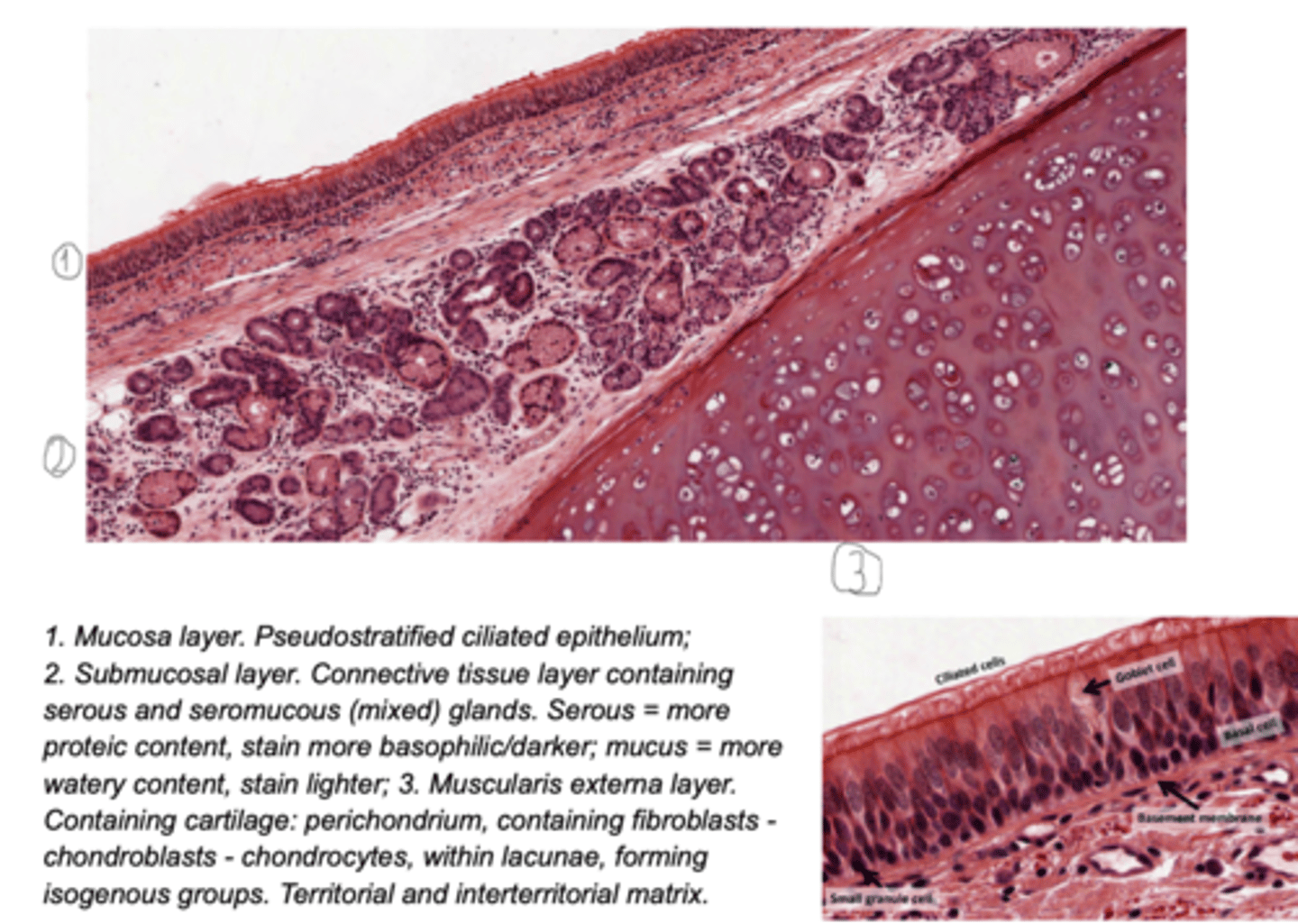
Structure of the trachea?
Respiratory epithelium is characteristic of the trachea.
columnar epithelium, containing cilia and some goblet cells.
The airway will be surrounded by cartilaginous rings which maintain its structure.
Smooth muscle cells surround the airways from the trachea down to the alveolar ducts. As we descend in the respiratory tract, the amount of cartilage decreases and the amount of smooth muscle increases.
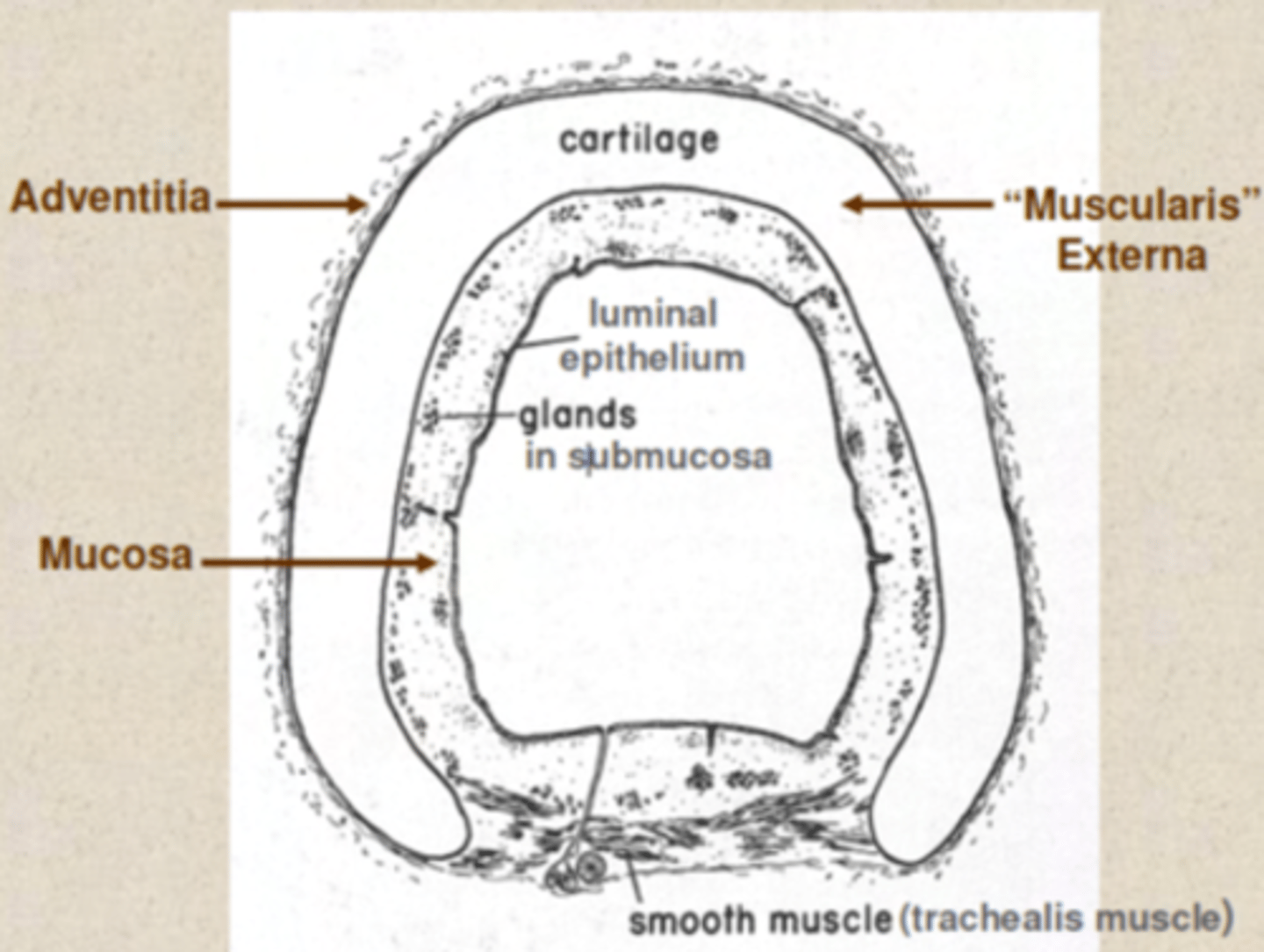
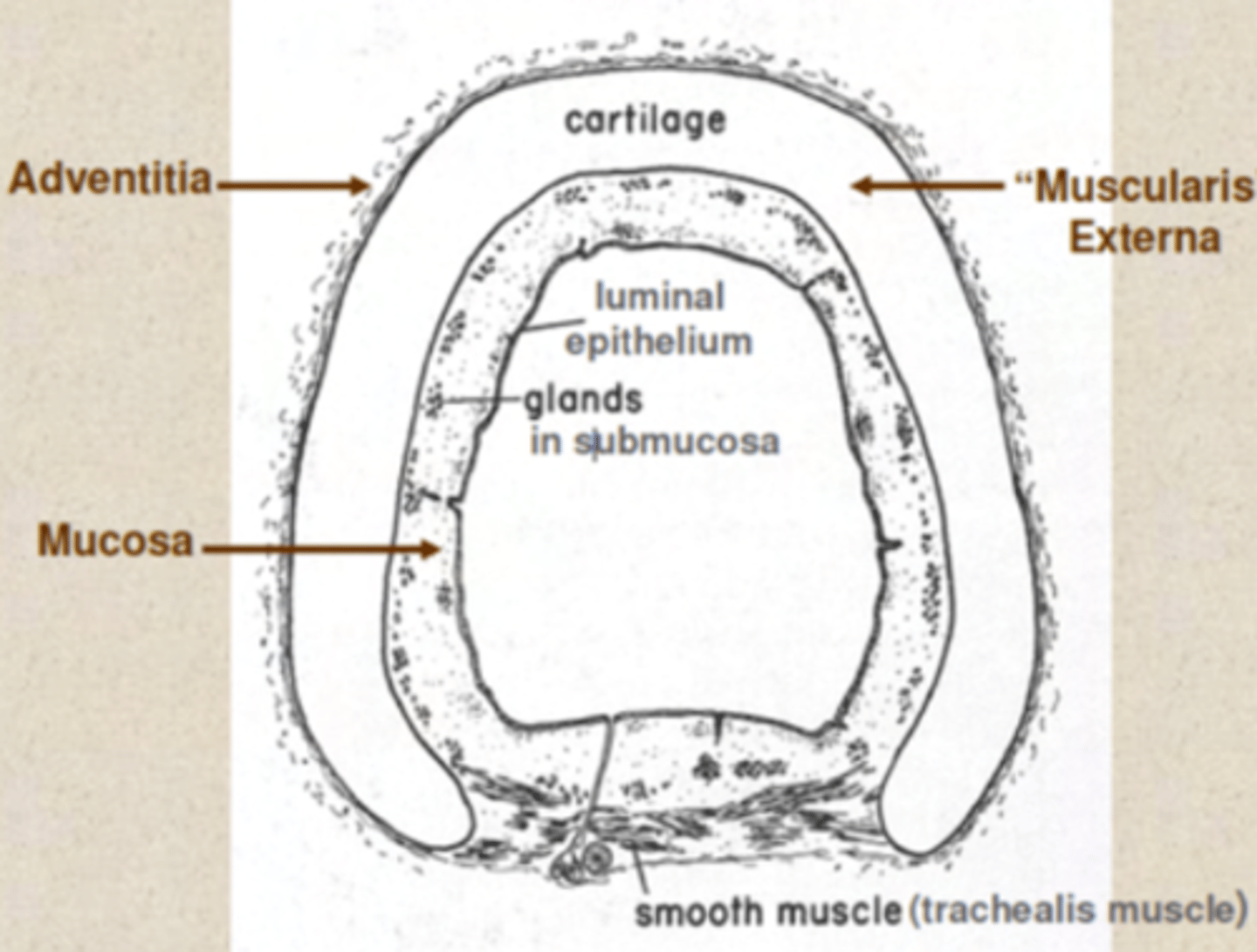
Which are the tissue layers of the trachea?
. Mucosa
. Submucosa: loose and dense fibroelastic CT, which contains
the glands (mainly tubuloacinar seromucous (mixed) glands)
. Muscularis externa - in the trachea, this layer comprises:
Hyaline cartilage rings,
Smooth muscle,
Adventitia - anchoring. Composed of loose FECT
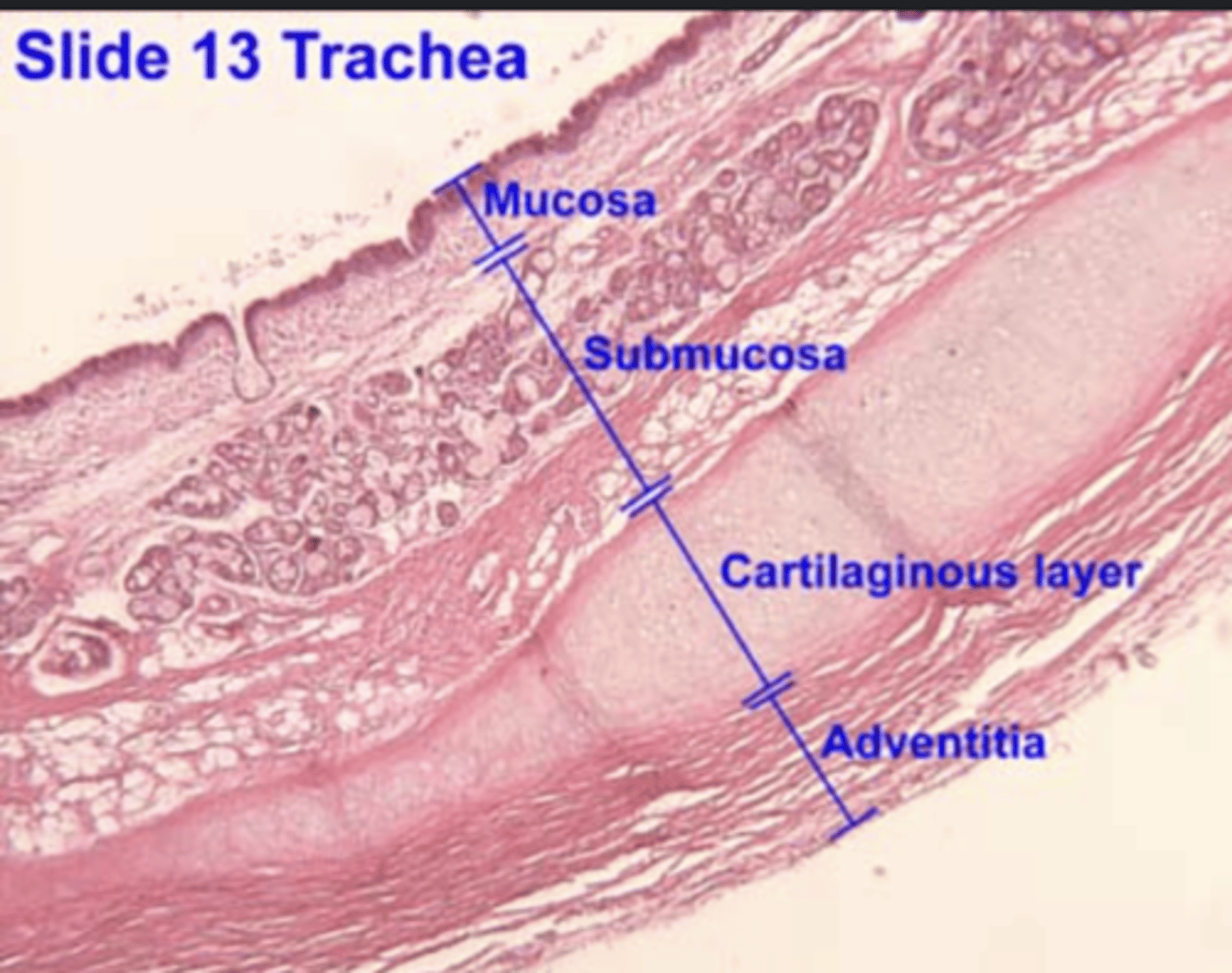
Trachea layers
mucosa, submucosa, hyaline cartilage, adventitia
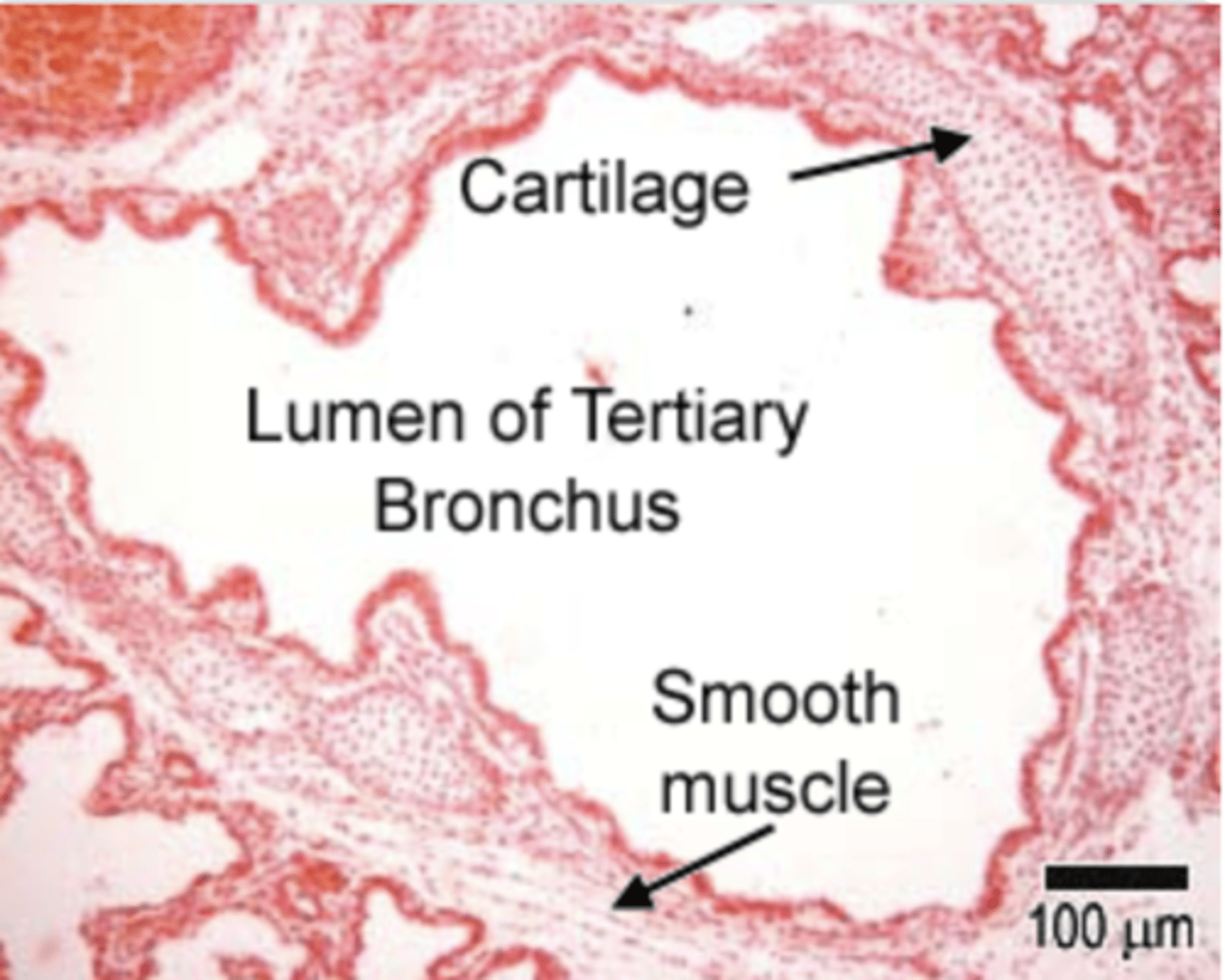
What are the main differences between trachea and bronchi and bronchioles?
. Bronchi have plates rather than rings of cartilage
.Present a layer of smooth muscle between lamina propria and submucosa
. There is less cartilage, and it does not completely encircle the lumen, as shown diagramatically above.
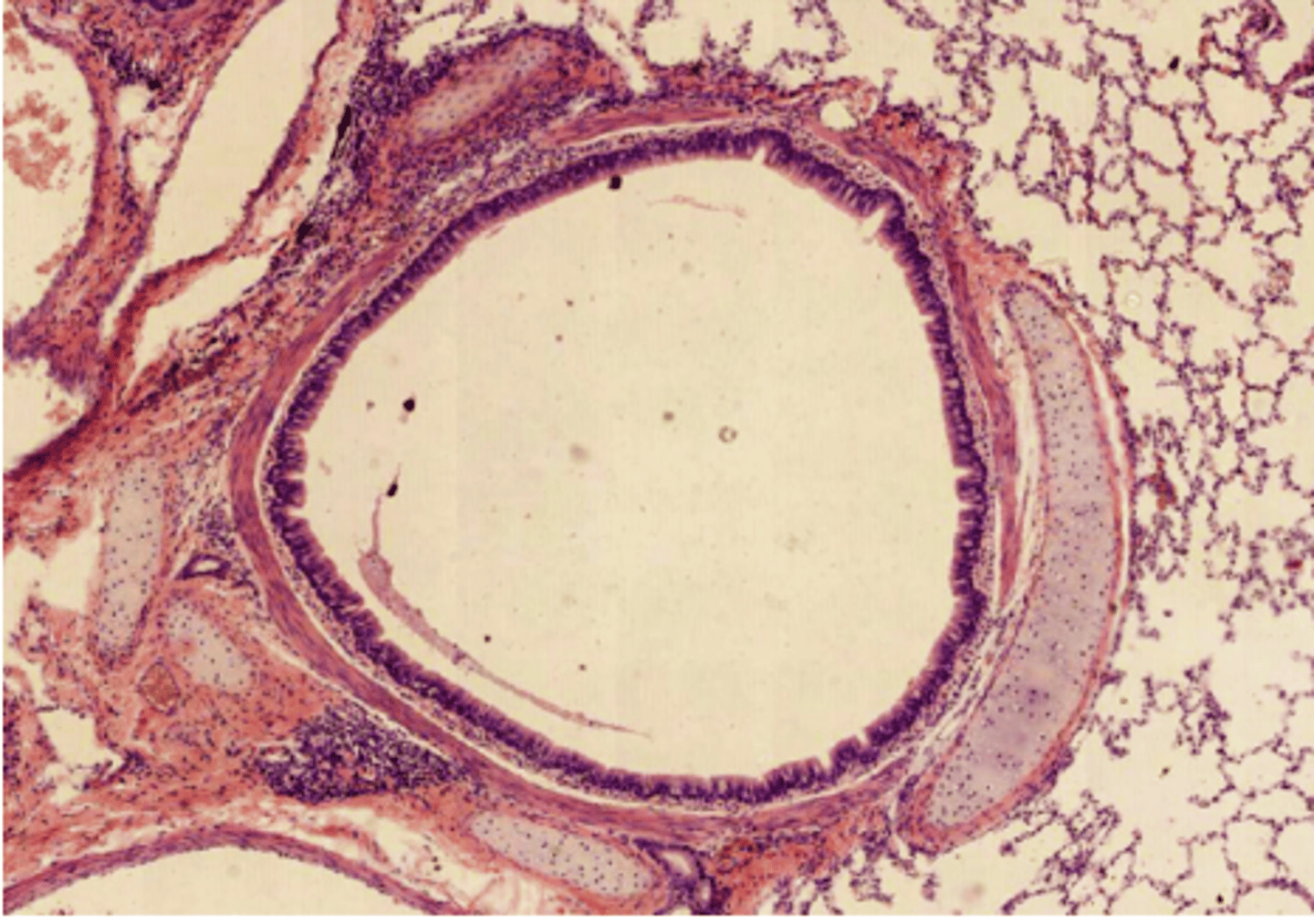
Bronchus photo
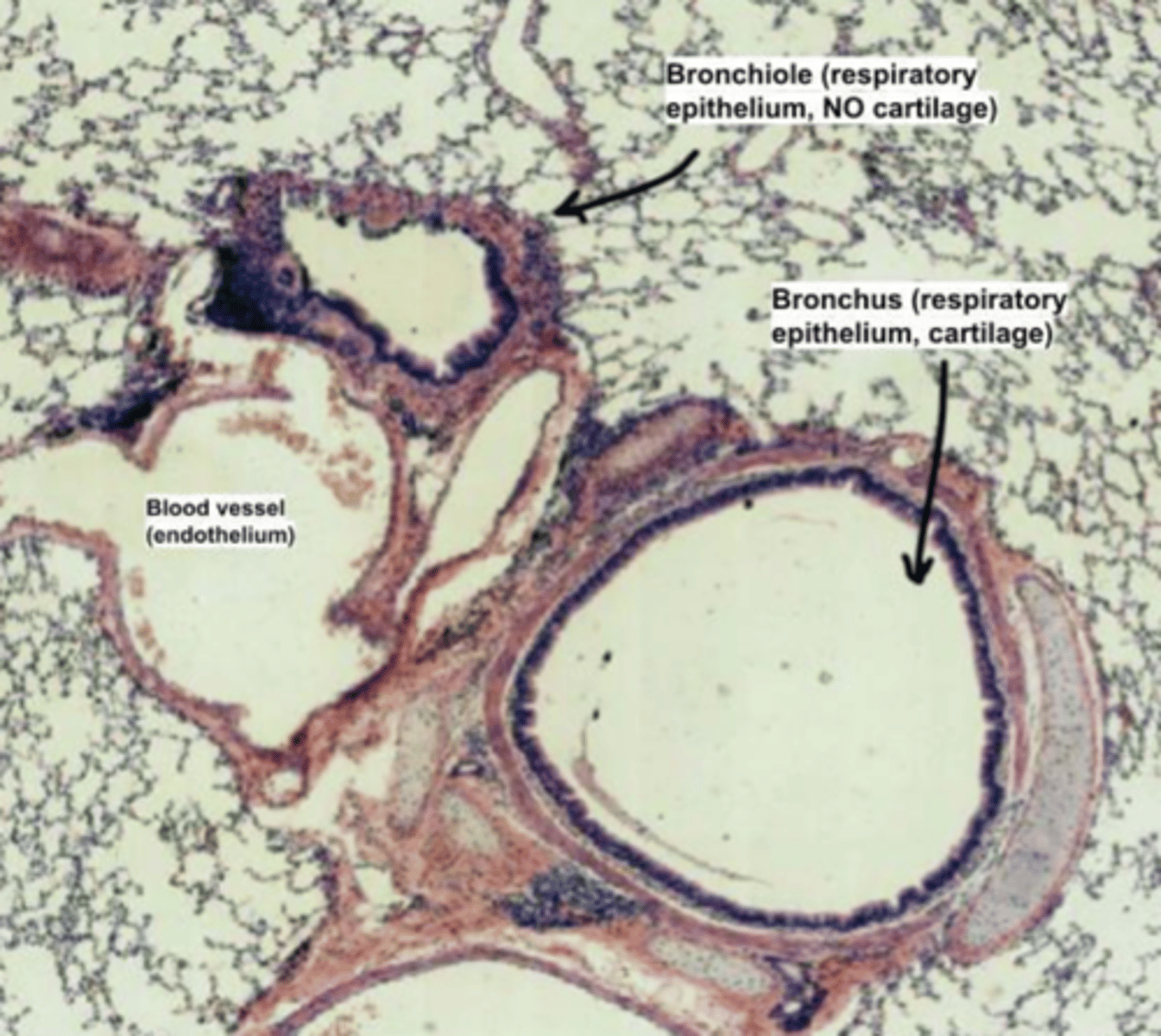
intrapulmonary bronchus, as we can see surrounding parenchyma. We determine it’s bronchus as we can still find cartilage, a horse-shoe shaped cartilage plate surrounding the tube.
What is the structure of the extrapulmonary bronchus?
. Mucosa - respiratory epithelium containing few Clara cells (they begin to replace goblet cells) +lamina propria
. Submucosa: loose - dense fibroelastic CT.
. Muscularis externa - Hyaline cartilage plates (horse-shoe shaped) + smooth muscle across the open ends of the cartilage
. Adventitia - Loose FECT anchoring the bronchus to surrounding tissue
EXTRAPULMONARY BRONCHUS portion of the bronchial tree that lies outside the lungs, before entering the lung tissue
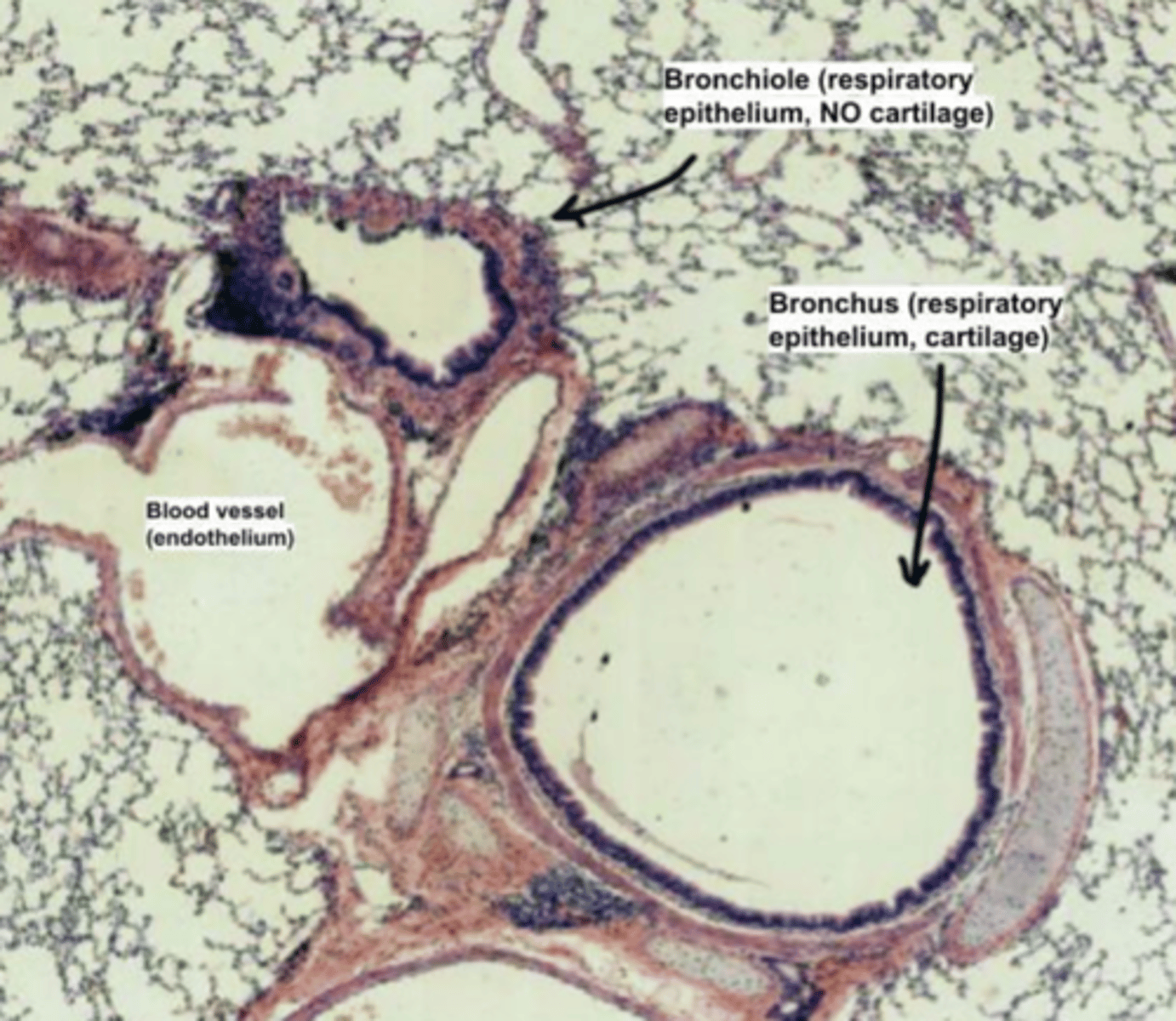
How do we distinguish a bronchus from a bronchiole?
Bronchi present a hyaline cartilage plate, while bronchioles
LACK cartilage. The muscularis externa layer will only
contain smooth muscle.
What is the structure of intrapulmonary bronchus?
. Mucosa - respiratory epithelium (with increasing number of Clara cells) + lamina propria
. Muscularis - contains spiral bundles of smooth muscle between the lamina propria and submucosa.
. Submucosa: loose - dense FECT which may still contain some seromucous glands
. Muscularis externa - small hyaline cartilage rings (disappearing, being replaced by SM) + smooth muscle connecting the open ends
. Adventitia - loose FECT anchoring to surrounding tissue
Basically as we go through the lungs, what happens with cartilage and glands type?
. Cartilage decreases, whereas the amount of smooth muscle increases
. Number of glands and goblet cells decreases, while Clara cells increase
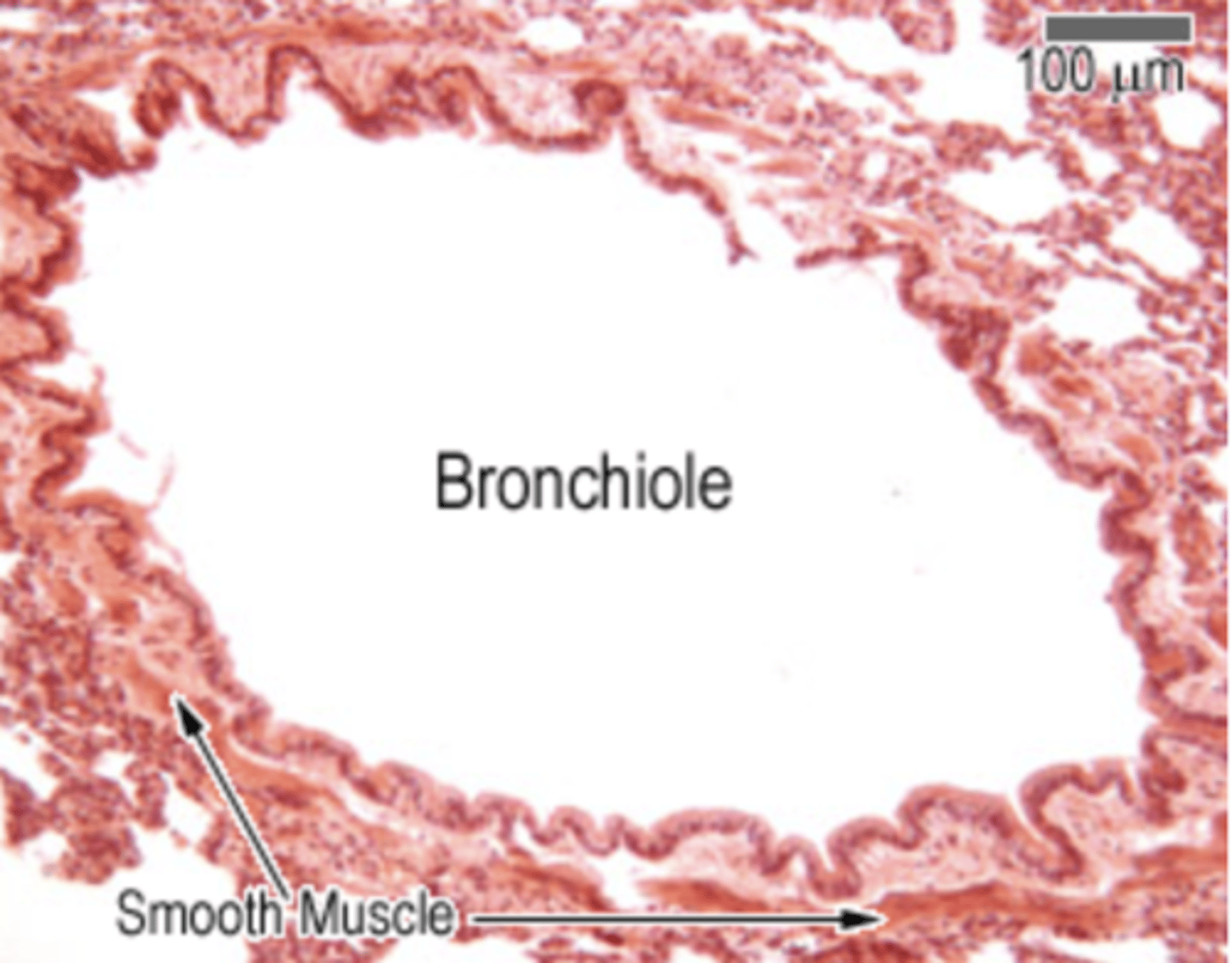
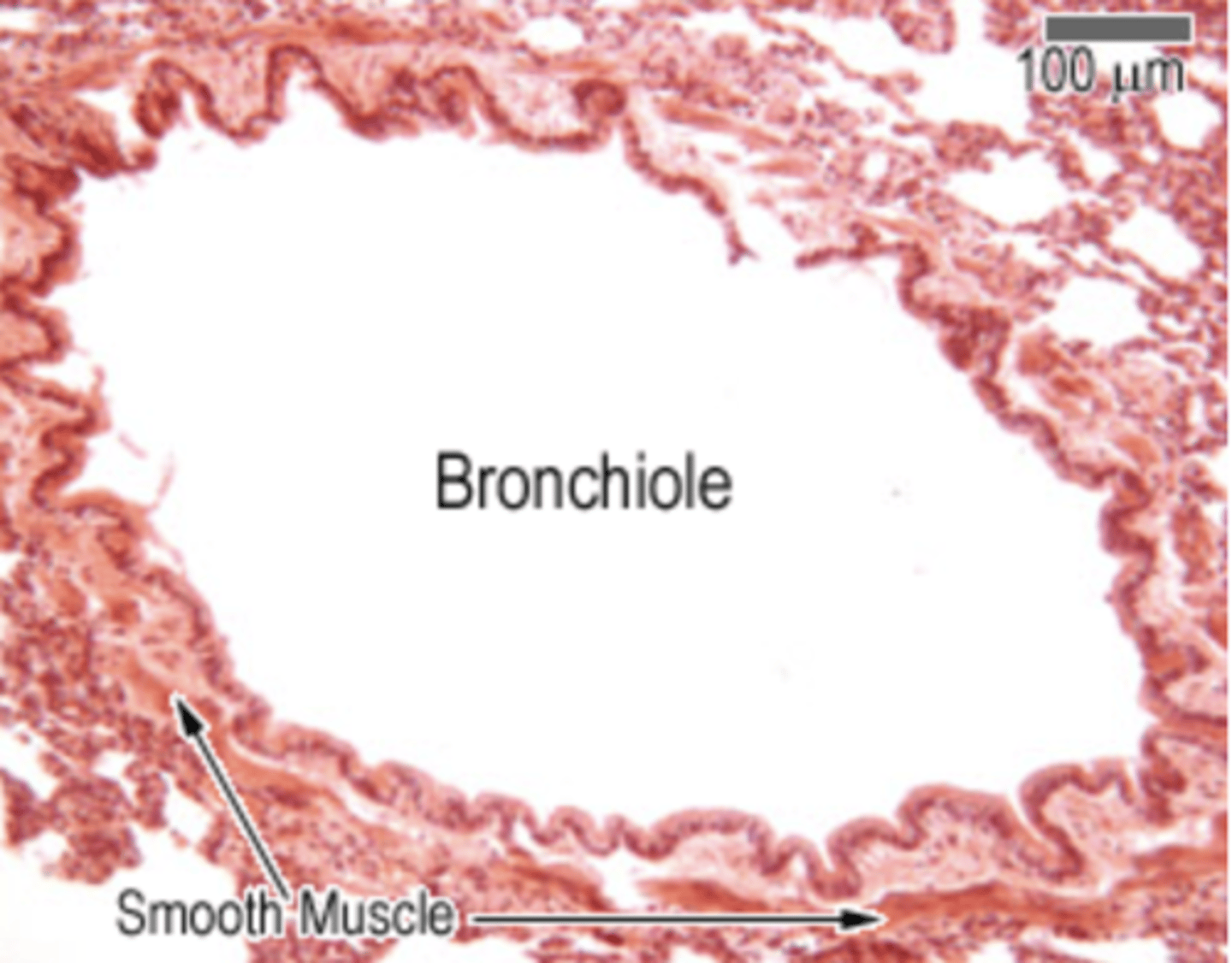
What is the structure of the bronchiolis?
. Mucosa: ranges from pseudostratified ciliated columnar in large bronchioles → to simple cuboidal (mixed with few ciliated cells) + Clara cells in terminal bronchioles, and NO goblet cells. Lastly, contains the lamina propria = loose FECT
. Muscularis - circularly arranged bundles of smooth muscle
. Submucosa - fused with the lamina propria, absent. No cartilage or glands
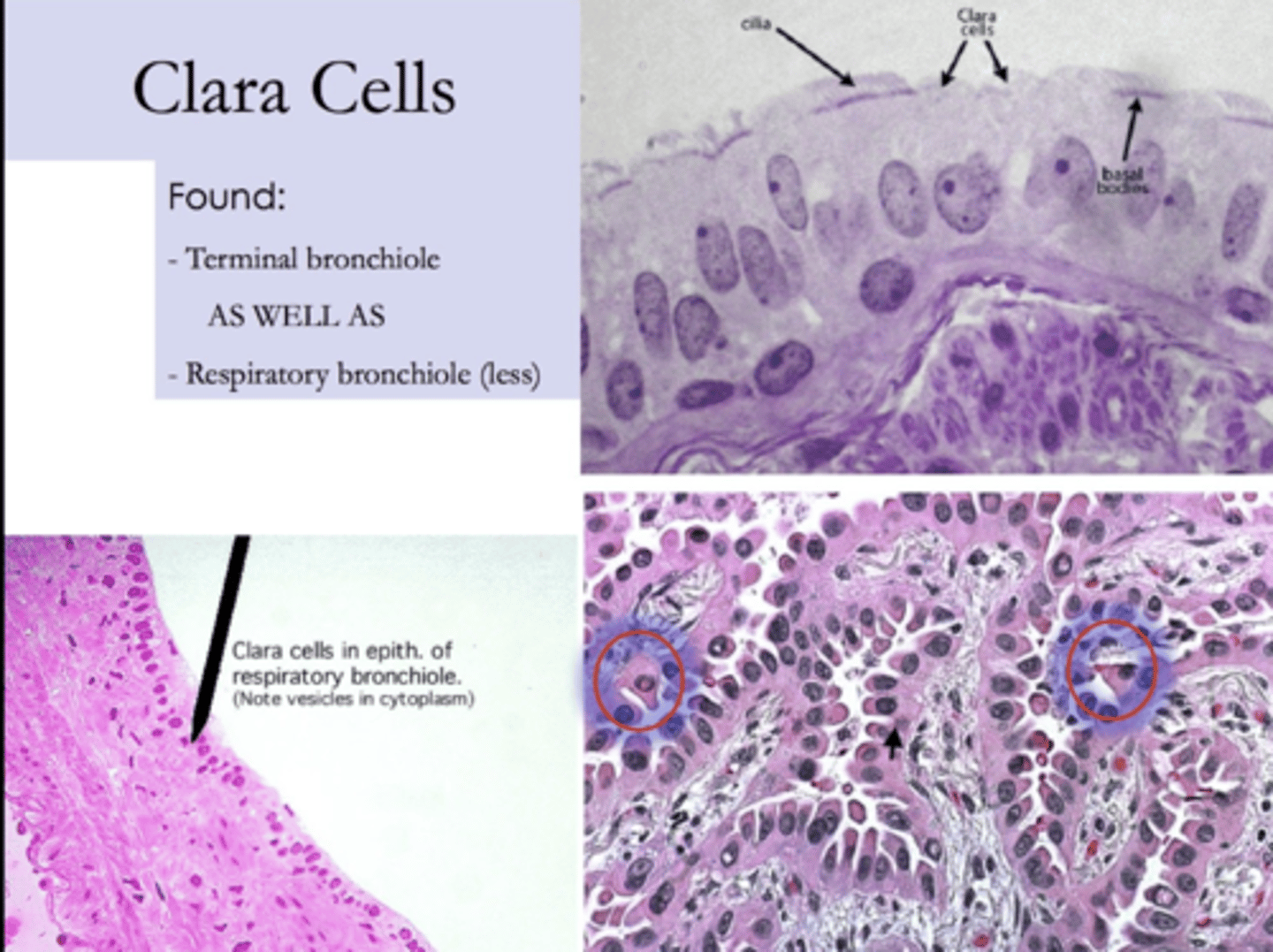
How are clara cells?
dome shaped. It’s difficult to mobilize surfactant, so in order to release it, the Clara cells release their whole apical region (apocrine secretions).
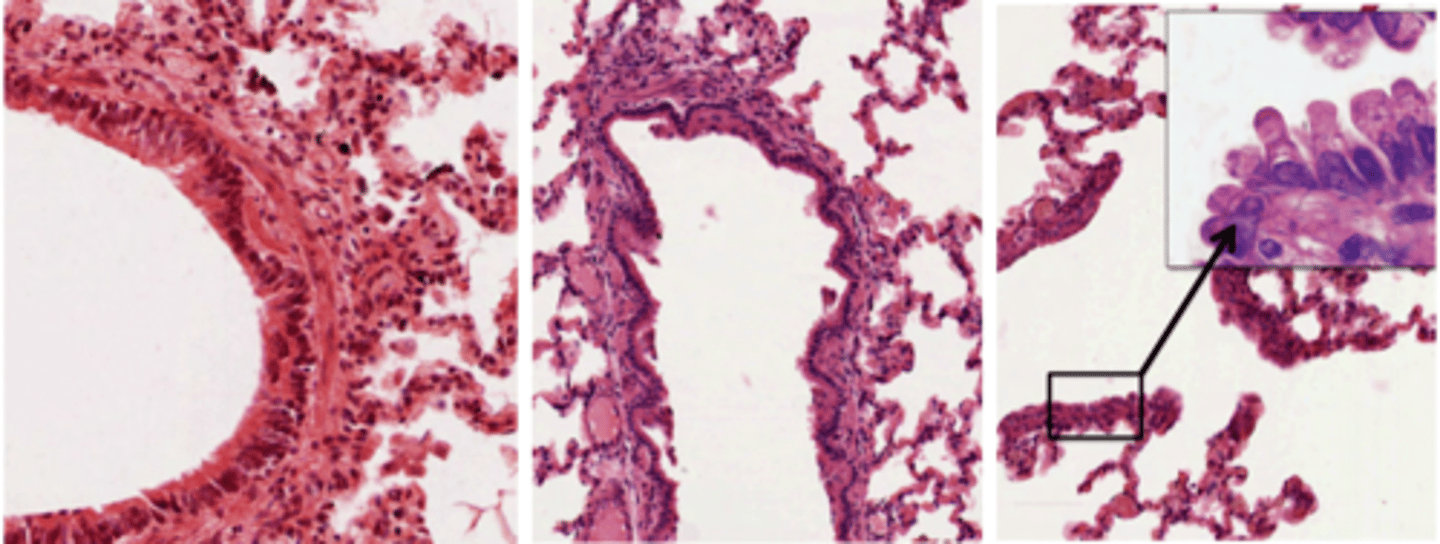
Bronchiolis image
Image I: bronchiole, with pseudostratified layer + smooth muscle;
Image II: terminal bronchiole, with some smooth muscle and cuboidal epithelium;
Image III: respiratory bronchiole, epithelium becomes thinner and lacks smooth muscle
How to distinghuis clara and goblet cells?
Goblet cells have a spear shape and are whiteish (mucus-secretions);
Clara cells are dome shaped and secrete surfactant,
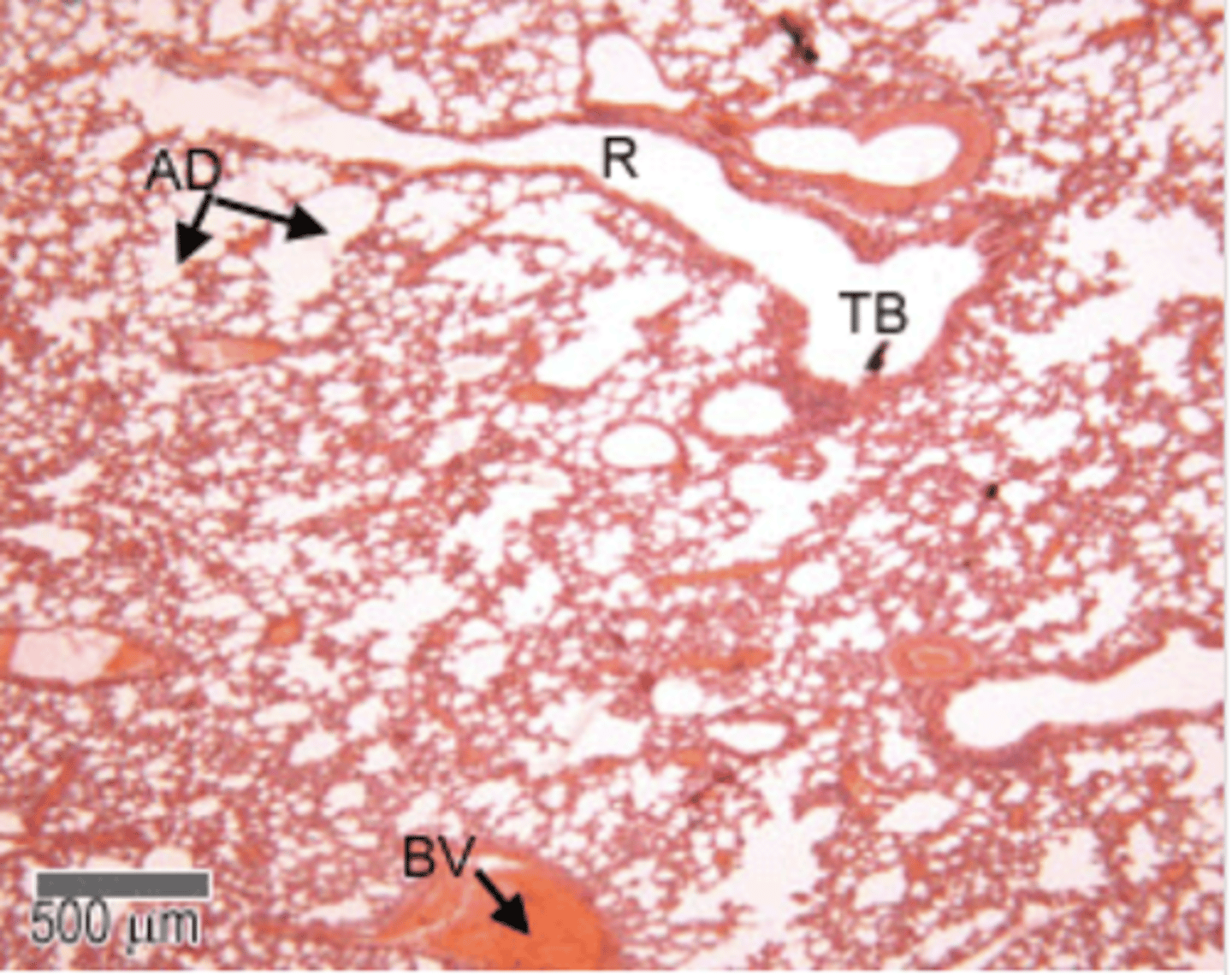
Terminal bronchioles
final branches of the bronchioles
These have a layer smooth muscle surrounding their lumens.
Stimulation of the vagus nerve (parasympathetic) causes the smooth muscle to contract, and reduce the diameter of the terminal bronchioles.
The respiratory bronchii have a few single alveoli off their walls.
Summary of Respiratory System