4.1.5 Trading blocs and the World Trade Organisation (WTO)
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
trading bloc
group of countries who come together and agree to reduce or eliminate any barriers to trade that exist between them
number of regional trade agreements in 2022
Globally,there were more than 320 regionaltrade agreements in eectin 2022
types of trading blocs
free trade areas
o customs unions
common markets o
monetary unions
free trade area
bloc in which countries agree to abolish trade restrictions between themselves but maintain their own restrictions with other countries
example of free trade
Canada–United States–Mexico Agreement(CUSMA)
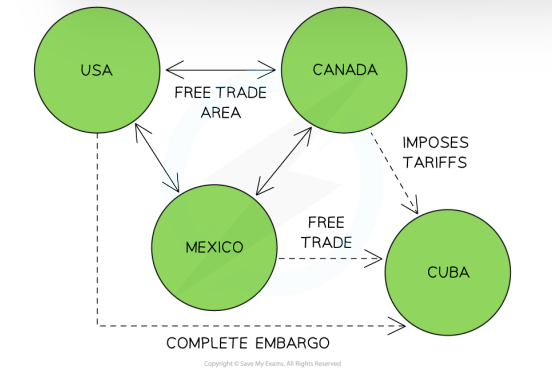
In the diagram above, Mexico, Canada and the USA have reduced/eliminated many trade restrictions between themselves The USA refuses to trade with Cuba and has placed a complete ban on all exports/imports to Cuba Canada trades with Cuba butimposes taris on all imports Mexico trades freely with Cuba
customs union
greement between countries in which all goods/services produced by members are traded tari free. Additionally, countries agree on common tari rates on imports from all external (third party) countries
example of customs union
In the diagram above, countries in the European Union have eliminated all tari barriers between themselves butimpose common tari barriers on third party countries such as the UK or China

common market
Similarly,to a customs union, goods/services are traded tari free in common markets. Additionally,the four factors of production ow freely between member countries The goal is to improve the allocation of resources between the common market members and lower costs of production
what is the eu
customs union and a common market
monetary union
akes integration a step further. Members enjoy all ofthe benets of a customs union and common market, butthen also establish a common central bank which issues a common currency and controls the monetary policy of member countries
example of monetary union
eurozone
essential conditions for a succesful monteray union
free movement of labour
similar trade cycles
mobility of finance
automatic fiscal transfers to countries performing poorely
movement of labour in eurozone
. The main languages ofthe Eurozone are English, French and German butlanguage is still a limiting factor
different trade cycles eurozone examle
afterthe 2008 Financial Crisis, Southern European countries were in a depression compared to the temporary recession in Northern European countries. This created extreme pressure on the survival ofthe Eurozone
examle of fiscal transfers eurozone
scaltransfers to Spain, Portugal and Greece post 2008 Financial Crisis were very weak. Political tensions emerged in which citizens of wealthier countries (Germany) did not wanttheirtax revenue used to bail out countries with perceived poor scal history (Greece)
benefits of regional trade agreements
trade creation improves efficiency and higher income
tariffs between member states eliminated
common tariffs to 3rd party countries simplify trading conditions
benefits of monetary union
A monetary union simplies trading costs and provides pricing transparency
Some member countries gain from improved monetary policy conditions e.g. European interest rates may well be lower than an individual country's rates would have been
There is less uncertainty surrounding exchange rates as members all use the same currency
costs of regional trade agreements
Trade diversion occurs as countries reallocate trade to partners in their agreement. This may worsen global eciency
Some domestic industries experience structural unemployment
Increased negative externalities of production, resource depletion and environmental damage
costs of monetary union
Transitioning to a monetary union can be expensive and firms may find it hard to adjust/change their menu prices
Member countries lose their ability to set interest rates and control the supply of money (monetary policy)
Loss of sovereignty
World trade organisation
The World Trade Organisation (WTO) was established in 1995 to promote free trade They believe free trade is the best way to raise living standards, create jobs and improve people's lives
trade liberalisation
process ofrolling back the barriers to free trade e.g. removing taris
WTO main roles in liberalising trade
. It brings countries together at conferences and encourages them to reduce or eliminate protectionist trade barriers between themselves e.g. The Doha Round conferences .
It acts as an adjudicating body in trade disputes. Member countries can file a complaint if they believe a trading partner has violated a trade agreement. The WTO will then run a hearing and make a judgement
evaluation of effectiveness of trade agreements
larger economies tend to selectively choose which rulings ofthe WTO to abide by. Smaller (usually developing) economies tend notto have thatluxury.
problem with WTO
WTO judgements are not legally binding. Members voluntarily submitto them (or not). A judgementin favour of a trade dispute does allow the aggrieved nation to put protectionist measures in place with the WTO's approval. The hope is thatthese measures willthen force the nation committing the violation to back down and resolve the trade issue.
conflicts between regional trade agreements and the WTO
While these are benecial to the members in the agreement(as they strengthen ties and create more trade between them),they also create conicts with the stated aim of the WTO - to liberalise trade Regional agreements often shift trade from a non-member who has comparative advantage,to a member who does not Regionaltrade members then often institute common trade barriers on nonmembers which is the opposite oftrade liberalisation (protectionism) Regionaltrade agreements can be benecialfor member countries but may result in global ineciency in the allocation ofresources The WTO advocates for free trade between all member countries
bilateral agreements
between 2 countries of trading blocs
multilateral agreements
between more than 2 countries of trading blocs