AP Chemistry Unit 3
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
London Dispersion Forces
Weakest
Found in all molecules
More electrons = more polarizable = stronger LDF
Dipole-Dipole Forces
Moderate Strength
Found in Polar Molecules Only
Hydrogen Bonds
Strongest
O-H, N-H, F-H
Ionic Solids
High Melting Point
Brittle
Conduct Electricity when dissolved in water
Covalent Network Solids
Highest melting point
Extremely high hardness
Strongest covalent forces
Molecular Solids
Low melting points
Weak IMFs
Metallic Solids
Sea of Electrons
Excellent conductor
Ideal Gas Law
PV = nRT
Pressure Gas Equations
Pgas = Xgas * Ptotal
Ptotal = Pgas1 + Pgas2 + …
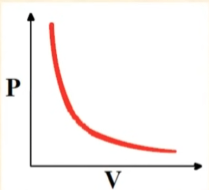
Pressure vs Volume
Exponentially Decreases
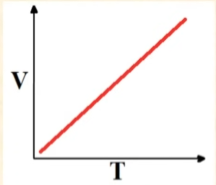
Volume vs Temperature
Linearly Increases
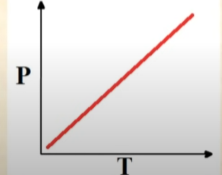
Pressure vs Temperature
Linearly Increases
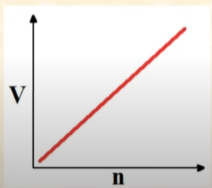
Volume vs Number of Moles
Linearly Increases
Boltzmann Distribution Curve
At high temperatures, more molecules have greater velocity and, thus, greater kinetic energy
Ideal conditions for real gases
High Temperature
Low Pressure
Very small molecule sometimes
Heterogeneous Mixtures
Different sections are visible to the naked eye
Homogeneous Mixture
Called solutions
Uniform composition throughout
Molarity
M = Moles/Liters
Like Dissolves Like
Polar Molecules dissolve in Polar Solvents
nonPolar Molecules dissolve in nonPolar Solvents
UV or visible light
Causes electrons to transition to different energy levels
Infrared Radiation
Causes molecules to vibrate
Microwave Radiation
Causes molecules to rotate
Wavelength & Frequency
c = λν
c = speed of light (2.998 × 10^8 m/s)
λ = wavelength in meters
v = Frequency in waves cycles per second
Energy of a Photon
E = hv
E= Energy of a photon
h = Plancks Constant (6.626 × 10^34 Js)
v = Frequency in waves cycles per second
Beer-Lambert Law
A = εbc
A = Abosrbance
ε = molar absorptivity
b = Path length of cuvette (Usually 1cm)
c = Concentration of the solution
High Outliers
Caused by contamination from solution of higher concentration
Low Outlier
Caused by Contamination from water or a solution of lower concentration