Atomic Structure and Symbolism
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
10^-10 m
The diameter of an atom is on the order of _______
10^-15 m
The diameter of the nucleus is roughly _______
100,000
The diameter of the nucleus is _______ times smaller
2×10^-23 g
Carbon atom weights less than _________
u
Symbol used for representing the unified atomic mass unit
e
Symbol used for representing the fundamental unit of charge
1.6605×10^-24 g
1 u = ? g
dalton (Da)
An alternative mass unit that is equivalent to the u.
1/12, carbon-12 isotope
The u is defined as exactly ____ of the mass of a single atom of the _________________
1.9926×10^-23 g
Mass of a carbon-12 isotope
1.602×10^-19 C
Value of e
0.00055
Mass of an electron in amu
0.00091×10^-24
Mass of an electron in grams
1.00727
Mass of a proton in amu
1.00866
Mass of a neutron in amu
1.67262×10*-24
Mass of a proton in grams
1.67493×10^-24
Mass of a neutron in grams
Mass defect
The “missing” mass from the sum of the atom’s subatomic particle’s mass which is not taken into the effect
Z
Symbol that represents Atomic number
A
Symbol that represents mass number
Ion
Electrically charged ion
Anion
An atom gains electrons, making it negatively charged
Cation
An atom loses electrons, making it positively charged atom
Iodine
An essential element needed to produce thyroid hormone
Goiter
An enlargement of the thyroid gland
53
Atomic number of iodine
International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry
Full form of IUPAC
Seaborgium
Name of the element representatives as (Sg)
Unnilhexium (Unh)
The former name for (Sg)
Glenn Seaborg
The Nobel prize winner after whom the Sg element was named
106
No. of protons in Sg
Lise Meitner
Person who discovered Nuclear Fission, and after whom the element (Mt) is named
Meitnerium
Full name of the element (Mt)
109
No. of protons in Meitnerium
Protium
Name given to hydrogen with no neutrons and has 99.989% of natural abundance
Deuterium
Name given to hydrogen with 1 neutron and has 0.0115% of natural abundance
Tritium
Name given to hydrogen with 2 neutrons
Paleoclimatology
The study of earth’s past climates
Oxygen-18 and Oxygen-16
The two isotopes that scientists use the ratio of, in an ice core to determine the temperature of precipitation over time.
Oxygen-18
The oxygen isotope which was critical to the discovery of metabolic pathways and mechanisms of enzymes.
Mildred Cohn
Pioneered the usage of isotopes to act as tracers so that researchers could follow their path through reactions and gain a better understanding of what is happening
Phosphate group
A tiny chemical made up of phosphorus and oxygen
Phosphorylation
The process when a phosphate group is added to a molecule like a protein or sugar
Often turns on or off in the body, which helps us to understand how cells work, grow, or respond to signals
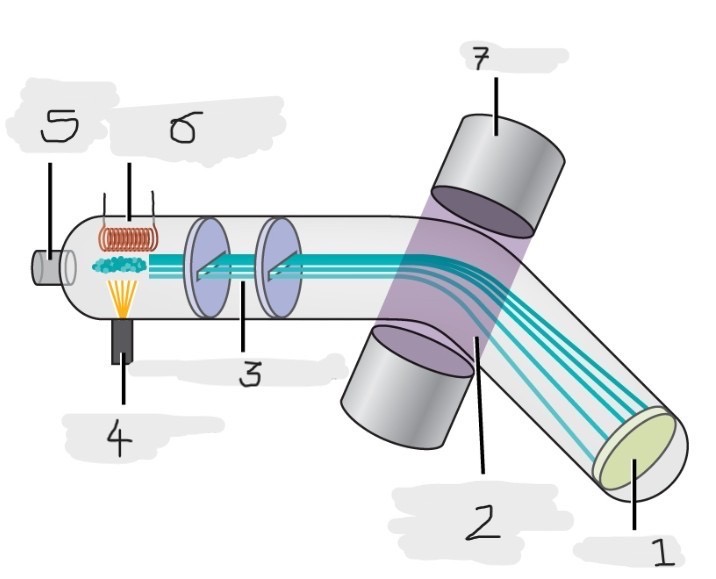
Mass spectrometer
Instrument used to experimentally determine the occurrence and natural abundances of isotopes
vaporized, high-energy electron beam
In a typical mass spectrometer, the sample is _________ and exposed to _________________________
electrically charged, losing
In a mass spectrometer, we have to cause the sample atoms to become ____________________, typically by ______ one or more electrons
electric, magnetic field, deflects, path, mass, charge
The cations in the mass spectrometer, pass through an ________ or ______________ that ________ each cation’s ____ to an extent that depends on both its ____ and ______
Mass spectrum
The method where the plotting for the graph of the relative numbers of ions versus that their mass-to-charge ratios is made
Detector
(1)
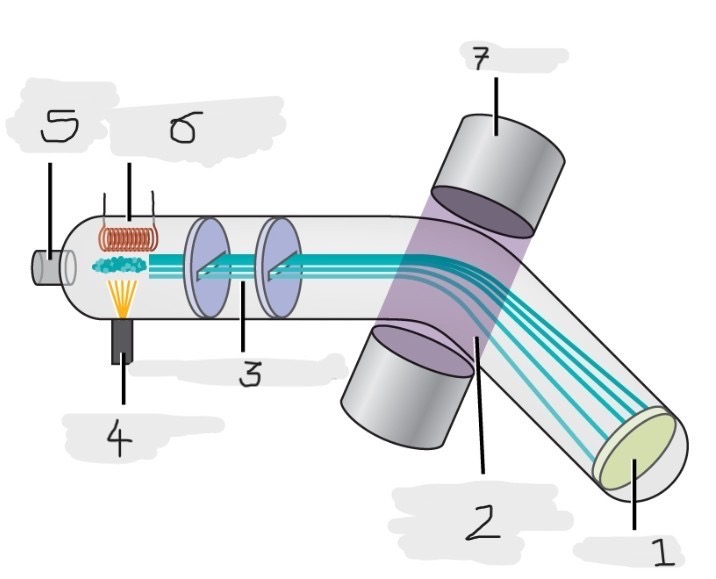
Magnetic field that deflects the lightest ions the most
(2)
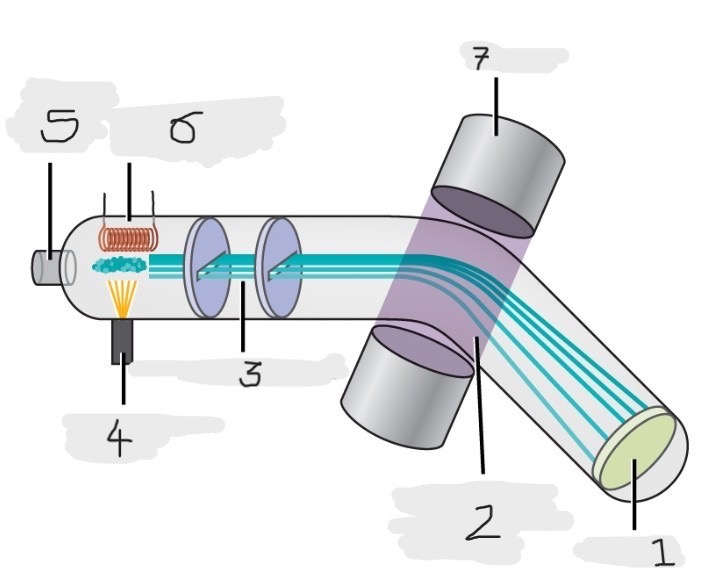
Accelerated ions
(3)
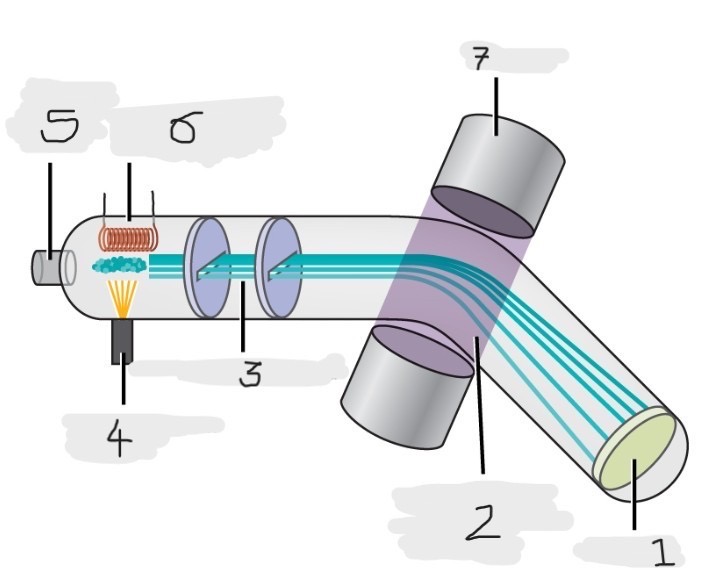
Electron beam source
(4)
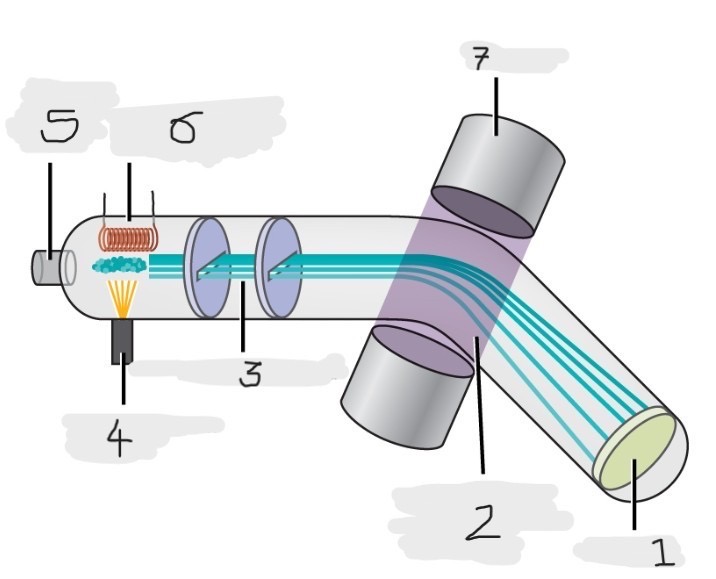
Place to enter the sample
(5)
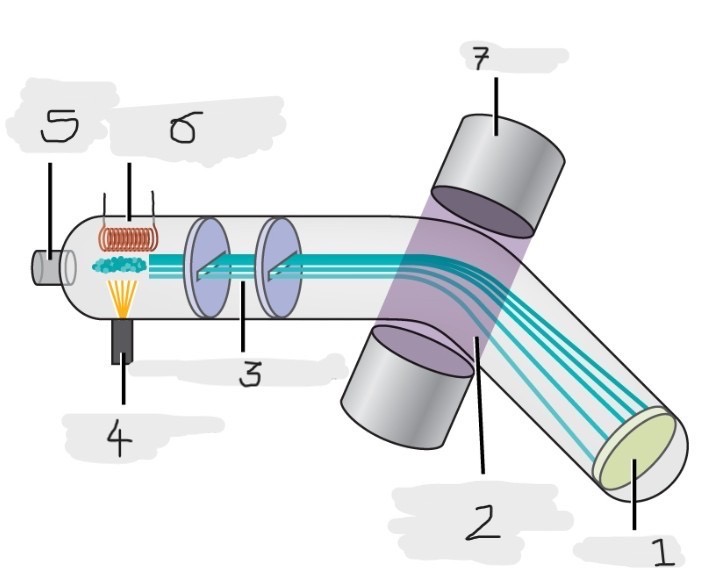
Heater to vaporize the samples
(6)
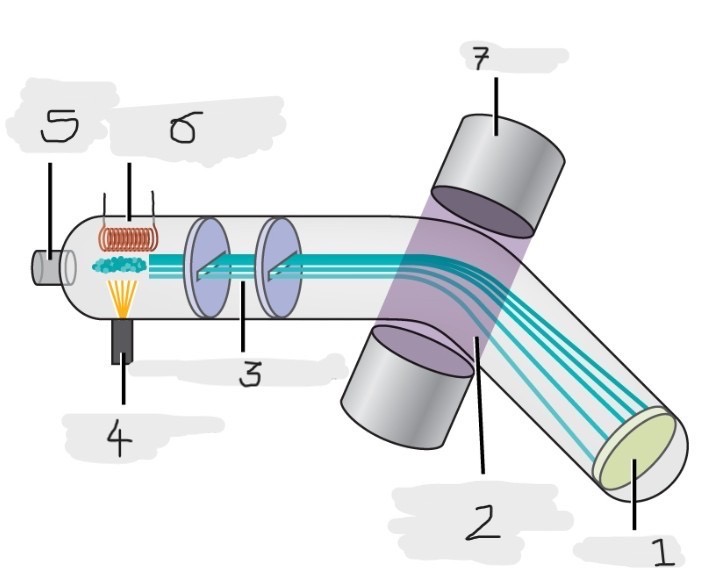
Magnet
(7)