Physio Lect 12 - Excitation Contraction Coupling
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What percent of body mass does skeletal muscle make up?
40%
What muscle is the main component of the heart?
cardiac
Where do we find most smooth muscle?
GI tract, bladder, airways, blood vessels (hollow structures)
T/F: Cardiac muscle is a striated voluntary muscle
F - striated but involuntary
T/F: Skeletal Muscle is a striated voluntary muscle.
T
Which muscles are striated?
Cardiac and skeletal
Rank the muscles from most to least on sarcoplasmic reticulum content:
Skeletal, cardiac, smooth
All muscles require ___ for contraction
calcium
An increase in calcium results in ____. While a decrease in calcium results in ______.
contraction
relaxation
How does calcium move through the cell?
comes in through the sarcolemma, the sarcoplasmic reticulum stores and releases calcium, the mitochondria has minimal role
T/F: we need to use ATP in our muscles or contractions/energy
T
What ATPases do we use that are specific for muscles?
Myosin ATPase and Calcium ATPase
Explain the steps of skeletal muscle contraction:
signal comes from brain to motor neuron
action potential moves down T-tubule
Calcium released from ryanodine receptors on SR
Calcium binds troponin C, moves tropomyosin and exposes actin binding sites for myosin to bind
The sliding filament with myosin binds to actin through ATP hydrolyzation
Explain the steps of skeletal muscle relaxation:
SR takes up Ca through the SR Ca ATPase
Calcium in the SR is bound to calsequestrin - stores Ca
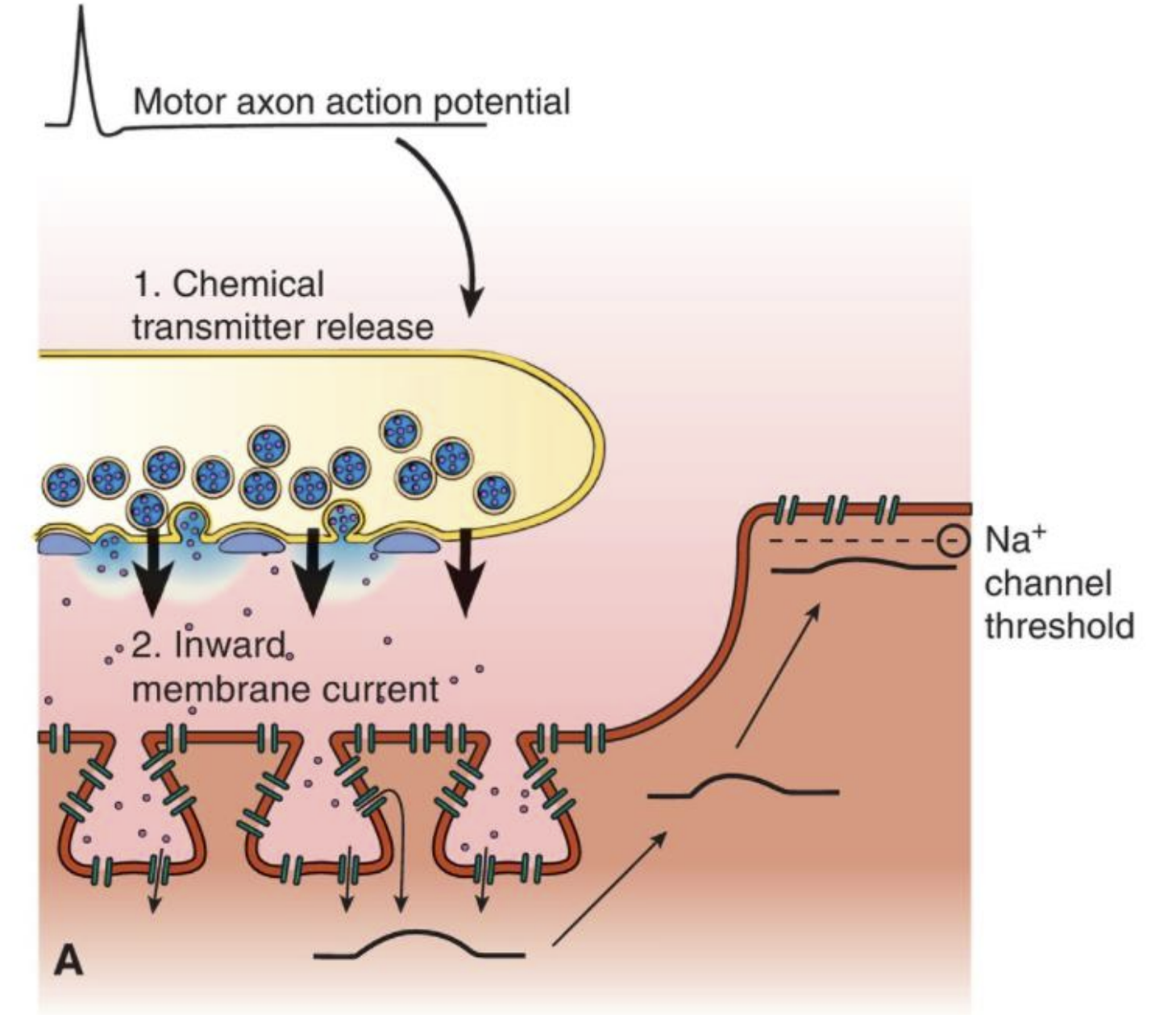
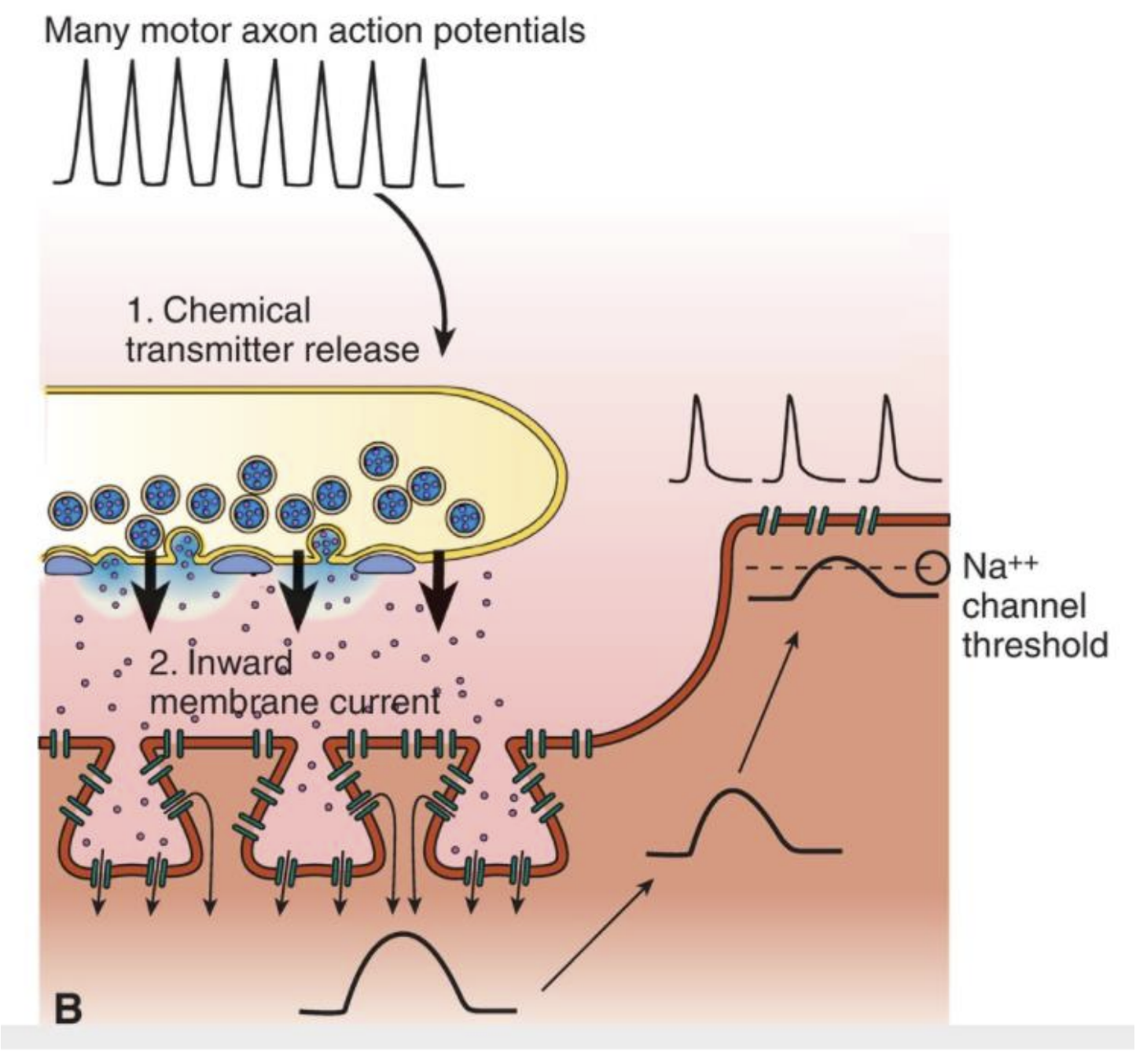
How do we increase contraction in skeletal muscle?
recruit more motor neurons to fire or increase the number of action potentials in the motor neuron in the limited amount of time.
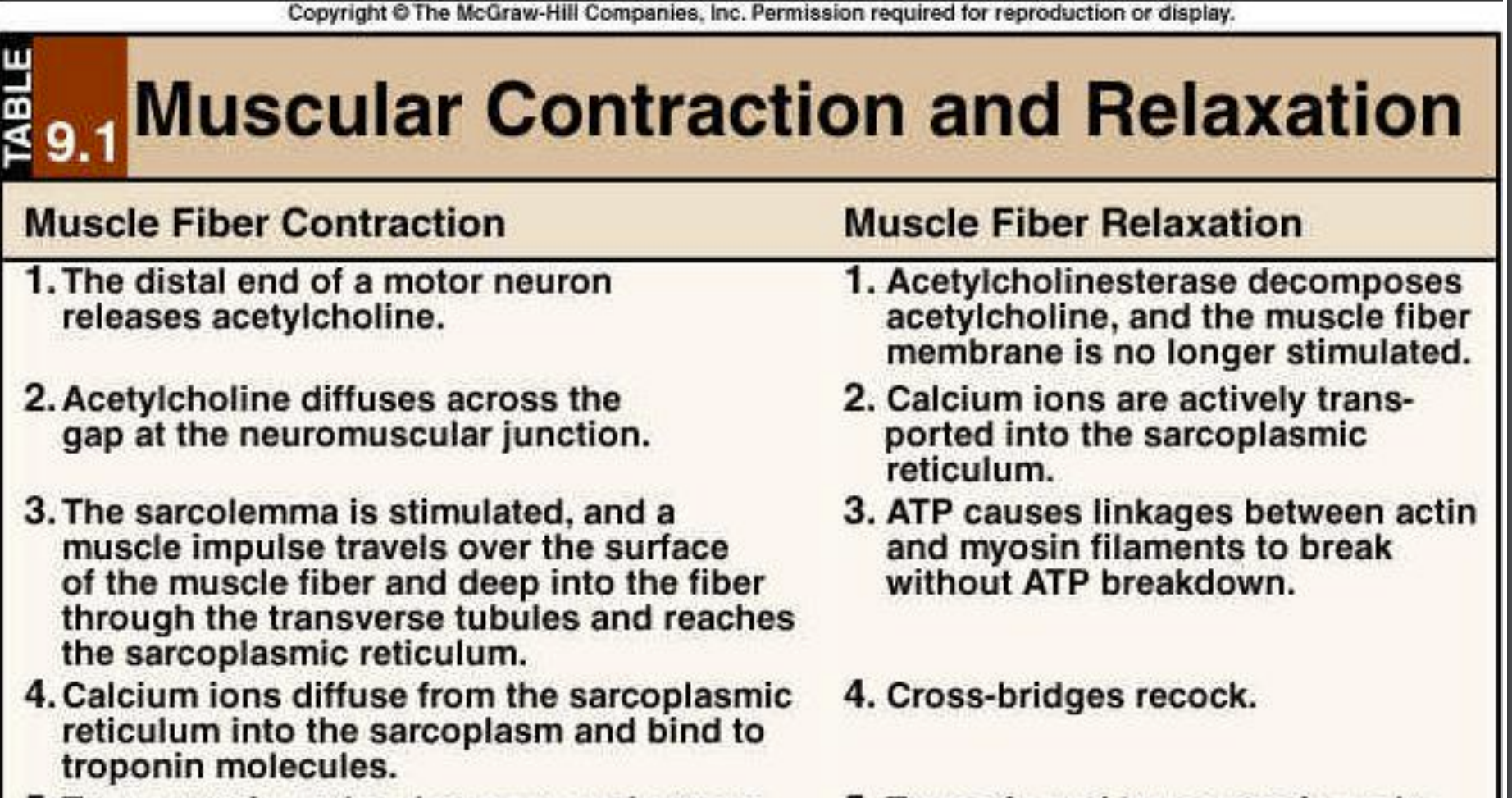
Understand steps 1-4 for contraction and 1-3 for relaxation (rest covered in later lecture)
yay
Cardiac Myocytes are _____ cells, they are ____ and share the same basic structure as a _____ muscle cell.
specialized and involuntary
striated
skeletal
Contraction for myocytes is ______, based upon the propagation of action potential from the _____ node through intercalated discs
involuntary
sinoatrial
What sets Cardiac Myocytes aside from skeletal muscle?
action potential duration
ions
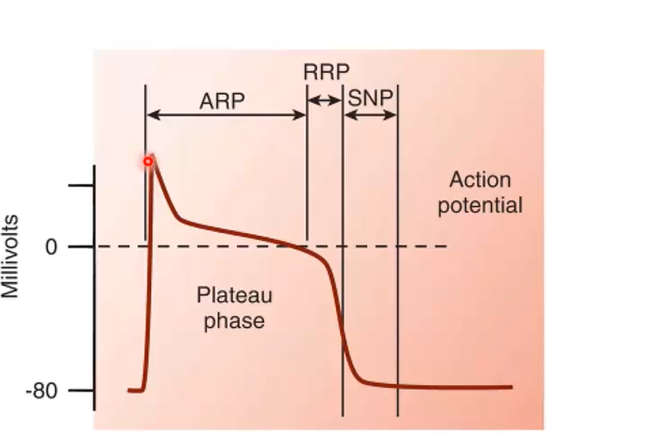
Looking at this diagram of the action potential, where is phase zero, and why do we see this spike?
This is due to sodium
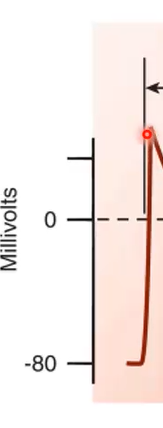
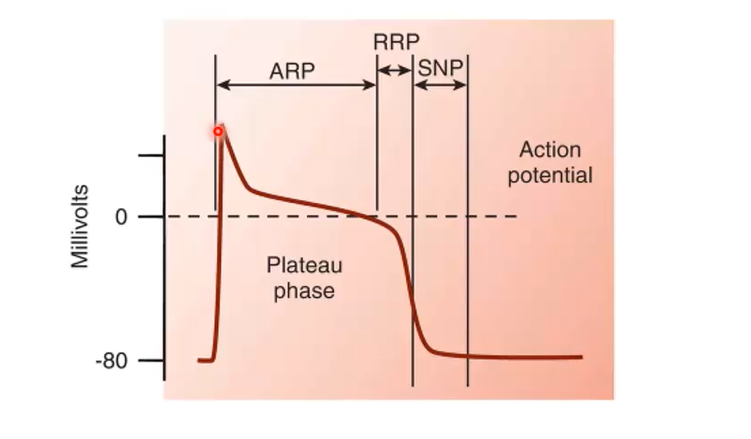
Looking at this diagram of the action potential, where is phase one, and why does it look like that?
Slight repolarization due to potassium

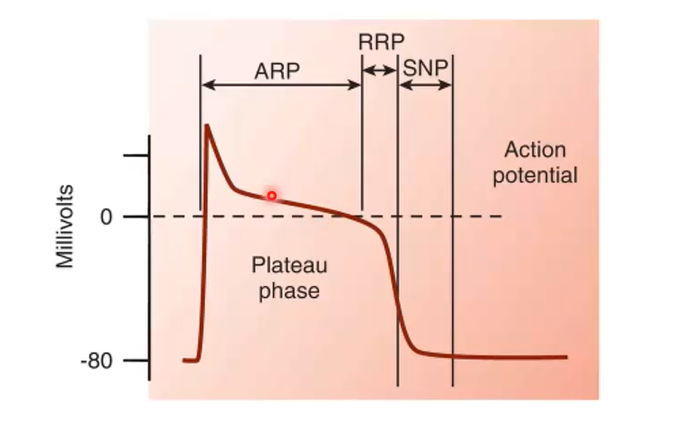
Looking at this diagram of the action potential, where is phase two, and why does it look like that?
When calcium ions are entering into the cell, right when phase two is occuring is when we get force generation and relaxation

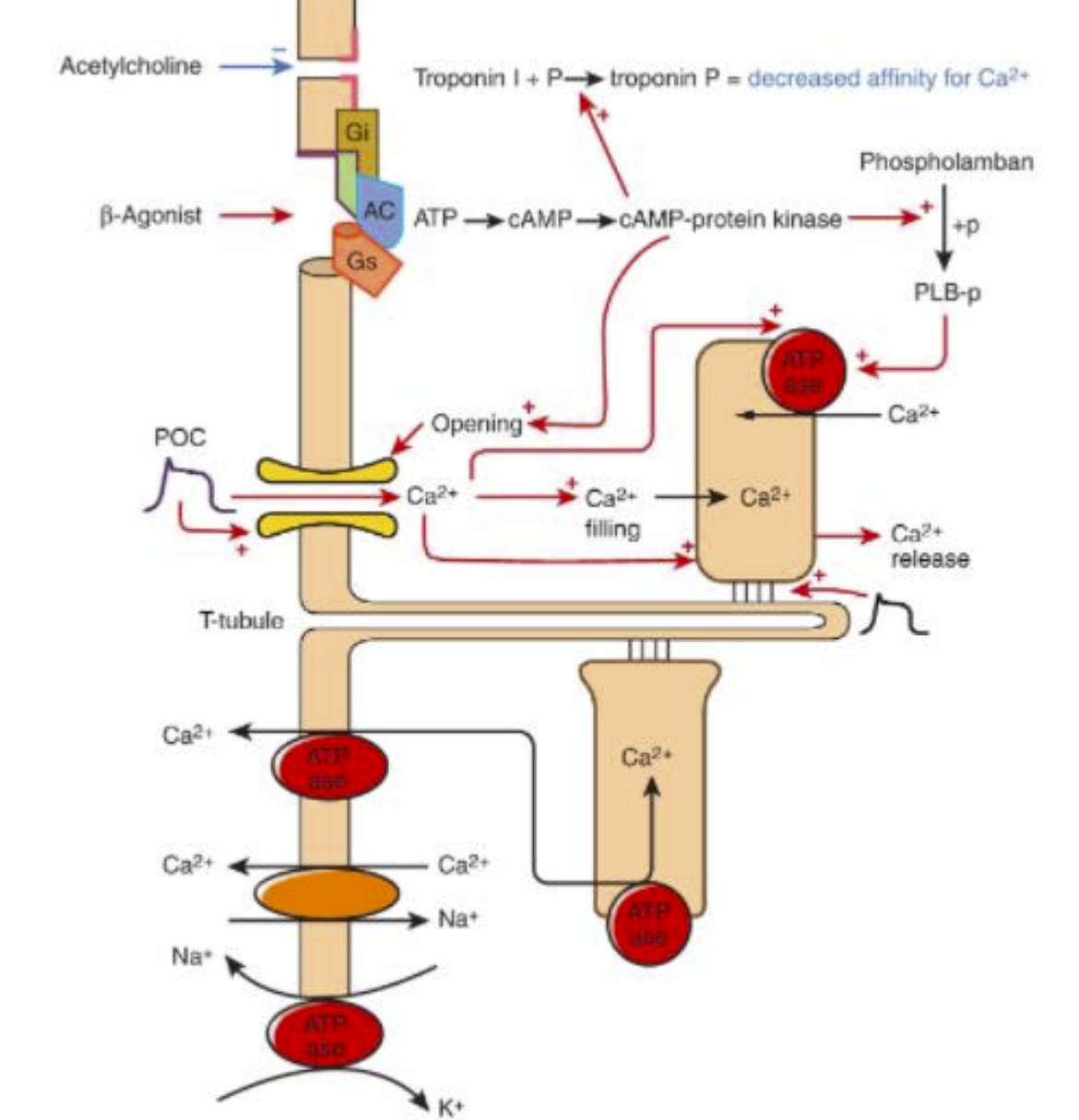
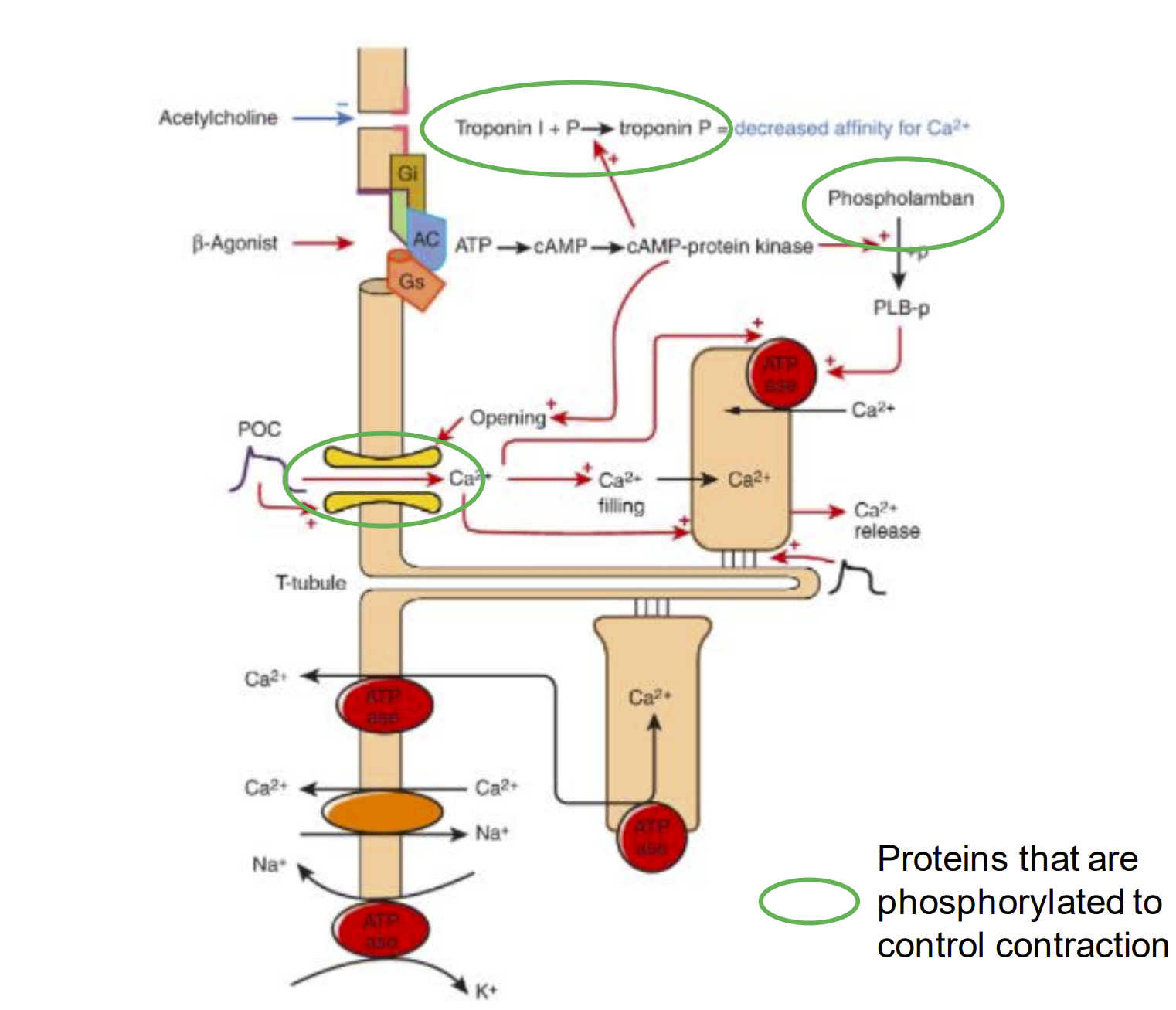
Understand the way that this diagram functions - it is very busy but you can do it.
great job
How can we increase cardiac muscle contraction?
we increase the action/myosin overlap (length tension relationship)
phosphorylation changes of proteins increase calcium sensitivity/activity of an enzyme (EG. phospholamban, calcium channel, troponin I)