Action and membrane potential + Synaptic transmission
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Resting membrane potential of cell
-70 mV
How does a cell maintain its ionic charge
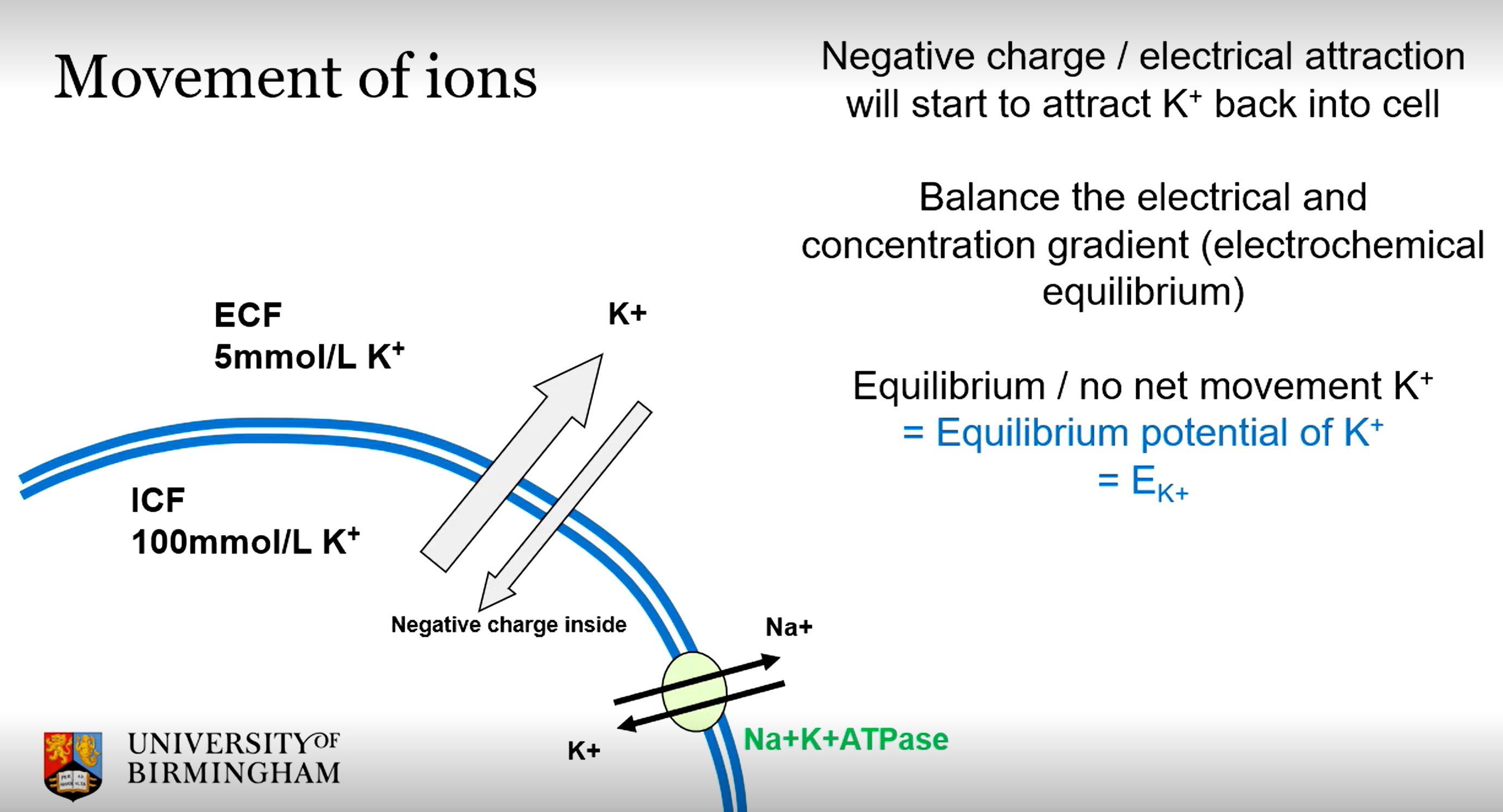
Using active transport pumps (e.g. Na+ K+ ATPase) to counteract the concentration potential trying to pump K+ out. Electrostatic attraction will also draw some K+ into the cell, as it is naturally negatively charged. The biggest factor, however is K+ efflux through K+ leak channels which increase permeability of K+ to the membrane
Nernst equation at 37C and its use
61mV/valence * log ( [ion outside]/[ion inside] )
Used to calculate equilibrium potential of one membrane permeable ion
![<p>61mV/valence * log ( [ion outside]/[ion inside] )</p><p>Used to calculate equilibrium potential of <strong>one membrane permeable ion</strong></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a7a09fa8-251c-4aca-8892-489e6c5d5311.png)
ICF and ECF concentrations and eion values for K+
ICF - 100 mM
ECF - 5mM
eIon - -80mV
ICF and ECF concentrations and eion values for Na+
ICF - 15 mM
ECF - 150mM
eIon - +62mV
ICF and ECF concentrations and eion values for Cl-
ICF - 13 mM
ECF - 150 mM
eIon - -65mV
ICF and ECF concentrations and eion values for Ca2+
ICF - 0.0002
ECF - 2mM
eIon - +123mV
Goldmann equation at 37C and its use
Used to calculate overall membrane resting potential, accounting for all ions and their permeability

What effect would hypokalaemia (low [K+] in ECF) have on resting membrane potential?
Would make it more negative, as it would shift the concentration gradient out the cell, causing a greater efflux of positively charged potassium out of the cell, making it more negative.
What voltage-gated channels open when a stimulus is applied
VGNaC open relative to stimulus applied (stronger stimulus, more Na+, which depolarises RMP)
What voltage-gated channels are activated to open when a the action threshold is reached?
VGNaC and VGKC, but VGKC open slower
What causes the action potential to spike so much once an action threshold is reached
VGNaC are fully open, causing a massive Na+ influx into cell, causing the potential to become very Positive (+30 mV)
What causes the the spike of action potential to go down
VGNaC deactivate and close, and the VGKC channels finish opening, causing a massive K efflux, dropping the potential and repolarising the cellW
Why does the membrane potential hyperpolarise after an action potential
VGKC stay open a little after the membrane is repolarised, causing more K+ to efflux and drop the membrane potential
Difference between absolute and relative refractory period
Absolute - No matter the strength of the stimulus, it will not trigger another action potential
Relative - A strong enough stimulus will cause another action potential
Why are absolute refractory period absolute
VGNaCs already opening (during depolarisation) or inactive (during repolarisation), and so cannot open again to trigger another aciton potential
Why are refractory periods important
Sets the maximum frequency action potentials are generated
Limits the rate that signals can be transmitted
Ensures one-way travel of action potential
3 factors that affect conduction velocity
Myelination - Insulated parts means it doesn’t need ion channels along those parts, and so less leakage occurs. Only need ion channels at Nodes of Ranvier
Axon Fibre Radius - action potential scales with diameter
Functional Ion Channel Number - less channels = less leakage = faster conduction (almost like maintain water pressure in a pipe)
Main example of a synchronised synapse use. Also how it achieves synchronisation
Cardiac muscle needs to be synchronised.
Achieves synchronisation by gap junctions
Define a reflex
A stereotyped, involuntary action caused by a specific stimulus
3 general functions of reflexes
Protective
(limb withdrawal, coughing etc)
Postural
(ensuring you don’t fall whilst walking, balance etc.)
Homeostasis
Maintaining blood pressure etc.
Reflex arc 5 (or 6) components
Func
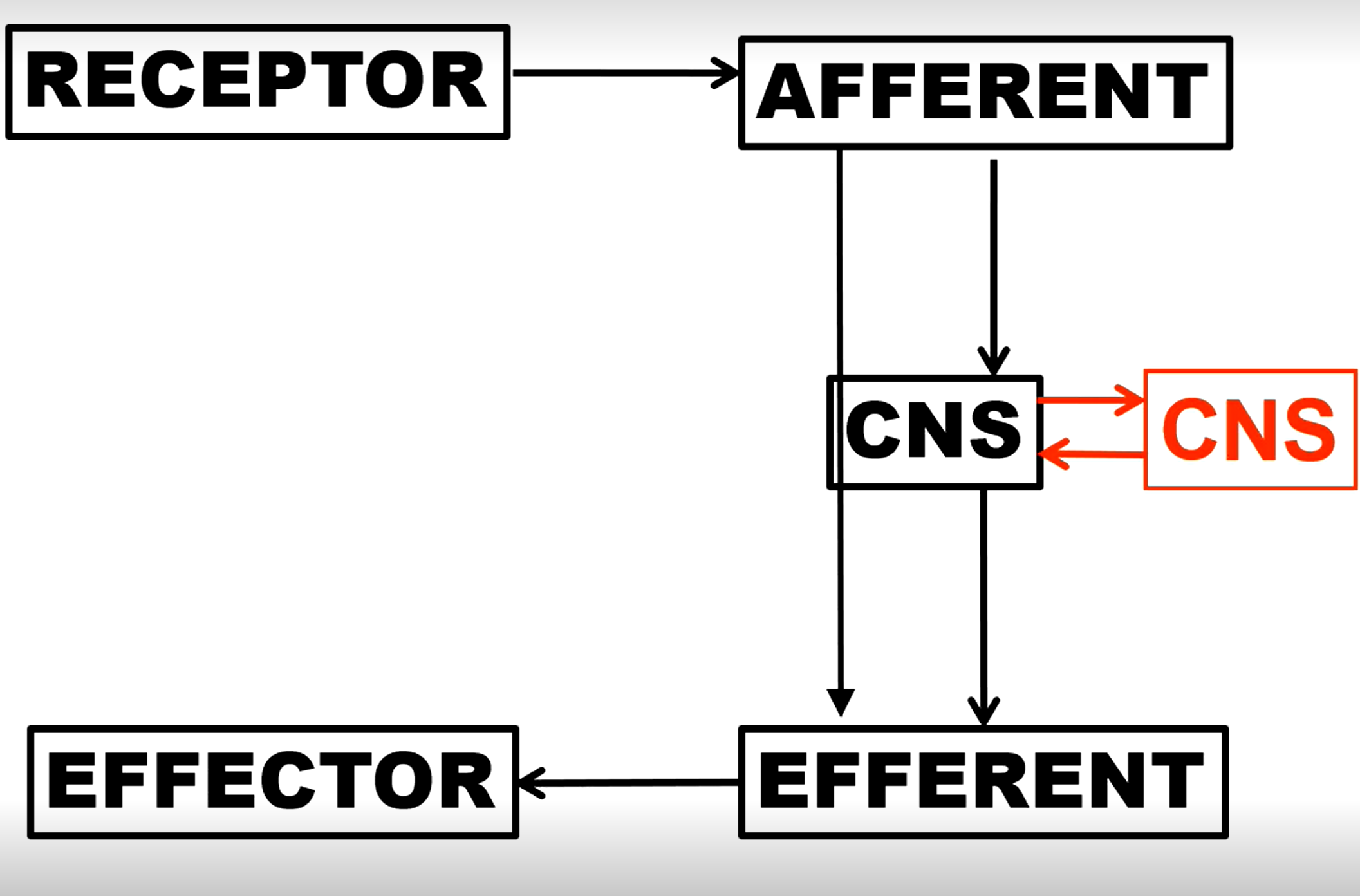
Function of muscle spindle
Causes muscle reflex to tense when under tension and relaxed to prevent damage
What makes the muscle spindle reflex arc different to a normal reflex arc
No interneurone, goes directly from sensor in spindle, through spinal cord to effector in muscle (only one synapse between effector and sensor (monosynaptic))
Why can’t you tense two antagonistic muscle simultaneously (e.g. quad and hamstring)
When tensing one, (voluntarily or no) interneurones sent an inhibitory NT to the other, preventing contraction
Purpose of Golgi tendon organs
To release inhibitory NT from the interneurone to the muscle when too much strain is placed on the tendon
Also control fine muscle tension (e.g. in fingers)