Bioeffects, New Developments, and QA Safety
1/135
Earn XP
Description and Tags
UT 200 Quiz 9
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
136 Terms
bioeffects
change to biological tissues as ultrasound beam travels through tissue
types of bioeffects
thermal
non-thermal
dosimetry
science of identifying and measuring characteristics of an ultrasound beam relevant to its potential for producing biological effects
dosimetric quantities that are measured
acoustic pressure
acoustic power
acoustic intensity
radiation force
acoustic pressure
acoustic variable
formula: force/unit area
units: Newton/m2 (Pascal) or Newton/cm2
peak pressures in an acoustic field are measured
compressions
areas of peak positive pressures
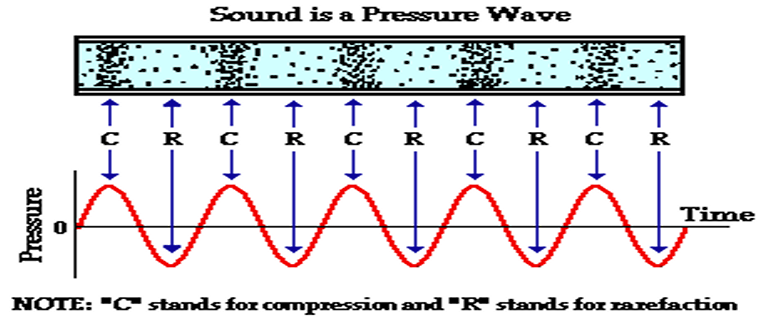
rarefactions
areas of peak negative pressures
acoustic power
AKA output or transmit power
rate at which work is performed
formula: acoustic energy/time
units: Joule/sec → Watt or mWatt
acoustic intensity
formula: acoustic power/beam area
units: Watt/cm2 or mWatt/cm2
not uniform over space or time
ex: think of a light bulb in a small room vs. a big room
the conversion of sound energy to heat is measured using the following instruments
calorimeter
thermocouple
liquid crystal
calorimeter
measures the total power in a sound beam through absorption (power of the entire beam)
thermocouple
measures the sound beam’s power at a particular location in the beam
liquid crystal
measures the change in temperature because the crystals change color to indicate different temperatures
hydrophone
measures acoustic pressures at a specific location
can also measure the period, PRP, PRF, and PD
two types are used to measure acoustic pressure or intensity (output power)
hydrophone probes
membrane hydrophones
grayscale imaging has the ___ output power, while PW doppler has the ___ output power
lowest; highest
hydrophone probes
have a tiny piezoelectric element
looks like a needle
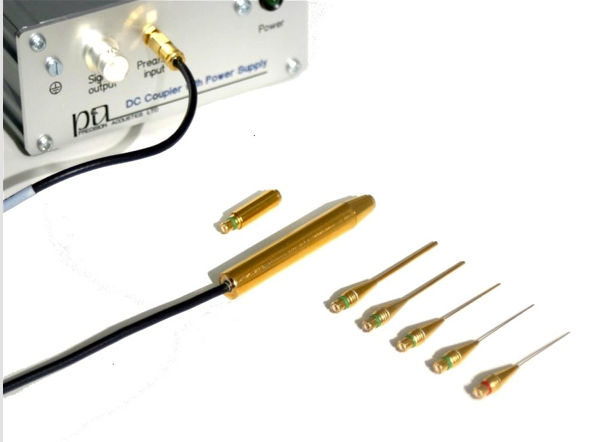

membrane hydrophones
membrane is made of polyvinylidene fluoride
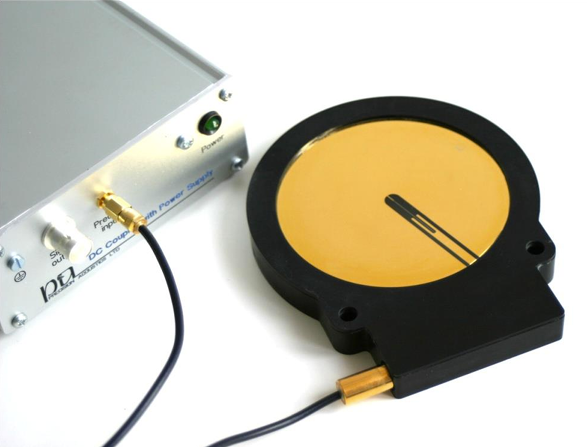

radiation force balance
the force that is exerted when an ultrasound wave hits a target that absorbs, scatters, or reflects energy
the target is a balance or a float, the measured force is related to the sound beam power
measured radiation force relates to the intensity or power of the sound beam
shear stresses and streaming of fluids can distort or disturb biological structures
acousto-optics
based on the interaction of sound and light
shows the hourglass beam shape
uses a shadowing system called Schlieren imaging to view the shape of an ultrasound beam in a medium
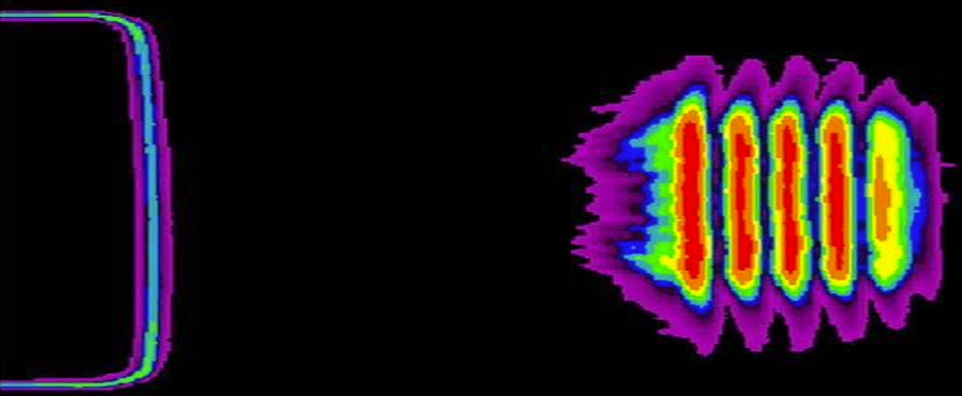
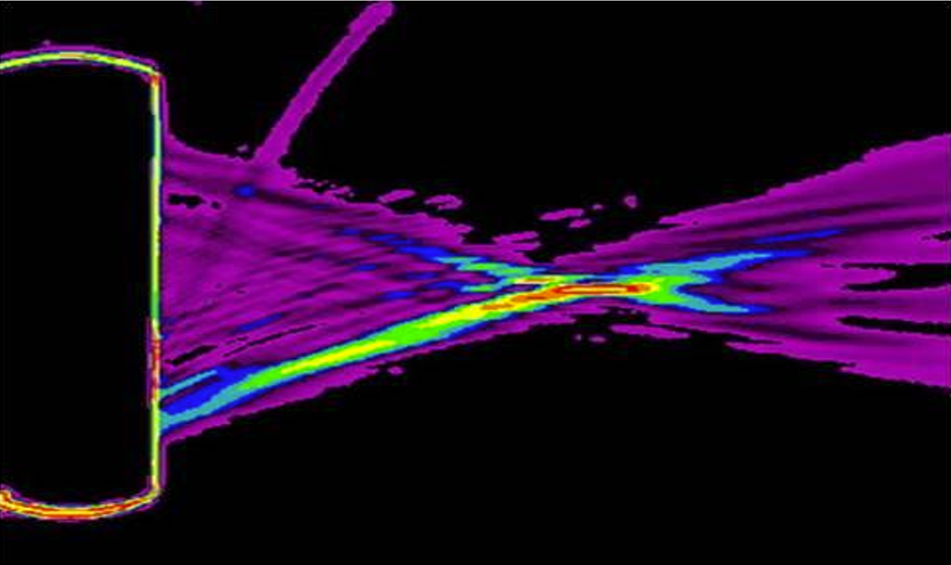
what does this picture show?
Schlieren image of a focused beam from a TDR with broken crystals
methods for measuring intensity
spatial peak - temporal peak (SPTP)
spatial average - temporal peak (SATP)
spatial peak - temporal average (SPTA)
spatial average - temporal average (SATA)
spatial average - pulse average (SAPA)
spatial peak - pulse average (SPPA)
___ is the most relevant intensity with respect to tissue heating because we are concerned about the highest energy over the on/ring time
SPTA
because peak measurements are larger than average measurements, ___ intensity has the highest value and ___ has the lowest value
SPTP; SATA
spatial distribution
refers to how the beam energy is distributed over physical space in the body
determined by the beam parameters
temporal distribution
refers to how the energy is distributed over time
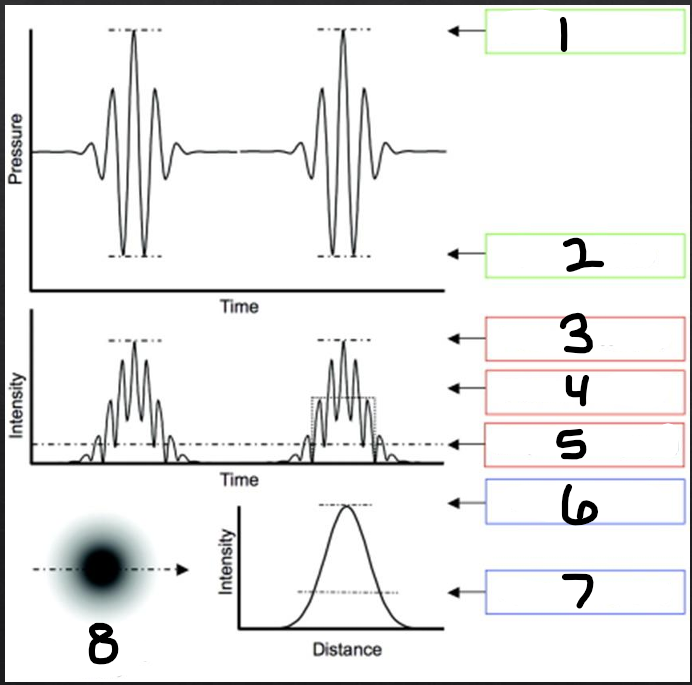
1
peak compression
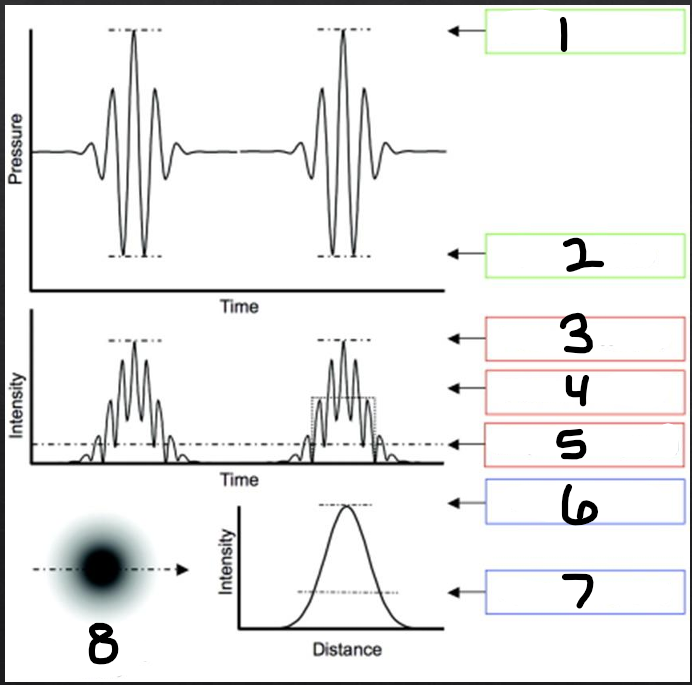
2
peak rarefaction
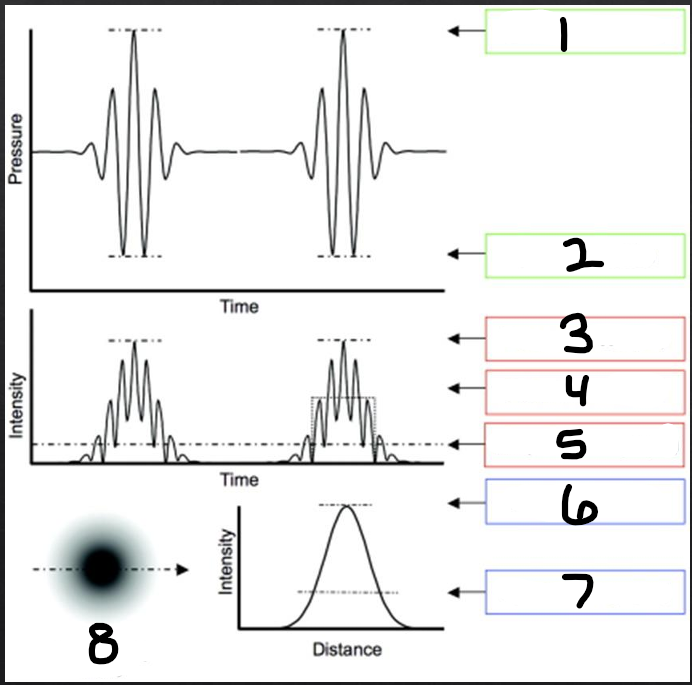
3
temporal peak (TP)
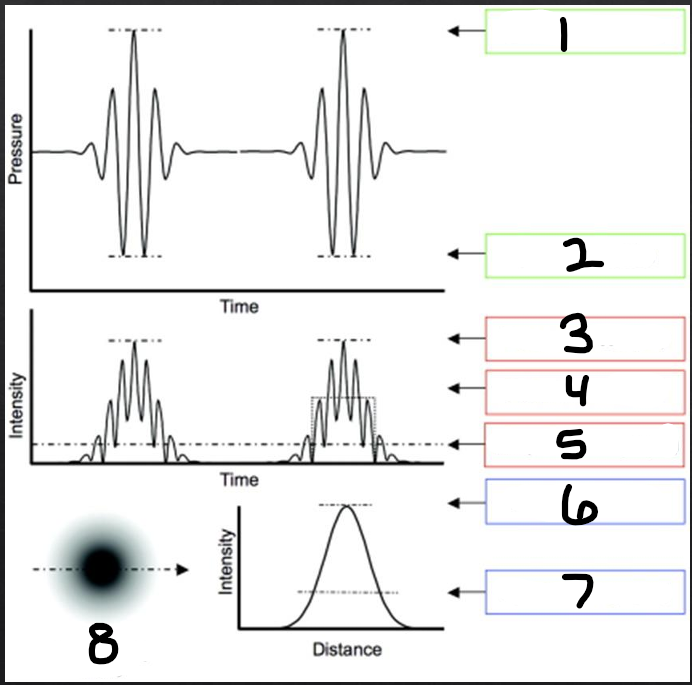
4
pulse average (PA)
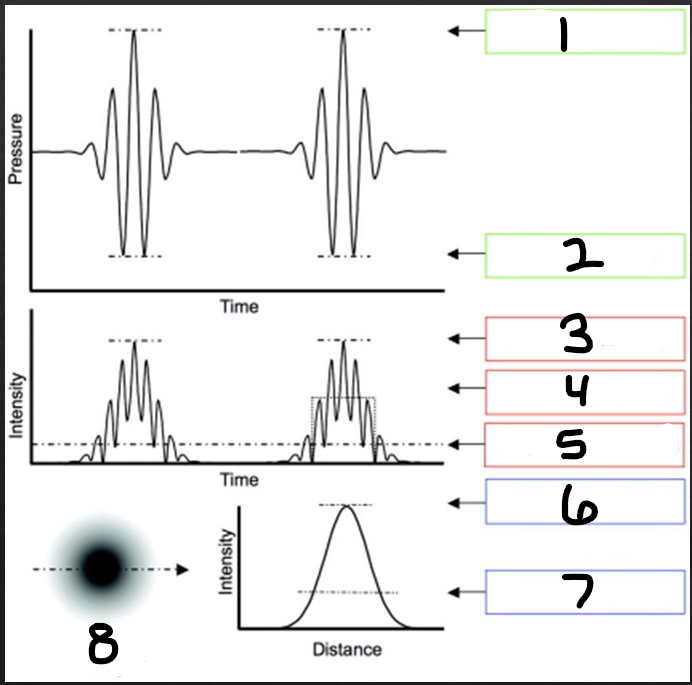
5
temporal average (TA)
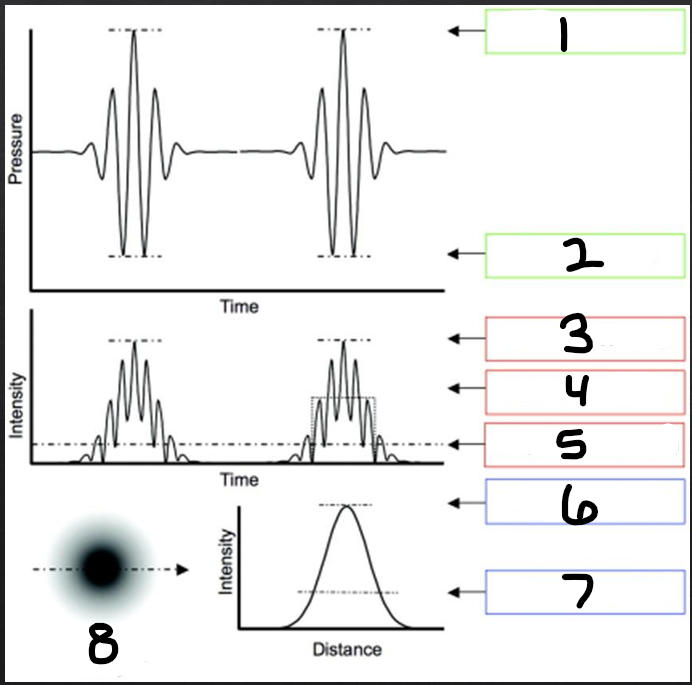
6
spatial peak (SP)
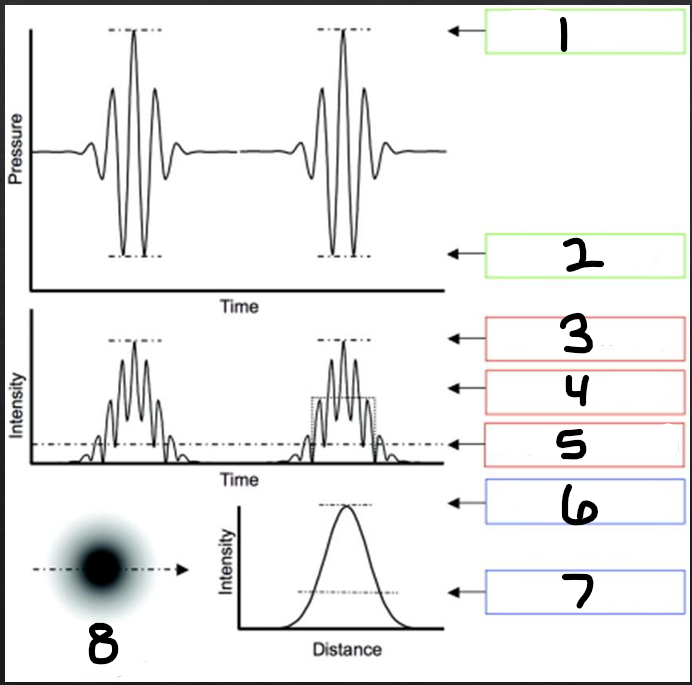
7
spatial average (SA)
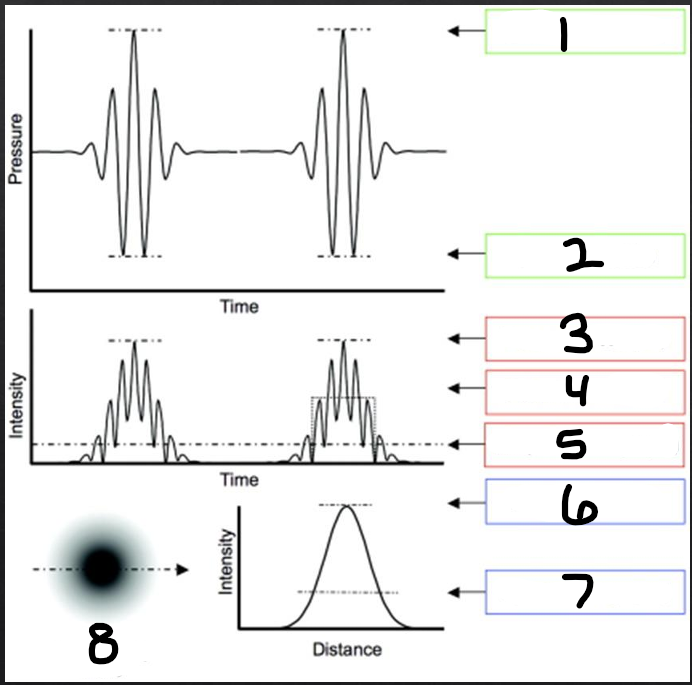
8
beam intensity profile
the amount of acoustic energy a patient is exposed to can be limited using the ___ principle
ALARA
ALARA means
as low as reasonably achievable
as medical professionals, it is our job to make sure
exams are medically justified
exams are not prolonged unless medically justified
patient exposure is minimized
___ acoustic intensities can cause damage to biological tissues
high
how to minimize patient exposure
use high receiver gain and low output power
thermal bioeffects
tissue temperature elevation
related to the output characteristics of the TDR and tissue properties
temperature and exposure time determine the likelihood of bioeffects
T/F: maximal heating is related to the beam’s SPTA intensity
true
SPTA should not exceed ___ for an unfocused beam
100 mW/cm2
SPTA should not exceed ___ for a focused beam
1W/cm2
there are no confirmed bioeffects for up to ___ elevation above normal and exposure time up to 50 hours
2°C
any exam causing temperature elevation greater than ___ could potentially harm a fetus
41°C
fetal tissues are ___ tolerant of tissue heating than adult tissues
less
T/F: fetal defects resulting from temperature elevation have not been documented
false
thermal index (TI)
used to predict an increase in temperature
there are 3 different thermal indices used for different imaging applications: TIS, TIB, and TIC
TIS
thermal index in soft tissue
TIB
thermal index in bone
TIC
thermal index in cranial bone
___ modalities have a greater risk of thermal bioeffects than ___ because the ultrasound beam is transmitted in the same direction (causing heat to build up)
non-scanned; scanned
scanned modalities
acquires information over a plane which allows time for the heat to dissipate
2-D (B-Mode) and color doppler
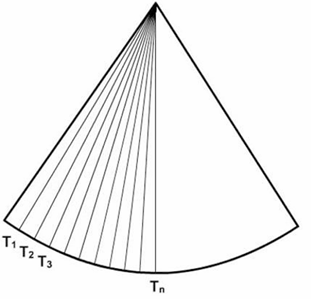
non-scanned modalities
ultrasound beam is transmitted in the same direction which causes heat to build up
CW doppler PW doppler, M-mode, and A-mode
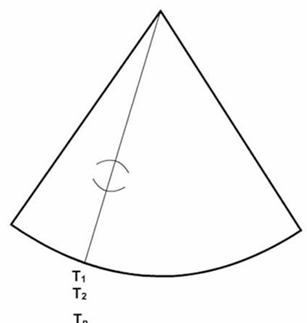
mechanical (non-thermal) bioeffects
damage caused by the actual oscillation of the sound wave on tissue
as the sound wave propagates through tissues, there are areas of compressions and rarefactions
can cause the formation of gas bubbles in tissues
types of mechanical bioeffects
radiation force
cavitation
streaming
cavitation
worrisome because bubbles generated can get larger, and the bubbles can rupture
2 types of cavitation: stable or transient (inertial)
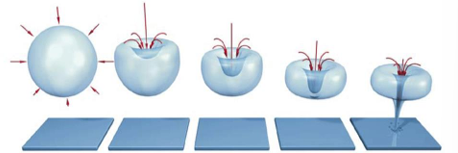
stable cavitation
produces bubbles that oscillate in a stable manner and do not rupture
transient cavitation
potential to cause the most bioeffects
larger bubbles are produced and rupture
results in an increase in tissue temperature
can cause cell death in the affected area
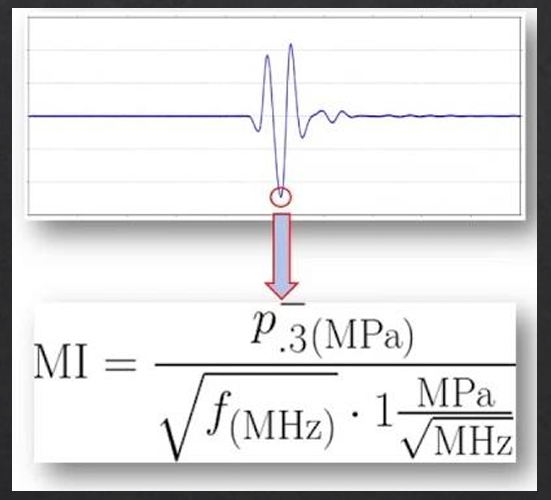
the risk of mechanical bioeffects can be measured using the
mechanical index (MI)
as the TDR frequency increases, MI ___
decreases
acoustic power and microbubble responses
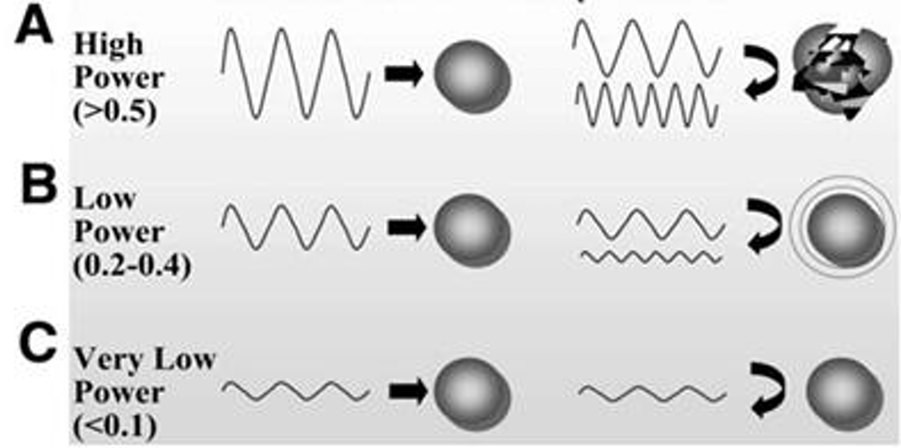
radiation force is another type of ___
MI
microstreaming
occurrence of shear stresses by the fluid surrounding the cells
useful with therapeutic ultrasound
promotes fluid mixing and targeted drug delivery (DNA, drugs, macromolecules into a cell)
bioeffects research may be conducted
in vivo or in vitro
in vivo research
performed within the living body of an animal or plant
in vitro research
“in glass”
performed outside the living body in an artificial environment
gives the opportunity to perform experiments that would be unethical or impossible to do in humans
in vitro ultrasound research
a computer model estimates the temperature elevation of tissues during exposure to ultrasound
previous study demonstrated that very high ultrasound intensities can cause genetic damage and cell death
epidemiology
branch of medicine associated with population studies
empirical studies provide an exposure response using
clinical surveys
many epidemiologic studies deal with ___ fetal exposure to ultrasound
in-utero
the best epidemiologic studies are
prospective
randomized
prospective studies
are forward-looking
provide a complete and accurate compilation of meaningful information from medical records
retrospective studies
are from the past
less desirable because data is from the past, less accurate, or incomplete
randomized studies
create 2 groups of patients
one group is exposed to ultrasound
one group is not exposed to ultrasound
risk factors that affect fetal outcome are present in both groups and are accounted for
limitations of studies
data can be inaccurate because indications, GA, MI, TI, and the required # of scans can be inconsistent between patients
other risk factors other than exposure to ultrasound can affect fetal growth or lead to abnormality
maternal age
environmental factors
poor nutrition
smoking
alcohol
drug use
skipped slide 32
come back if needed
electrical and mechanical hazards
instruments should be checked for proper condition
inspected to ensure proper physical status
transducers have the greatest risk because it is in contact with the patient
check for electrical shock from a cracked transducer housing
image quality is compromised when cracked
advancements in imaging architecture
virtual beamforming
big data
enhanced digital signal processing (eDSP)
bit by bit frame creation
conventional beamforming
beamformer generates the voltage that drives the transducer and determines the PRF and intensity
amplify returning echoes and compensate for attenuation
with a conventional beamformer, pulses are fired separately and returned separately and must be sorted out
limitations of conventional beamforming
spatial resolution vs. frame rate are traded for image optimization
some relevant data can be lost during the process
virtual beamforming utilizes
graphic processing units (GPUs)
graphic processing units (GPUs)
specialized processor originally designed to accelerate graphics rendering
can process many pieces of data simultaneously, making them useful for machine learning, video editing, and gaming applications
determines the echo received from each pixel location
GPUs overcome the limitations of conventional beamforming, which are
beam divergence
slice thickness
beam breakage
lobe artifacts
benefits of virtual beamforming
detail resolution
contrast resolution
temporal resolution
increased sensitivity
increased penetration
artifact reduction
improved doppler operation
simultaneous grayscale, color, and spectral doppler
big data
eDSP
bit-by-bit frame creation
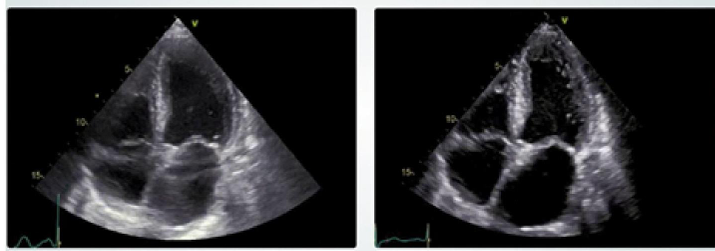
which image uses virtual beamforming?
the image on the left uses conventional beamforming
the image on the right uses virtual beamforming
big data
the ability to acquire, transfer, process, and store massive volumes of digital data received through virtual beamforming
in ultrasound applications, ___ ___ represents the interaction of acoustic energy with human soft tissue and provides the potential for a new generation of diagnostic possibilities
big data
the four V’s of big data
volume (amount)
variety (type and sources)
veracity (quality and trust)
velocity (speed)
enhanced digital signal processing (eDSP)
analyzes the enormous size and diversity of the acoustic data generated by virtual beamforming
further processes the big data
software algorithms identify, separate, and group acoustic information into digital “siloes”
this process provides a thin ultrasound beam image
benefits of eDSP
improved temporal resolution
automated sound speed compensation
enhanced B-mode tissue characterization
tissue transparency
automated radiofrequency-generated B-mode measurements
attenuation imaging
bit-by-bit frame creation
data populated by the “big data” is processed into individual pixels in the back end using bit-by-bit frame creation
after creation, additional digital signal processing software algorithms can be applied before the frame is presented for operator interpretation
___ sonographic imaging platforms utilize a line-by-line frame method
conventional
the use of bit-by-bit frame creation allows for
speckle tracking
contrast enhanced ultrasound
vector flow imaging
hemodynamic imaging
temporal resolution transparent exceeds 1000 frames/sec
synthetic spatial compounding
conventional imaging integrates data from 3 different angles of insonation to produce a single frame
spatial compounding uses data received from eDSP thereby reducing frame time
quality assurance (QA)
routine and period evaluation of all ultrasound systems to guarantee optimal image quality
required for all diagnostic labs
needed to obtain and maintain lab accreditation
equipment performance testing and statistical analysis of lab results
QA includes
assessment of systems components
repairs and record keeping
inspection, evaluation, and calibration
preventative maintenance
patient tracking
peer review
QA meetings
evaluation of oversights and errors
develop protocols that are consistent and methodological to minimize the number and severity of errors
five goals of QA
proper operation of the system
detects gradual changes in image quality
minimize downtime
reduce the number of non-diagnostic exams
reduce the number of repeat scans
QA device categories
tissue equivalent phantom
doppler phantom
beam profile/slice thickness
performance measurements during QA
axial resolution
lateral resolution
depth calibration (vertical distance)
horizontal distance calibration
system sensitivity
registration accuracy
dead zone
image uniformity (tissue texture)
lesion detection (anechoic cyst and mass resolution)
grayscale contrast resolution (displayed dynamic range)
focal zone
depth of penetration
sensitivity
ability of a system to display low-level echoes