accounting midterm 3
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Working Capital
Current assets - current liabilities
key working capital accounts: A/R, Inventory, A/P
Working Analysis
Assess operational efficiency and liquidity
i.e collecting from customers fast enough? selling inventory too slow? paying off suppliers too fast/slow?
Accounts Receivable Turnover (ART)
the number of times a company collects its average accounts receivable balance during a period (receivable → cash)
high ration is better: credit is turning into cash faster.
Days Receivable Outstanding
the average number of days to collect cash payment for a sale
365/ART
Inventory Turnover (IT)
how many times a company sells and replaces its inventory during a period
Days Inventory outstanding
average number of days that a company holds inventory before turning it into sales
365/IT
Accounts Payable Turnover (APT)
how many times a company purchases on account and pays off its bill during the period.
Days Payable Outstanding
average number of days it takes a company to pay back its accounts payable to suppliers
365/APT
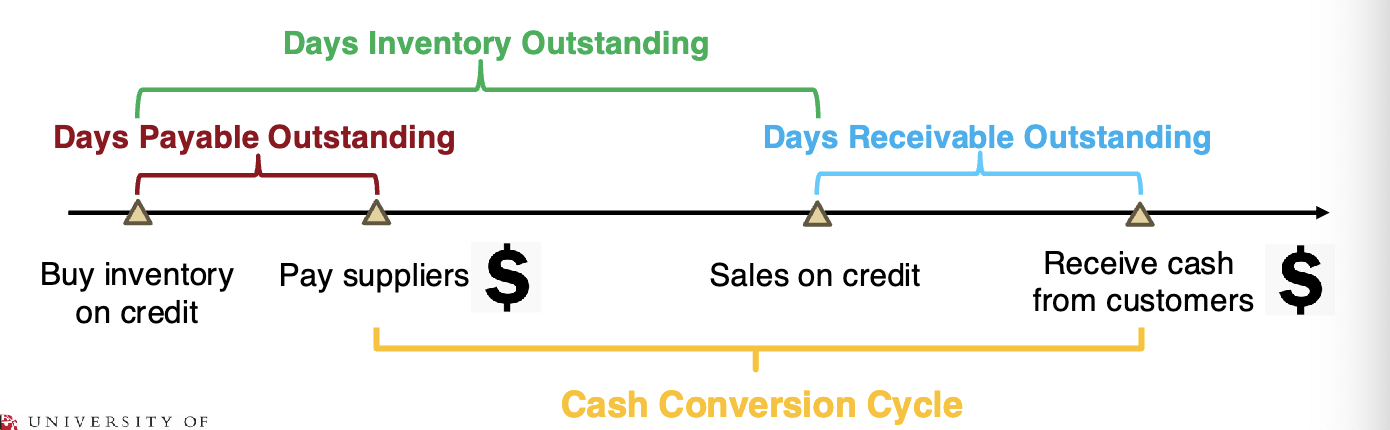
Cash Conversation Cycle
the number of days it takes to convert the cash spent on inventory back into cash from sales
CCC= Days Inventory Outstanding + Days Receivable Outstanding - Day Payable Outstanding
measures working capital efficiency
Negative CCC represents strong bargaining power over suppliers.
Debt Securities
issued by other institutions and corporations
i.e short-term debt securities, CDs, commercial paper, treasury bills, corporate bonds
if apple bought debt securities (bonds) from other company, the company pays apple interest and return the principal at the end of the term.
Equity securities
investments in stocks of other company
voting rights:
less that 20%: no influence (just an investor)
20-50%: can exert significant influence, but no control
more than 50%: has control over investee.
Passive Investments (type of intercorporate investments)
debt or equity securities (less than 20% voting rights)
no influence or control
earn interest, dividend, and capital gain
accounting method: fair value or historical cost
3 types: Held-To-Maturity, Trading, Available for Sale
Significant influence
equity securities (20-50% voting rights)
can exert significant influence, but no control
results from legal agreements and being a sole supplier/customer
Control
equity securities (more than 50%)
has control over investee company
sometimes occur through legal agreements
Why do companies make investments
short-term use of excess cash (generate cash during slow periods, counter strategic moves by competitors, quickly respond to acquisition opportunities)
alliances for strategic purposes (gain access to R&D, supply or distribution channels, or marketing and production expertise)
market penetration or expansion (vertical or horizontal intergration, enter new or growing markets)
Held To Maturity Securities
Intention: hold until they mature
includes only debt securities
interest income is recognized on IS
unrealized gain/loss is not recognized on IS
accounting method: historical cost method
Trading Securities
intention: actively buy and sell for trading profits
includes all marketable equity securities and debt securities that are actively traded
Interst/dividend income is recognized on the IS
unrealized gains/losses recognized on the IS at the end of accounting cycle
realized gains/losses recognized on the IS at the time of sale
accounting method: fair value (mark-to-market) method
Available for sale Securities
intention: hold for a longer term for capital gains and interest income, but to sell before they mature
includes only debt securities
interest income is recognized on the IS
unrealized gain/loss bypass IS → recorded in accumulated other comprehensive income (AOCI) part of SE without affecting Net Income
realized gain/losses are recognized on IS at the time of sale
accounting method: fair value (mark-to-market)
Fair Value Accounting
reports fair value on the B/S
Potential for manipulation
when market value is increasing: AFS → Trading or sell AFS. allows unrealized or realized gains to be recognized on the Income Statement
when market value is decreasing: Trading → AFS so unrealized losses bypass the income statement
Long-lived (long-term) Assets
assets that company expects to use for more than 1 year
tangible assets (PP&E)
intangible assets: patents, trademarks, copyrights, goodwill
How do PP&E affect income statement
cost of PP&E assets is allocated to expenses over the time period that the assets help to generate revenue.
depreciation: cost transferred from BS to the IS
How are PP&E reported on the BS
net book value (net PP&E): Cost (Gross PP&E) - Accumulated Depreciation
Identifiable Intangibles
separately transferable
can be sold, licensed, or transferred on its own
e.g patents, trademarks, copyrights, franchise rights, customer lists, or unpatented technology
Goodwill
not separately transferable
the excess of purchase price over the fair value of net assets acquired in a business combination
Goodwill = purchase price - FV of identifiable net assets of the target (how much target company is worth: assets - liabilities)
why? pay premium because of future growth potential, synergies, intangibles
indefinite life → intangible assets → no amortization of goodwill
patents
exclusive right to use, manufacture, and sell product (20 years) to prevent someone copying innovation
if purchased from another company → capitalized (assets)
if developed internally → all costs are expensed
Trademarks
registed name, logo, package design, image, jingle, or slogan associated with a product
if purhcased from another company → capitalized
if developed internally → expense it
generally, trademarks and patents have indefinite lives → do not amortize
not present on BS
accounting for intangibles
purchased (acquire externally) → acquisition costs are capitalized → definite lives (amortization) or indefinite lives (no amortization)
internally developed → costs are expensed (except legal costs and software cost when technological feasibility [company has established that product can be produce to meet design specification] is established)
R&D
US GAAP required that R&D costs be expensed as incurred.
Amortization
cost allocation process for intangible assets
only intangible assets that have definite lines are amortized
merger
describes two firms joining forces to move forward as a single new entity
acquisition
one company purchasing most or all of another company’s shares to gain control of that company
common stock
the most common class of stocks in a corporation
with voting rights
class A vs class B
company must issues these
preferred stock
has liquidation and dividend preference relative to common stock
hybrid between common stock & bonds
usually w/o voting rights
treasury stock
contra-SE account
when a company repurchases its stocks and hold them
par value
arbitrary amount set by company organizers at the time of formation
specifies the allocation of proceeds from stock issuances between par value (common stock) and additional paid-in capital
additional paid-in capital
paid-in capital (contributed capital) in excess of par
reflects differences between the amount provided by shareholders and the par value of issued shares.
(the premium investors are willing to pay for stock)

accounting for contributed capital
contributed capital: amount of cash or assets that shareholders have given a company in exchange for stock
accounted for at historical costs.
fluctuations in stock price after IPO do not directly affect the financial statements of the issuing company
never any gain/loss reported on the purchase and sale of the company’s own stock or payment of dividends
total proceeds from stock issuance
common stock = par value per share x # shares issued
common stock + additional paid-in capital = total proceeds from stock issuance.
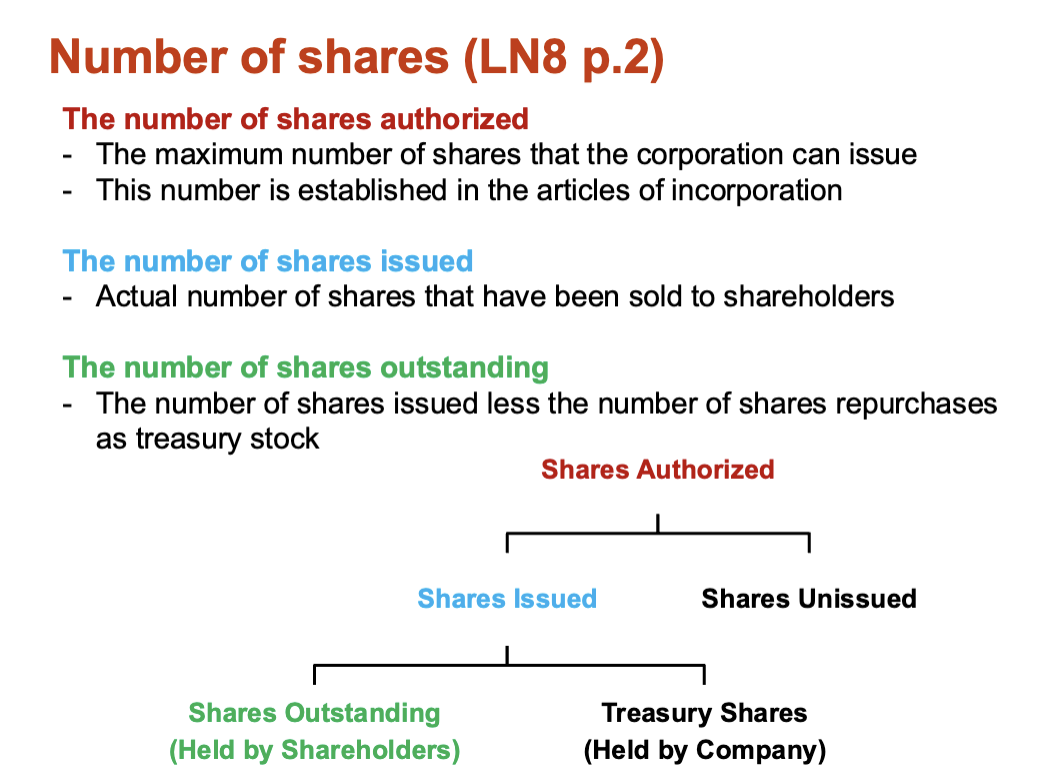
The Number of Shares authorized
maximum number of shares that the corporation can issue
established in the articles of incorporation
the number of shares issued
actual number of shares that have been sold to shareholders
the number of shares outstanding
the number of shares issued less than the number of shares repurchases as treasury stock.
Why do companies buy their stock back
to increase stock price if price is undervalue
stock price is closely link to executive compensation
to increase earnings per share (EPS)
tax-efficient way to return capital to investor (tax is only applicable on the actual sale of shares and receiving dividends)
stock splits
increase the number of shares outstanding → lower price per share
e.g 2-for-1 split: number of shares is doubled, price per share (EPS) is halved
True Split
adjust the numbers proportionately
number of shares (authorized, issued, and outstanding) and all per share amounts (EPS, dividend per share, stock price per share, par value per share)
split effected in the form of a stock dividend.
Why do a stock split
increase shareholder base (more affordable to small investors)
increase stock liquidity
signal management’s expectation on future growth
Numbers affected by stock split
IS: EPS, shares used in computing EPS
BS: shared authorized, issued, and outstanding
SSE: dividend per share
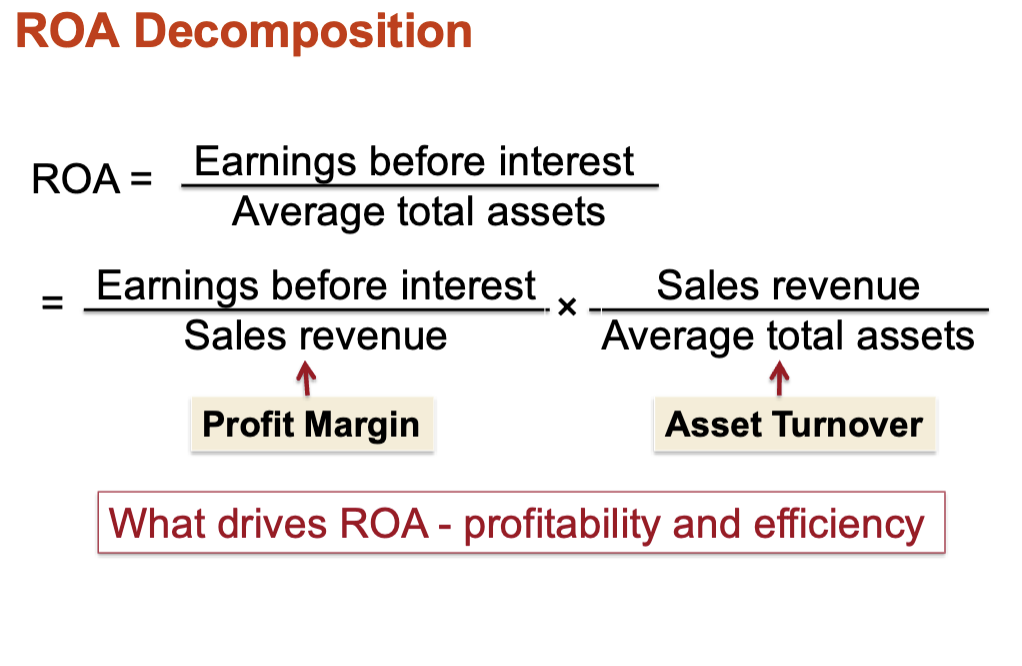
Return on Assets (ROA)
the return earned on assets that company invests in
earnings before interest / average total assets
affected by asset turnover and net profit margin
Return on Equity
the return earned on investments made by company shareholders
net income / average shareholder’s equity
Gross profit margin
the % of revenue left after deducting direct cost of sales
Gross Profit / Sale Revenue
gross profit = sale revenue - COGS
so (Sale Revenue - COGS) / Sale Revenue
Net profit margin
the % of revenue left after deducting operating expenses, depreciation, amortization, interest, and income taxes.
net income / sale revenue
financial ratios
time-series analysis: comparing its own performance
cross-sectional analysis: comparing across industry peers
Alternative Data
not disclosed by firms in their official reports
more objective since generated by 3rd parties, more timelier than 10K, 10Q
ex: social media, sentiment, satellite image, point of sale retail scanner data
Why types of info do analysts gather?
10k, 10q, press release, earnings conference call, management guidance (earnings forecast), corporate site visits, alternative data