BSCI170: Cellular Respiration - ETC
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Where does the ETC take place?
eukaryotes: inner mitochondrial membrane
prokaryotes: plasma membrane
What are the 2 steps of the ETC?
Oxidative phosphorylation
Chemiosmosis
What does complex 1 do?
oxidizes NADH to NAD+
pumps H+ ions against their concentration gradient into the intermembrane space
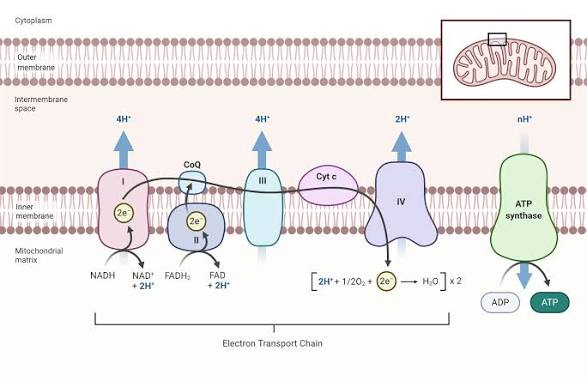
What does complex 2 do?
oxidizes FADH to FAD
What does complex 3 do?
pumps H+ ions against their concentration gradient into the intermembrane space
What does complex 4 do?
pumps H+ ions into intermembrane space against their concentration gradient
reduces 2 H+ and 1/2 O2 into H2O using 2 electrons
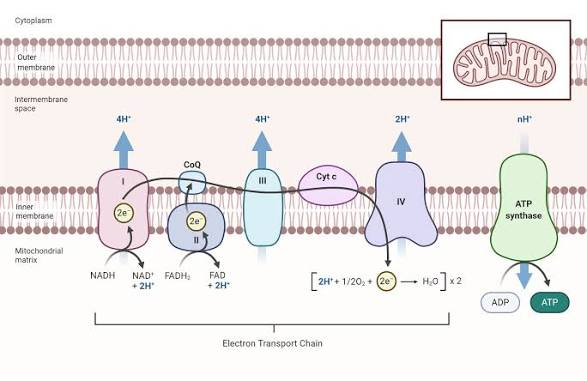
What does ubiquinone do?
transports electrons from complex 1 and 2 and puts them into complex 3
What does cytochrome C do?
moves electrons fromn complex 3 to complex 4

What membrane spaces are used in the ETC
intermembrane space
inner mitochondrial membrane
mitochondrial matrix
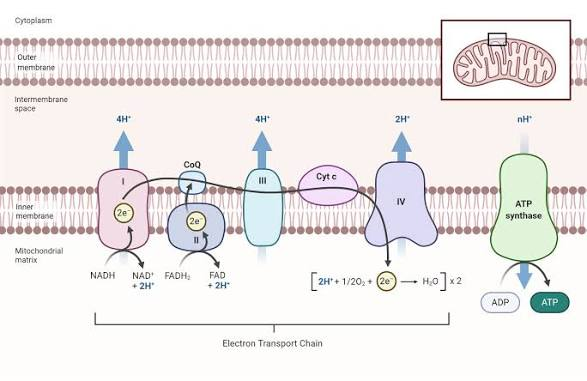
Which space has a higher H+ concentration?
intermembrane space
Which space has a lower H+ concentration?
Mitochondrial matrix
What makes up oxidative phosphorylation
the complexes, cytochrome C, and ubiquinone
what makes up chemiosmosis?
ATP synthase
Chemiosmosis definition
the movement of ions across a semipermeable membrane down their electrochemical gradient to generate ATP
Oxidative phosphorylation (you don’t need to know the exact definition)
he process where electrons are passed through a series of carriers in the electron transport chain, ultimately transferring them to oxygen (O2) and generating ATP by using the energy released to pump protons across a membrane, creating a proton gradient that then drives ATP synthesis through ATP synthase.
What happens to the electrons in NADH and FADH2?
It gets transferred to O2, which is why oxygen is the final electron acceptor (this forms water)
Which part of ATP synthase is F0 and F1?
Top part: F0 proton channel
Bottom part: F1 ATP synthase enzyme
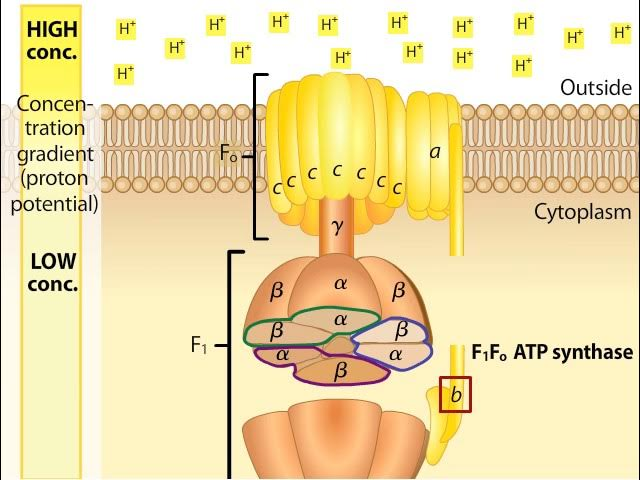
What does ATP synthase do?
moves H+ ions down concentration gradient from intermembrane space to mitochondrial matrix
exergonic reaction
How many ATP is made through an oxidized NADH?
2.5 ATP
How many ATP is made per oxidized FADH2
1.5 ATP
How does ATP synthase work?
H+ ions are diffused down F0 and F1 begins to spin and exposes the active site for ATP synthesis
How much ATP is made by ETC?
26-28 because it depends on whether the electrons made 2 FADH2 or 2 NADH.
26: 8 NADH and 4 FADH2
28: 10 NADH and 2 FADH2
How are the amount of H+ ions and the amount of ATP produced related?
the less H+ ions diffused through ATP synthase, the less ATP produced
Net product of ETC
26-28 ATP
8-10 NAD+ (can go back into glycolysis/citric acid cycle)
2-4 FAD (can go back to citric acid cycle)
12 H2O
How many H+ ions to create 1 ATP?
~4 H+ ions