Enzymes Study guide
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Inorganic activators
Cofactors
the most common in oraganic activators are
Cu
Fe
Mg
Mn
Zn
Ca
Coenzymes are mostly
Organic vitamins
Hoe do coenzymes bind
loosley
Prosthetic group
An organic cofactor tightly or covalently bound to an enzyme to aid in catalyzing a reaction
Apoenzyme
an inactive protein or enzyme
Holoenzyme
the enzyme portion with its respective coenzyme, forming a complete and active system
What are four factors affecting enzyme reaction
substrate concentration
enzyme concentration
Ph
temp
1st order
the rate of reaction is directly proportional to the substrate concentration
0 order kinetics
The rate depends on the enzyme concentration only
most ideal for measuring enzyme activity
lareg excess substrate so the amount of enzyme is the only rate limitor
One international unit of enzyme activity is
1umol/min
Michalis menten constant is
Km=1/2V
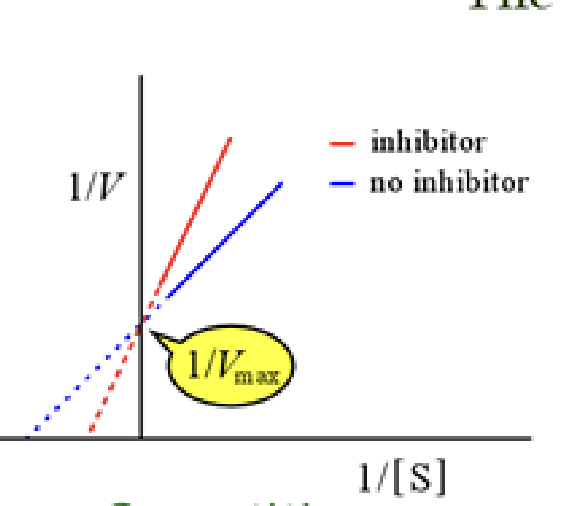
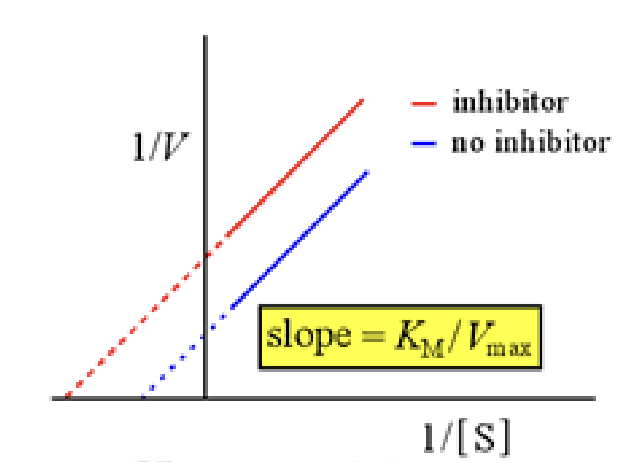
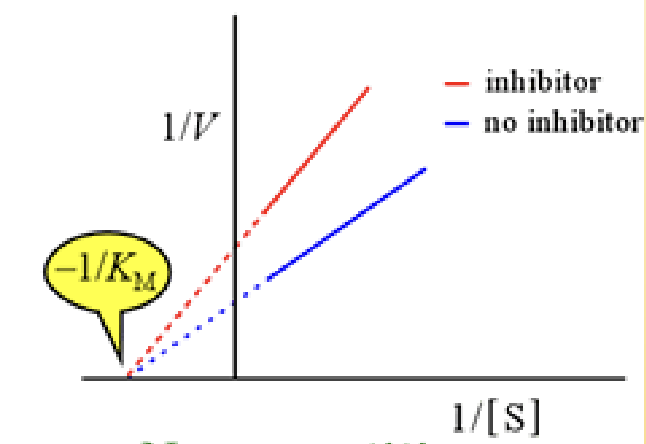
in a line weaver burk plot y intercept
1/Vmax
In a line weaver burk plot what is the x intercept
-1/Km
What are the three kinds of enzyme inhibitors
competative
uncompetative
noncompetative
competitive inhibitor
can bind to an active site and competes with substrate. it can be over come with more substrate
Noncompetitive inhibitor
bind at another site and do not compete with the substrate and can be reversible, alters the enzyme structure so it cant bind to anything
Uncompetitive
binds to the Enzyme substrate complex brining the reaction to a grinding halt
additional substrate increases inhibition
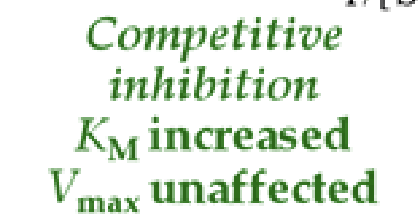
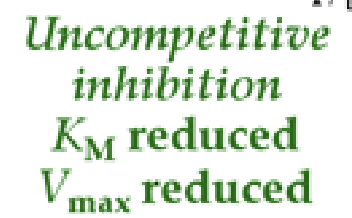
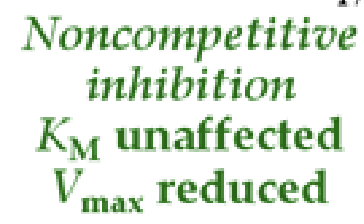
Fixed time monitoring
reactants are combined
Rxn proceeds for defined period
Rxn is stopped
measurment of chromogen is made
Continuous monitoring
multiple measurements during the rxn
usually absorbance changes
specific intervals
continuously recording spectrophotometer
ALT
released when liver is damaged
AST
released when liver is damaged
ALP
cystolic- hepatobiliary, released when there is a hepatobiliary obstruction
GGT
cystolic- hepatobiliary, released when there is a hepatobiliary obstruction
macroamylase
disease defined by the elevation in serum amylase activity due t the precense of complex macromolecules whose huge size inhibits their elimination via the urinary system
macroamylase presents as
unable to excrete amylase, so hyperamylasemia
How are most enzymes tested for
spectroscopic techniques, specifically absorption and fluorescence measurements
LD
Converts pyruvate to lactate while oxidizing NADH to NAD
How is LD measured
rate of decreased absorbance of NADH at 340nm is proportional to LD
ALP
found in the bone, intestinal mucosa, renal tubules, biliary tree, leukocytes, placenta and some tumors, increases when something is wrong or not exiting
Heat stability for ALP is used for
identifying the source of having an elevated ALP
What are the most heat stable enzymes
placental
what is the most stable isoenzyme associated with rare neoplasms
Regan and Nagao
What is the most heat liable enzyme
bone
ALP activity is measured before and after heating he serum, what temp is it heated to
56C for 10 min
CKBB
Brain, GI, prostate, uterus
CKMB
acute myocardial infarction
CKMM
Muscle injuries and heart
LD is hisotrically MI
“flipped isoenzyme pattern (LD1>LD2)