Afib Pharmacology
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What causes depolarization in phase 0?
“funny” HCN channel activity
adjacent cell depolarization
HCN = hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channel
What occurs in phase 1?
sodium channels become inactive
brief repolarization (notch) due to efflux of potassium
What channels are involved in phase 2?
L-type calcium channels
slow delayed rectifier potassium channels
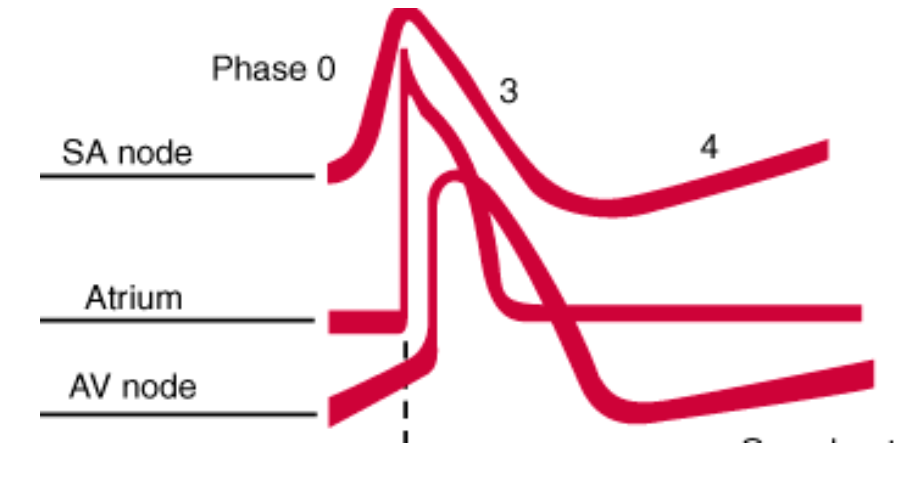
What is depolarization primarily achieved by in the SA and AV nodes?
Calcium currents
Which action potentials have less-steep slopes?
SA and AV node action potentials (due to kinetics of calcium currents)
What is the function of the funny HCN channels?
They are the pacemaker cells in the SA node for automaticity
(hyperpolarization-activated means they conduct more current as the cell becomes more polarized - occurs in phase 3 and 4)
How is automaticity regulated by the ANS?
Funny HCN channels are cyclic nucleotide-gated, meaning the activity is controlled depending on levels of cyclic nucleotides (cAMP, cGMP)
How does the PSNS reduce heart rate?
Activation of Gai-coupled type II muscarinic receptors by ACh (inhibits adenylate cyclase and reduces cAMP levels, decreasing HCN channel activity)
How does the SNS increase heart rate?
Activation of the Gas-coupled beta-1 receptors (by dobutamine or other agonist) - stimulates adenylate cyclase which increases cAMP levels to increase HCN channel activity)
In what 3 states can sodium channels exist it?
resting (closed)
activated (open) (due to depolarization to threshold voltage)
inactivated (closed)
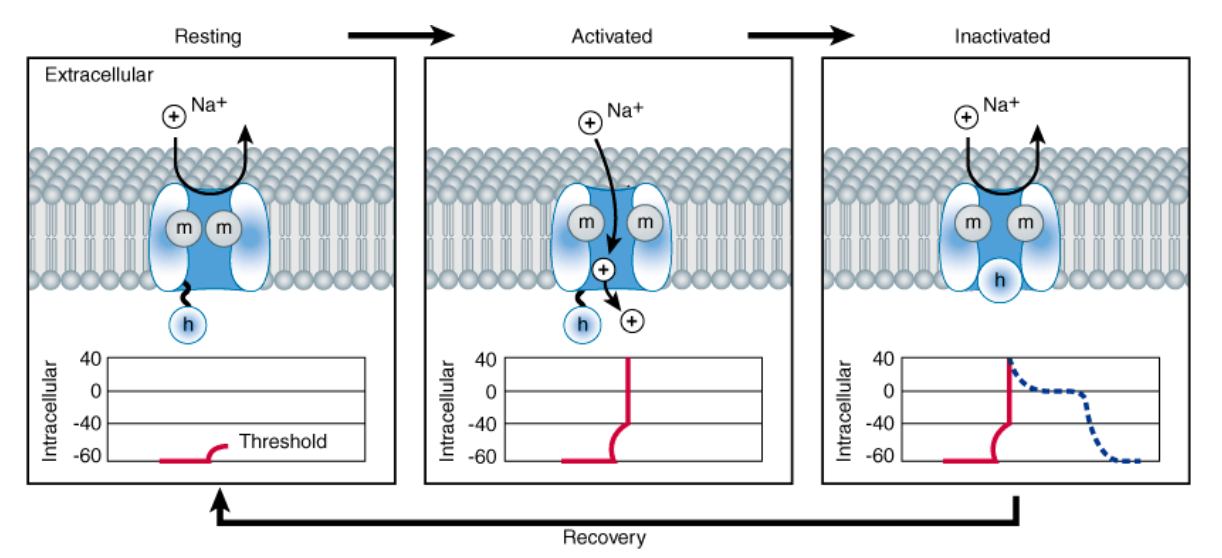
What is the equilibrium potential that is reached when an action potential occurs?
Approx. +70 mV (point at which sodium channels will close)
How do calcium channels compare to sodium channels?
similar mechanism for activation and inactivation
transitions occur more slowly and at more positive potentials
reflected in plateau phase of action potential where sodium current is turned off and calcium current continues to rise and slowly fall
What can cause changes in refractoriness?
altered recovery from inactive state
altered action potential duration
Categories and examples of anti-arrhythmics
Ia - quinidine, disopyramide
Ib - lidocaine
Ic - flecainide, propafenone
II - BBs
III - amiodarone, dronedarone, dofetilide, sotalol
IV - verapamil, diltiazem
Note: amiodarone could technically fit into all 4 classes
Goal of anti-arrhythmics regardless of MOA
To reduce ectopic pacemaker activity or modify conduction or refractoriness in re-entry circuits
Why don’t anti-arrhythmics totally disrupt cardiac electrophysiology?
Relatively more selective for ectopic pacemakers than SA node
relatively more selective for depolarized tissue than in normal tissue
What causes selectivity seen in anti-arrhythmics?
Channel-blocking drugs bind to activated and inactivated channels, but bind poorly to resting channels. They block activity when there is fast tachycardia (more channels active/inactive at the same time) or when there is significant loss of resting membrane potential (more channels inactive)
MOA of class I anti-arrhythmics
Sodium channel blockers
What does the extent of sodium channel block depend on?
Critically dependent on HR and resting membrane potential (since drugs bind active and inactive state, not rested state)
When sodium channels are blocked, the threshold for excitability is ____.
Increased (so need more depolarization to open sodium channels to evoke action potentials)