The Nervous System Quiz
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Sensory Input
Receives stimuli via millions of sensory receptors throughout the body.
Integration
Processes input stimuli and decides what should be done.
Motor Output
Activates effector organs to cause a response.
Nervous Tissue
Composed of neurons and neuroglia.
Neurons (nerve cells)
Excitable cells that respond to stimuli by conducting impulses to transmit signals.
Neuroglia (glial cells)
Supportive cells that provide nutrition, insulation, and help with signal transmission.
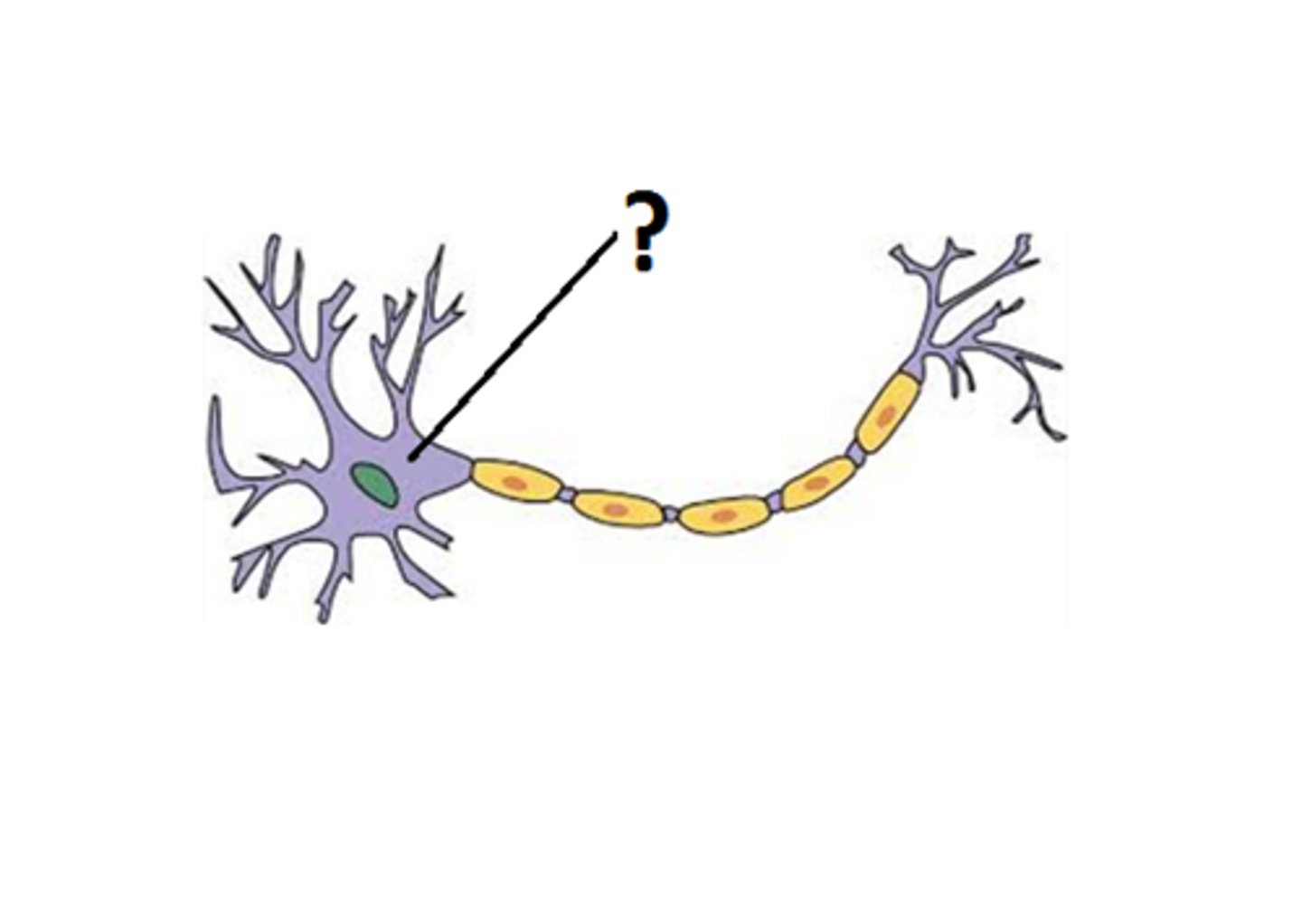
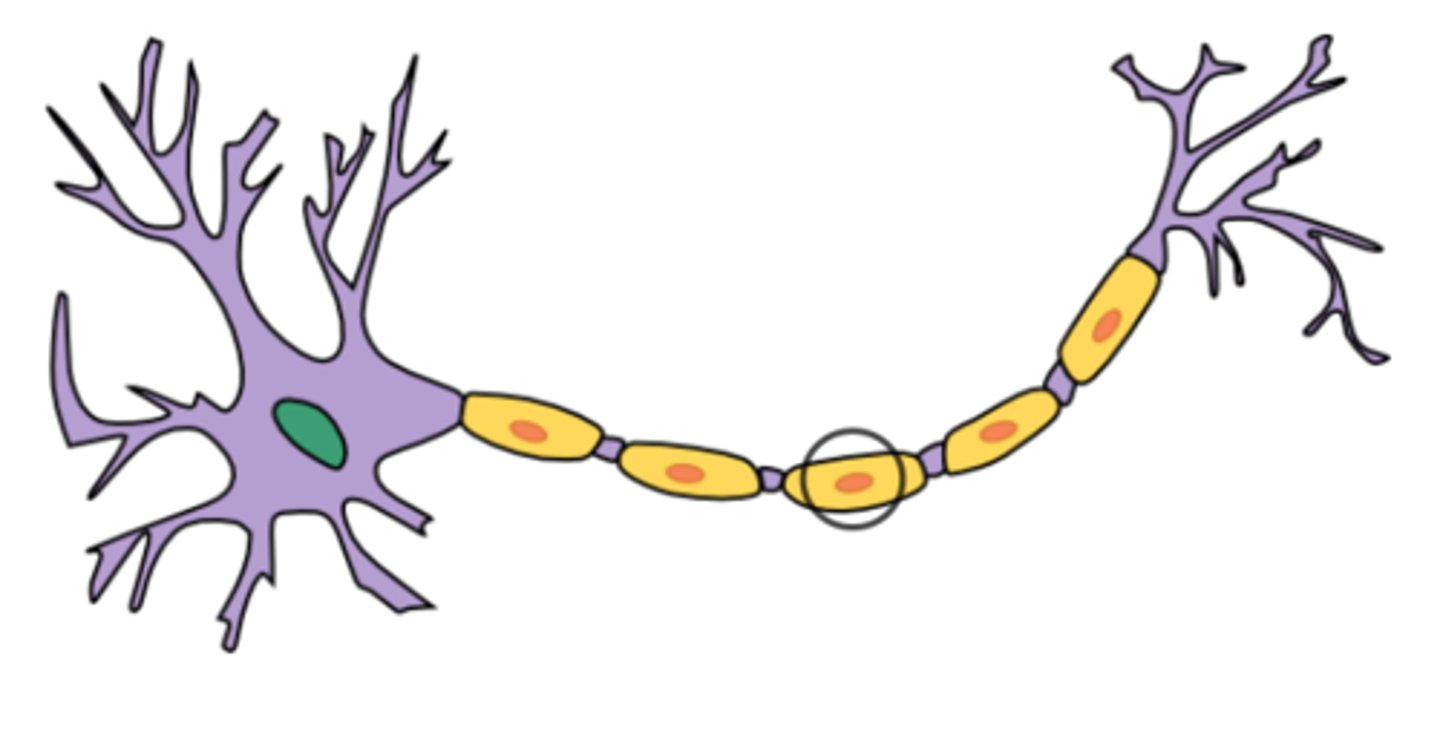
Soma (cell body)
Life support of the neuron, containing the nucleus and organelles.
Processes
Extensions from the cell body.
Dendrites
Main receptor of signals; input region.
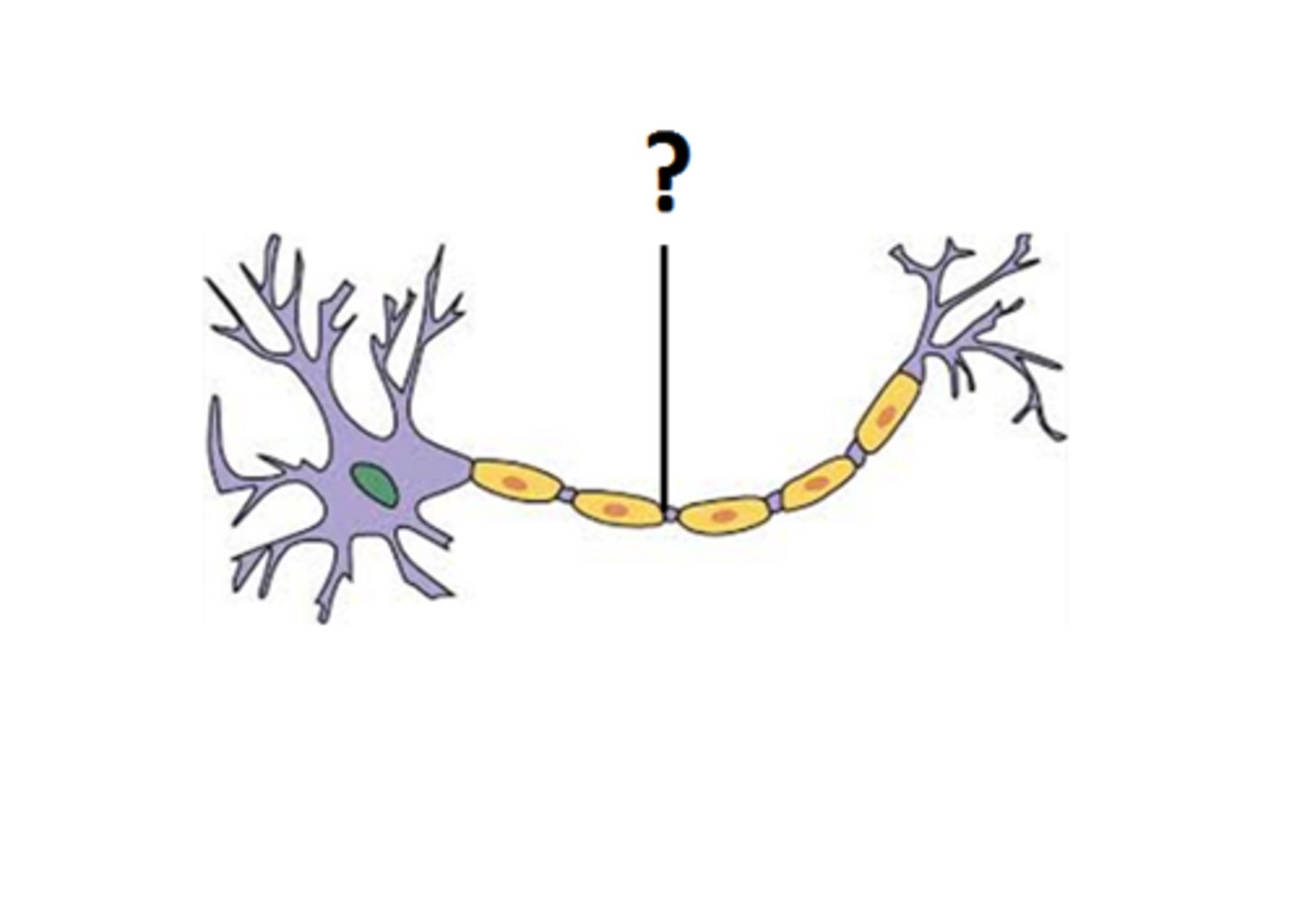
Axon
Generates and transmits nerve impulses; conducting region (also called a nerve fiber).
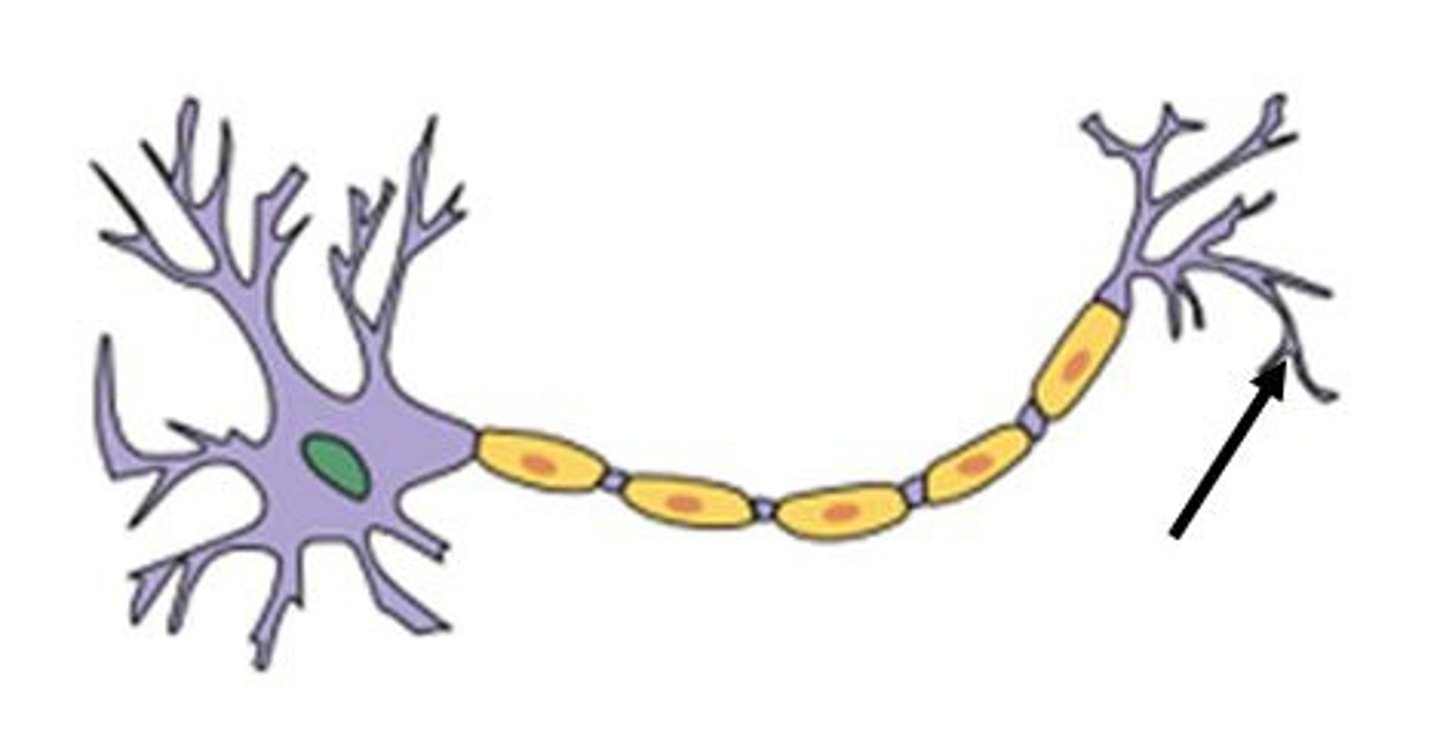
Axon Terminals
End of the axon that releases neurotransmitters at a synapse; secretory region.
Myelin Sheath
Covers long axons to protect and electrically insulate, increasing impulse speed.
Nodes of Ranvier
Unmyelinated gaps that help increase nerve signal velocity.
Nerves
Bundles of axons extending from the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body.
Ganglion
Collection of nerve cell bodies located outside the brain or spinal cord.
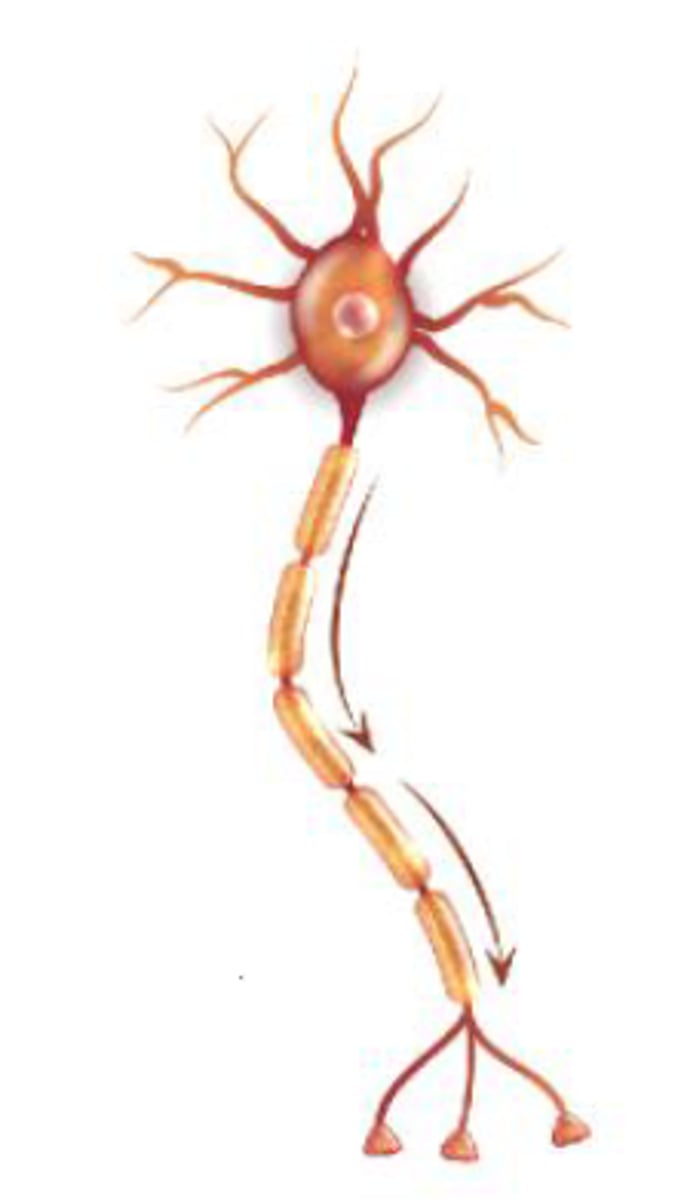
Multipolar Neurons
More than 3 processes (1 axon, 2+ dendrites); 99% of neurons.
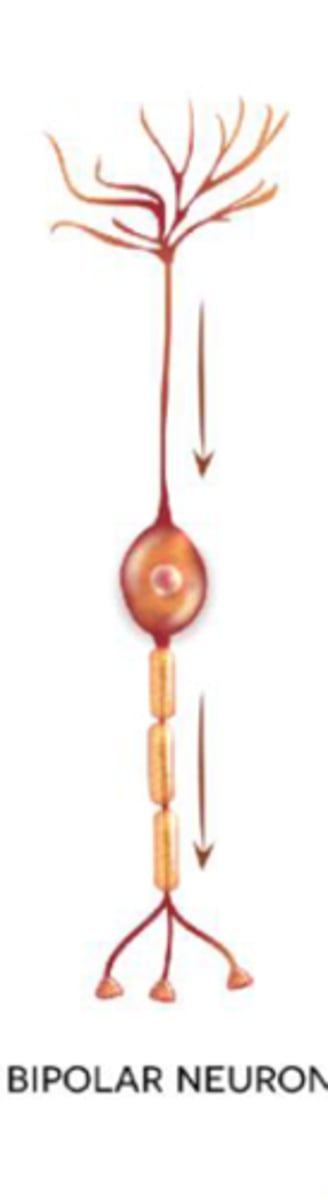
Bipolar Neurons
2 processes (1 axon, 1 dendrite); rare, found in special sense organs.
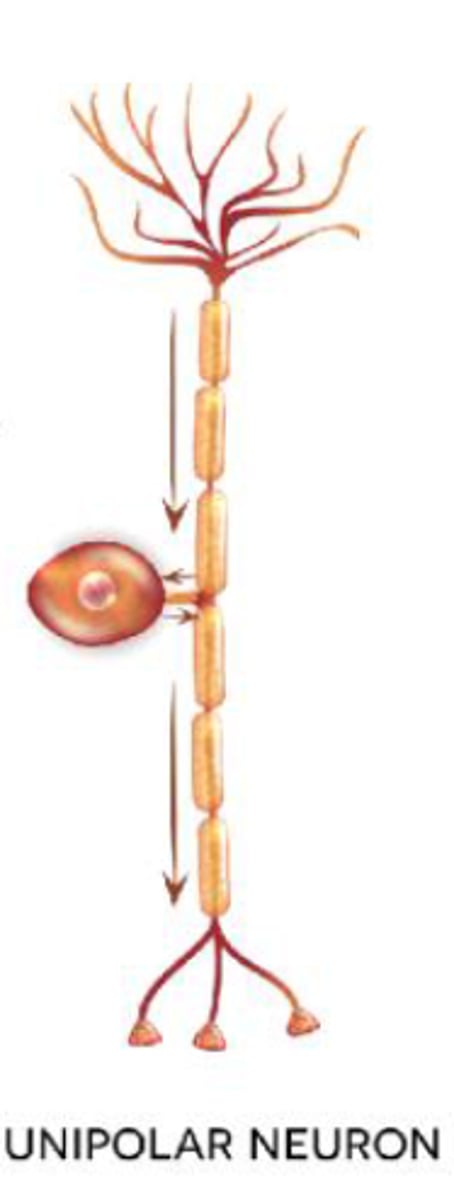
Unipolar Neurons
1 process dividing from the cell body like a T; found in PNS ganglia.
Sensory (afferent) neurons
Transmit info from sensory receptors to CNS; mostly unipolar.
Motor (efferent) neurons
Transport info from CNS to body; mostly multipolar.
Interneurons (association neurons)
Housed in CNS; transmit info between sensory and motor neurons; mostly multipolar.
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Brain and spinal cord; integration and control center.
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Spinal and cranial nerves; communication system between CNS and body.
CNS Protection
The brain is protected by the skull, meninges, and cerebrospinal fluid.
Ventricles
Hollow fluid-filled cavities in the brain containing the choroid plexus, which produces cerebrospinal fluid.
Cerebrum
Largest part of the brain; left and right hemispheres, divided into 4 lobes; functions in learning, speech, emotion, reasoning, vision, hearing, and fine movements.
Cerebellum
Under the cerebrum; maintains posture and balance; coordinates timing and patterns for smooth, agile, subconscious movements.
Brainstem
Base of the cerebrum, anterior to the cerebellum; includes medulla oblongata, midbrain, and pons; relays info between the brain and spinal cord.
Frontal Lobe
Handles decision-making, planning, problem-solving, and voluntary muscle movement.
Parietal Lobe
Processes touch, temperature, pain, and helps with spatial awareness.
Occipital Lobe
Responsible for processing visual information.
Temporal Lobe
Manages hearing, memory, and understanding language.
Thalamus
Acts as a relay station, directing sensory information to the appropriate areas of the brain.
Hypothalamus
Regulates body temperature, hunger, thirst, sleep, and hormone release.
Pituitary Gland
Produces and releases hormones that control growth, metabolism, and other endocrine glands.
Pineal Gland
Produces melatonin, which regulates sleep-wake cycles.
Spinal Cord
Transmits signals between the brain and the body and coordinates reflexes.
Dendrites
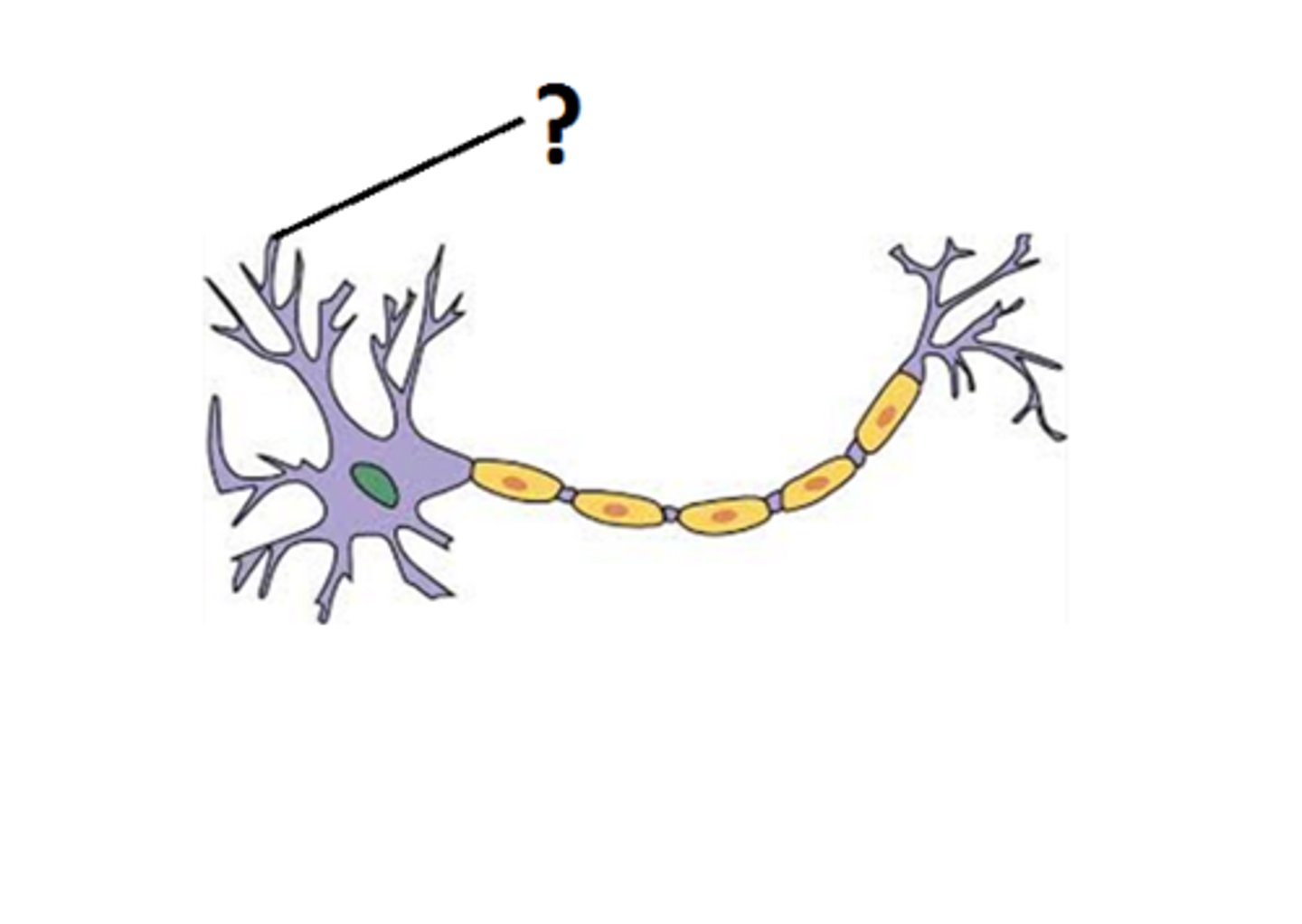
cell body
axon
axon terminal
myelin sheath
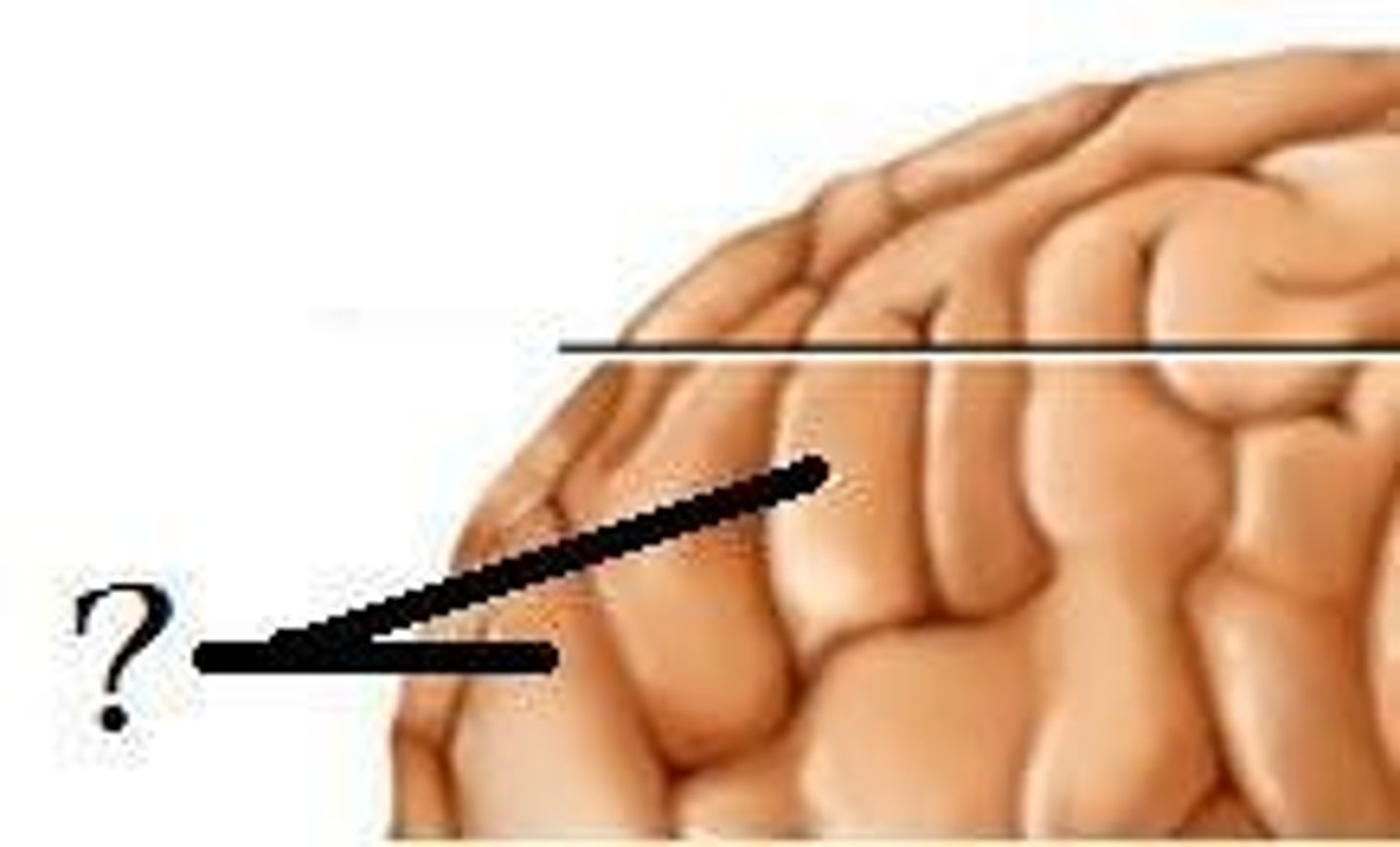
sulci
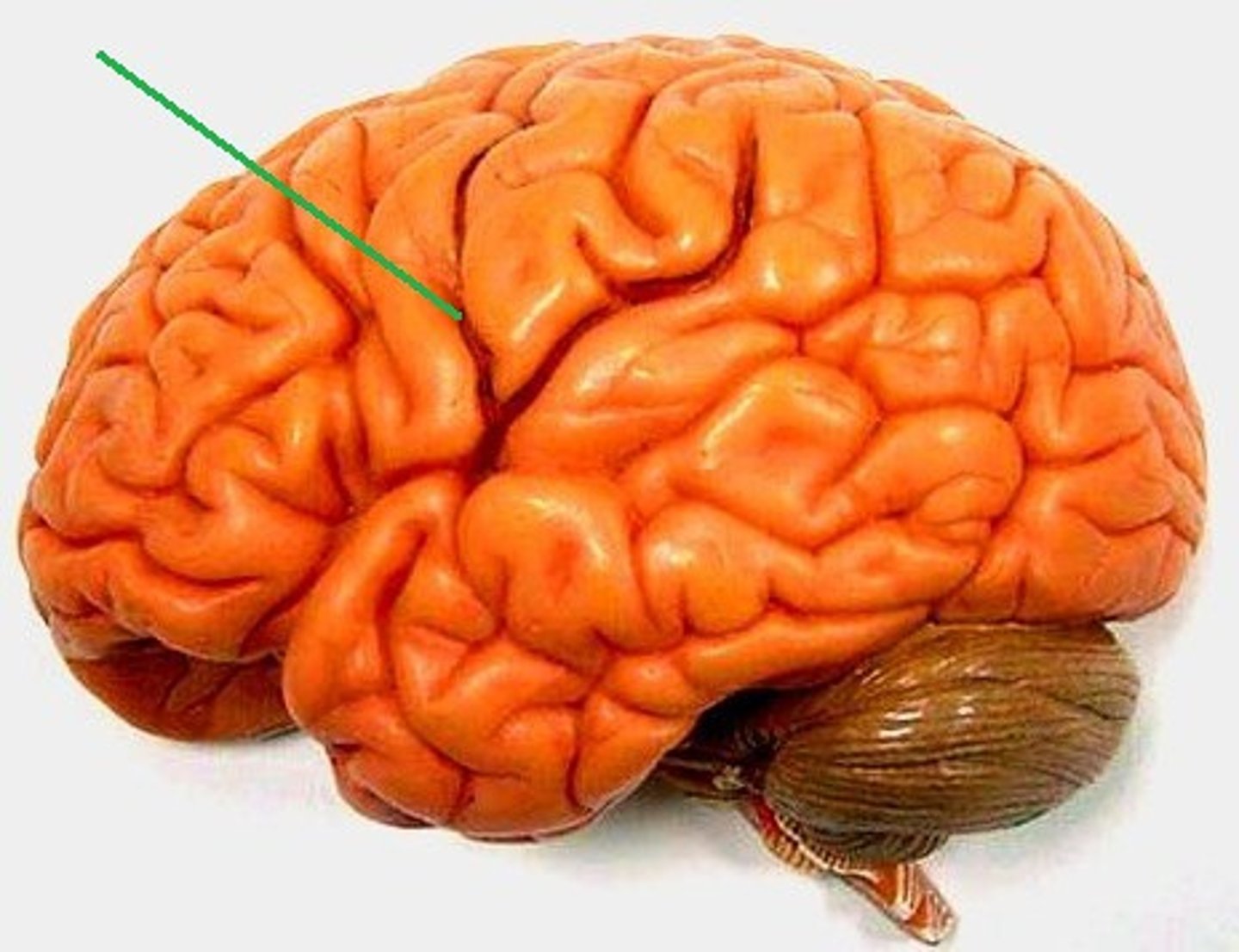
gyri