Evolutionary Biology Exam #3
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
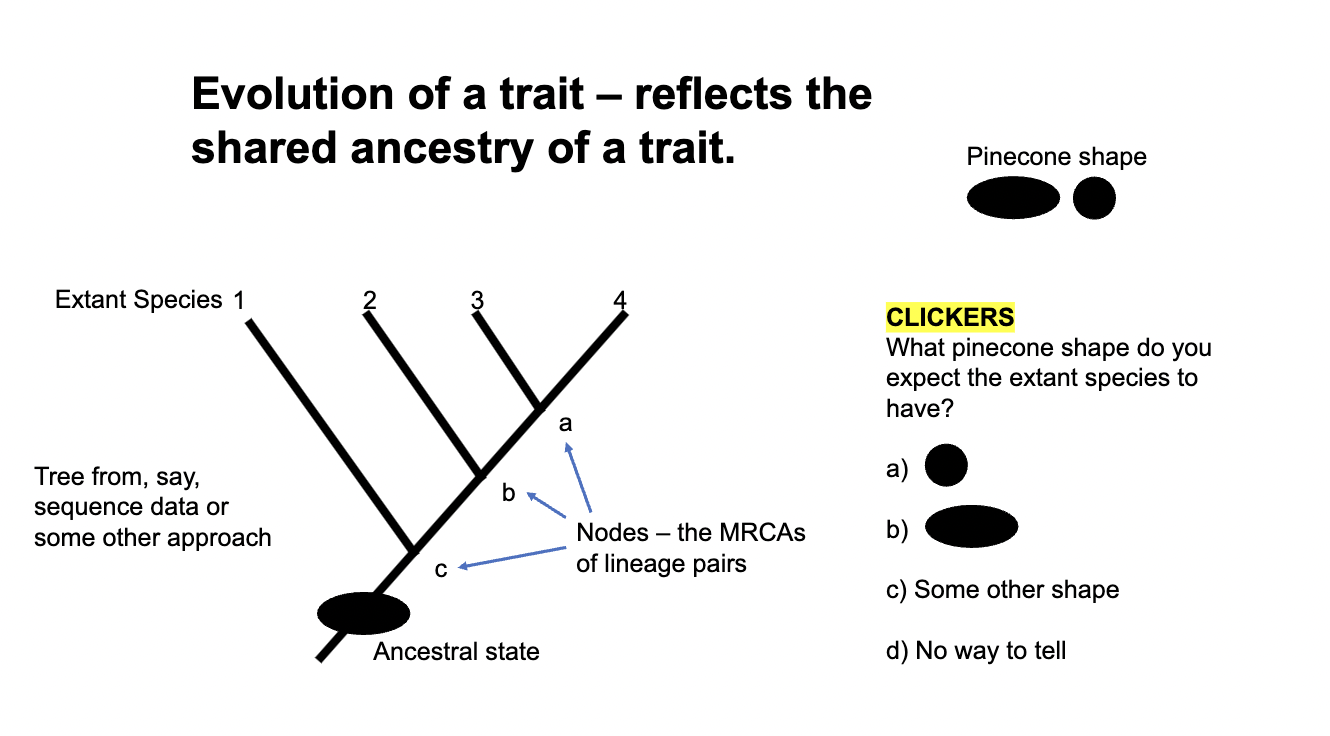
A
A) Yes
B?

E) B and C

All of them could be correct
B
B
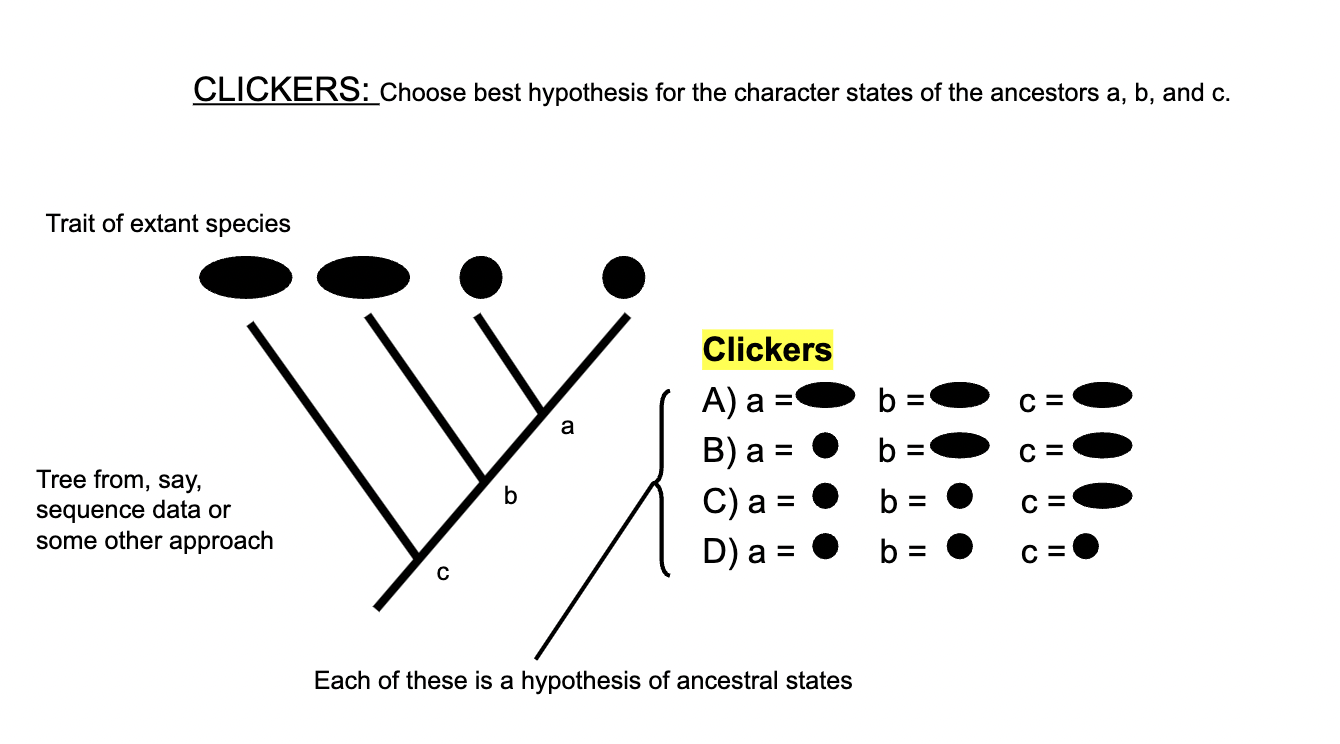
B
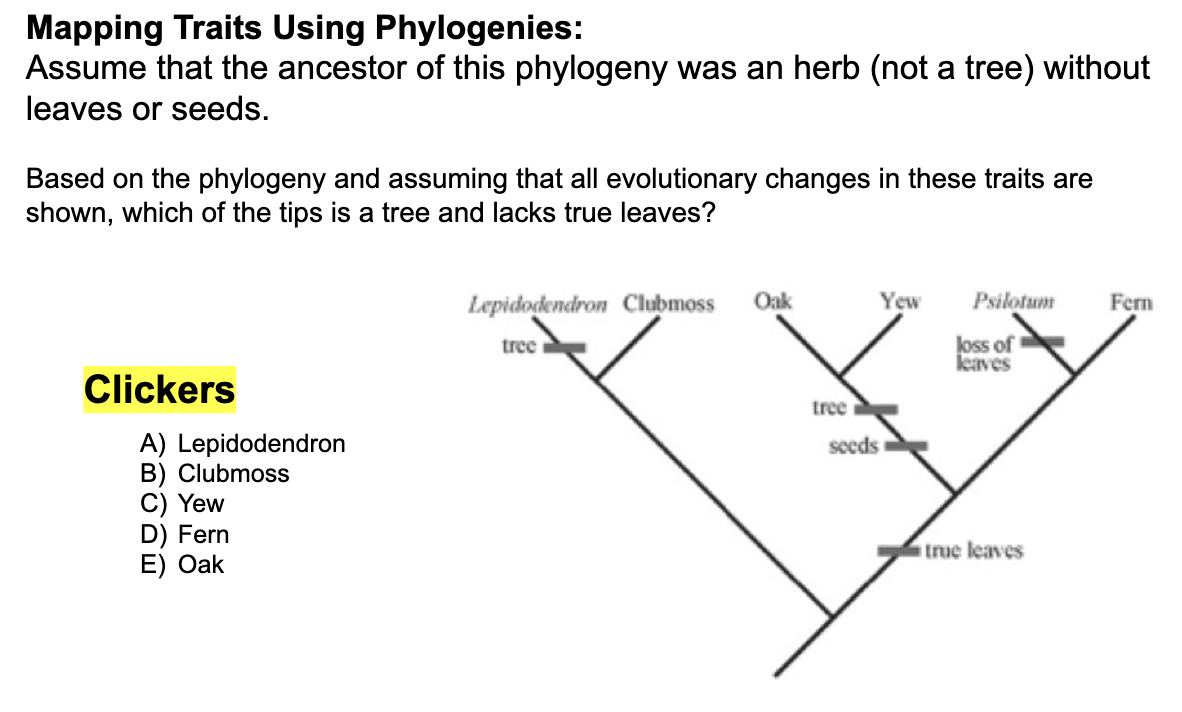
A) Lepidodendron
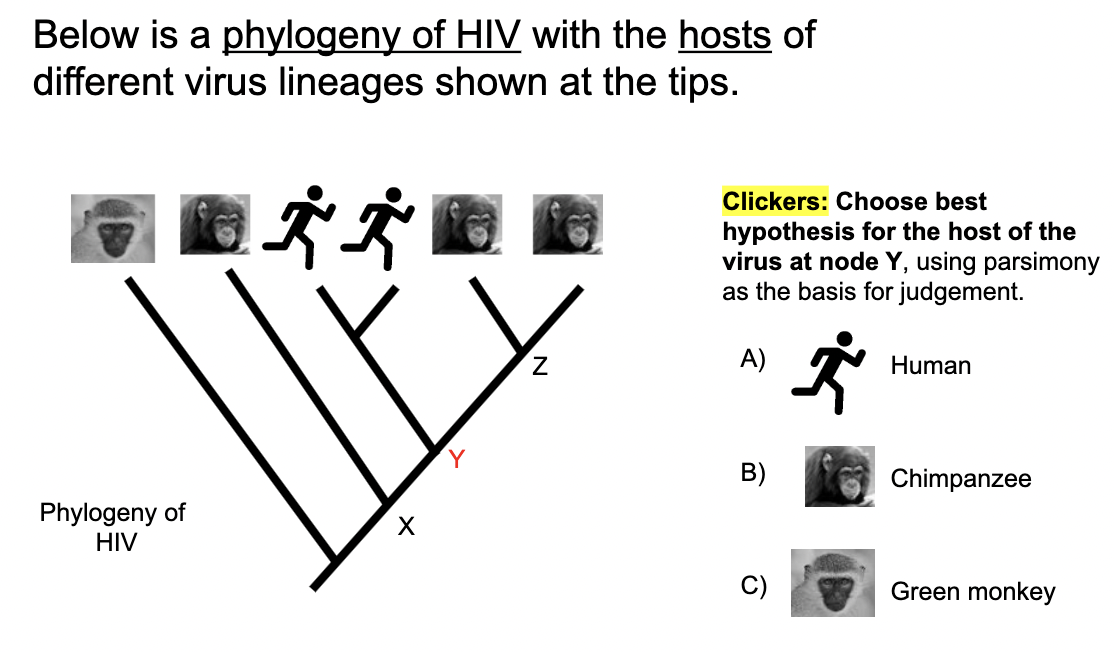
B) Chimpanzee
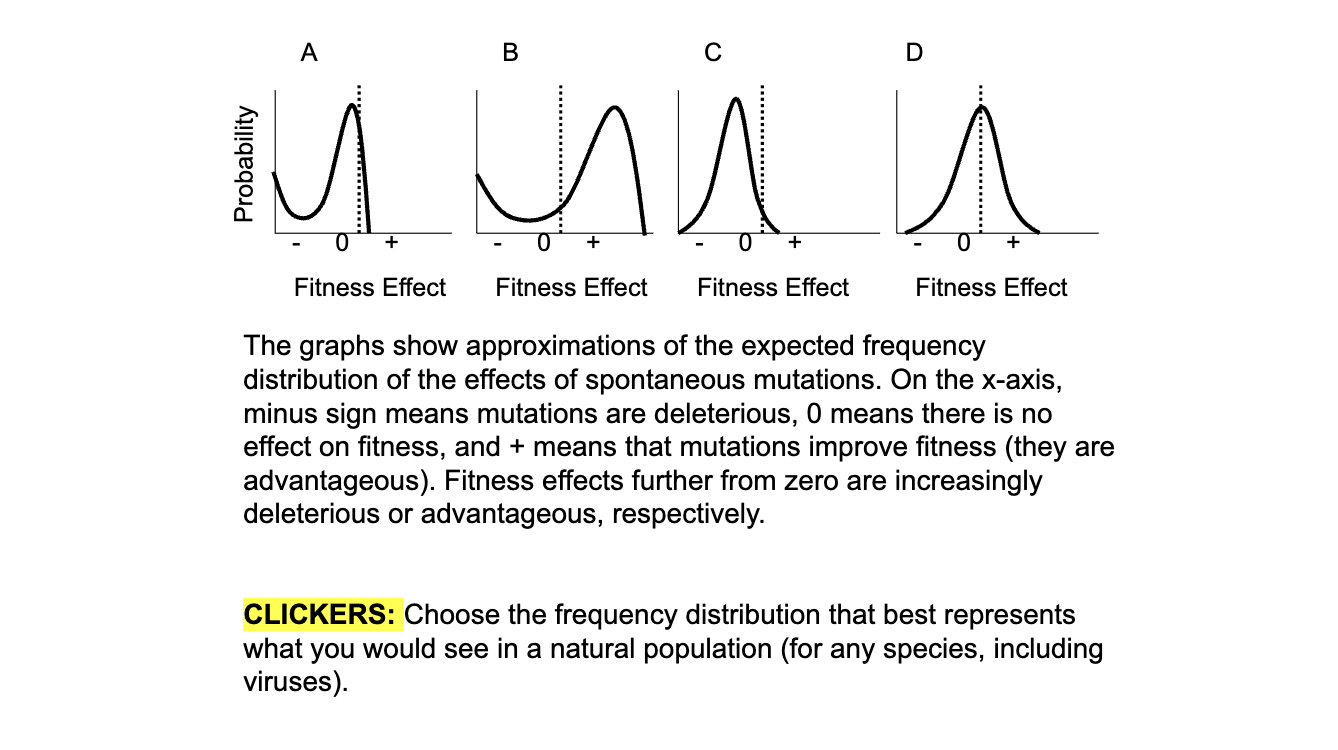
A
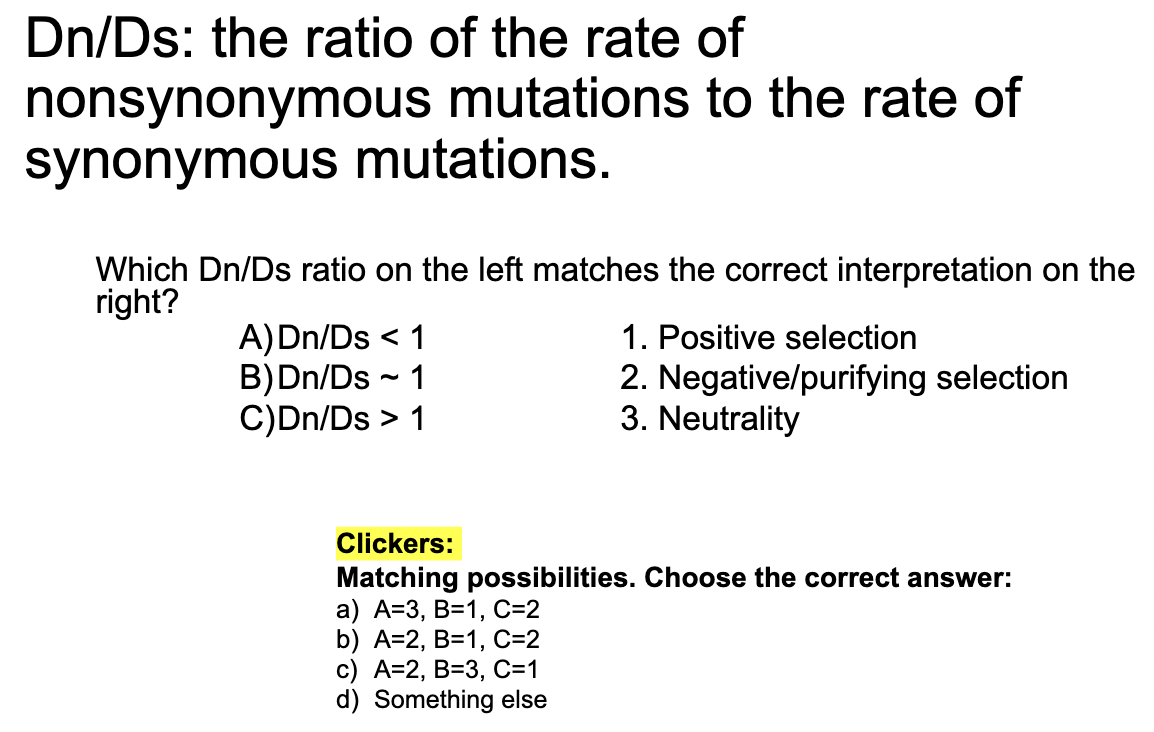
C) A = 2, B = 3, C = 1
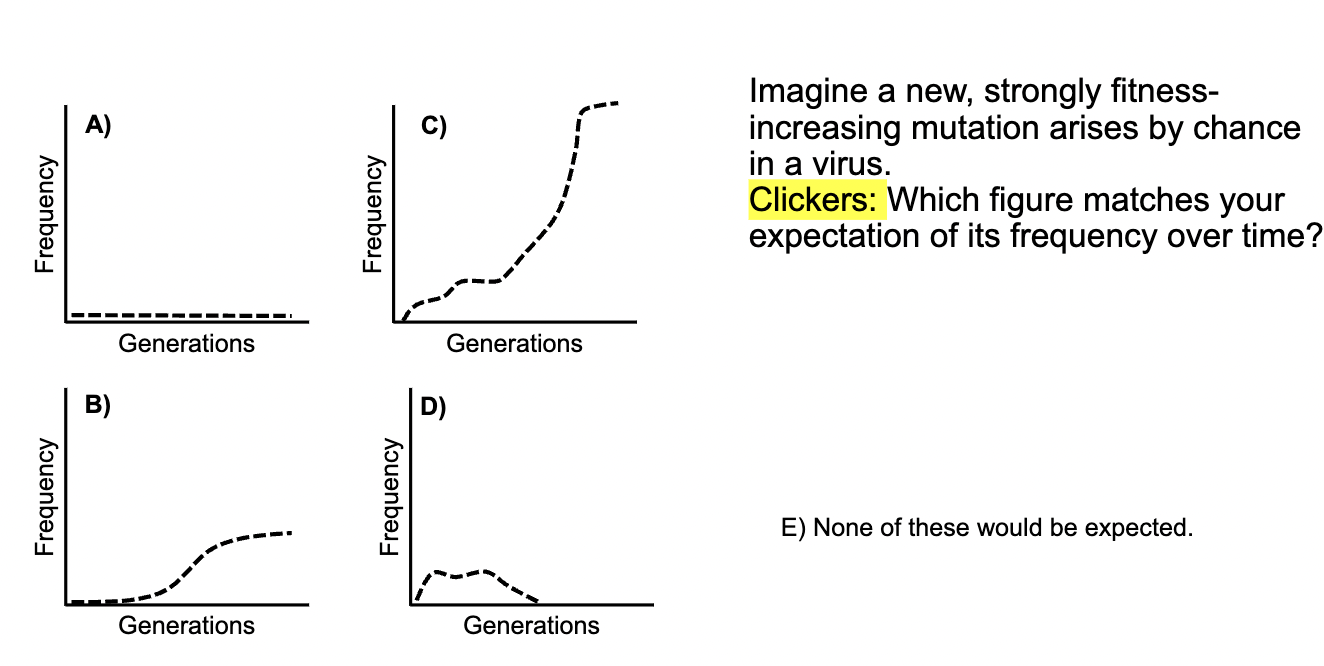
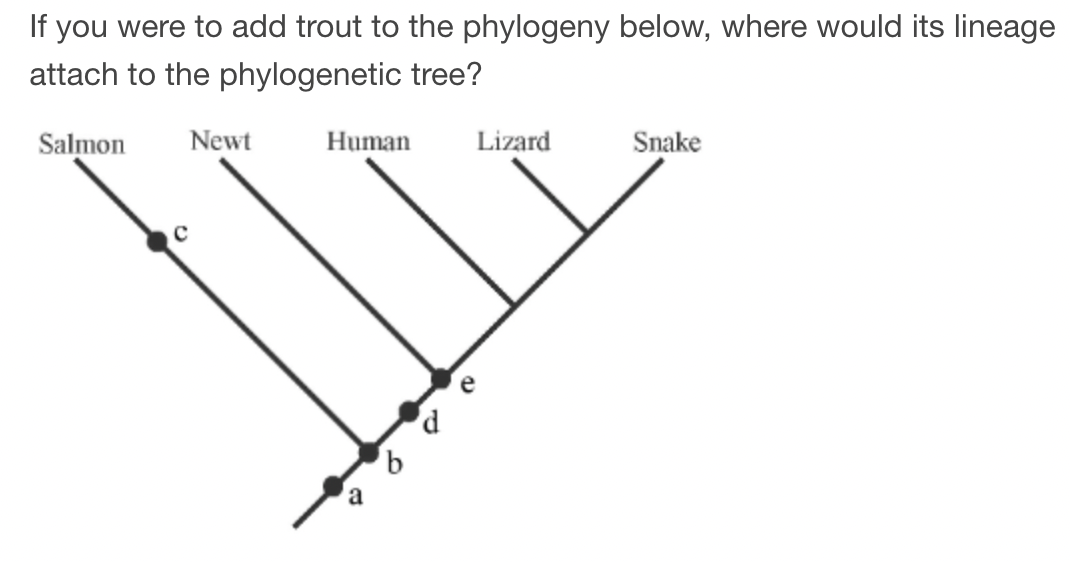
C
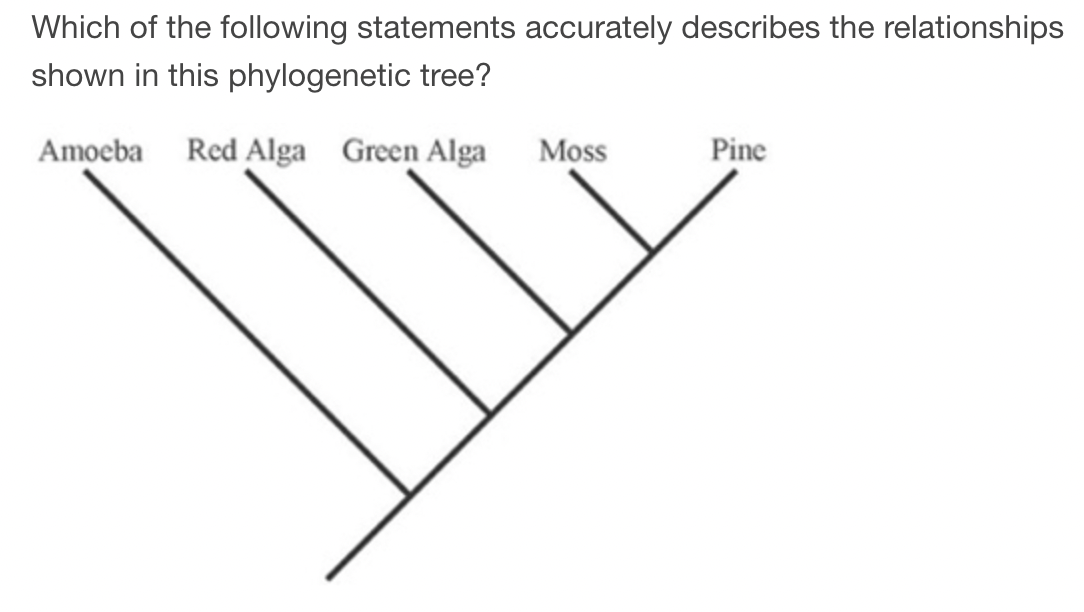
A) A green alga is more closely related to a moss than to a red alga.
B) A green alga is more closely related to a red alga than to moss.
C) A green alga is equally related to a red alga and a moss.
D) A green alga is related to a red alga, but is not related to a moss.
A) A green alga is more closely related to a moss than to a red alga

B) A crocodile is more closely related to a bird than to a lizard
C
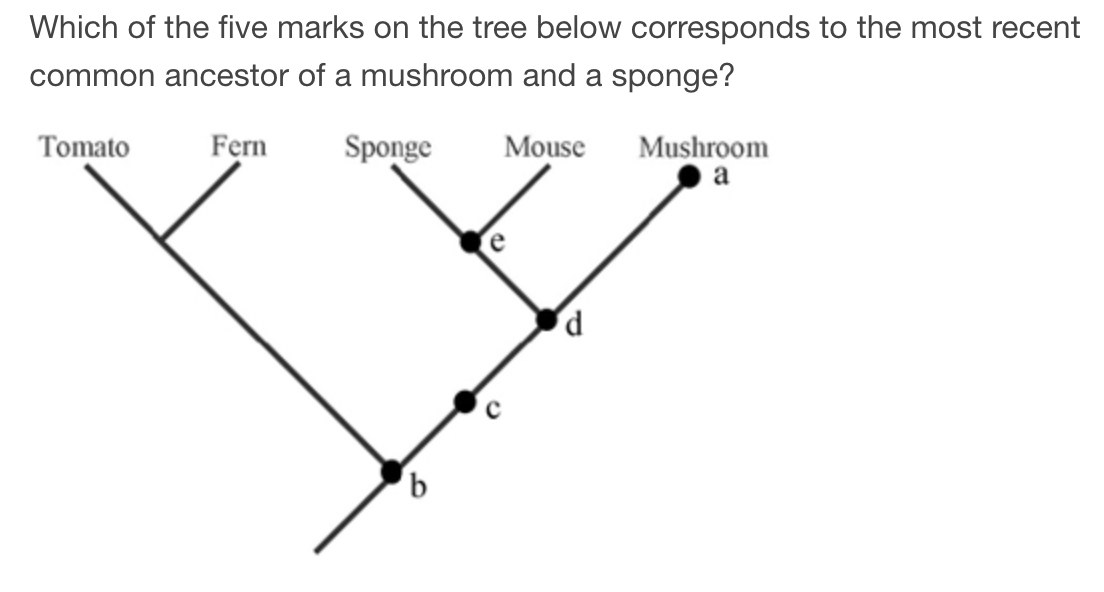
D
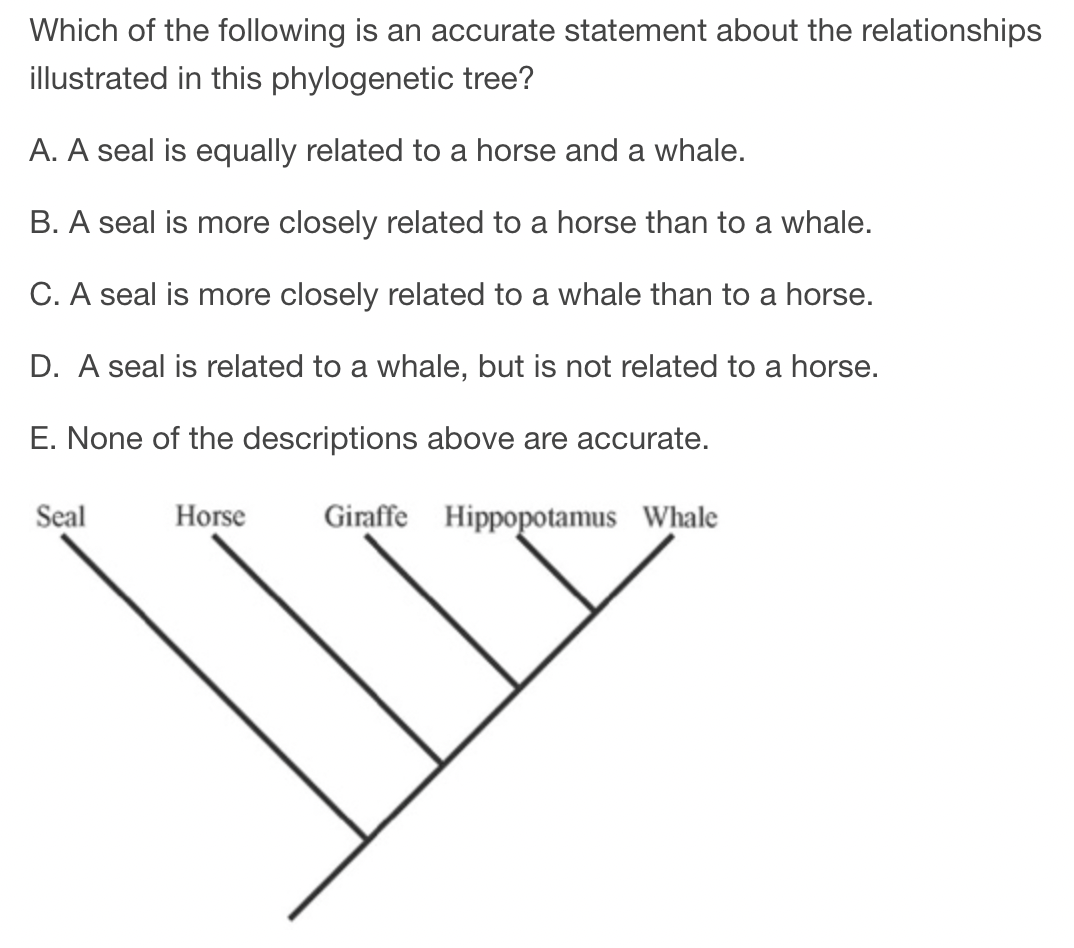
A) A seal is equally related to a horse and a whale
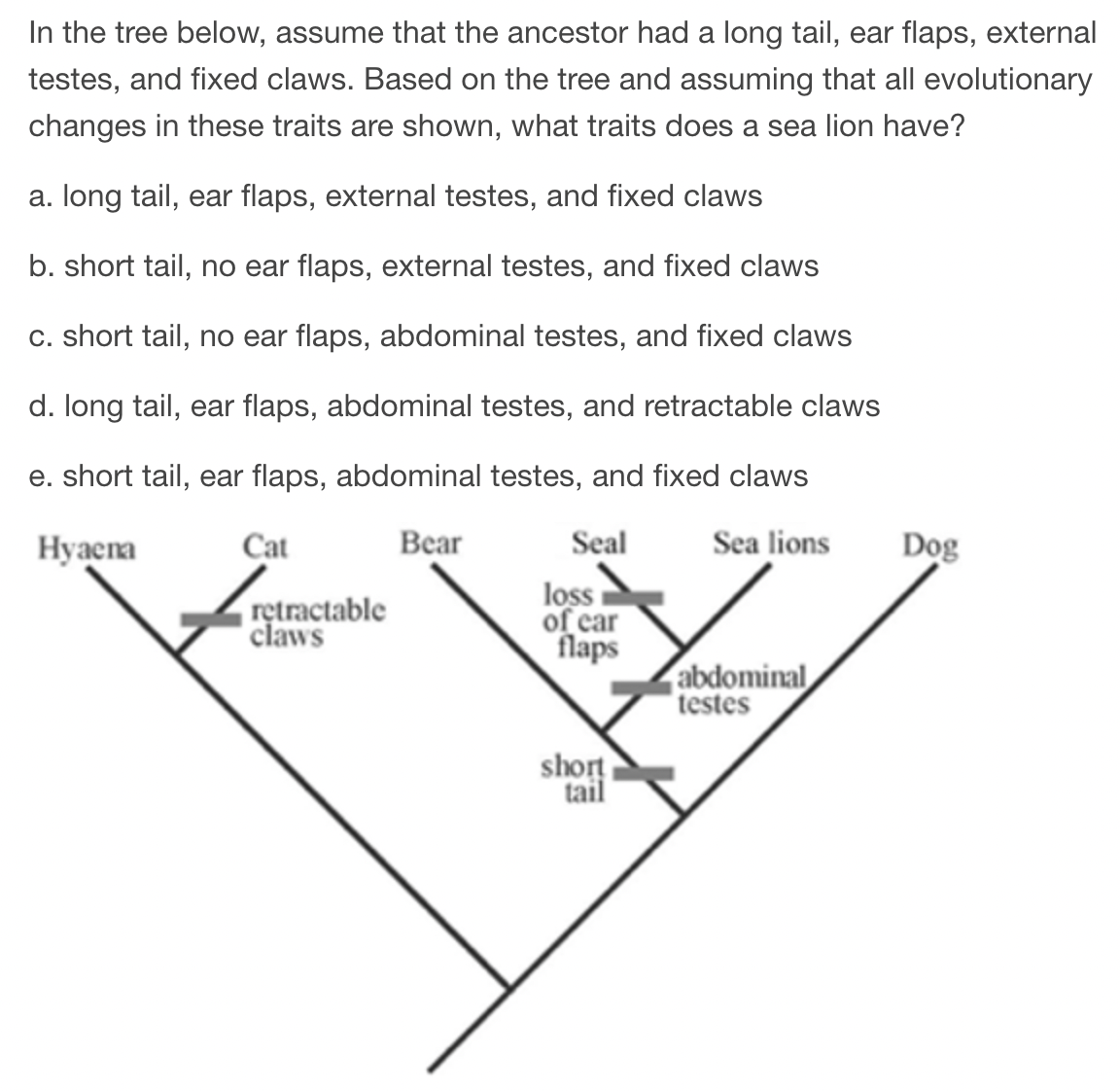
E) short tail, ear flaps, abdominal testes, and fixed claws
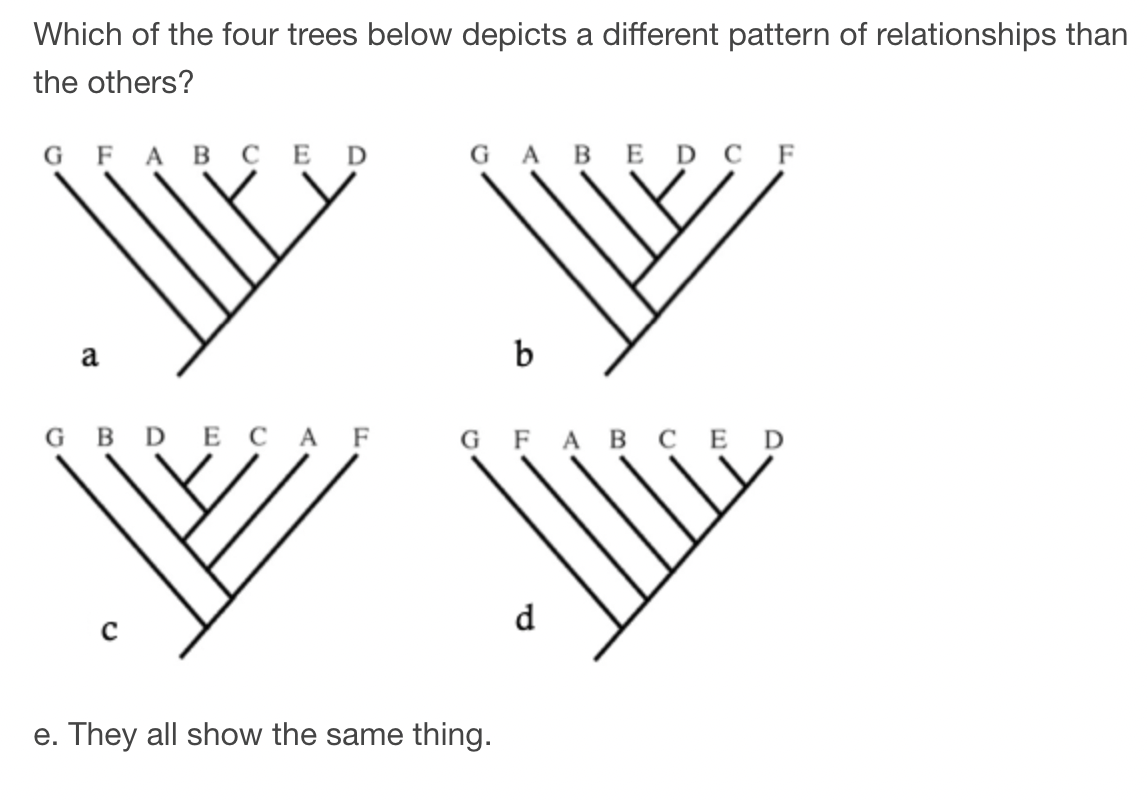
A
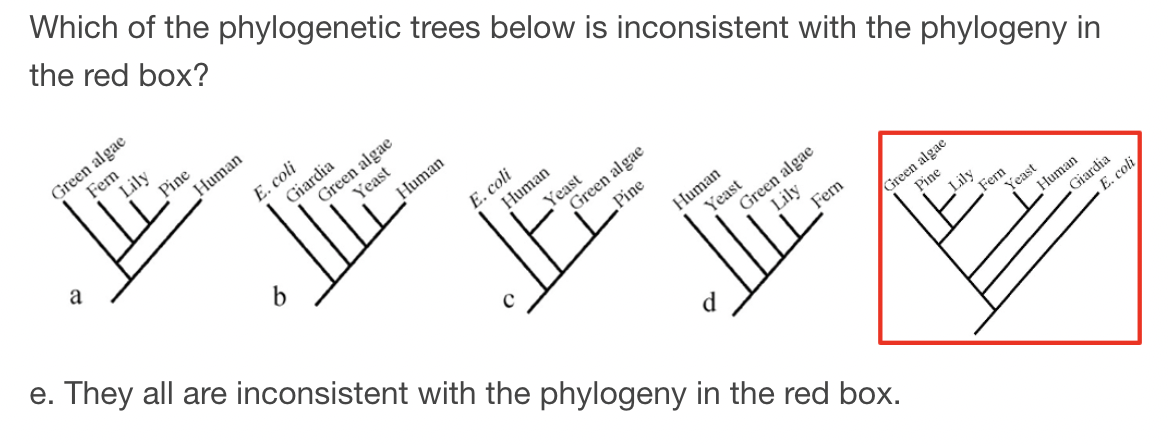
D
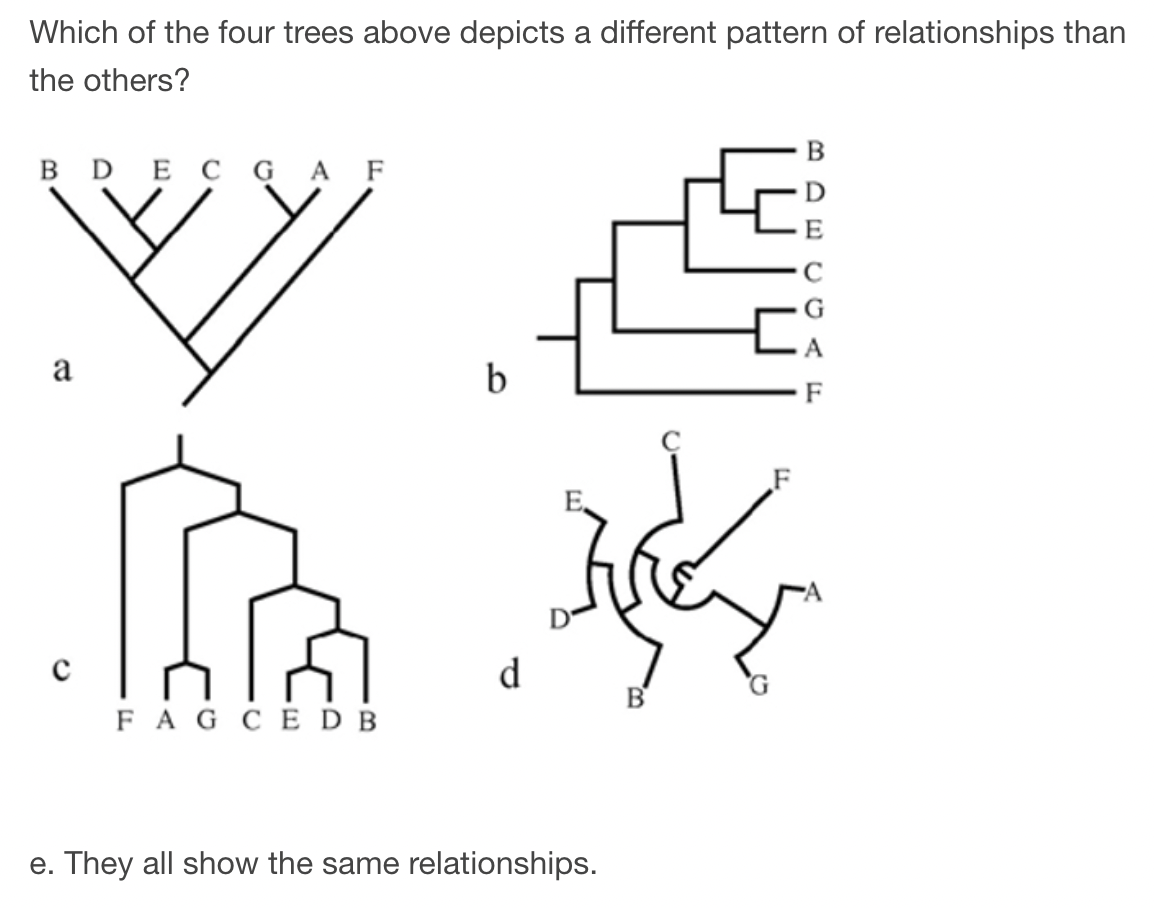
A
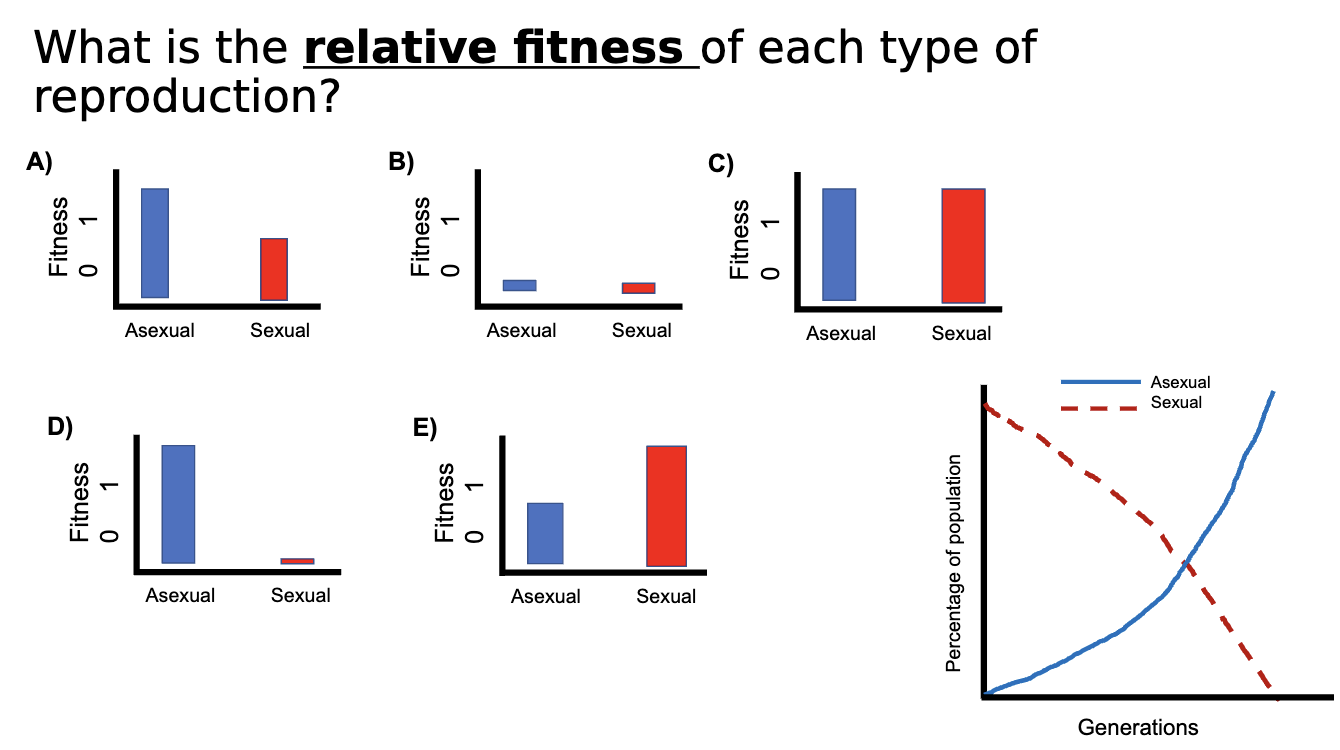
What is the two-fold cost of sex?
The difference in reproductive rate between sexual and asexual individuals, all else being equal.
The cost of energy invested in sex plus the risk of infection that accompanies sexual reproduction, all else being equal.
The fitness cost plus the energetic cost of sex relative to asexual reproduction, all else being equal.
The combined fitness costs of disease transmission, energetic requirements and reproductive output due to sexual reproduction is approximately two-times greater than asexual reproduction.
The difference in reproductive rate between sexual and asexual individuals, all else being equal.
What is the relative fitness of asexual and sexual genotypes in a population, assuming the two genotypes have identical fecundity and survivorship? (Hint: remember how to calculate relative fitness.)
0 and 1, respectively.
2 and 1, respectively.
1 and 0.5, respectively.
1 and 0, respectively.
1 and 0.5, respectively.
What evidence from the reading suggests that parthenogenesis can originate by mutation?
Recombination is suppressed when sexually reproducing.
Mutation in the osd1 gene can cause the loss of reductive meiosis and yield diploid gametes.
Most mutations are deleterious and the loss of meiosis is deleterious.
Surveys of populations indicate that parthenogenesis originates at high rates in areas with lots of radiation.
Mutation in the osd1 gene can cause the loss of reductive meiosis and yield diploid gametes.
What is the name of the kind of parthenogenesis that leads to haploid male offspring?
All kinds of parthenogenesis lead to male offspring.
Thelytoky
No kinds of parthenogenesis lead to male offspring.
Arrhenotoky
Arrhenotoky
An environment with parasites is hypothesized to favor sexual reproduction because...
parasites can evolve, so they are always changing, and sexual reproduction generates offspring that are different from each other and their parents, and thus have a greater ability to evolve in response to the parasites.
an individual produced by sexual reproduction will always have higher resistance (e.g., a stronger immune system) against a parasite than an individual produced by asexual reproduction.
an individual produced by sexual reproduction will always have a stronger recovery rate after infection by a parasite than an individual produced by asexual reproduction.
sexual reproduction produces more offspring, and thus larger population sizes that are likely to persist even under pathogen attack.
parasites can evolve, so they are always changing, and sexual reproduction generates offspring that are different from each other and their parents, and thus have a greater ability to evolve in response to the parasites.
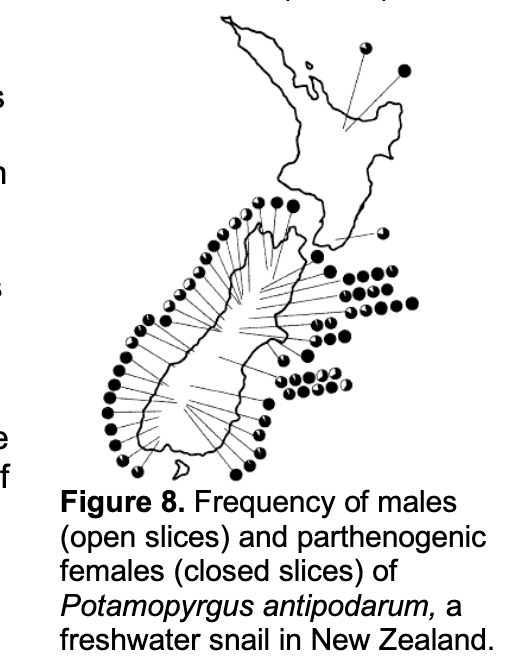
Fig. 8 of the reading assignment shows that
There is variation among snail populations in their mode of reproduction (sexual vs. parthenogenic).
sexual reproduction is more common than parthenogenic reproduction in snails across New Zealand.
there are more parasites in southern New Zealand than there are in northern New Zealand.
parasites cause snail populations to reproduce sexually.
there is variation among snail populations in their mode of reproduction (sexual vs. parthenogenic).
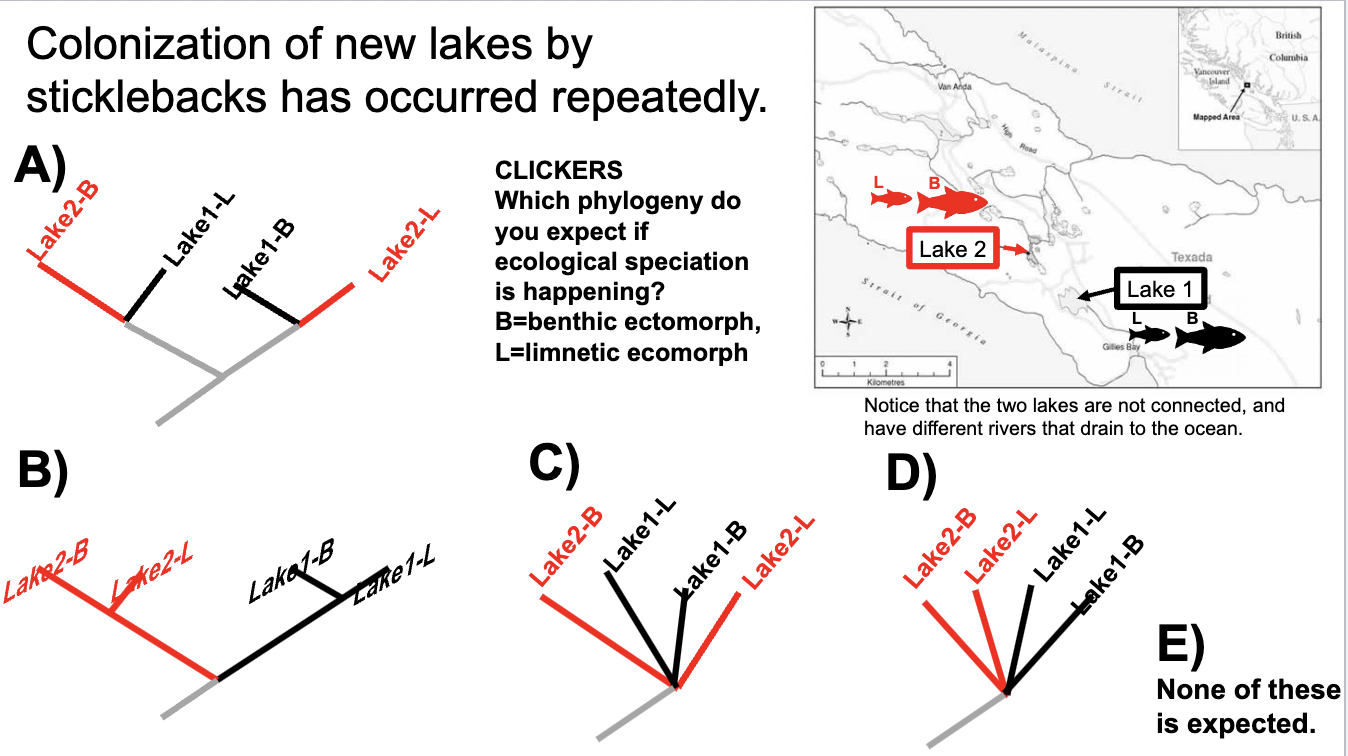
Fill in the blank: In sticklebacks, benthic-limnetic hybrids have _________ growth rate in open water compared to the limnetic form.
A) higher
B) lower
C) equal
B) lower
A limitation of the biological species concept is that
A) species are usually distinct biologically before they are distinct phylogenetically, so the biological definition of a species usually contradicts the phylogenetic definition of a species.
B) it cannot be used to distinguish species in asexually reproducing organisms.
C) it does not make a clear prediction about barriers to gene flow.
D) complex crossing designs are required to determine if two populations are capable of interbreeding or not.
B) it cannot be used to distinguish species in asexually reproducing organisms.
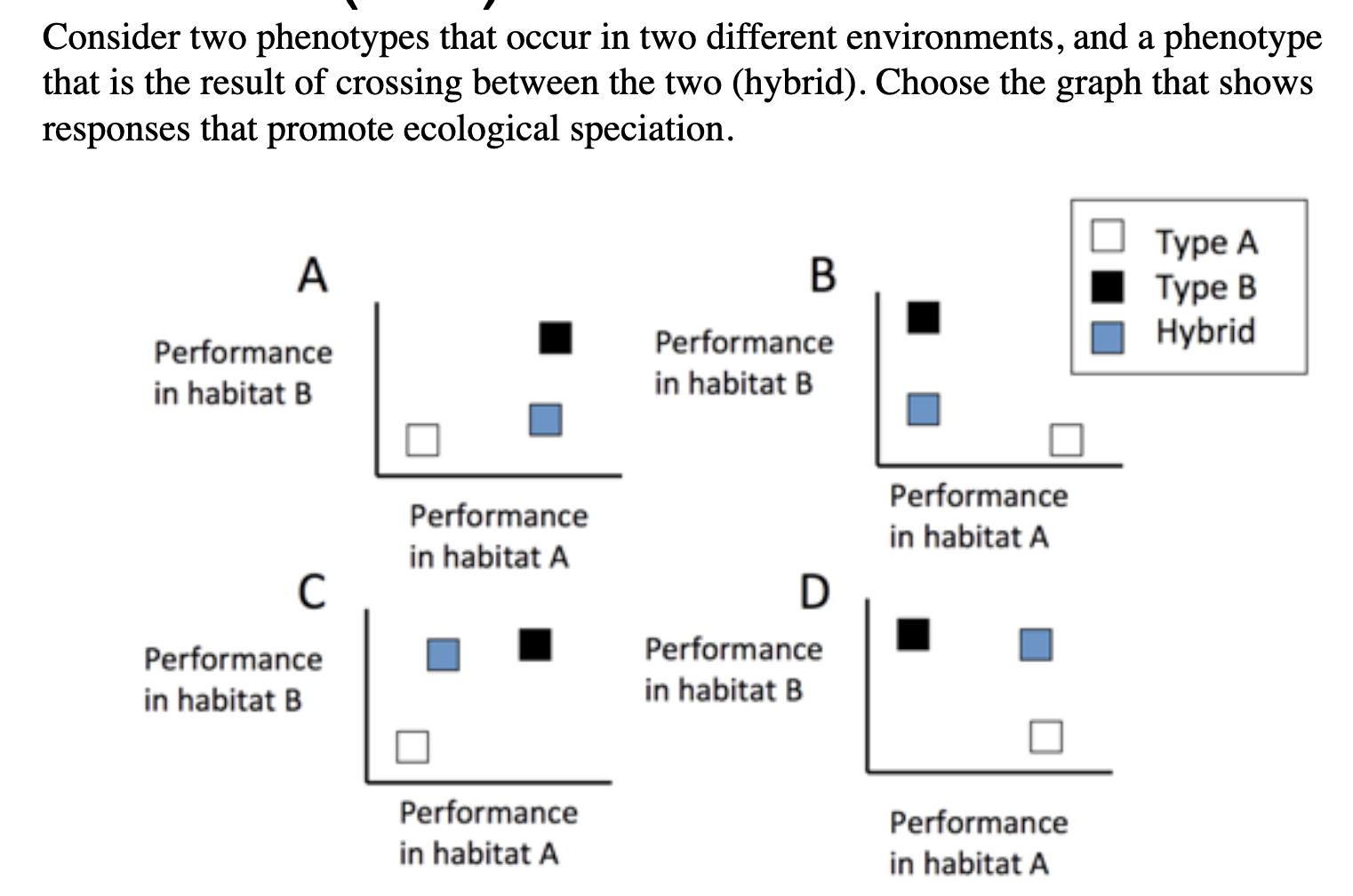
Which of the following is NOT an example of the allopatric model for speciation?
A) The rise of the Isthmus of Panama isolated populations of marine organisms in the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, eventually leading to different species on either side of the land bridge.
B) Fish populations in Death Valley that were once connected by rivers become isolated as the climate became hotter and dryer over the last 10,000 years, leaving only a few isolated springs, which now have different species of fish that share a common ancestor
C) The formation of the Grand Canyon in Arizona caused a single population of squirrels to diverge into two species, one on the north rim and another on the south rim.
D) Benthic and limnetic stickleback fish diverged within post-glacial lakes due to the presence of two niches and competition for food resources within lakes.
D) Benthic and limnetic stickleback fish diverged within post-glacial lakes due to the presence of two niches and competition for food resources within lakes.
Sister clade comparisons provide a powerful tool for testing hypotheses about diversification rates because
A) the use of sister pairs doubles the replication in any study.
B) sister pairs should always have similar diversification rates, so they introduce an inherent control into a study.
C) sister taxa are likely to have similar extinction probabilities, so they provide a control for extinction rates
D) they share a common ancestor, and thus provide a control for the total time since divergence
D) they share a common ancestor, and thus provide a control for the total time since divergence
Why are there so many species of beetles? Identify the hypothesis below for which there is strong support (based on the reading):
A) Beetles do not fly very far, so there is little gene flow among populations that occupy different regions.
B) The evolution of phytophagy in beetles allowed beetles to exploit a large suite of new niches on plant hosts, which promoted high rates of ecological speciation.
C) Beetles have unusually high mutation rates, leading to rapid evolution of reproductive isolation in allopatric populations.
D) Their modified front wings and hard exoskeleton protect them from predation, which reduces extinction risk.
B) The evolution of phytophagy in beetles allowed beetles to exploit a large suite of new niches on plant hosts, which promoted high rates of ecological speciation.