Lipids
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
What is a lipid?
Category that includes many different types of hydrophobic molecules
What are the three functional types of lipids?
Storage → triacylglycerols
Structural → sphingolipids/glycerophospholipids
Signaling → hormones
What are fatty acids?
Carboxylic acids with long hydrocarbon chains 14-20 carbons long
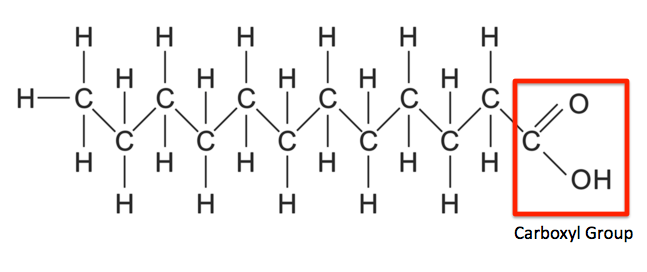
What are the three types of fatty acids? What are their characteristics?
Saturated: Full of H, no double bonds, fully reduced
Unsaturated: Double bonds, usually cis (kink)
Polyunsaturated: 2 or more double bonds
Why are fatty acids called fatty acids?
Because of the carboxylic acids at the top
Properties of saturated fatty acids
Packed tightly together with higher melting temperature
Properties of unsaturated fatty acids
Side chains flow freely past each other due to kink in chain resulting in lower melting temperature
Do cis or trans fats have higher melting temps
Trans due to their linear structure
Naturally ocurring unsaturated fatty acids almost always have ____ double bonds, putting a ____ bend in the hydrocarbon chain.
Cis
30 degree
Where are trans double bonds found?
In processed foods
How to name fatty acids
Delta
# of C: # of double bonds
Count from COOH, indicate first position of change
Indicate positions of ALL double bonds
Omega: # of C: # of double bonds
# of C: # of double bonds
Count from end
Indicate position of first double bond only with (-)
If not indicated, should you assume a fatty acid is cis or trans?
Cis
How to indicate trans omega and delta nomenclature?
trans Δ, trans ω
Structure of glyceraldehyde
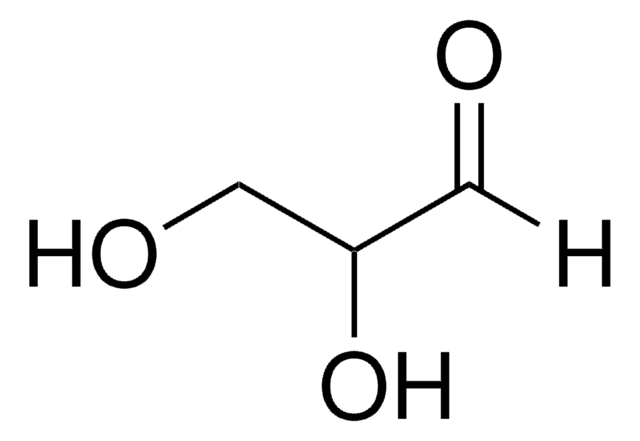
What is the backbone for carbohydrates and lipids
Glyceraldehyde and glycerol
What lipids are used as energy storage
Triglyceride = triacylglycerol (TAG)
3 fatty acids attached to glycerol backbone
How the body stores energy as fat
What are adipocytes
Fat cells specialized to store TAGS
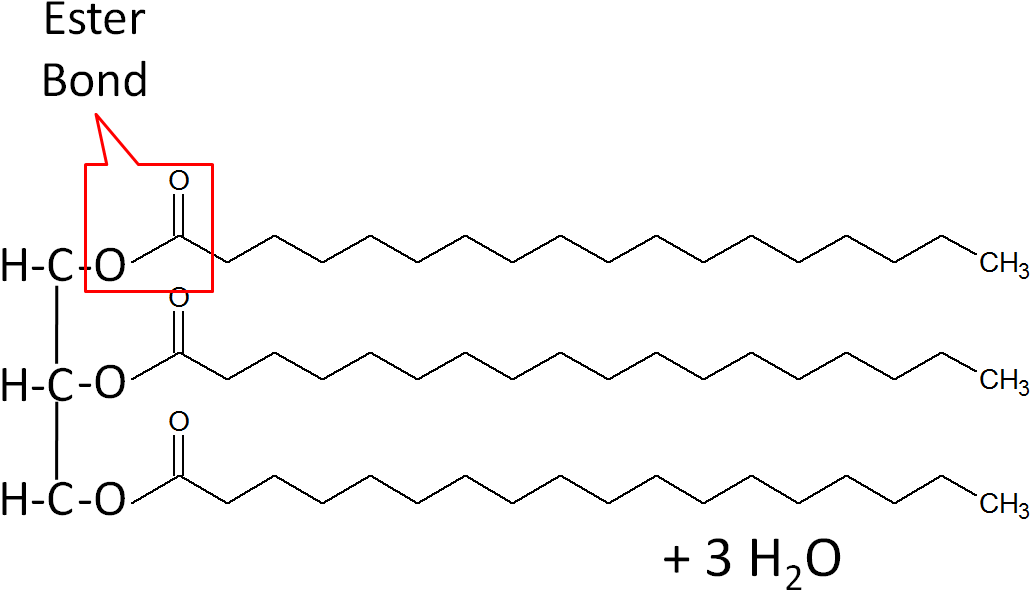
How are triglycerides formed?
condensation reaction
How are triacylglycerols (TAGS) broken down?
Lipase enzymes that hydrolyze fatty acids off a TAG
What classification of enzyme is a lipase?
Hydrolase
Do triacylglycerides, proteins or carbohydrates store energy better?
Triacylglycerides
What is SDS page?
Separating proteins based on molecular weight using an electric field and gel. SDS denatures proteins and coats them with a negative charge and PAGE provide matrix for proteins to migrate.
What are peripheral proteins?
Proteins present in the plasma membrane transiently associated with the membrane by H bonding and have electrostatic interactions.
Can be disrupted with salt or pH change
What are integral proteins?
Proteins in the plasma membrane tightly associated with the membrane by inserting itself by hydrophoboc interactions and require disruption with harsh conditions (detergent)
In what ways can membrane lipids change their orientation?
Transverse diffusion (flip-flop)
Lateral diffusion
What is transverse diffusion?
The movement from one leaflet of membrane to another (outer → cytosolic) and requires ATP or enzyme to occur
What is lateral diffusion?
Movement within the same leaflet and happens readily
What does it mean when something is fat soluble?
Can easily cross the membrane
What does it mean when something is water soluble?
Hard to cross membrane
When a molecule has more OH, is it more polar or non polar?
Polar
What is a glycerophospholipid?
Glycerol backbone
2 fatty acid tails
1 phosphate head group
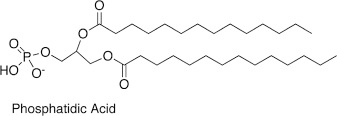
What is phosphatidic acid?
Fatty acids
Glycerol backbone
Phosphate
H
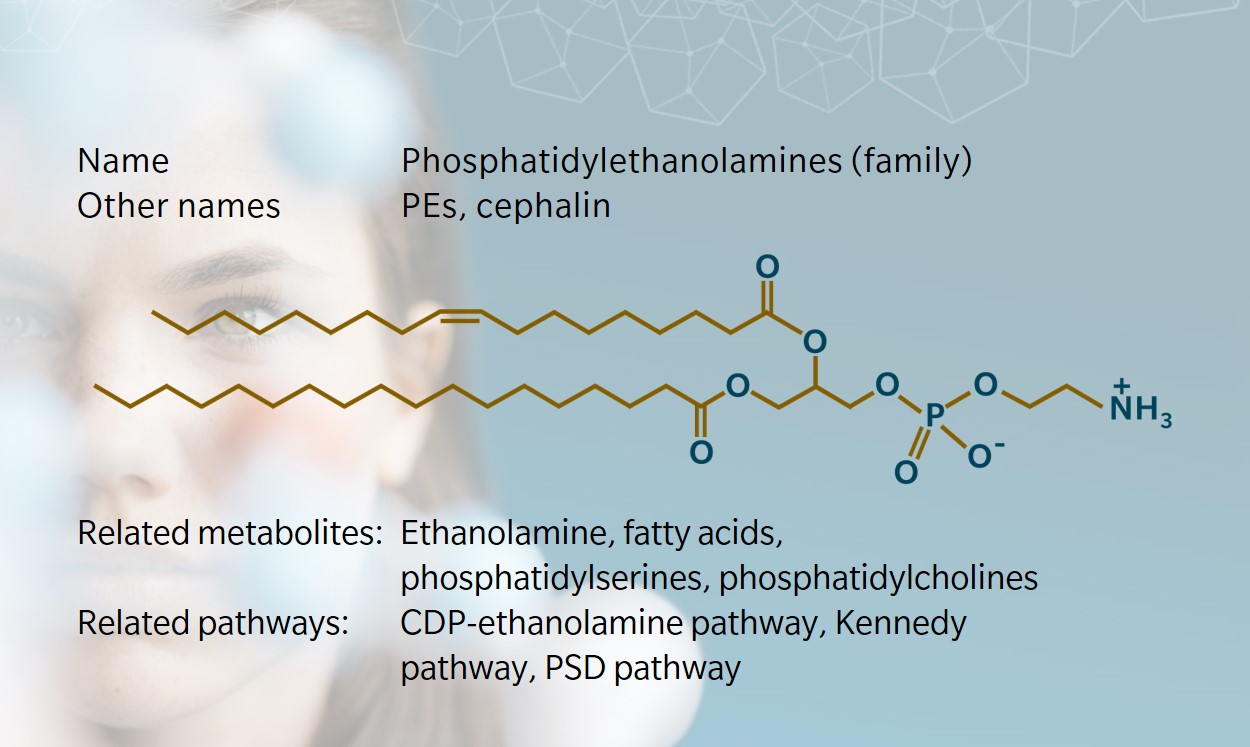
What is phosphatidylethanolamine?
Fatty acid chains
Glycerol backbone
Phosphate
OCH2CH2NH3+
What is phosphatidylcholine?
Fatty acid chains
Glycerol backbone
Phosphate
OCH2CH2N+(CH3)3
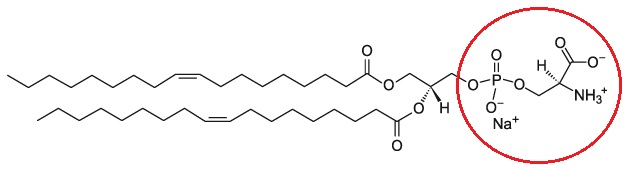
What is phosphatidylserine?
Fatty acid chains
Glycerol backbone
Phosphate
OCH2NH3+COOH
Net charge of phosphatidic acid at pH 7
-2
Net charge of phosphatidylethanolamine at pH 7
0
Net charge of phosphatidylcholine at pH 7
0
Net charge of phosphatidylserine at pH 7
-1
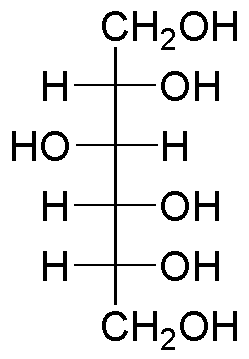
What are sugar alcohols?
No carbonyl, instead have CH2OH at top and bottom of fischer projection, no O in ring
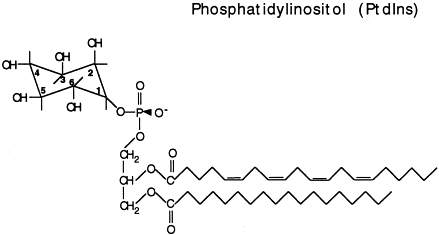
What is phosphatidylinositol?
Diacylglycerol (DAG) + phosphate + inositol inserted into membrane with fatty acid
How does phosphatidylinositol signaling work?
Pip2 is cleaved by phospholipase C to release DAG and IP3
What are glycerophospholipids ether lipids?
Ether lipids: 1 fatty acid chain linked to diacylglycerol by ether (R-O-R) linkage instead of ester
What are galactolipids?
No phosphate head group, instead have galactose
Most abundant membrane lipid
What role do galactolipids play in plants?
They are essential for thylakoid membranes in chloroplasts, and are involved in photosynthesis and chloroplast development
What are waxes?
Alcohol + fatty acids via ester linkage with no glycerol backbone (hydrophobic)
What are sphingolipids?
Fatty acids with a sphingosine
What are sphingosines?
18 carbon amino alcohol with trans double bonds and long fatty acid chains
What are glycosphingolipids?
Sugar + sphingolipid
What role do glycosphingolipids play in the body?
Determining blood type
How do O, A, and B blood types differ?
1 sugar difference
O = missing last sugar
A = GelNAc last sugar
B = Gal last sugar
For people with A blood type, what antibodies do they have and what antigens are present on their RBCs?
Anti-B antibodies in plasma
A antigen in RBC
For people with B blood type, what antibodies do they have and what antigens are present on their RBCs?
Anti-A antibodies in plasma
B antigen in RBC
For people with AB blood type, what antibodies do they have and what antigens are present on their RBCs?
No antibodies in plasma
A and B antigens in RBC
For people with O blood type, what antibodies do they have and what antigens are present on their RBCs?
Anti-A and Anti-B antibodies in plasma
No antigens in RBC
What allows AB blood types to get blood from any blood type?
No antibodies against any other blood types
What allows O blood types to donate to all blood types?
No antigens on RBCs
What are antigens?
Molecules that generate an antibody response
What are sterols?
Lipids with 4 fused rings
3 are 6-membered
1 is 5-membered
When more OH are present on a molecule is it more hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
Hydrophilic
What do bile acids do?
Surround fat to make it more soluble
What are steroid hormones?
Oxidized derivatives of sterols and more soluble due to polar substituents
What are the fat soluble vitamins?
A, D, E, K
What is retinal?
A form of vitamin A and a required cofactor covalently bound to rhodopsin (GPCR)
What is rhodopsin?
A photoreactive protein with a G protein couple receptor formed in the retina from B-carotene
When interacting with light: cis → trans isomerization of cofactor retinal and induces a conformational change G protein cascade = vision
What is vitamin D, E and K?
D = calcium uptake
E = antioxidant
K = blood clotting
What two components are waxes made of?
A long chain fatty acid and a long chain alcohol
Which type of linkage is used to join fatty acids to a glycerol?
An ester linkage
Which type of membrane proteins have transmembrane alpha helices?
Integral membrane proteins
Forming a triglyceride from a glycerol backbone and fatty acids requires what type of reaction?
Condensation (building molecules)
If the pH is less than the pKa, is the molecule protonated or deprotonated?
If the pH is greater than the pKa, is the molecule protonated or deprotonated?
Protonated
Deprotonated
What types of interactions hold peripheral proteins onto the membrane?
Non-covalent
H bonding
Electrostatic interactions
What types of interactions hold integral proteins onto the membrane?
Hydrophobic interactions
What is the most abundant membrane lipid in photosynthetic organisms?
Galactolipids
How to read a hydropathy plot
Positive values: Indicate a more hydrophobic (water-repelling) region, which is likely buried within the protein's core or embedded in a cell membrane.
Negative values: Indicate a more hydrophilic (water-attracting) region, which is likely exposed to the aqueous environment on the protein's surface.
How to know how many transmembrane regions a protein has based on hydropathy plot
The peaks of the graph correspond to transmembrane domains b/c high indices indicate hydrophobicity
Why are lipid rafts semi-solid and why do these clusters tend to aggregate within the membrane?
Lipid rafts are semi-solid because they are liquid-ordered domains enriched in cholesterol and saturated sphingolipids that pack together more tightly than the surrounding, more fluid, liquid-disordered membrane