Quiz 2 - Freezing point depression
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
The units used for concentration in freezing point depression and boiling point elevation experiments are:
Moles solute/kg solvent (Moles/kg)
In the equation ΔT = Kf x Concentration, what are the units for Kf ?
C x kg solvent/moles solute
Colligative properties depend upon ____________.
The number of solute particles
The solution has to be continually stirred during the freezing process to collect accurate results. (t/f)
True
Kf x m
ΔTf
Molality of solution is calculated by
ΔTf/Kf
Moles of solute are calculated by
Molality of solution x mass of solvent (mole/kg x kg)
Molar mass of solute is calculated by
Total mass of solute/moles of solute
A student performing a freezing point depression experiment had some solid solute stick to the side of the test tube and not dissolve in the solution. How does the undissolved solute affect the freezing point of the solution?
Freezing point lower, temp higher
Freezing point lower, temp lower
Freezing point higher, temp lower
Freezing point higher, temp higher
Freezing point higher, temp lower
A student performing a freezing point depression experiment had some solid solute stick to the side of the test tube and not dissolve in the solution. How does the undissolved solute affect the calculated molar mass?
Molar mass will be higher because the change in temperature will be lower.
Molar mass will be higher because the calculated moles will be higher.
The molar will not be affected.
Molar mass will be lower because the change in temperature will be higher.
Molar mass will be lower because the calculated moles will be lower.
Molar mass will be higher because the change in temperature will be lower.
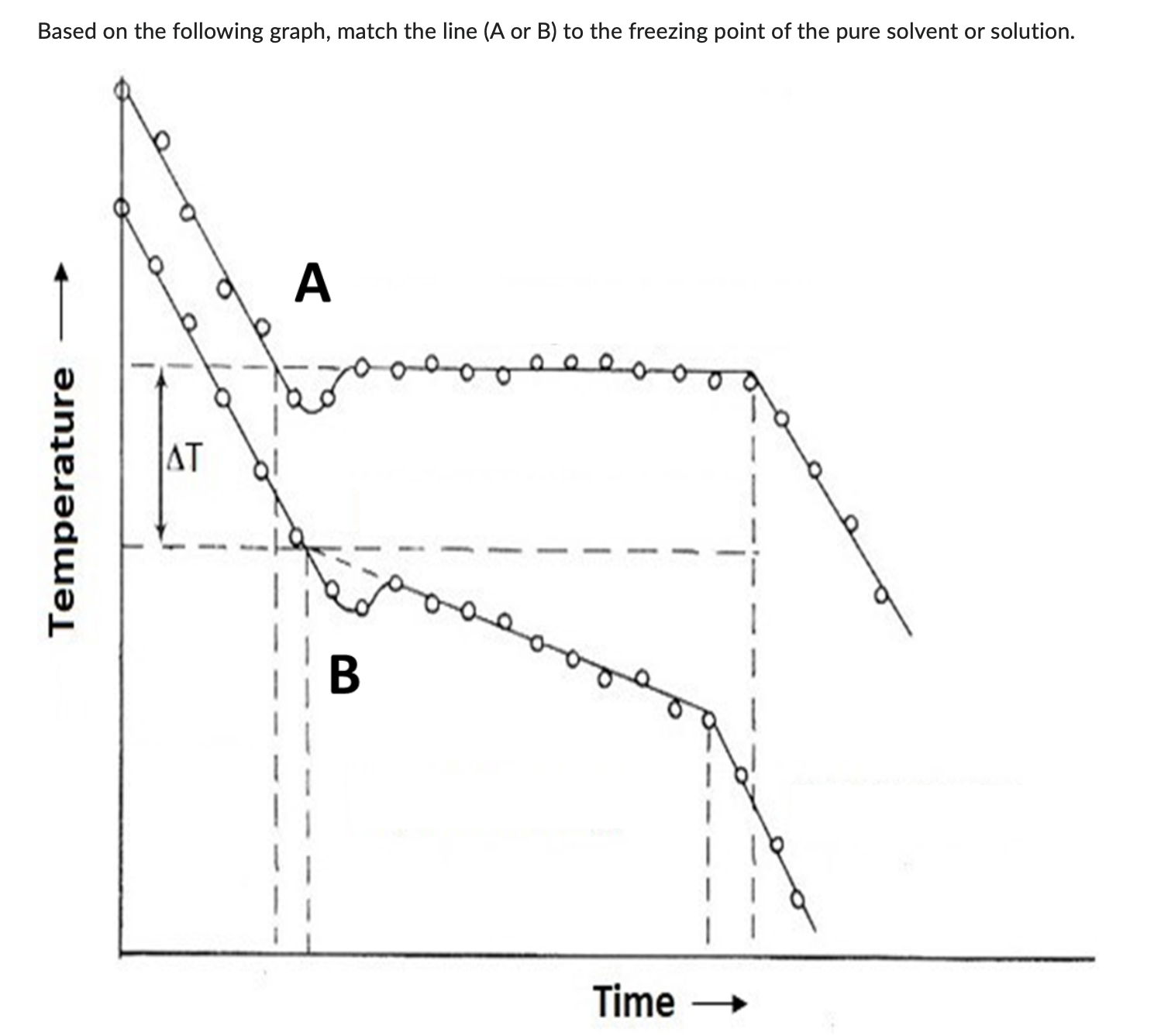
Freezing point of pure solvent
Freezing point of solution

A is freezing point of pure solvent
B is freeing point of solution
A 0.7445 g sample of unknown solute is dissolved in 15.6 g of cyclohexane. The resulting solution has a freezing point of -2.04 oC. For cyclohexane, Tf is 6.50 oC and Kf is 20.0 oC kg/mol.
Calculate Change of Tf . You do not need to include the units, oC.
Calculate the molality of the solution
Calculate the number of moles of solute in the solution
Calculate molar mass of the solute
6.50 -(-2.04)=8.54 8.54 (ΔTf=Tf∘−Tf)
ΔTf=Kf⋅m where m=8.54/20.0=0.427 mol/kg
m= moles of solute/kg of solvent sp 0.427 × 0.0156 = 0.00666 mol
mass of solute/moles of solute so 0.7445/0.00666=112 g/mol