EX1 Medchem Questions
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Differences between sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system
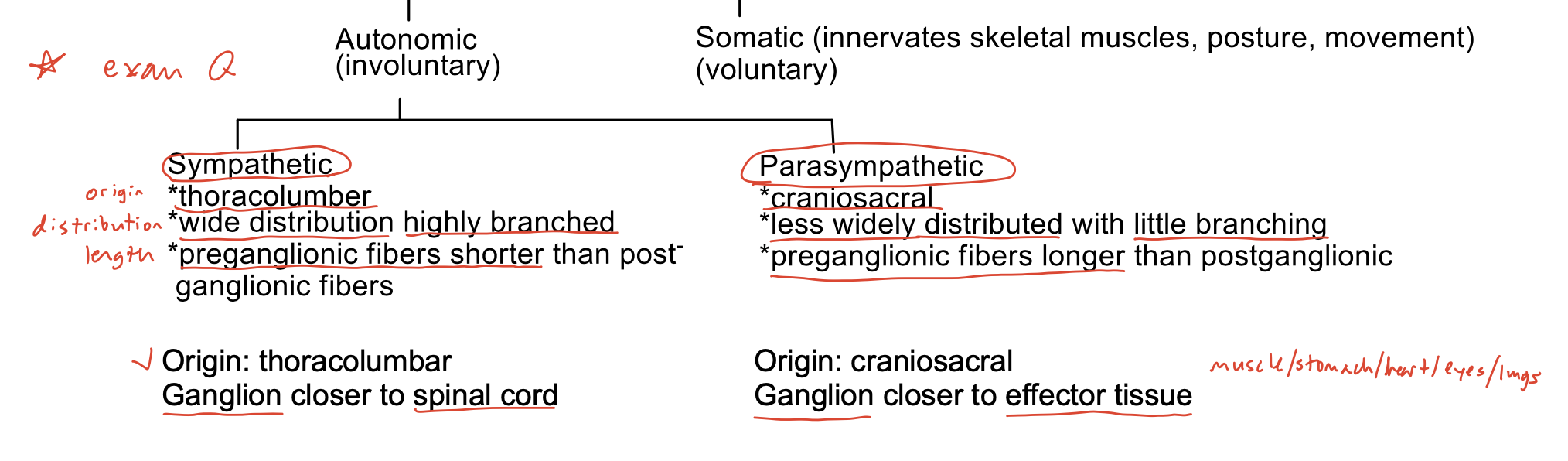
The sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system act
opposite of one another
Chemical Neurotransmission in the Peripheral (and Central) Nervous System
“place in order” question
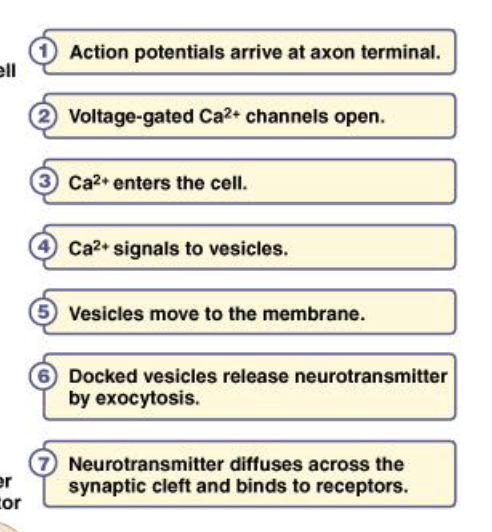
In general, most neurotransmitters function via the following steps:

Biosynthesis of acetylcholine drop a pin Q

Is calcium the neurotransmitter or is it part of the signal?
Part of the signal (secondary messenger)
fill in blank type of Q
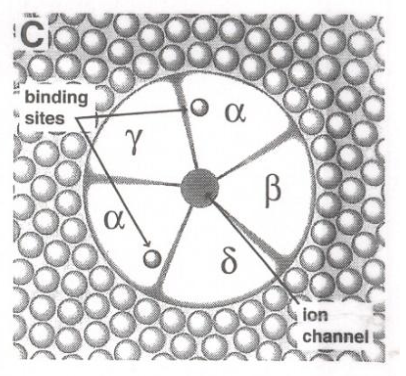
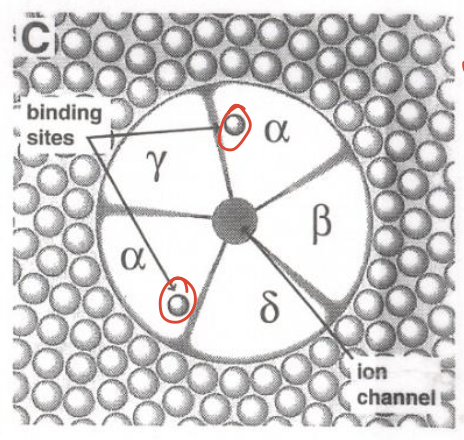
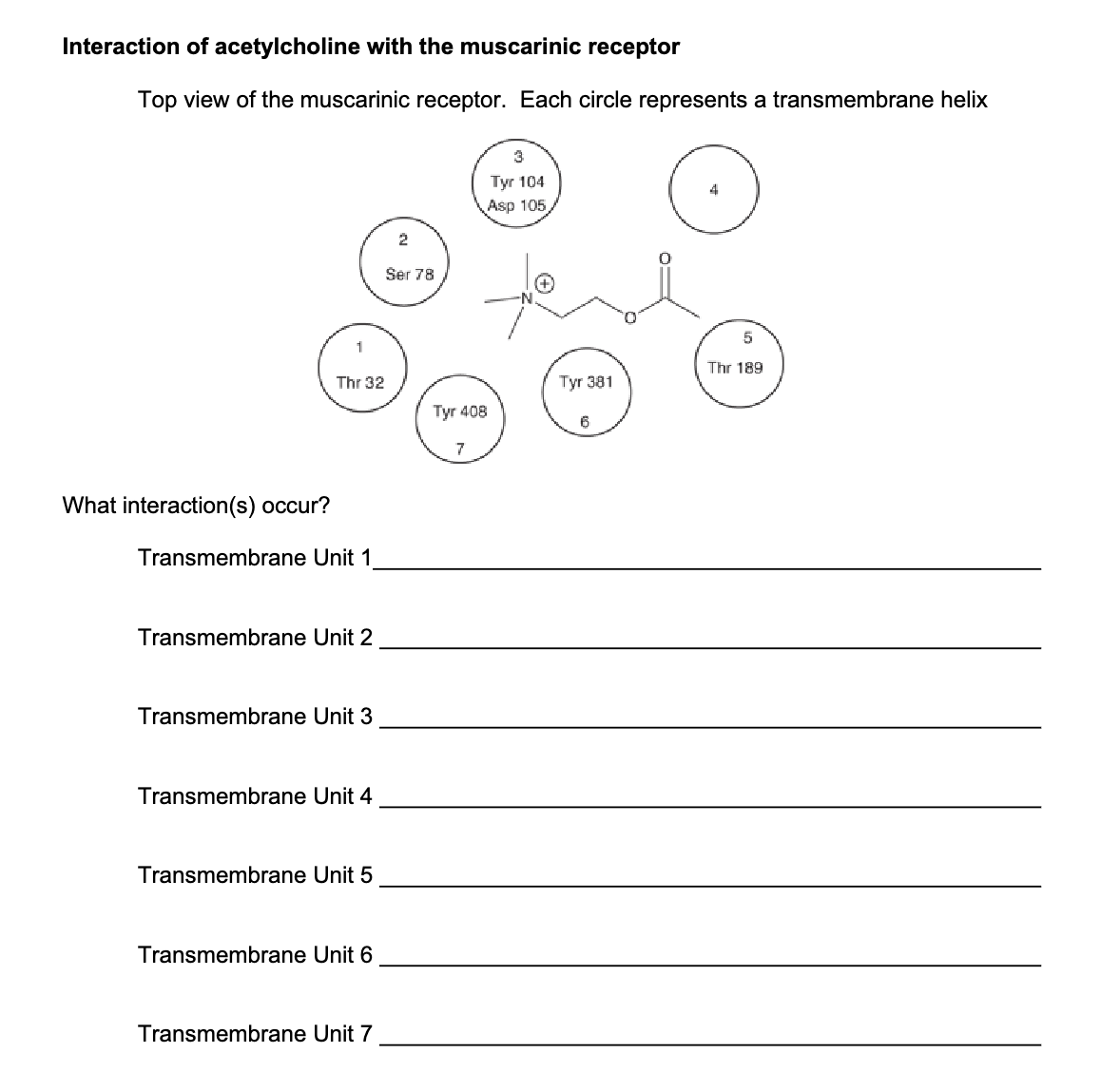
“If I show you this, know where ACh binds”

story problem
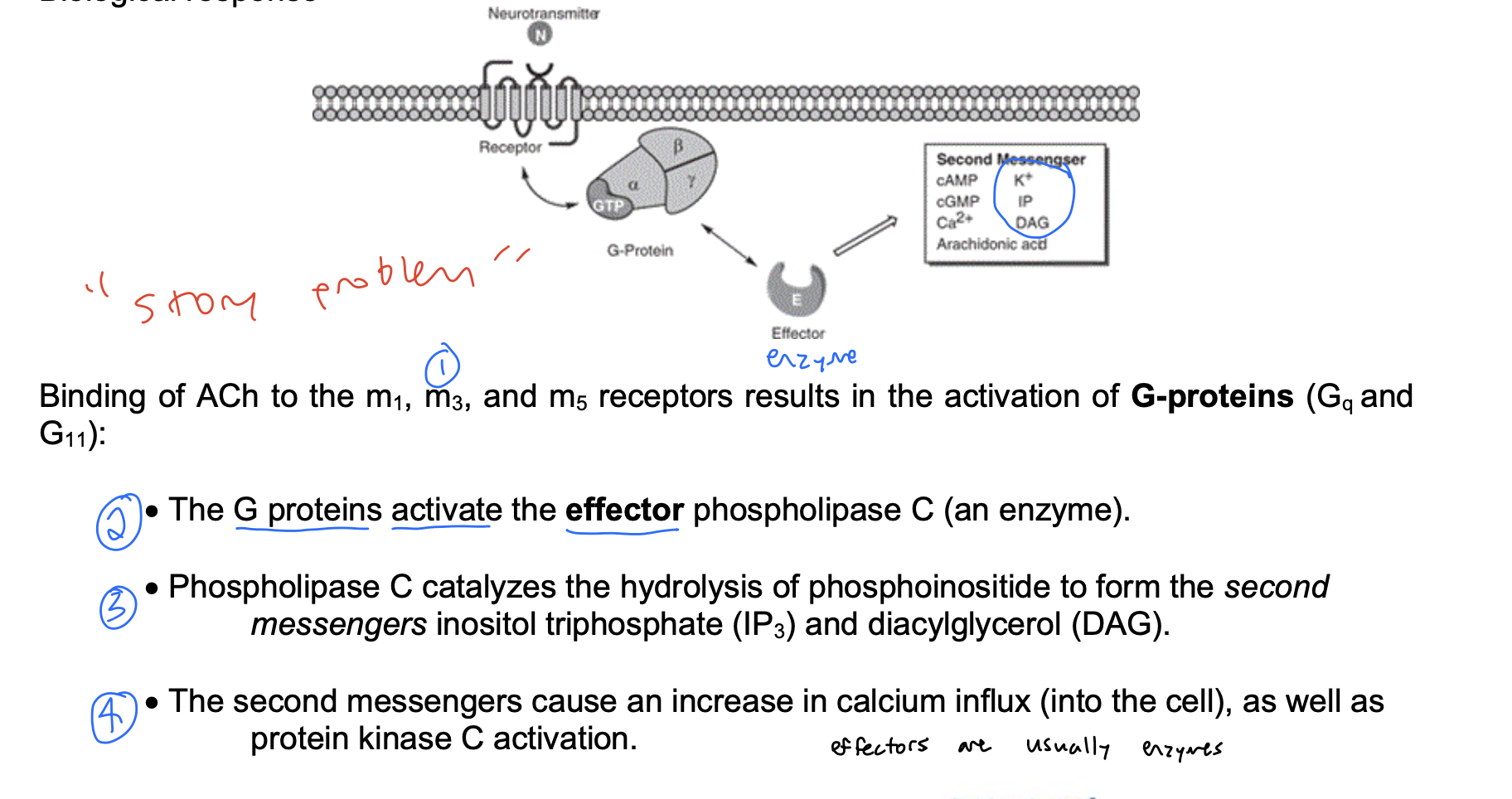
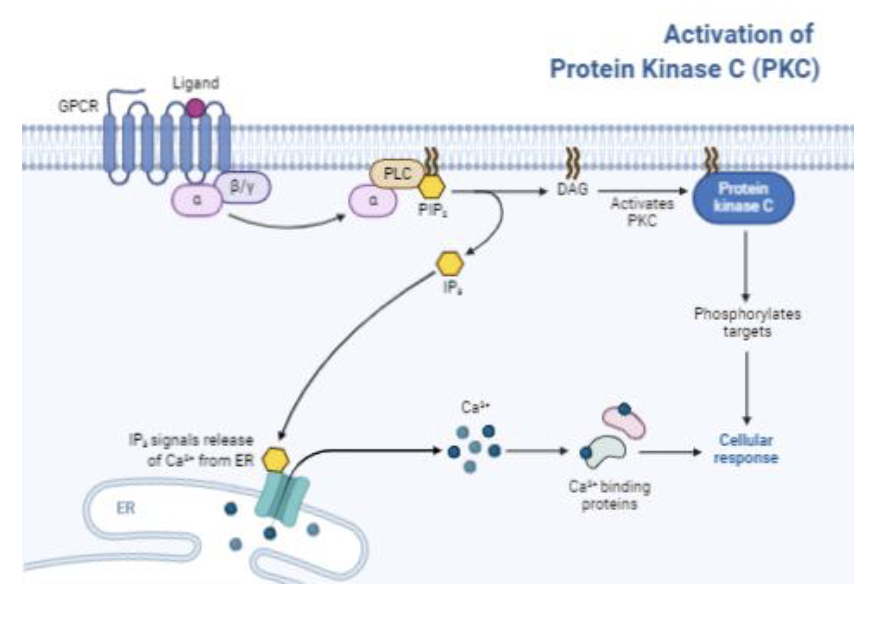
drop a pin Q
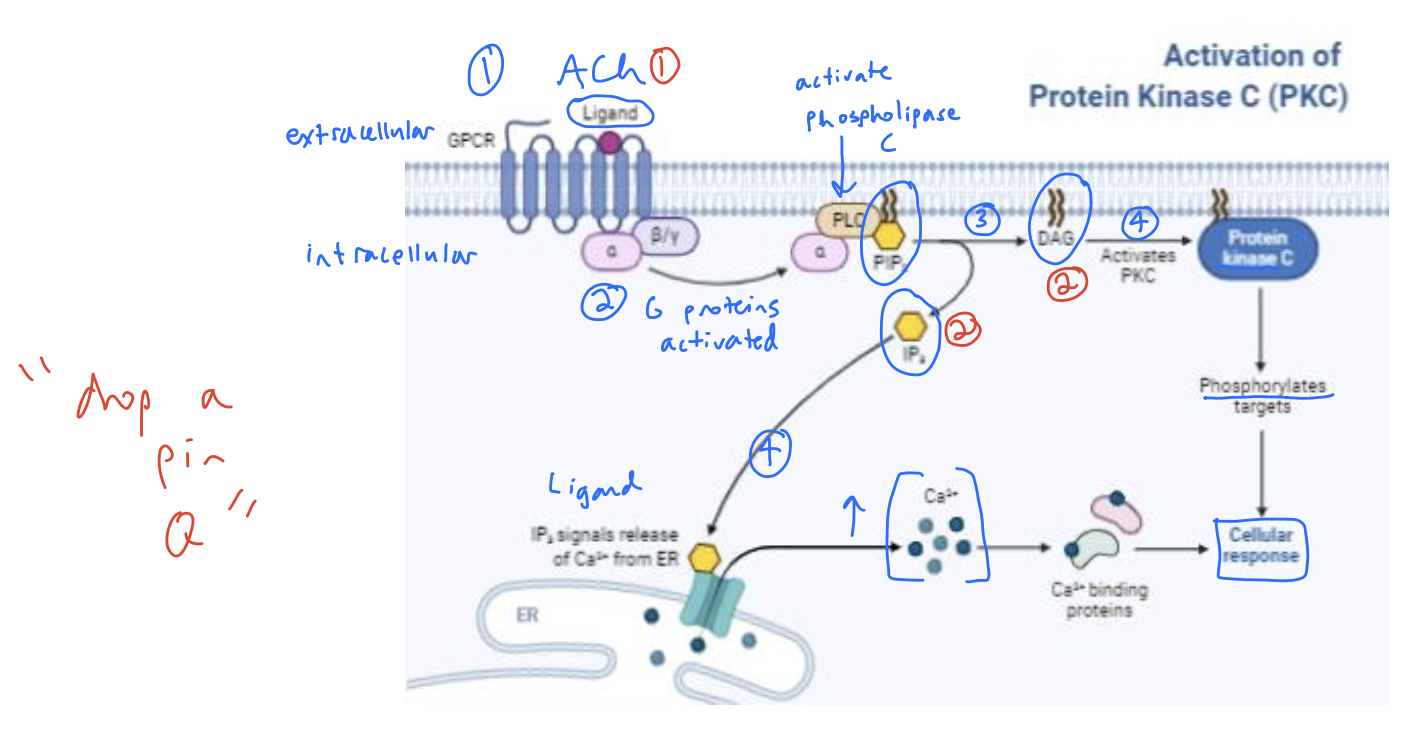
Which enzyme is responsible for the formation of IP3 and DAG?
Phopsholipase C (PLC)
Exam Q fill in blank
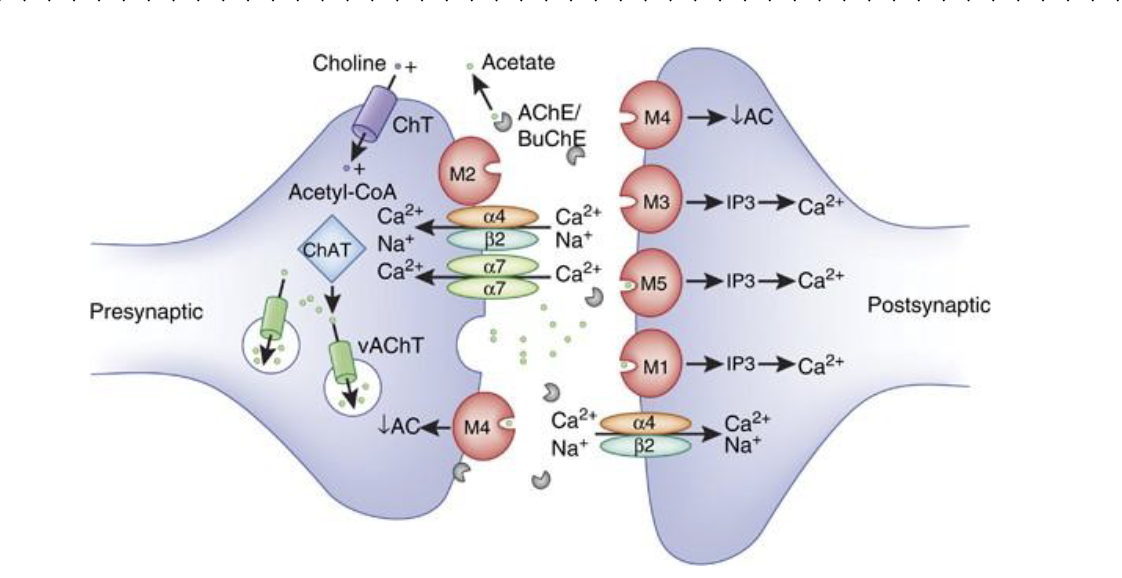
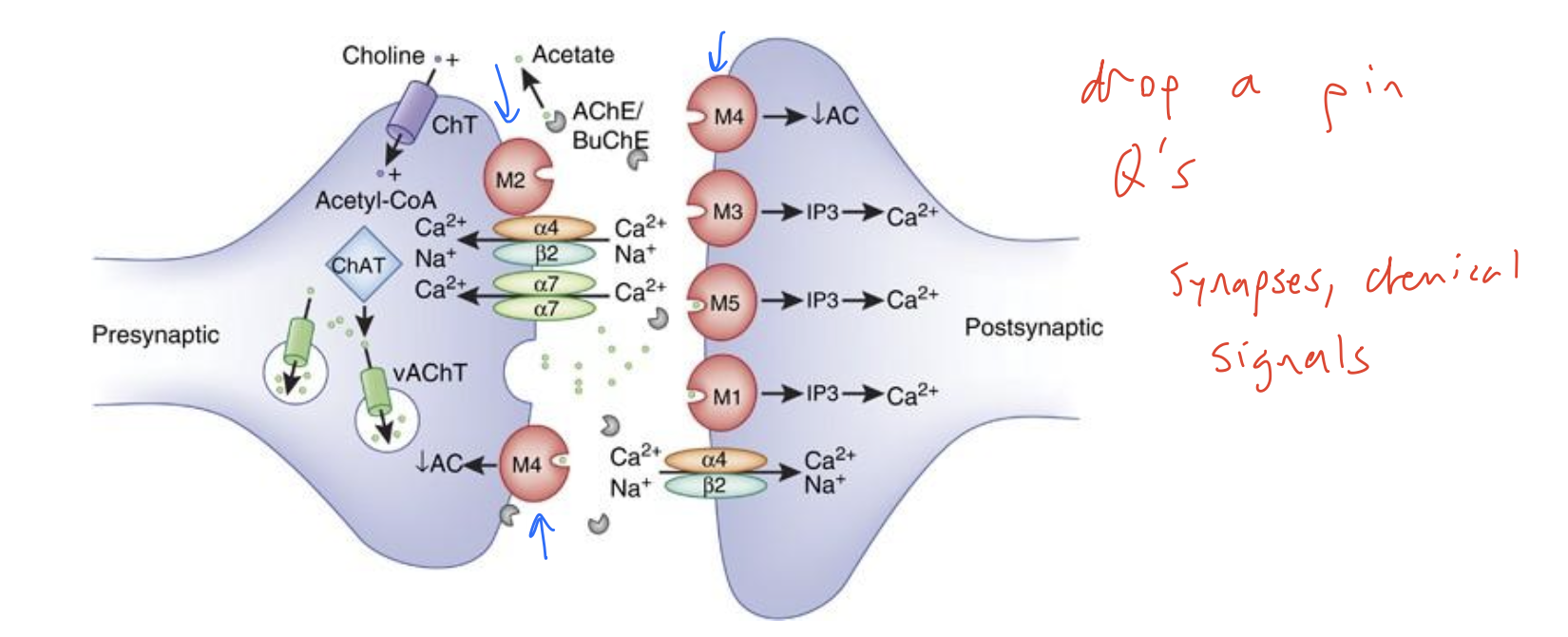
Binding of ACh to the m2 and m4 receptors activates two sets of events
Activation of the Gi G-protein inhibits the effector adenylate cyclase (an enzyme). This causes a decrease in the conversion of ATP to cAMP, the second messenger that normally produces a biological response (generally muscle contraction). Inhibition of AC decreases the conversion of ATP to cAMP. There is therefore less cAMP (second messenger) available and there is a corresponding decrease in muscle contraction.
2. Activation of the Gi or Go G-protein that regulates K+ channels
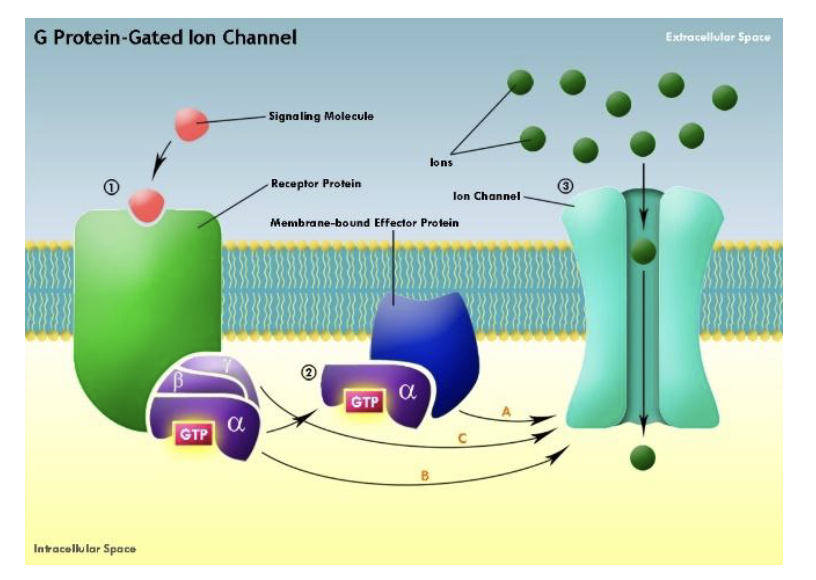
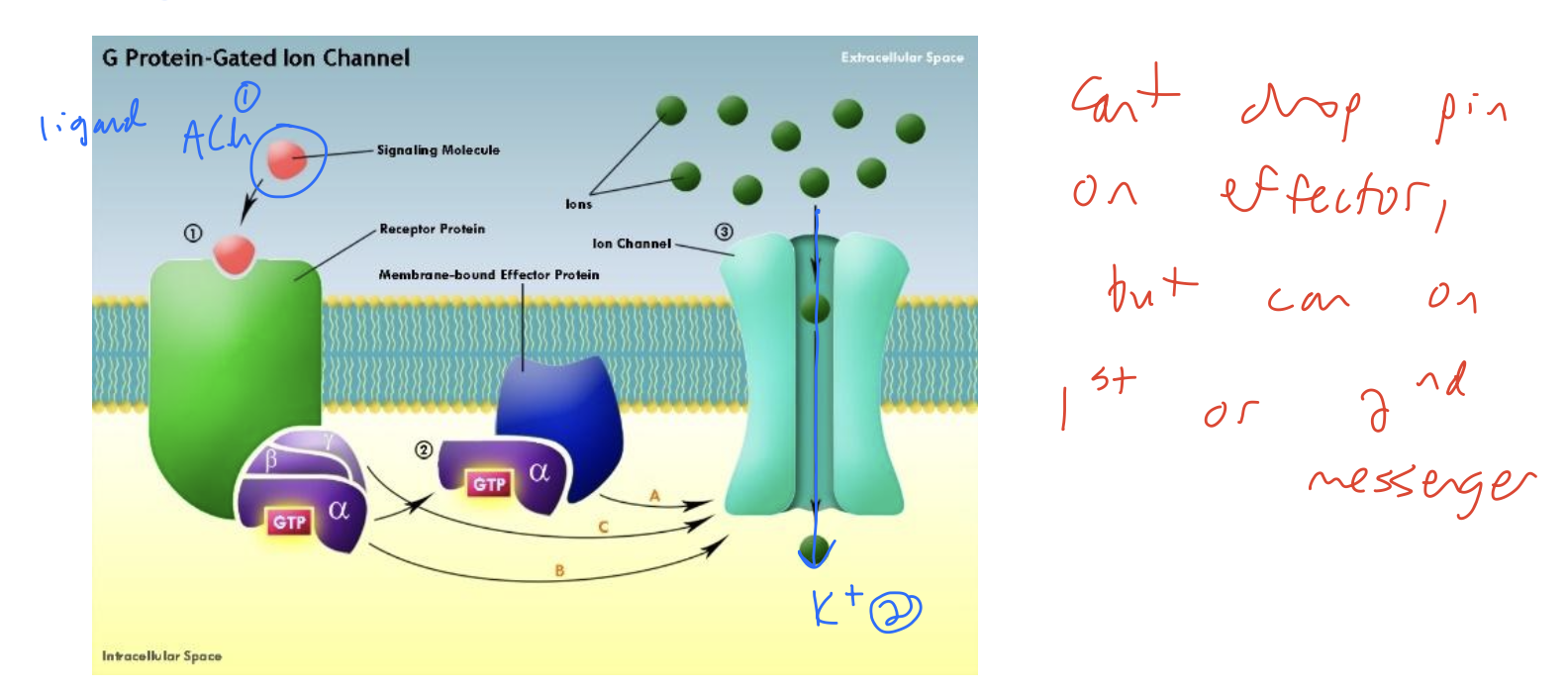
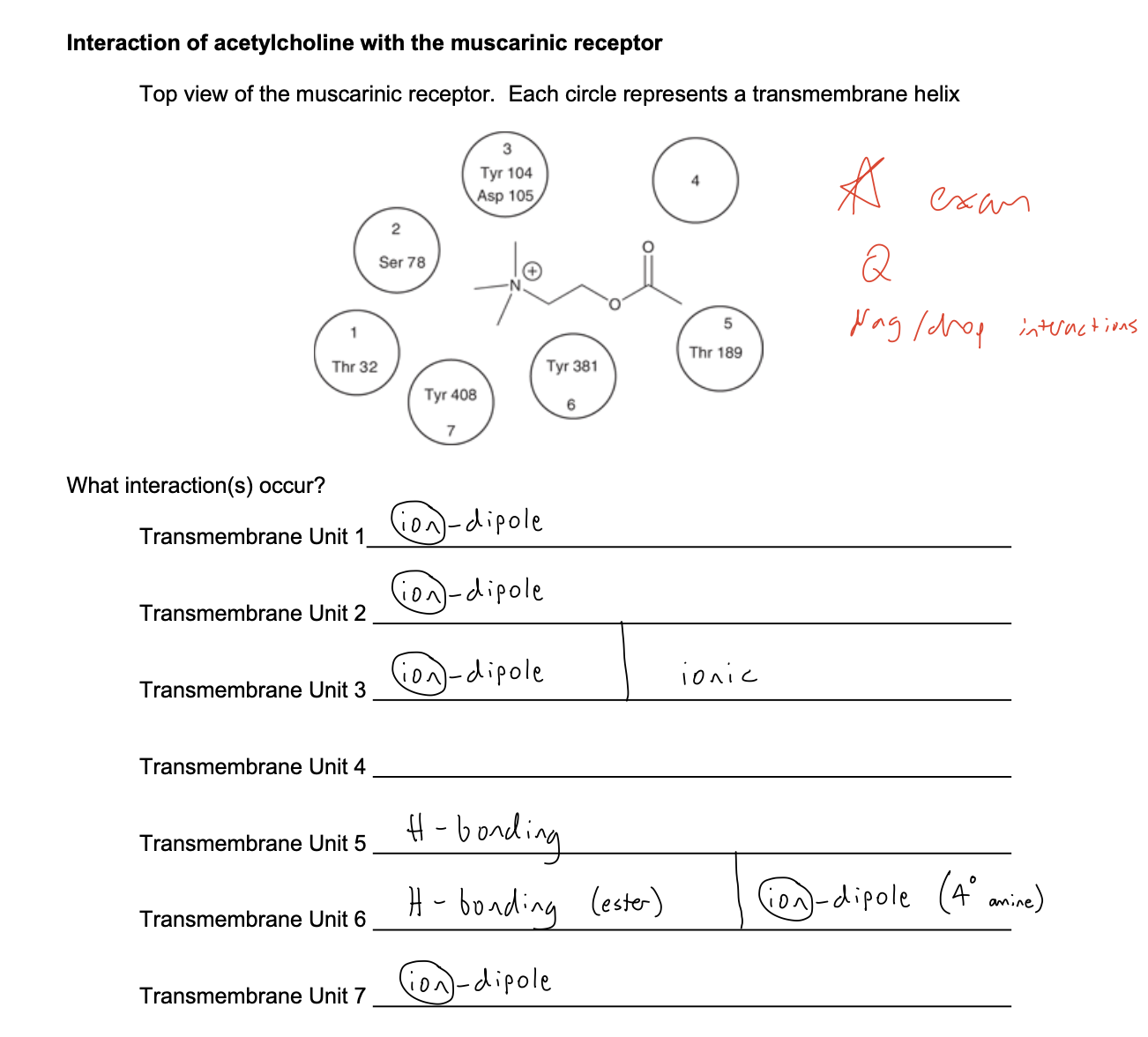
Do antagonists have intrinsic activity?
No, they do not. They cannot “cause” anything. They prevent activation/things from happening
unionized vs ionized nicotine
ionized cannot cross BBB → no cns effects
mechanism of action
include both action + biological target
(ex- agonist at nicotine receptor)
bulk tells
antagonist action