BioE002- Fundamentals of Molecular Biology Chapter 1
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Transcription
Process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA
Translation
Process of by which a cell makes proteins using the genetic information carried in messenger RNA (mRNA)
Origin of first cell
Appeared 3.8 billion years ago by enclosure of a self-replicating RNA in a phospholipid membrane.
Metabolism
Conversion of energy in food to energy available to run all processes, conversion of food to building blocks of proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins, elimination of metabolic waste
Glycolysis
Process that uses ATP as a primary energy source. C6H12O6 (glucose) → 2C3H3O3 (pyruvate). Generates 2 ATP
Photosynthesis
Process that uses ATP as a primary energy source. 6CO2 + 6H2O -(sun)→ C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6O2
Oxidative Metabolism
Process that uses ATP as a primary energy source. C6H12O6 → 6CO2 + 6H2O Generates 36-38 ATP
Prokaryotic Cell
Cell with no nucleus found in single cell organisms (bacteria, archae). Surrounded by cell wall containing plasma membrane. No nucleus, DNA is in the nucleoid. Most of these organisms are small, simple creatures.
Eukaryotic Cell
Found in plant and animal cells. In both cells they are surrounded by plasma membrane and have nucleus. Plant cells have chloroplasts used in photosynthesis.
Lysosomes
Metabolizes waste
Animal Cell Only
Lysosomes, centrioles, flagella
Plant Cell only
Chloroplasts, central vacuole and tonoplast, cell wall, plasmodesmata
Prokaryote
No nucleus, around 1um diameter, no cytoplasmic organelles, single cellular DNA molecule
Eukaryote
present nucleus, 10-100um diameter, present cytoplsamic organelles, Multiple linear DNA molecules
Germ layer
Layer of cells that forms during embryonic development.
Endoderm
Innermost germ layer in early embryo. Codes for lungs, thyroid, pancreatic cells
Mesoderm
Middle germ layer in early embryo. Codes for cardiac, skeletal muscle, tubule, red blood, smooth muscle cells.
Ectoderm
Outermost germ layer in early embryo. Codes for epidermis, neuron, pigment cells.
Origin of mitochondria
Arose from internalization of aerobic bacteria by the archaeal ancestor to eukaryotes, after which they continued living symbiotically.
Animal Cell culture process
Tissue dispersed into suspension of individual cells → cells plated in culture dish in nutrient medium → cells in primary culture attach to dish and grow until culture dish surface is covered → cells can be removed from culture dish and replated at lower density to form secondary culture
Plant tissue culture process
tissue sample scraped from parent → sample placed in agar growth medium containing nutrients and auxins → samples develop into tiny plantlets → plantlets placed into compost
Fluorescent microscopes
Use fluorescent stains to produce an image and identify pathogens, find species, distinguish cells
Confocal microscopes
Use lasers to construct 3D images on computer, allowing examination of thick specimens
Excitation of fluorophore
Entails absorption of light energy of a certain wavelength, causing an electron to transition to a higher, excited energy state. Electron will return to ground state, resulting in emission of light at a longer wavelength
Multiphoton Microscopy
Useful for visualizing cells positioned deeper within living tissue
Centrifugation
Allows different subcellular components to be separated at certain speeds.
Density Gradients
Can be used to separate sub cellular components based on buoyant density independent of size and shape
Differential Centrifugation
Used in subcellular fractionation studies of archaea, bacteria, and eukaryotes
Adenine 5’-Triphosphate (ATP)
All cells use this as their primary energy source.
Cell Wall
Surrounds cell. Beneath this organelle, is the cell membrane
Prokaryote examples
Bacteria and Archae
Chloroplast
Organelles responsible for photosynthesis
Large Vacuole
AKA central vacuole. A sac-like organelle in plant cells that stores water, nutrients, and waste products
Endosymbiosis
One cell living inside another. Mitochondria arose from endocytosis (internalization) of
aerobic bacteria by the archaeal
ancestor to eukaryotes, after which
they continued living symbiotically. Like Russian nesting dolls.
Yeasts
Simplest eukaryotes
Eubacteria
Lactococus lactis
Mass of archaeans
Human blood cells in false color
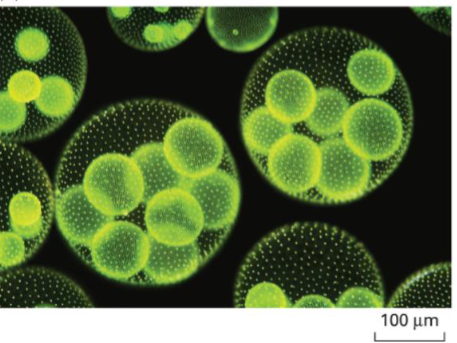
Colonial single-celled green alga, Volvox aureus
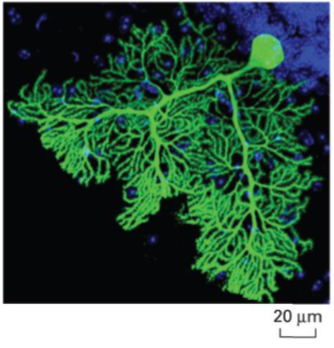
Single Purkinje neuron of the celebrum
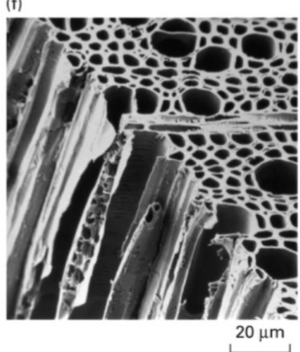
Plant cells are fixed firmly in vascular plants
Supported by rigid cellulose skeleton
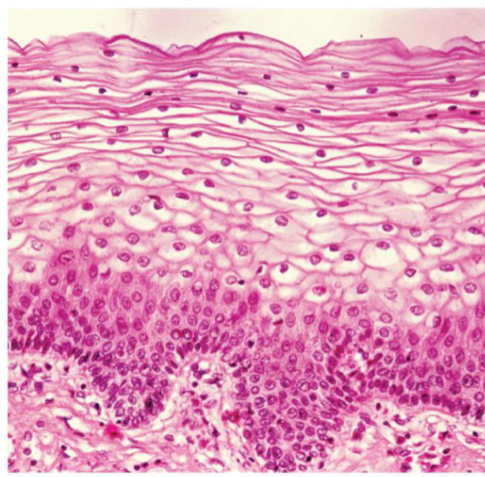
Epithelial cells
Form the covering of all body surfaces, line body cavities and hollow organs, and are the major tissue in glands. They perform a variety of functions that include protection, secretion, absorption, excretion, filtration, diffusion, and sensory reception.
Fibroblasts
cells that create and maintain connective tissues, which support and connect organs and tissues. They also play a role in wound healing.
Blood cells