Year 8 Science AT2 Flashcards
1/124
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Includes the following: Elements and compounds 8.1 definitions First 20 periodic table elements + 10 additional Revision of cell requirements, diffusion and osmosis, cell organisation This was created for personal use so information I find easier to remember may not appear
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
Atom
The smallest whole part of matter
Nucleon
Referring collectively to protons and neutrons
Order of terms on periodic table element (top to bottom)
NSWN.
Number
Symbol
Weight (round off)
Name
What does an element's atomic weight/mass represent?
Number of nucleons found in the atoms of that element
What does an element's atomic number represent?
Number of protons found in the atoms of that element
How to calculate amount of neutrons in an atom?
(Atomic mass) - (Atomic number)
Where are the non metals found on the periodic table?
On the right hand side, Hydrogen being the exception
Where are the metals found on the periodic table?
On the left hand side
What are the two elements that are liquid at room temperature (25 degrees C approx)?
Br and Hg (bromine and mercury)
Compound
A type of matter made of two or more different types of atoms chemically bonded together.
Element
A type of matter made of one type of atom
Molecule
A type of matter made of two or more atoms chemically bonded together.
Mixture
A combination of two or more substances that are not chemically combined. Made of different elements and/or compounds where there is no fixed ratio. Can be separated using physical means
Neutron
A subatomic particle with a neutral charge, found in the nucleus of an atom. Number of such is found by subtracting the atomic number from the atomic weight of an element.
Proton
A positively charged subatomic particle found in the nucleus of an atom. Equivalent to the atomic number of an element.
Electron
A subatomic particle with a negative charge. Orbits the nucleus of an atom. Equivalent to the amount of protons in a neutral atom.
Dalton's atomic model
The billiard ball model. A solid spherical ball, hard and indivisible.

JJ Thomson's atomic model
The plum pudding model. Described to be a positive matrix with electrons spread throughout.

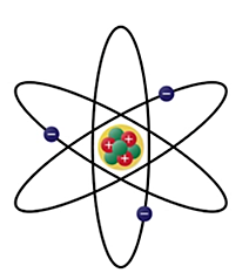
Rutherford's atomic model
The nuclear model. Dense positive nucleus consisting of protons only, orbited by electrons.
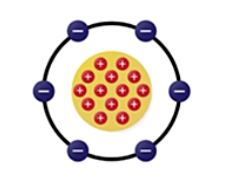
Bohr's atomic model
The planetary model. Dense nucleus made of protons and neutrons. Orbited by electrons. Protons and electrons are equal in amount in a neutral atom.
How many electrons can be the found in the shells of atoms?
2 in the first shell, 8 in the second shell, 8 in the third shell
The law of conservation of mass
States that in a chemical reaction, mass is neither created nor destroyed
Concentrated solution
Lots of solute, little solvent
Dilute solution
Little solute, lots of solvent
Subatomic
Relating to or being inside the atom
H
Hydrogen
He
Helium
Li
Lithium
Be
Beryllium
B
Boron
C
Carbon
N
Nitrogen
O
Oxygen
F
Fluorine
Ne
Neon
Na
Sodium
Mg
Magnesium
Al
Aluminium
Si
Silicon
P
Phosphorus
S
Sulfur
Cl
Chlorine
Ar
Argon
K
Potassium
Ca
Calcium
Cu
Copper
Fe
Iron
Au
Gold
Pb
Lead
Ag
Silver
Zn
Zinc
Hg
Mercury
I
Iodine
Br
Bromine
Sn
Tin
Lustre
Definition: The manner in which a newly exposed surface of a metal reflects light
Antonym: Dull
Metals: Lustrous
Non-metals: Non lustrous
Ductile
Definition: The ability of a metal to be drawn out to form a wire
Antonym: Brittle
Metals: Ductile
Non-metals: Brittle
Malleable
Definition: The ability of a metal to be beaten to form shapes without breaking
Antonym: Brittle
Metals: Malleable
Non-metals: Brittle
Sonorous
Definition: Able to produce a bell-like sound when struck
Antonym: Non-sonorous
Metals: Sonorous
Non-metals: Not sonorous
Thermal conductivity
Definition: The ability of a substance to allow heat to travel through it
Metals: Conduct heat well
Non-metals: Poor conductors
Electrical conductivity
Definition: The ability of a substance to allow electricity to travel through it
Metals: Conduct electricity well
Non-metals: Usually poorer conductors
Reaction with dilute acid
Metals: Form hydrogen gas bubbles
Non-metals: Usually do not react with dilute acids
Chemical change/reaction
When one or more substances are changed into one or more new substances by breaking existing bonds and forming new bonds.
Physical change
A type of change in which matter changes its physical state or phase as a result of energy charges
Decomposition
A type of chemical reaction where one substance is broken down into two or more simpler substances.
Synthesis
A type of chemical reaction where two or more simple substances chemically combine to form a more complex substance.
Electrolysis
The use of electricity to cause a chemical reaction
Parts of a chemical reaction?
Reactant → product
Alloy
Mixture of metals made by combining two or more metallic elements which results in different physical properties.
Acid
A compound that reacts with metals to produce hydrogen and reacts with bases to form a neutral solution
Metal
A type of matter which is typically a solid, shiny, malleable, and ductile, with good electrical and thermal conductivity
Salt
A compound consisting of a metal and a non-metal
Extraction
The action of removing something by effort or force
Precipitation
The action by which a solid settles to the bottom of a solution
Neutralisation
A reaction where an acid and a base react to form a salt and water
Petroleum
A liquid mixture of hydrocarbons which can be extracted from rock strata, and refined to produce fuels including petrol, paraffin, and diesel
Chemical formula for water
H₂0
Chemical formula for carbon dioxide
CO₂
Word equation for respiration
Glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water + ATP
Chemical equation for respiration
C₆H₁₂0₆ + 60₂→ 6CO₂ + 6H₂O
Word equation for photosynthesis
Carbon dioxide + water → Glucose + oxygen
(Under the presence of light energy and chlorophyll)
Chemical equation for photosynthesis
6CO₂ + 6H₂O → C₆H₁₂0₆ + 60₂
(Under the presence of light energy and chlorophyll)
Chemical formula for glucose
C₆H₁₂0₆
Signs of a chemical reaction
Permanent change in colour
Change in temperature
Energy given off
Fizzing/effervescence (gas given off)
Appearance of a new substance
Disappearance of an original substance (not always)
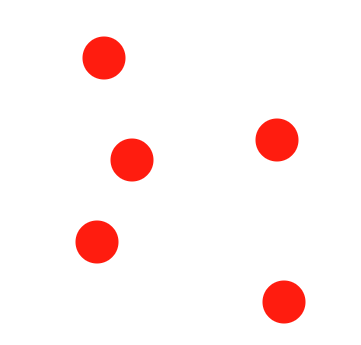
Describe the diagram
Pure element OR atoms of an element (only one type of atom is present)
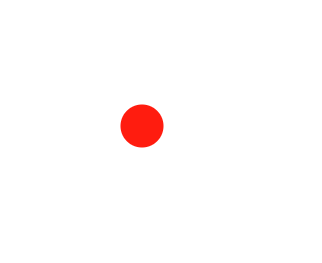
Describe the diagram
Pure element OR atom of an element (only one type of atom is present)
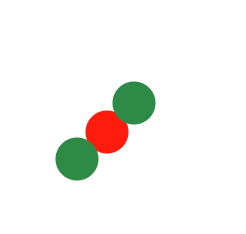
Describe the diagram
Pure compound OR molecule of a compound (one type of compound present)
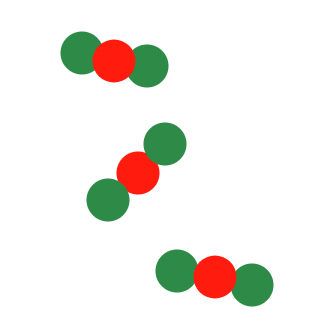
Describe the diagram
Pure compound OR molecules of a compound (one type of compound present)
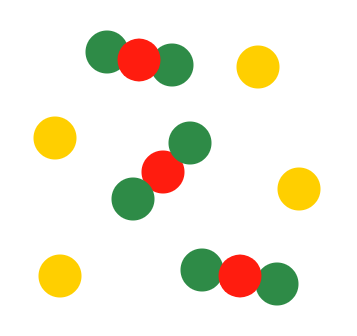
Describe the diagram
Mixture of a compound and an element (one type of compound and one type of element present)
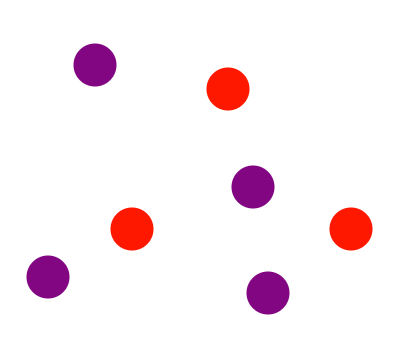
Describe the diagram
Mixture of two elements (two types of uncombined atoms present)
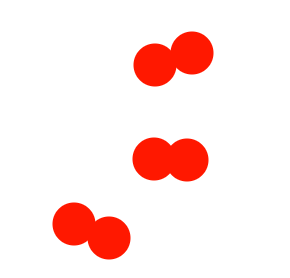
Describe the diagram
Pure element OR molecules of an element (only one type of atom present)
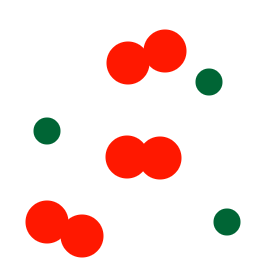
Describe the diagram
Mixture of two elements (one element is a molecule and the other is atoms)
High area of concentration
Substance’s particles are closely packed
Low area of concentration
Substance's particles are spread out.
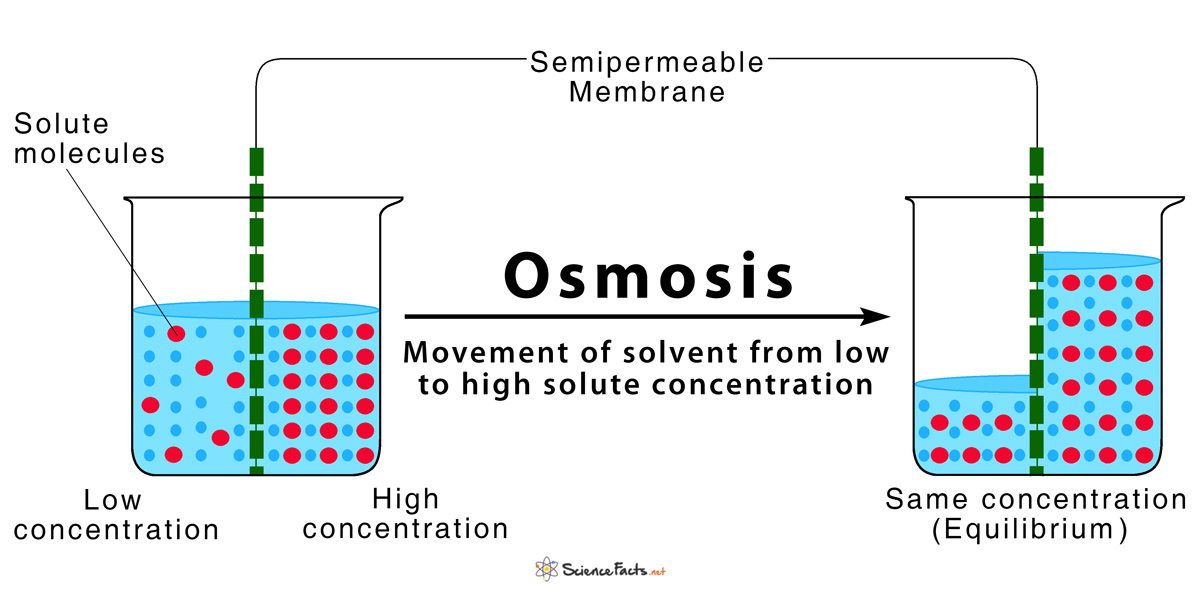
Osmosis
The movement of water from a dilute solution to a concentrated solution OR The movement of a solvent from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration across a semipermeable membrane.
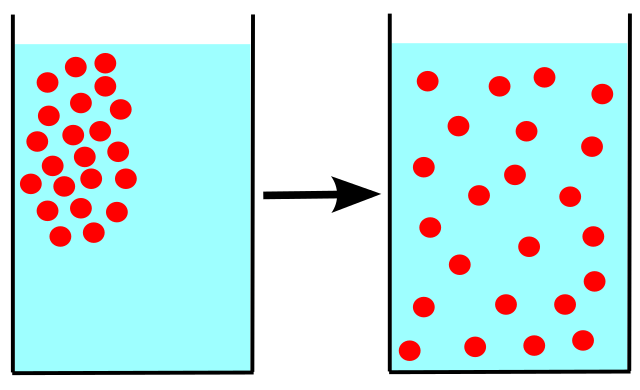
Diffusion
Particles move from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration. Caused by the constant random motion of particles.
Animal and plant cells contain…
My New Vibrant Red Car Cruises Carefree (acronym)
Mitochondria, Nucleus, Vacuole (small), Ribosome, Cell membrane, Cytosol, Cytoplasm
Plant cells additionally contain…
Chloroplast, larger vacuole, cell wall
MRS AR
Movement, Respiration, Stimuli, Assimilation, Reproduction
Levels of cell organisation
Cell → Tissue → Organ → Organ system → Organism