Psych 454 Exam 1
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
127 Terms
Identify the two main cell types in the nervous system.
Neurons
Glial Cells
Neurons
The primary signaling cells responsible for transmitting information
Describe any main subtypes or categories of neurons
Sensory neurons: Transmit sensory information
motor neurons: Control muscle actions
interneurons: Connect neurons within the central nervous system
Glial Cells
Support neurons in various ways
Describe any main subtypes or categories of Glial cells
Astrocytes: nutritional support
Oligodendrocytes/Schwann cells: Myelination
Microglia: immune defense
Ependymal cells: produce cerebrospinal fluid
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
The source of energy for use and storage at the cellular level
Identify the main organelles of the neuron that are involved in energy or protein production.
Mitochondria
Ribosomes
Golgi apparatus
Mitochondria
Provide energy (ATP) for neuronal functions
Ribosomes
Synthesize proteins
Golgi apparatus
Modifies and packages proteins
What are the parts of the neuron
Soma (Cell Body)
Dendrites
Axon
Axon Hillock
Axon Terminals
Soma (Cell Body)
Contains the nucleus and organelles
Dendrites
Receive incoming signals from other neurons
Axon
Transmits signals to other cells
Axon Hillock
Where action potentials are initiated
Axon Terminals
Release neurotransmitters into the synapse.
Synapse
The points where neurons connect and communicate with each other
What are the parts of the synapse
Presynaptic Terminal
Synaptic Cleft
Postsynaptic Membrane
Presynaptic Terminal
Contains synaptic vesicles filled with neurotransmitters
Synaptic Cleft
The gap between the presynaptic and postsynaptic cells
Postsynaptic Membrane
Contains receptors that bind neurotransmitters
Amino acids
Molecules that combine to form proteins
Define axoplasmic transport and describe why it is important
The process of moving materials (proteins, organelles) along the axon. It is essential for the neuron’s health and function, as it delivers necessary materials from the cell body to the axon terminal.
Identify the two most important ions for neural function and describe the forces that act upon them, including their net effect on the direction of ion flow.
Sodium (Na+)
Potassium (K+)
Sodium (Na+)
Driven by both concentration gradient and electrochemical forces to flow inward
Potassium (K+)
Concentration gradient drives it out of the cell, but electrochemical forces attract it inward
Define the resting membrane potential
The electrical potential difference across the neuron's membrane when it is not actively sending a signal, typically around -70mV.
Explain what the sodium-potassium pump is and how it helps establish ionic concentration gradients across the neuronal membrane.
A membrane protein that actively transports 3 Na+ ions out of the cell and 2 K+ ions into the cell, helping to maintain the resting membrane potential and establish ionic gradients.
Action Potential
A rapid change in voltage across a cell membrane, which is caused by the opening and closing of ion channels
Describe the phases of the action potential in terms of depolarization, repolarization, hyperpolarization, and the ion flow that is involved
Depolarization: Na+ channels open, and Na+ flows in, making the inside more positive.
Repolarization: K+ channels open, and K+ flows out, restoring negative potential.
Hyperpolarization: Excess K+ flows out, making the inside briefly more negative than resting potential.
Explain why the action potential is an all-or-none phenomenon
Once the threshold potential is reached, an action potential is generated. It either occurs fully or not at all; there is no partial action potential.
Absolute relative refractory period
No new action potential can be initiated because Na+ channels are inactivated.
Relative relative refractory period
A stronger-than-normal stimulus can initiate an action potential as the membrane is hyperpolarized.
Explain the roles of voltage-gated ion channels in the action potential
Open in response to changes in membrane potential, allowing specific ions (Na+ and K+) to flow, generating and propagating the action potential.
Identify where the action potential is initiated in a stereotypical multipolar neuron
The axon hillock, where there is a high density of voltage-gated Na+ channels
Explain how the myelin sheath impacts the speed of conduction of the action potential
By insulating axons and allowing action potentials to jump between nodes of Ranvier in a process called saltatory conduction which greatly increases conduction speed.
Explain what gap junctions are
Direct connections between cells that allow ions and other small molecules to pass, facilitating rapid and direct electrical communication between neurons
Describe where amino acid neurotransmitters are synthesized
The neuron’s cytoplasm
Describe where amine neurotransmitters are synthesized
The presynaptic terminal
Describe where peptide neurotransmitters are synthesized
The rough Endoplasmic Reticulum and Golgi apparatus and then transported to the axon terminal
Identify the most common excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system
Glutamate
Identify the most common inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system
Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA)
Describe how neurotransmitters are released at the synapse
When an action potential reaches the axon terminal, it triggers the opening of voltage-gated calcium channels, causing calcium influx, which then leads to the fusion of synaptic vesicles with the presynaptic membrane and release of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft and into the other neuron’s dendrites.
Explain the differences between transmitter-gated ion channels and G-protein coupled receptors
Transmitter-gated ion Channels open directly in response to neurotransmitter binding, allowing ions to flow and cause rapid changes in membrane potential. G-Protein Coupled Receptors trigger slower, more prolonged responses through intracellular signaling cascades.
Articulate why it is misleading to describe a neurotransmitter as excitatory or inhibitory
Because the effect depends on the type of receptor it binds to and the cellular context
Describe how excitation and inhibition work at the synapse and the principles of synaptic integration
Excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) bring the membrane closer to the threshold, while inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs) make the membrane more negative, moving it away from the threshold. Synaptic integration is the process by which these signals are summed to determine if an action potential will occur
Explain Dale’s principle and identify whether or not most neurons follow it
States that a neuron releases the same neurotransmitter at all its synapses. Most neurons do not strictly follow this principle as they can release multiple neurotransmitters under certain conditions.
Cholinergic Neurons
Neurotransmitter: Acetylcholine (ACh).
Role: Involved in muscle activation, memory, and learning.
Serotonergic Neurons
Neurotransmitter: Serotonin.
Role: Regulates mood, sleep, appetite, and cognition.
Amino Acidergic Neurons
Neurotransmitters: Include GABA (inhibitory) and glutamate (excitatory).
Role: Critical for balancing excitation and inhibition in the brain.
Identify the dorsal direction at the level of the cerebrum
Towards the top of the brain
Identify the ventral direction at the level of the cerebrum
Towards the bottom of the brain
Identify the superior direction at the level of the cerebrum
Up toward the head
Identify the inferior direction at the level of the cerebrum
Down away from the head
Identify the anterior direction at the level of the cerebrum
Back of the brain to front of the brain
Identify the posterior direction at the level of the cerebrum
Front of the brain to back of the brain
Identify the rostral direction at the level of the cerebrum
Towards the front of the brain
Identify the caudal direction at the level of the cerebrum
Towards the back of the brain
Identify the medial direction at the level of the cerebrum
Toward the center or midline of the brain
Identify the lateral direction at the level of the cerebrum
Toward the sides
Identify the coronal sections of the cerebrum
Divides the brain into anterior (front) and posterior (back) parts
Identify the horizontal section of the cerebrum
Divides the brain into superior (top) and inferior (bottom) parts
Identify the sagittal sections of the cerebrum
Divides the brain into left and right halves (mid-sagittal section cuts through the midline)
Central Nervous System
Central Nervous System (CNS): Includes the brain and spinal cord.
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): Includes all neural elements outside the CNS (nerves and ganglia), which connect the CNS to the rest of the body.
Peripheral Nervous System
Includes all neural elements outside the CNS (nerves and ganglia), which connect the CNS to the rest of the body
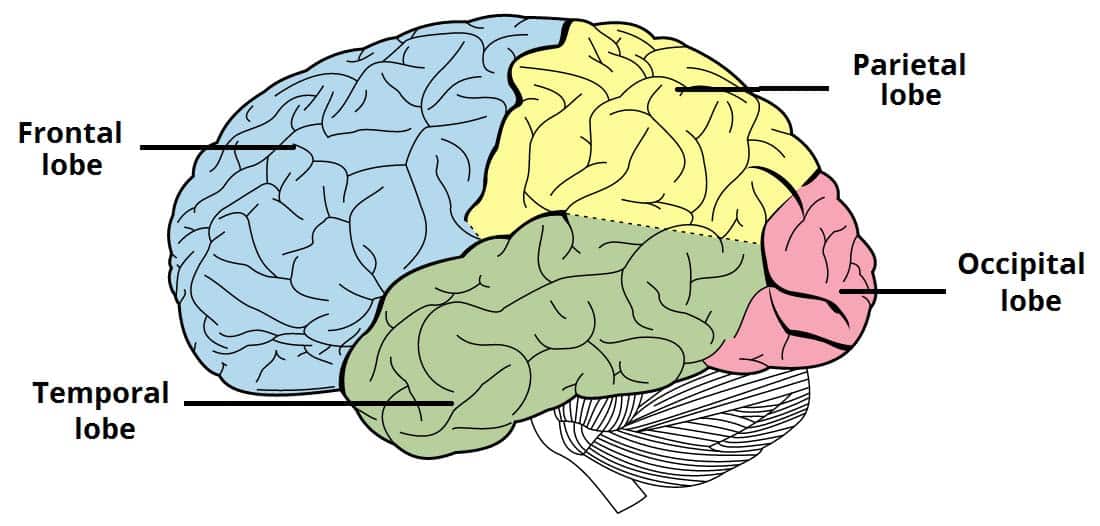
Recognize the lobes of the cerebrum
Frontal Lobe
Parietal Lobe
Temporal Lobe
Occipital Lobe
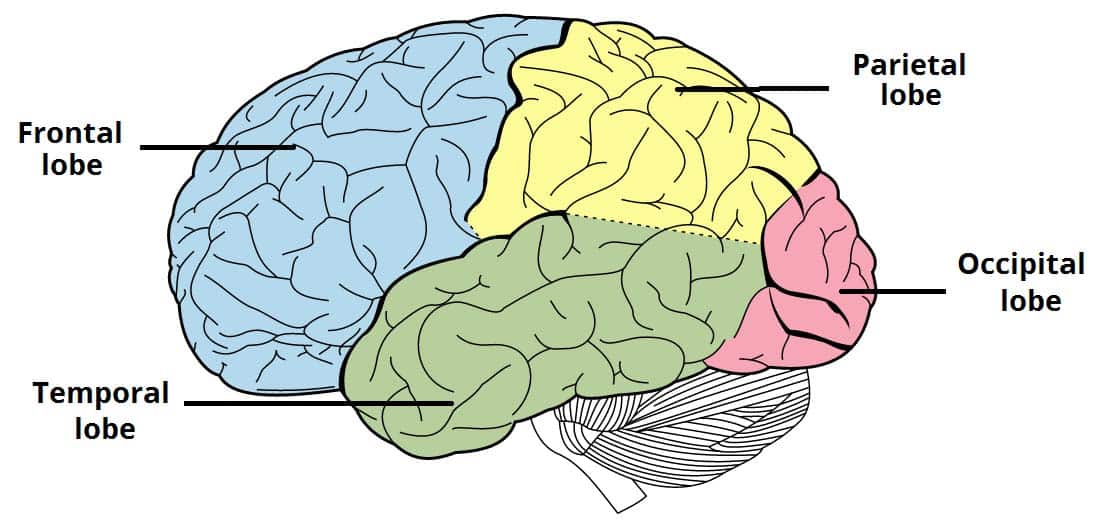
Frontal Lobe
Involved in decision-making, voluntary movement, planning, and personality
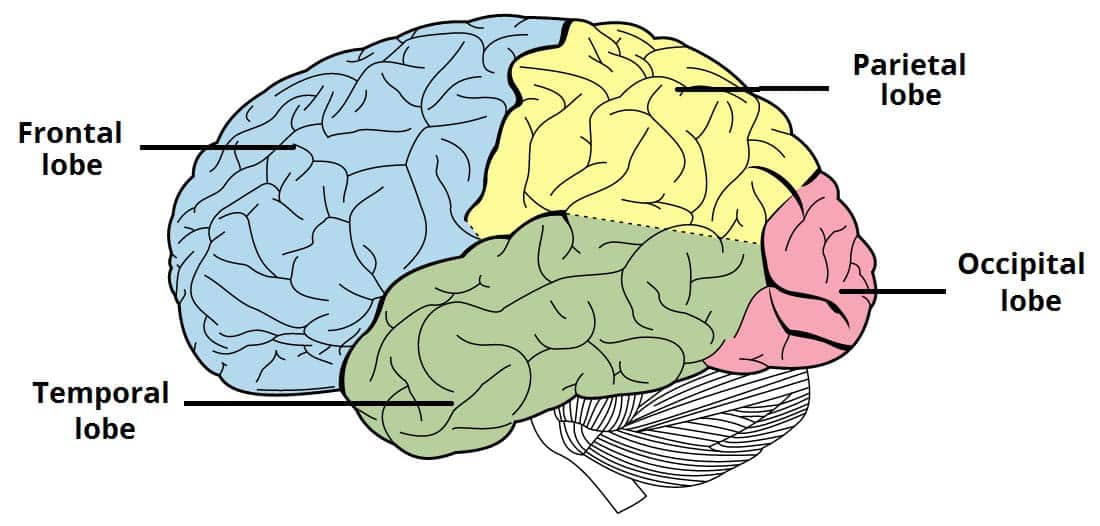
Parietal Lobe
Processes sensory information like touch, temperature, and pain
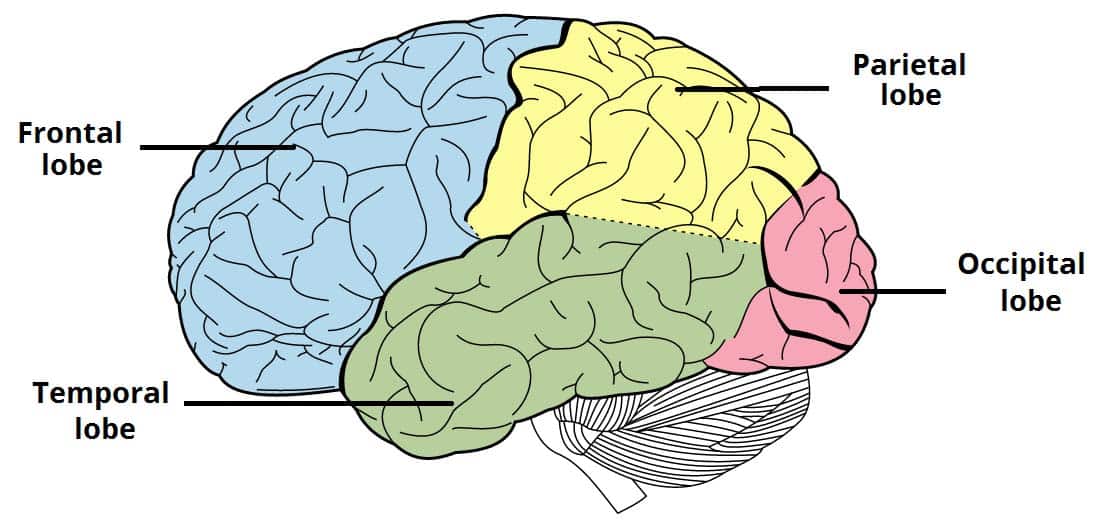
Temporal Lobe
Involved in auditory processing, language, and memory
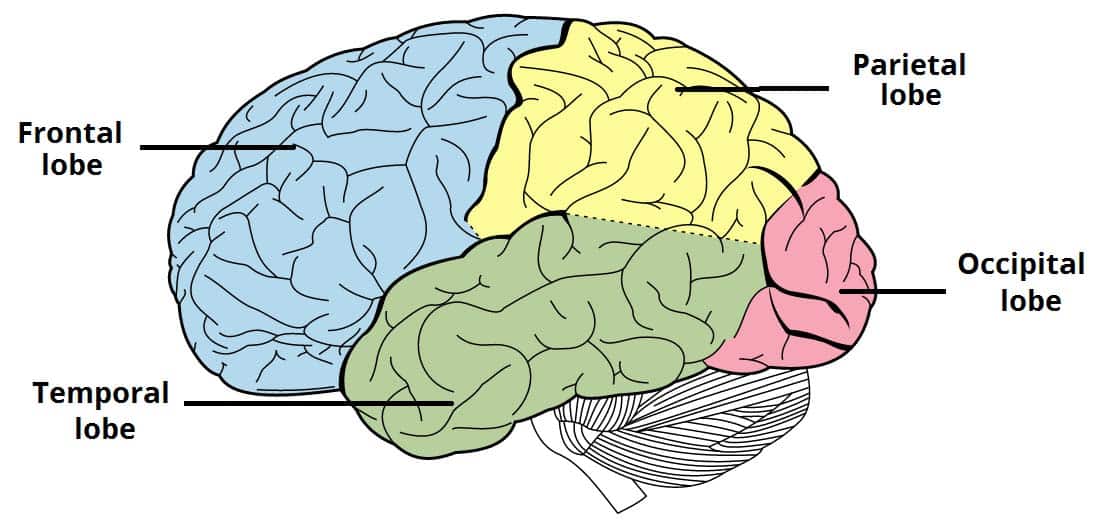
Occipital Lobe
Primarily responsible for vision
Central Sulcus
Separates the frontal and parietal lobes
Longitudinal Fissure
Separates the two cerebral hemispheres
Lateral Fissure (Sylvian Fissure)
Separates the frontal and parietal lobes from the temporal lobe
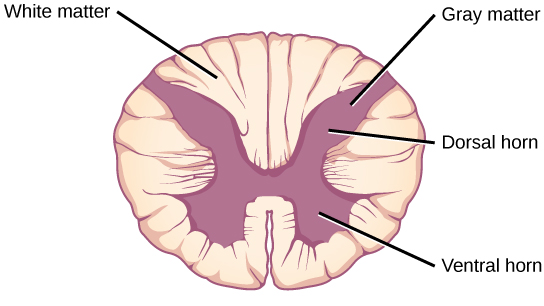
Gray Matter
Composed of neuronal cell bodies, dendrites, and synapses; found in the cerebral cortex, brainstem nuclei, and spinal cord’s dorsal and ventral horns.
White Matter
Composed of myelinated axons; found in subcortical areas, brainstem tracts, and the spinal cord's outer regions
Recognize how many layers are found in the neocortex
Six
Describe what a sulcus is
A groove or depression on the brain’s surface, usually separating gyri.
Describe what a gyrus is
A ridge or fold on the brain's surface, between sulci.
Explain what ventricles are
Cavities in the brain that produce and circulate cerebrospinal fluid
Explain what cerebrospinal fluid is
A clear fluid that cushions the brain, removes waste, and circulates nutrients
Explain what the choroid plexus is
A specialized structure in the ventricles that produces CSF
Explain where the hippocampus is and describe its general functions
Located in the temporal lobe, involved in memory formation
Explain where the thalamus is and describe its general functions
Near the center of the brain, relays sensory information to the cerebral cortex
Explain where the hypothalamus is and describe its general functions
Below the thalamus, controls homeostatic functions like temperature regulation, hunger, and hormone release
Explain where the corpus callosum is and describe its general functions
Near the center of the brain, a large band of white matter connecting the two cerebral hemispheres, allowing communication between them
Know the major divisions of the brainstem
Midbrain
Pons
Medulla Oblongata
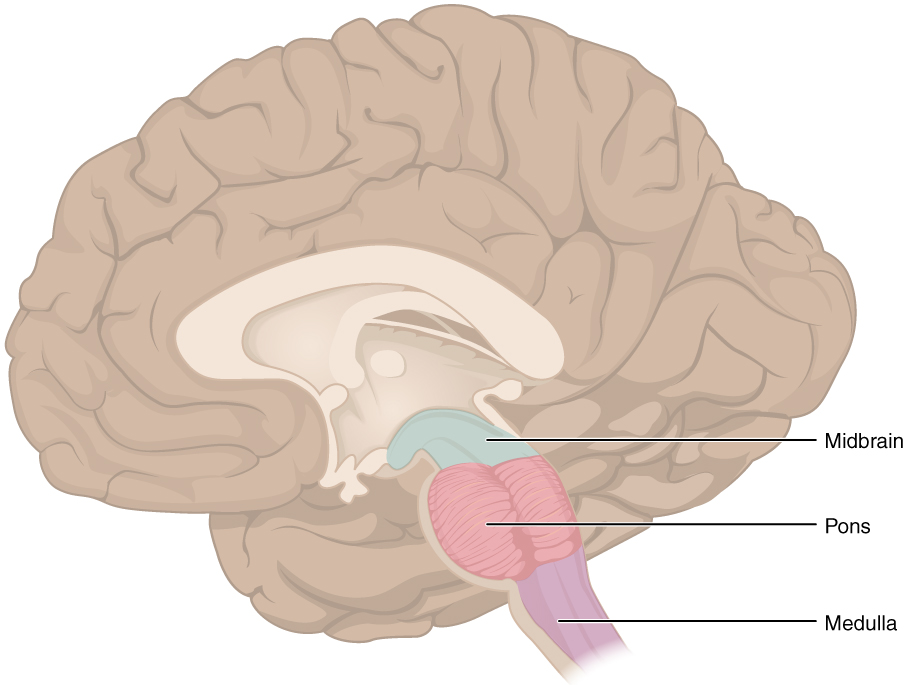
Identify the general functions of the brainstem
Controls basic life-sustaining functions like heart rate, respiration, and sleep.
Serves as a conduit for information between the brain and spinal cord.
Describe the general structure and functions of the cerebellum
Located at the back of the brain, it has two hemispheres and a highly folded surface.
Involved in motor control, balance, coordination, and motor learning.
Name the major white matter pathways that connect the cerebellum to the brainstem
Superior, Middle, and Inferior Cerebellar Peduncles: Connect the cerebellum to different parts of the brainstem and relay information.
Describe the general organization of the spinal cord
Gray Matter (central): Organized into dorsal (sensory) and ventral (motor) horns.
White Matter (outer): Contains ascending sensory tracts and descending motor tracts
Describe what a cranial nerve is and how many there are
Nerves that arise from the brain, there are 12 pairs of them
Identify the two cranial nerves that are considered to be part of the central nervous system
Optic Nerve (CN II)
Olfactory Nerve (CN I)
Optic Nerve (CN II)
A bundle of nerve fibers that carries visual information from the retina at the back of the eye to the brain
Olfactory Nerve (CN I)
Sensory nerve responsible for your sense of smell
Differentiate the autonomic from the somatic nervous system
Autonomic Nervous System: Controls involuntary functions (e.g., heart rate, digestion).
Somatic Nervous System: Controls voluntary movements and sensory processing (e.g., reaching out to grab your coffee)
Differentiate the sympathetic from the parasympathetic nervous system with respect to the levels of the CNS that their nerves arise from and the locations of their ganglia.
Sympathetic: Arises from the thoracolumbar region; ganglia are close to the spinal cord. Prepares the body for "fight or flight."
Parasympathetic: Arises from the craniosacral region; ganglia are close to target organs. Responsible for "rest and digest" functions.
Describe the relative wavelengths associated with red, blue, and green perception (i.e., long, medium, or short)
Blue: Short wavelengths (~450-495 nm)
Green: Medium wavelengths (~495-570 nm)
Red: Long wavelengths (~620-750 nm)
Describe the three ways in which light can interact with physical objects
Reflection
Absorption
Transmission
Reflection
Light bounces off the surface of an object
Absorption
Light is absorbed by the object and converted to energy (e.g., heat)