Neurons, Glia and Action Potential
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Physiological Psychology Lesson Two
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What are the three main types of neurons based on structure?
Multipolar (many dendrites, one axon) 2. Bipolar (one dendrite stalk, one axon) 3.Unipolar (one projection branching into dendrite and axon).
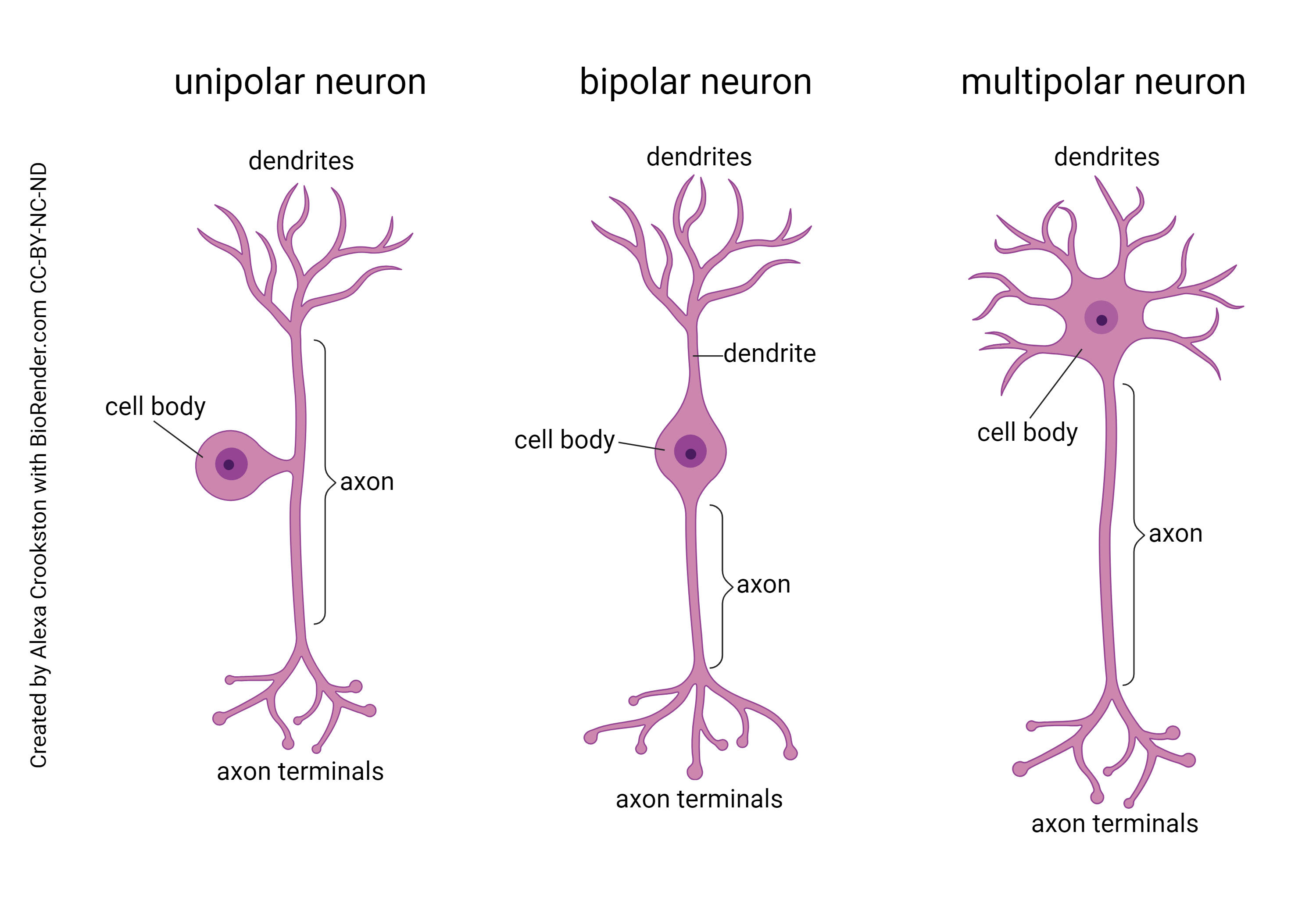
What is the function of the neuronal membrane?
It encloses the neuron, is semipermeable, and regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
What are dendritic spines and their components?
Small protrusions on dendrites that contain a spine head, neck, actin filaments, postsynaptic density (with receptors and ion channels), adhesion molecules, and mitochondria.
What is spine motility?
The ability of dendritic spines to change shape in response to brain activity
What cytoskeletal elements are found in axons?
Actin filaments (thin), neurofilaments (medium), and microtubules (thick).
What is fast axonal transport and which proteins are involved?
The movement of cargo along microtubules using kinesin (anterograde) and dynein (retrograde). Myosin Va transports vesicles along actin filaments.
What do astrocytes do?
Form the blood-brain barrier, regulate blood flow, supply nutrients, support neurons structurally, and participate in tripartite synapses.
What is the difference between oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells?
Oligodendrocytes (CNS) myelinate multiple axons and do not aid regeneration. Schwann cells (PNS) myelinate one axon segment and help axon regrowth.
What is the resting membrane potential of a neuron?
-70 millivolts (mV).
What happens during depolarization and hyperpolarization?
Depolarization makes the inside of the neuron less negative; hyperpolarization makes it more negative.
What triggers an action potential?
A depolarization that reaches the threshold of excitation.
What is the role of sodium and potassium during an action potential?
Sodium rushes in during depolarization; potassium exits during repolarization and hyperpolarization.
What are the absolute and relative refractory periods?
Absolute: No new AP can be triggered.
Relative: A stronger stimulus can trigger an AP during afterhyperpolarization.
How does the action potential travel in myelinated vs. unmyelinated axons?
Unmyelinated: Passive spread along the axon.
Myelinated: Saltatory conduction between Nodes of Ranvier.
What is Multiple Sclerosis?
An autoimmune disorder causing demyelination in the CNS, leading to muscle, sensory, and cognitive symptoms.
What causes MS symptoms to worsen over time?
Ongoing damage to oligodendrocytes and axons, which the brain can no longer fully compensate for.
What are three ways the brain compensates for demyelination in early MS?
1) Remyelination by converting NG2 cells to oligodendrocytes
2) Creating new sodium channels
3) Rerouting function to healthy neurons
How can gut bacteria influence MS?
Dysbiosis can damage the intestinal wall, allowing bacteria into the blood, which weakens the BBB and leads to CNS inflammation.
What is microbial translocation?
The leakage of bacteria from the intestine into the bloodstream, triggering immune responses that affect the brain.
How does nitric oxide contribute to axonal damage in MS?
It damages mitochondria, reduces ATP, disrupts ion pumps, increases sodium and calcium levels, and activates enzymes that break down the axon.