Matter and change
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Mass
A fundamental property that measures the amount of matter in a substance or an object.
Matter
Anything that has mass and occupies space (has volume).
Volume
Matter takes up space. This space is referred to this thing. Even gases, which might seem "empty," occupy a specific volume.

Substance
A pure material with a uniform and definite composition.
Can’t be separated into components using physical means.
Can be a solid, a liquid, or a gas, depending on the temperature.
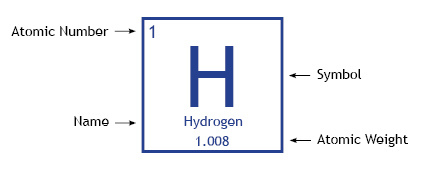
Element
The simplest form of a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by any chemical means.
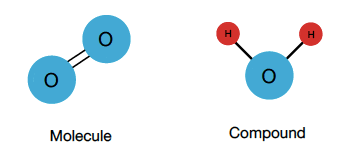
Compound
pure substance formed when two or more different elements are chemically bonded together in a fixed ratio by mass.
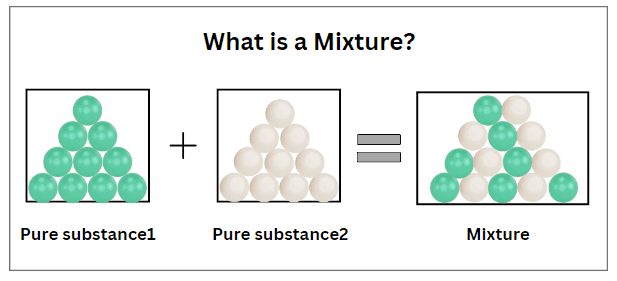
Mixture
A material consisting of two or more pure substances that are physically combined but not chemically bonded. The components of a mixture retain their individual properties and can often be separated by physical means.

Physical properties
A characteristic of a substance that can be observed or measured without changing the identity of the substance.
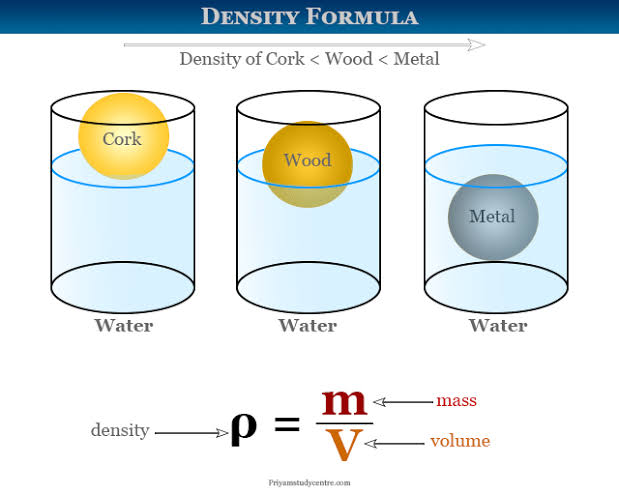
Density
a measure of how much "stuff" (mass) is packed into a given space (volume)

Intensive properties
A property is a property of matter that depends only on the type of matter in a sample and not on the amount.

Extensive Properties
A property that depends on the amount of matter in a sample
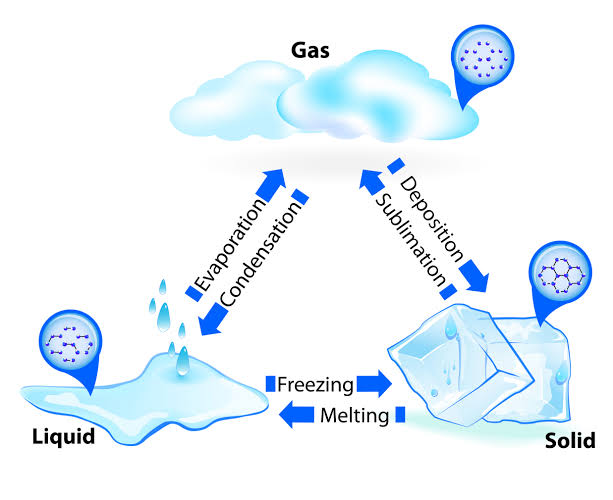
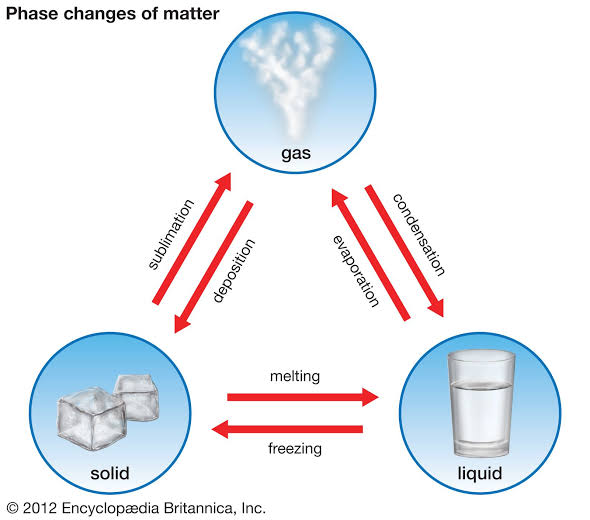
States of matter
Solids have a definite shape and volume.
Liquids have a definite volume, but take the shape of the container.
Gases have no definite shape or volume

Plasma
A state of matter that resembles a gas but has certain properties that gases do not have. Like a gas, plasma consists of particles of matter that can pull apart and spread out, so it lacks a fixed volume and a fixed shape.

Physical change
separate mixtures into their component compounds, but can not usually be used to separate compounds into chemical elements or simpler compounds.

Chemical change
the atoms are rearranged and the reaction is accompanied by an energy change as new products are generated.

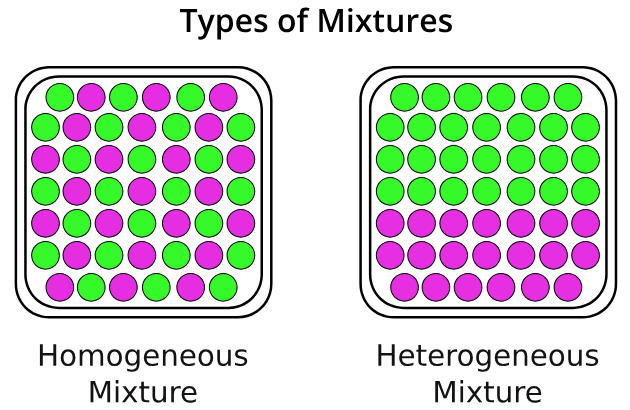
homogeneous mixture
A mixture in which the composition is uniform throughout the mixture.
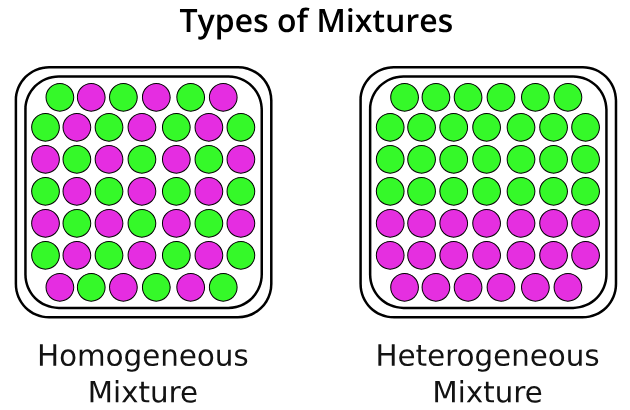

Heterogeneous mixture
a mixture in which the composition is not uniform throughout the mixture.