APES ( AP ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE) UNIT 3
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Specialists vs. Generalists
specialists- use only a few types of food, live in few places
generalists- using most food types, live anywhere
K-selected species characteristics
•Long development, long lived
•Live near carrying capacity
•Slow reproduction
•Few offspring, but high investment
r-selected species characteristics
- small size
- fast paced life
- large # offspring
- limited parental care
biotic potential
Maximum rate at which the population of a given species can increase when there are no limits on its rate of growth.
age cohort
an aggregate group of people born during the same time period
survivorship curve
Graph showing the number of survivors in different age groups for a particular species.
type 1 curve of survivorship
Most survive while young, die off quickly when they are older (Ex. Humans)
Type 2 Curve (Survivorship)
Equal survivorships (Ex. rodents)
Type 3 Curve (Survivorship)
Most die when young, then they survive a long time (Ex. fish)
K-selected species
type 1 survivorship curve - long lifespan
r-selected species
type 3 survivorship curve- short lifespan
Carrying capacity refers to
the maximum number of individuals that can be supported by an ecosystem
Overshoot
when a population becomes larger than the environment's carrying capacity
Dieback
a sudden decline in population
limiting resource
A short supply of resources restricting the growth of a population (Ex. food, shelter, water)
mortality
death
Fucundity
fertility
rapid growth
when population grows quickly
negative growth
the actual decline in population due to less than replacement births or extensive diseases
population momentum
continued population growth that does not slow in response to growth reduction measures
3 factors that influence TFR
educational opportunities for females, access to family planning, gov. acts and policies
replacement-level fertility rate
average number of children a couple must have to replace themselves (2.1)
infant mortality rate
The percentage of children who die before their first birthday within a particular area or country.
CBR (Crude Birth Rate)
The total number of live births in a year for every 1,000 people alive in the society.
CDR (Crude Death Rate)
The total number of deaths in a year for every 1000 people alive in the society.
density dependent
disease, competition, predation
density independent
temperature, natural disasters
Rule of 70 formula
number of years to double = 70/growth rate
theory of demographic transition
the theory that as a country moves from a subsistence economy to industrialization and increased affluence it undergoes a predictable shift in population growth
pre-industrial stage
birth and death rates high, population grows slowly, infant mortality high
transitional stage
death rate lower, better health care, population grows fast
post-industrial stage
low birth and death rates
characteristics of a developed country
more money, low birth rates, more sanitation, more health care, lower death rates
characteristics of a developing country
Poor, struggling economies which lack diversity, lack of technology, poor schooling, limited access to healthcare.
exponential growth model
a mathematical description of idealized, unregulated population growth, not limited by resources (j-curve)
logistic growth model
a mathematical description of idealized population growth that is restricted by limiting factors (s-curve)
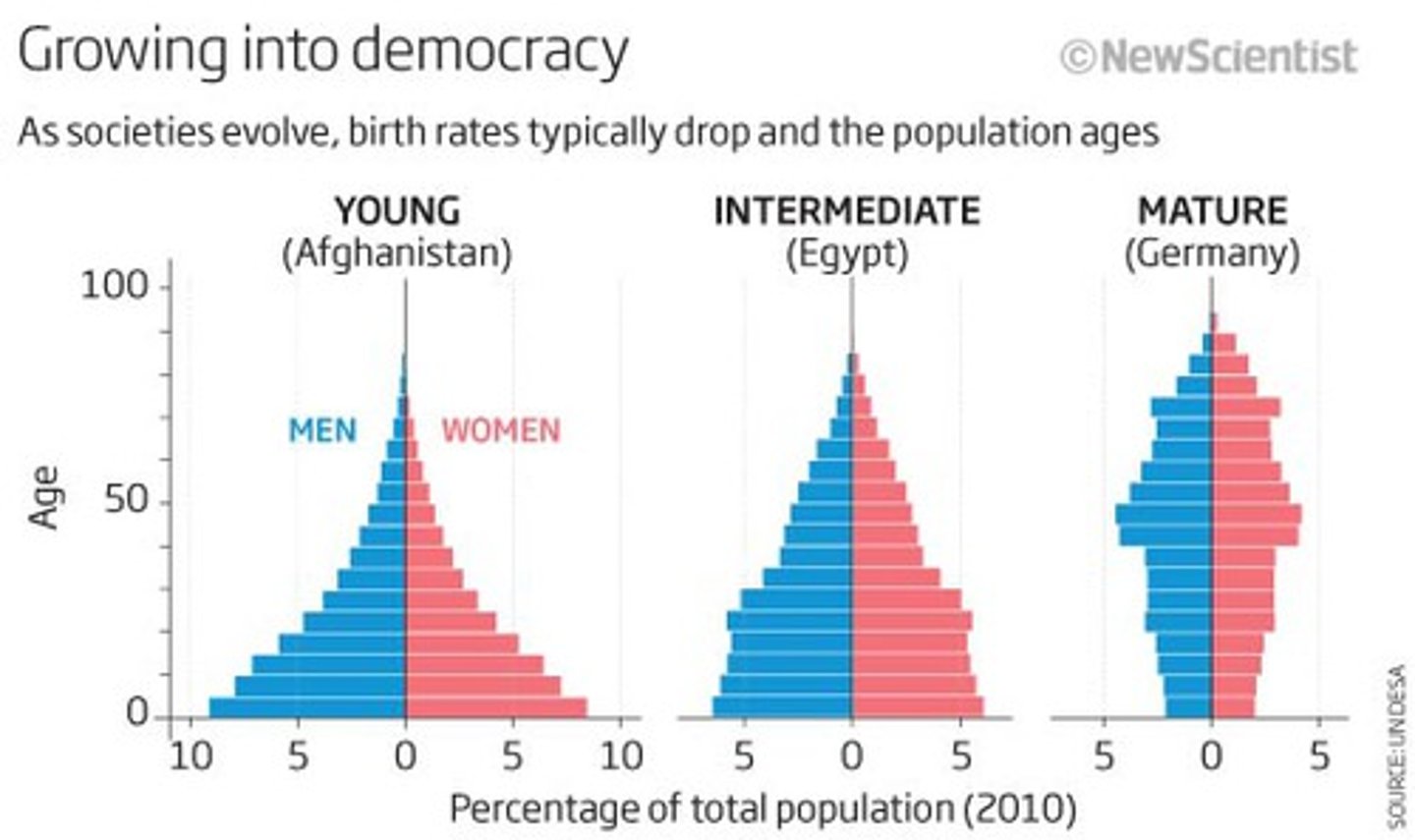
population age structure
how many individuals fit into age categories. Shown by age structure diagrams
growth rate equation
(CBR-CDR)/10
Total Fertility Rate (TFR)
an estimate of the average number of children that each woman in a population will bear throughout her childbearing years