Ch. 4 Endocrine Responses to Resistance Exercise
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
What is the endocrine system?
A system that consists of glands that synthesize, store, and release hormones into the blood.
How does the endocrine system differ from the nervous system?
The endocrine system uses hormones as chemical messengers, while the nervous system uses electrical signals.
What are hormones?
Chemical messengers synthesized, stored, and released into the blood by endocrine glands and certain other cells.
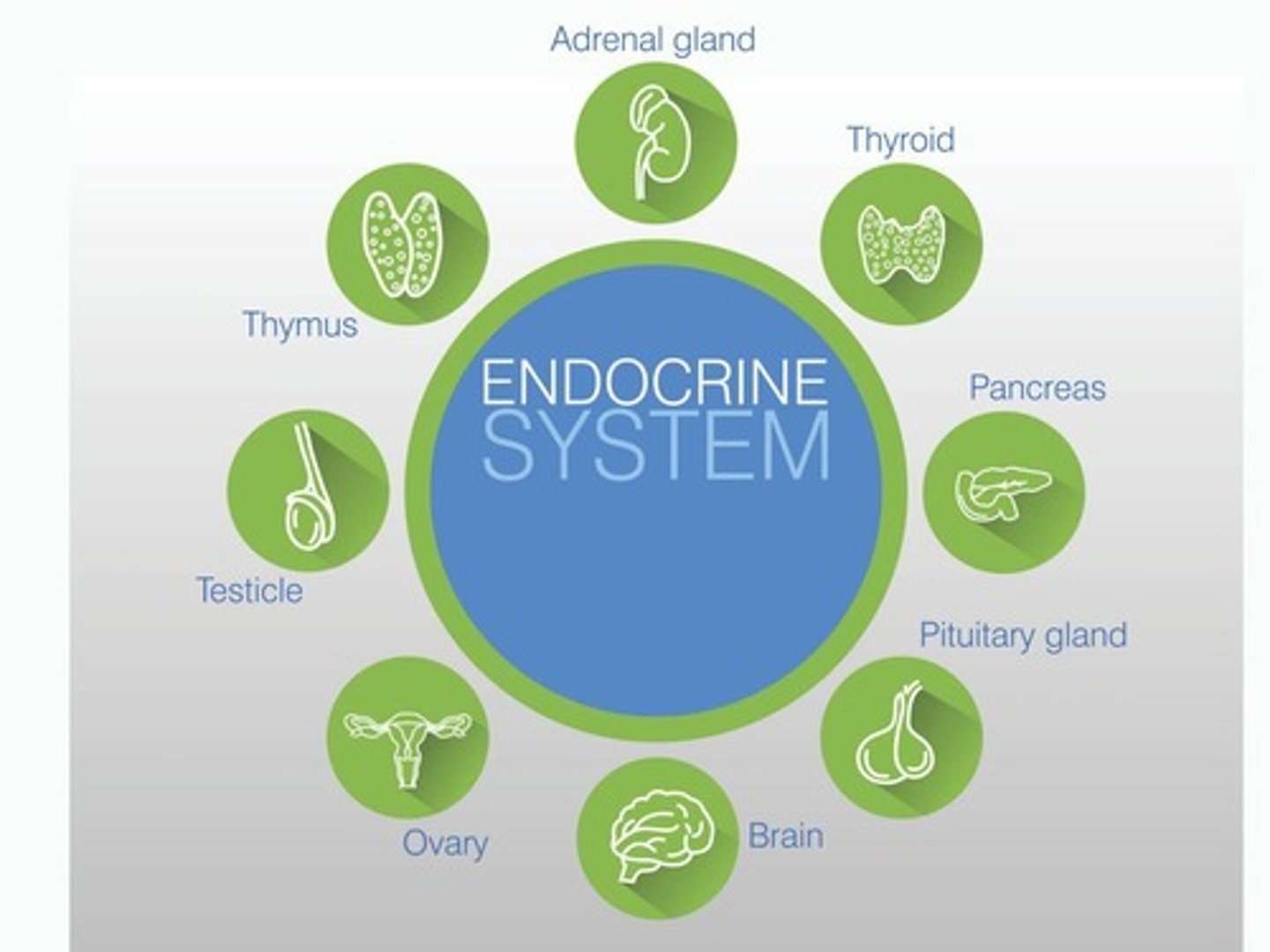
How many principal endocrine glands are there in the human body?
There are 8 principal endocrine glands.
What are endocrine glands?
Body structures specialized for making and releasing hormones into the blood.
What are the three types of hormone secretion?
Humoral, Neural, and Hormonal.
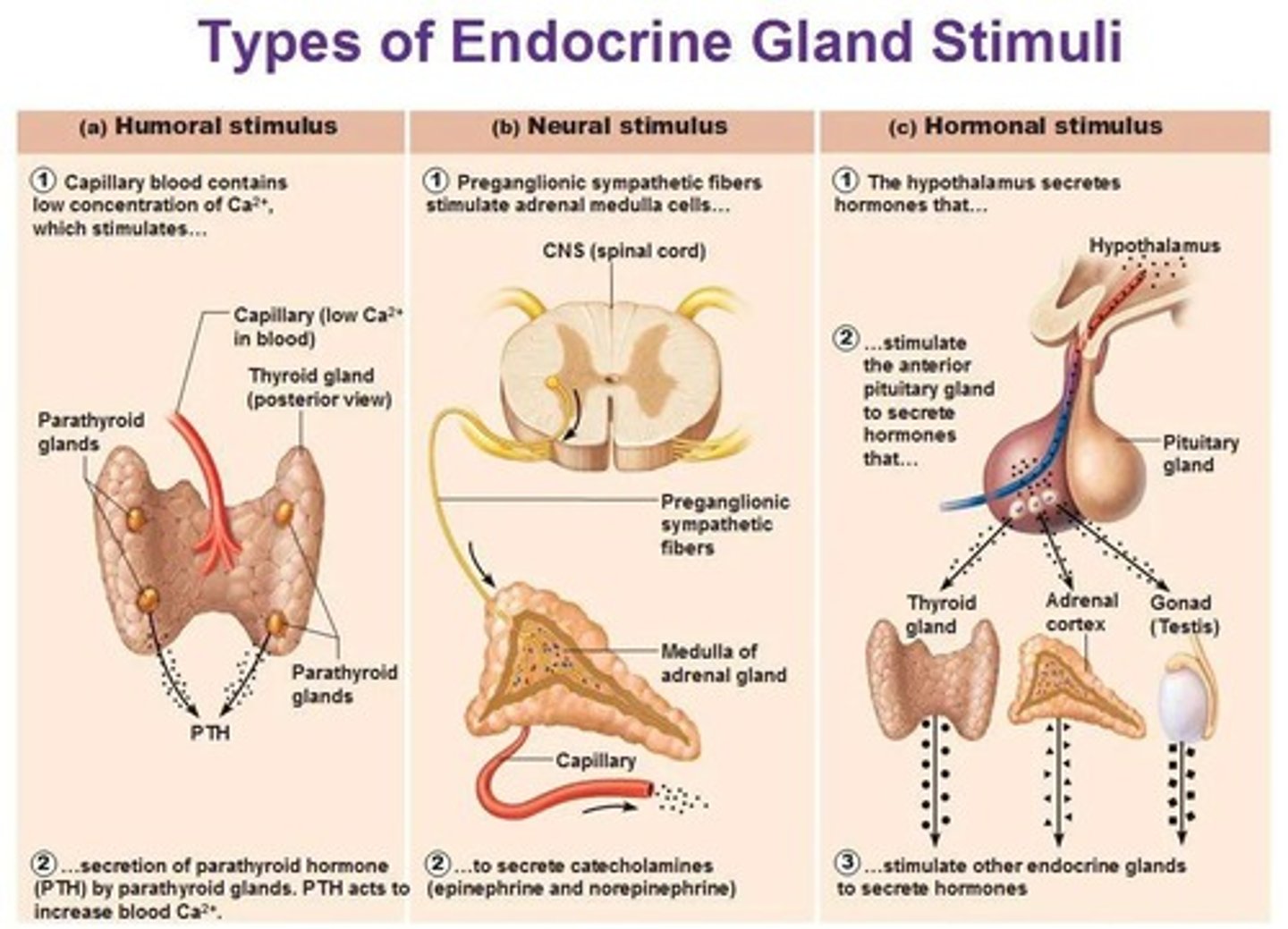
What is humoral hormone secretion?
Hormone secretion controlled by non-hormonal substances such as glucose, insulin, and ions.
What is neural hormone secretion?
Hormone secretion controlled by the autonomic nervous system.
What is hormonal hormone secretion?
Hormone secretion controlled by hormones secreted from other glands.
What does the lock-and-key theory refer to in hormone action?
It refers to how a hormone's signal is relayed only to target cells that express the specific receptor for that hormone.
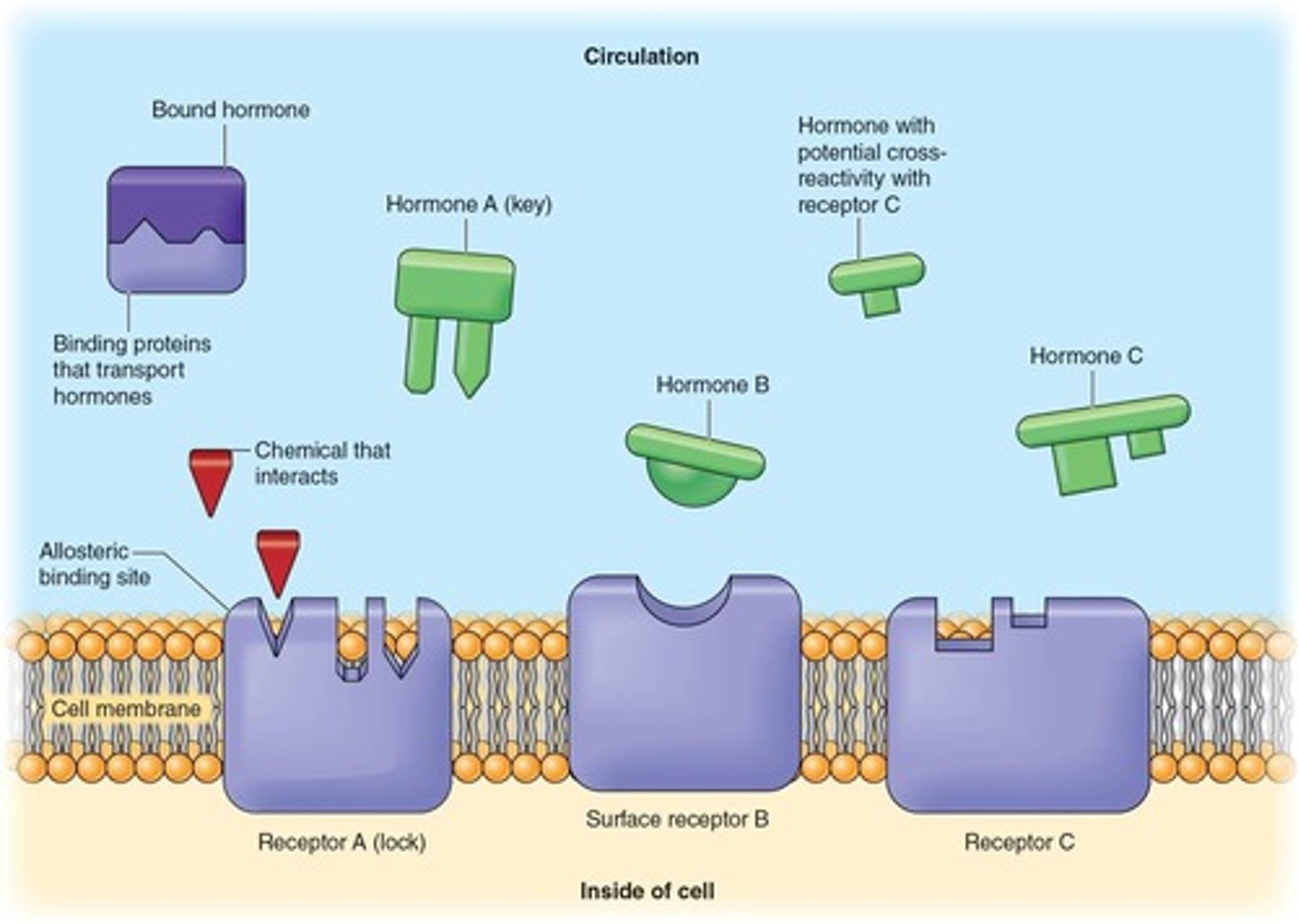
What is downregulation in hormone interaction?
The inability of a hormone to interact with a receptor, often due to overstimulation or adaptation.
What can cause downregulation of hormone receptors?
Overstimulation by a hormone or when an adaptation is no longer possible.
How can alterations to a receptor's binding characteristics affect hormone interaction?
They can be as significant as the release of increased amounts of hormone from an endocrine gland.
What tissues can hormones affect in the body?
Hormones can affect multiple tissues including bone, connective tissue, kidney, and liver.
What is the primary target of hormonal interactions discussed in this class?
Skeletal muscle tissue.
How do hormones influence muscle adaptations to resistance exercise?
Hormones are involved with protein synthesis and degradation mechanisms.
What are the two types of hormones involved in muscle adaptations?
Anabolic hormones (promote tissue building) and catabolic hormones (degrade cell proteins).
Name examples of anabolic hormones.
Insulin, insulin-like growth factors (IGFs), testosterone, and growth hormone.
What are examples of catabolic hormones?
Cortisol and progesterone.
What are the three main categories of hormones?
Steroid hormones, polypeptide (or peptide) hormones, and amine hormones.
Which two categories of hormones will be primarily focused on in this class?
Steroid and polypeptide hormones.
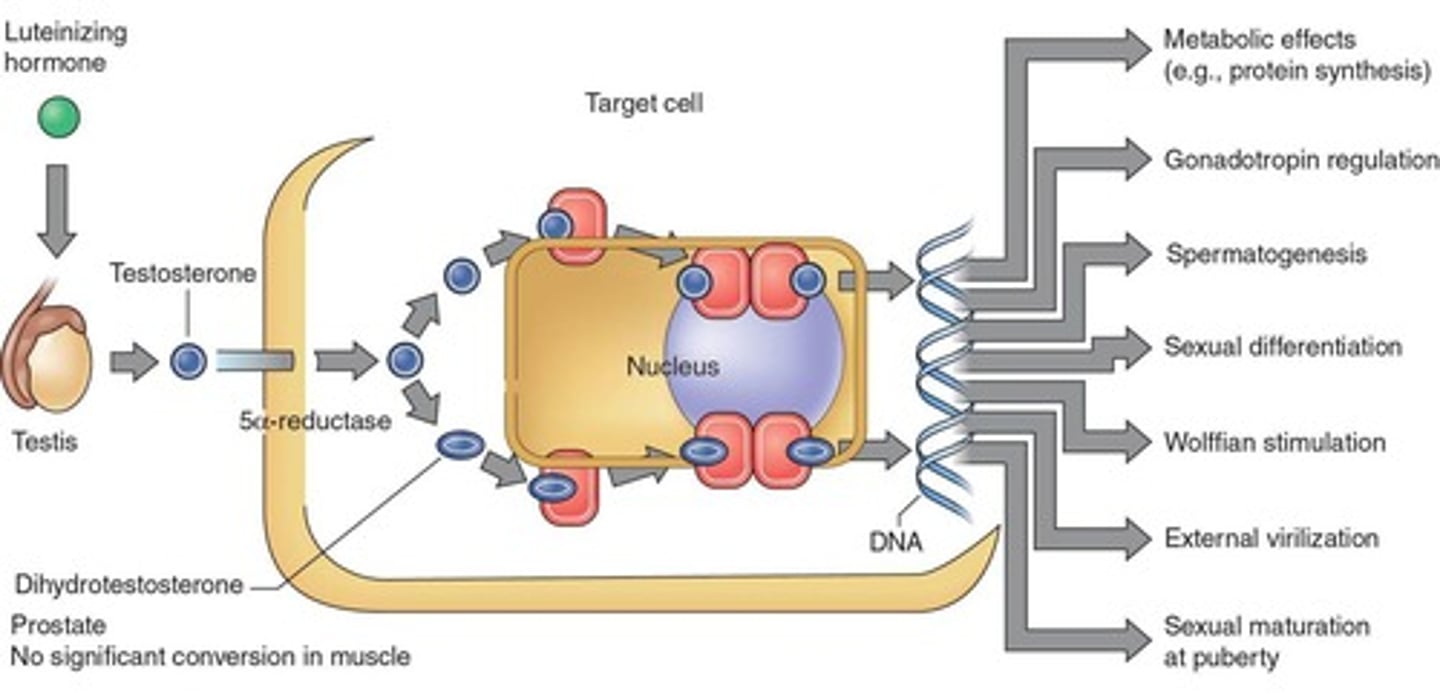
What is a characteristic of steroid hormones?
They are fat-soluble and can passively diffuse across the cell membrane.
From where are steroid hormones derived?
They include hormones from the adrenal cortex (e.g., cortisol) and the gonads (e.g., testosterone and estradiol).
What is a defining feature of polypeptide hormones?
They are water-soluble and cannot cross the cell membrane.
How are polypeptide hormones activated inside the cell?
By activating secondary messengers through a conformational change in the receptor induced by hormone binding.
What is the effect of heavy resistance exercise on hormone secretion?
Hormones are secreted before, during, and after the resistance exercise due to physiological stress.
How can heavy resistance exercise affect androgen receptors in muscle?
As few as one or two heavy resistance exercise sessions can increase the number of androgen receptors in the muscle.
What is the relationship between testosterone and heavy resistance training?
Heavy resistance training can increase the absolute number of testosterone receptors, even if testosterone concentrations do not change significantly.
What types of exercises can acutely increase total testosterone concentrations in men?
Large muscle group exercises (like deadlifts and squats) with adequate volume.
What exercise variables can increase serum testosterone concentrations?
Large muscle group exercises, heavy resistance (85-95% of 1RM), moderate to high volume, short rest intervals, and two years or more of resistance training experience.
What percentage of total testosterone is free testosterone?
Free testosterone accounts for only 0.5% to 2% of total testosterone.
How does heavy resistance exercise affect free testosterone levels?
It can acutely increase free testosterone in both men and women, though the increase is smaller for women.
What is the difference in testosterone concentrations between men and women?
Women have about 15- to 20-fold lower concentrations of circulating testosterone than men.
How can testosterone concentrations vary among women?
Some women may secrete higher concentrations of adrenal androgens.
What happens to testosterone levels in response to exercise demands?
Testosterone increases in response to exercise demands, and receptors may increase binding to utilize elevated testosterone.
What can prevent receptors from increasing binding to testosterone?
A lack of need for the signal to increase muscle-related metabolism.
What factors may influence the concentration of testosterone during training?
Training time and experience are important factors that can alter resting and exercise-induced concentrations of testosterone.
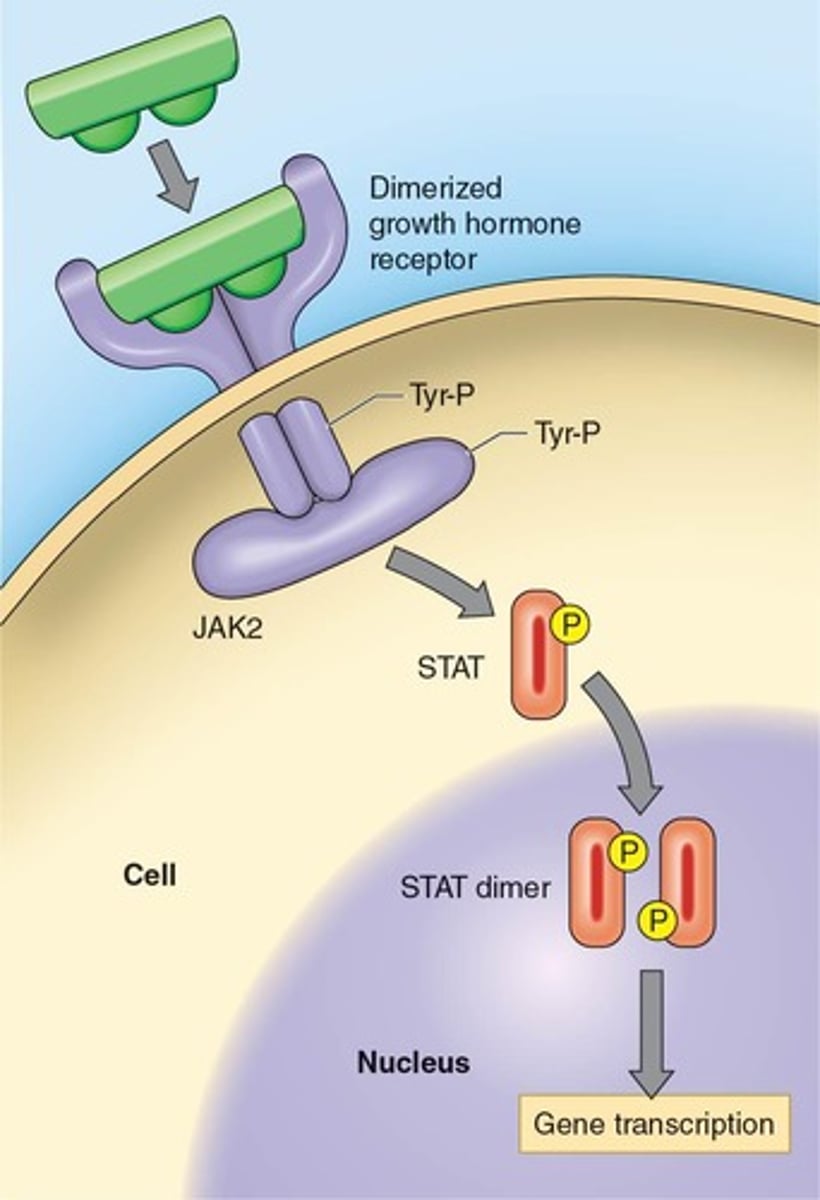
What is the role of Growth Hormone (GH) in resistance training?
GH is vital for normal development, adapts the body to resistance training stress, decreases glucose utilization, increases protein and collagen synthesis, stimulates cartilage growth, enhances immune function, and increases lipolysis.
How does the menstrual cycle affect hormone responses in women during exercise?
Hormone concentrations and responses to exercise in women vary with menstrual phase, with reduced testosterone concentrations being a notable difference from men.
What is the significance of measuring GH concentrations over longer periods?
GH concentrations need to be measured over 2-24 hours to determine changes that occur with resistance training.
What are the major catabolic effects of cortisol?
Cortisol stimulates the conversion of amino acids to carbohydrates, increases proteolytic enzymes, inhibits protein synthesis, and suppresses glucose-dependent processes.
Which muscle fiber type is more affected by cortisol?
Cortisol has a greater effect on Type II fibers than on Type I fibers.
How does resistance exercise affect cortisol levels?
Resistance exercise protocols that create a dramatic stimulus to anaerobic metabolism can increase cortisol levels, which may not have negative effects after adaptation.
What are the roles of catecholamines during exercise?
Catecholamines increase force production, muscle contraction rate, blood pressure, energy availability, muscle blood flow, and hormone secretion rates.
How does heavy resistance training affect catecholamine secretion?
Heavy resistance training increases an athlete's ability to secrete greater amounts of epinephrine during maximal exercise.
What is the relationship between catecholamines and other hormones during resistance exercise?
Catecholamines are involved in metabolic control and the response mechanisms of other hormones such as testosterone and growth hormones.
What are some hormones implicated in growth and repair during exercise?
Insulin, thyroid hormones, and beta-endorphin are implicated in growth, repair, pain analgesia, and exercise stress mechanisms.
What training protocols lead to increased serum cortisol values?
Resistance exercise protocols that use high volume, large muscle groups, and short rest periods result in increased serum cortisol values.
What is the impact of chronic high cortisol concentrations?
Chronic high concentrations of cortisol may have adverse catabolic effects, but acute increases contribute to muscle tissue remodeling and maintenance of blood glucose.
What adaptations occur in hormone responses with resistance training?
Adaptations include changes in hormone concentrations and responses, particularly in GH and catecholamines, which may improve performance.
How does cortisol affect immune cell function?
Cortisol suppresses immune cell function as part of its catabolic effects.
What is the role of testosterone in relation to cortisol during resistance training?
Adaptation to training may disinhibit cortisol at the testis level, maintaining testosterone's influence on its nuclear receptors.
What is the significance of the area under the time curve in hormone measurement?
The area under the time curve helps determine whether changes in hormone release have occurred over time.
What are the physiological roles of Growth Hormone (GH)?
GH decreases glucose utilization, increases protein and collagen synthesis, stimulates cartilage growth, enhances immune function, and increases lipolysis.
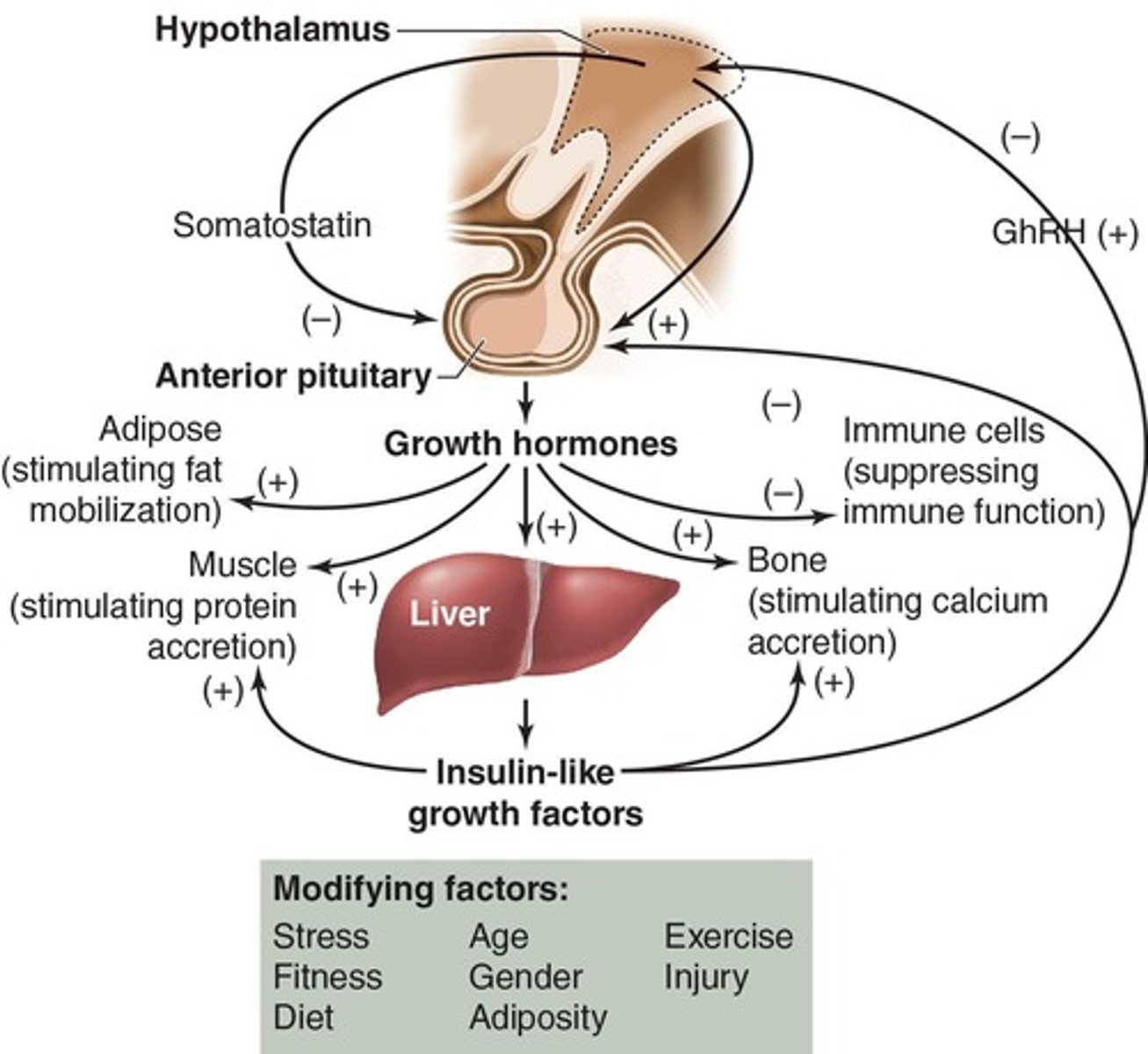
What are the effects of high volume exercises and short rest intervals on GH?
High volume exercises (e.g., 3 x 15) and short rest intervals (e.g., 30 seconds) are important for stimulating GH responses.
How do catecholamines affect muscle blood flow?
Catecholamines increase muscle blood flow through vasodilation.
What is the effect of resistance exercise on cortisol in trained individuals?
In trained individuals, increases in cortisol may not have negative effects due to adaptation.
What is the relationship between GH and stress adaptation in children?
GH plays a vital role in the normal development of a child and adapting to the stress of resistance training.