Production Animal Lameness + Ruminant Foot Structure
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Lameness
clinical sign not disease - adjustment of gait to relieve pain
physiological distress → decreased production
nutritional and hormonal impacts
consider at individual and herd level
herd level → management/husbandry improvements
88% feer
other sites - dislocated hips, spinal issues or nerves
Clinically relevant anatomical key words
Ruminant foot anatomy → lameness causes
often solved by foot trimmers rather than vets
Laminae → laminitis
White line (junction between horn of wall and sole of foot)
When foreign body invades white line → white line disease
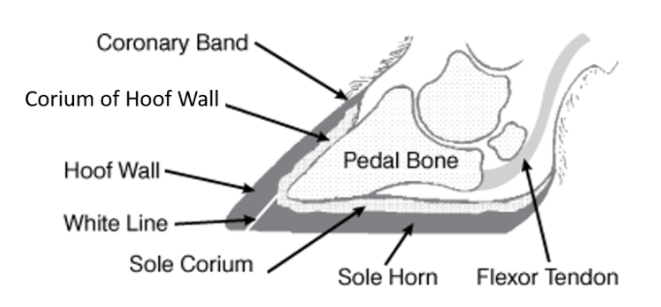
Hoof wall, pedal bone, sole horn
Corium (dermis)
Sits underneath pedal bone
Sits above horn of sole and dorsal wall of foot
Digital cushion
Fat pad → acts as shock absorber as pedal bone bounces on top of corium
Sits under pedal bone process
Skinny cow/Poor horn growth → depleted fat in digital cushion → hook process of P3 presses against the corium → sole ulcer
Most frequent ruminant foot lesions [4]
sole ulcer
white line disease
digital dermatitis
strawberry raw lesion at palmar/plantar aspect at cleft underneath dewclaws
Fouling foot (foul)
penetration injury of digital space
bacteria grows in hoof soft tissues
swelling + infection of hoof
pressure builds in enclosed space → swelling inside hoof capsule seen at coronary band
3+ 4} infections → can appear together
1+2} claw horn traumatic disruption lesions, requires debridement
Sheep lameness
Infectious causes more common than noninfectious
Scald-footrot complex biggest problem (65%)
Scald
Shelly hoof → white line disease
Toe abscess
Toe granuloma
CODD → contagious ovine digital dermatitis
Footrot
Infectious vs traumatic
Traumatic (claw horn disruption lesions)
Sole ulcer → most often affects outer hind claw
White line disease
Sole bruising
Infectious
Digital dermatitis - most sheep lesions
Both often involved simultaneously
Lameness clinical signs
Arched back
Swelling on non weight bearing foot
Dull
Struggling to stand
Lameness consequences
Reduced ability to stand and move freely
Reduced ability to feed
reduced appetite (pain/immobility)
unable to reach food
competition from other cows
Results in:
reduced milk yield
reduced BCS/ weight loss → reduced digital cushion
Reduced fertility
reduced detection → not mounting cows in heat
will not stand for bull
low BCS → struggle to get into calf, hormone imbalances → irregular cycles → high cull rate
Direct costs of lameness
Treatment fees
Labour time
Decreased milk yield:
Wasted due to drug withdrawal time
Reduced milk yield
Indirect costs of lameness
Reduced future fertility
Increased culling
Mobility scoring (AHDB)
0, 1, 2, 3
0 not lame, 3 non weight bearing
Can be used to distinguish animals needing treatment
Can be used as prevalence indicator at herd level
Score 0
Walk with even weight bearing and rhythm on all 4 feet
Flat back
Long fluid strides possible
Scoring timing/frequency: 100 day in milk check and dry off trim may be good routine for sound cows
Score 1
Uneven steps (rhythm or weight bearing) or strides shortened
Slight arch to back?
Affected limb(s) not immediately IDable
Remedial attention → routine trimming and further observation
Score 2
Uneven weight bearing on limb that is immediately IDable
Obviously shortened strides may be seen (usually with arch to centre of back)
Lame → feet should be lifted and examined ASAP
Score 3
Unable to walk as fast as brisk human pace → cannot keep up with healthy herd
Signs of score 2
Lame → urgent attention and treatment, should be kept on straw yard on pasture
Culling if severe to relieve pain → best catch lameness earlier before it reaches 3
Prevalence
Mobility scoring
Number of lame cows on farm AT GIVEN TIME TESTED
36/100 cows were score 2 or 3 when tested → prevalence is 36% during time tested
Incidence
Lameness records (multiple scores/recordings) → serial records
Number of NEW cases that have occurred in given period of time
does not take into account when one cow has multiple incidences
36 cases recorded in 100 cows in 3 years → incidence is 12 cases per 100 cows per year
200 new cases recorded in 100 cows in a year → incidence is 200 cases per 100 cows per year (cows had more than 1 new case in that period)
Husbandry Factors Affecting Lameness 1
White Line
Husbandry Factors Affecting Lameness 2
Digital Dermatitis
Husbandry Factors Affecting Lameness 3
Solar Ulcer
Key lameness prevention
Mobility scoring, keep records
Rapid treatment of clinical cases
Footbath schedule
Morning → formalin
Ensure footbath is long enough to be covered in a couple of strides
All feet dunked in
Afternoon → CuSO4
Routine trimming
Summary info
Huge welfare/economic impact
Large number of husbandry/farming factors involved in lameness
Apply herd level approach to:
Understand pathogenesis
Spot control points
Use evidence based interventions
Farm factors for cow lameness
Lack of routine trimming
Prolonged standing
Bad biosecurity
Slurry management
Biotin supplementation for horn quality
Bedding material
Cubicle comfort
Stocking density
Feed space
Surface issues
Slippery/uneven concrete
Wet conditions
Rough tracks
Cow factors
Low BCS
Distal phalanx descent
Toe length and foot angle overgrowth
Horn quality
Chronic pedal bone changes + fat pad scarring
Matrix metalloproteinase + relaxin released during calving period → slackens suspensory ligament and DFTs
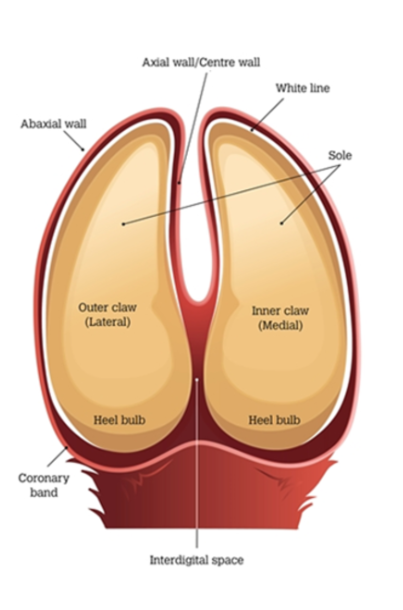
Ruminant Claw
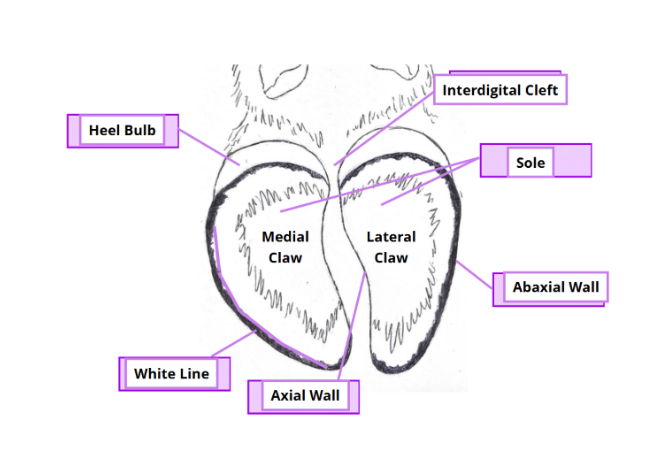
Cloven - hoof → Split = interdigital cleft
Inside split of interdigital cleft = axial surface btw 2 claws
Abaxial - outside (lateral surfaces) = remaining rounded surface of the claw
2 digits on each foot
Regions
Sole → slightly concave region on palmar/plantar aspect of each digit
Heel (Bulb) → slightly convex region at heel of sole
Wall
Abaxial aspect - convex + merges with bulb
Axial aspect - junction with bulb has groove = axial cleft
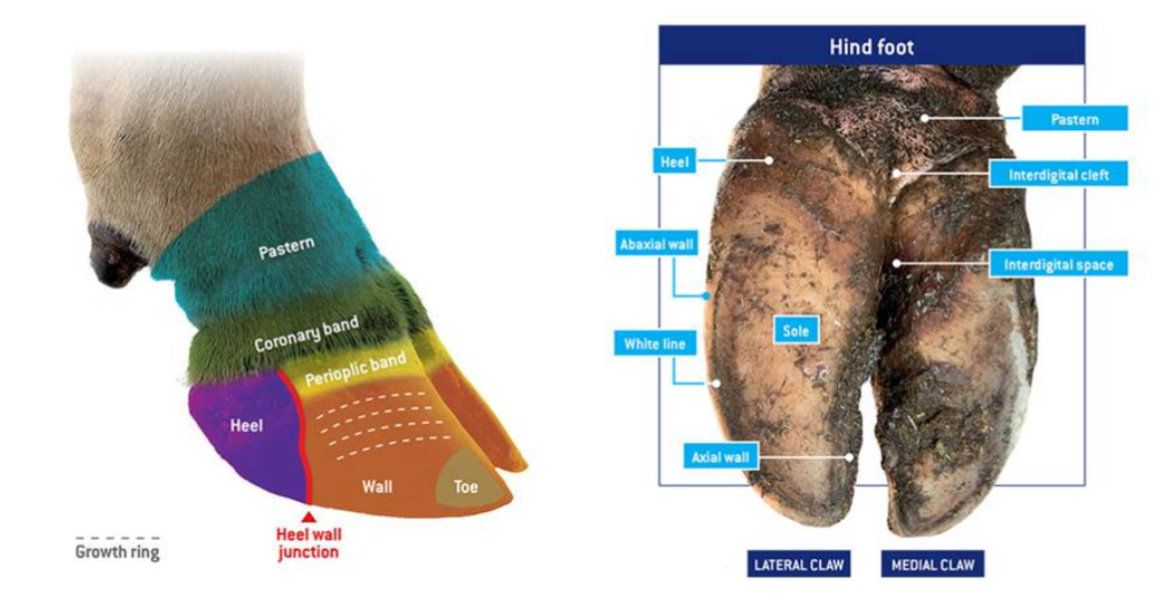
Dermis = Corum of wall
Similar to horse - arranged in laminae
Interdigitates with the epidermal horn - produced by papillon coronary region
dermal layer of the coronary band
contains papillae = make coronary and solar hoof wall
supply nutrients to hoof wall and sole
lamellae - suspend and attach P3
Horn on the sole & bulb - also produced by papillae
Hypodermis in bulb - forms pad of fibrous elastic tissue = digital cushion
Dewclaws - present in most ruminants - do not make contact with ground
Consist of wall and bulb but no practical importance
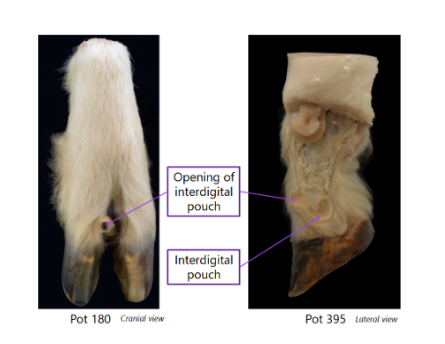
Ovine interdigital pouch
Found in fore and hindlimbs of both sexes
Pouches are tubular invaginations of the skin
Walls of pouch contain sebaceous & serous glands
Discharge waxy secretion which spreads down onto hooves
Serves as trail-marker
Horn Growth
Horn of hoof grows at rate of 5mm per month
Growth should = wear in cattle move freely
Intensively kept cattle → Growth > Wear ⇒ foot trimming required to maintain optimal shape and angle
Horn overgrowth: coffin joint is gradually overextended and deep flexor tendon tensed
Greater weight placed over caudal part of the hoof and can cause pain and lameness