Final Exam Study Guide: Ecosystems to Genomics
1/175
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
176 Terms
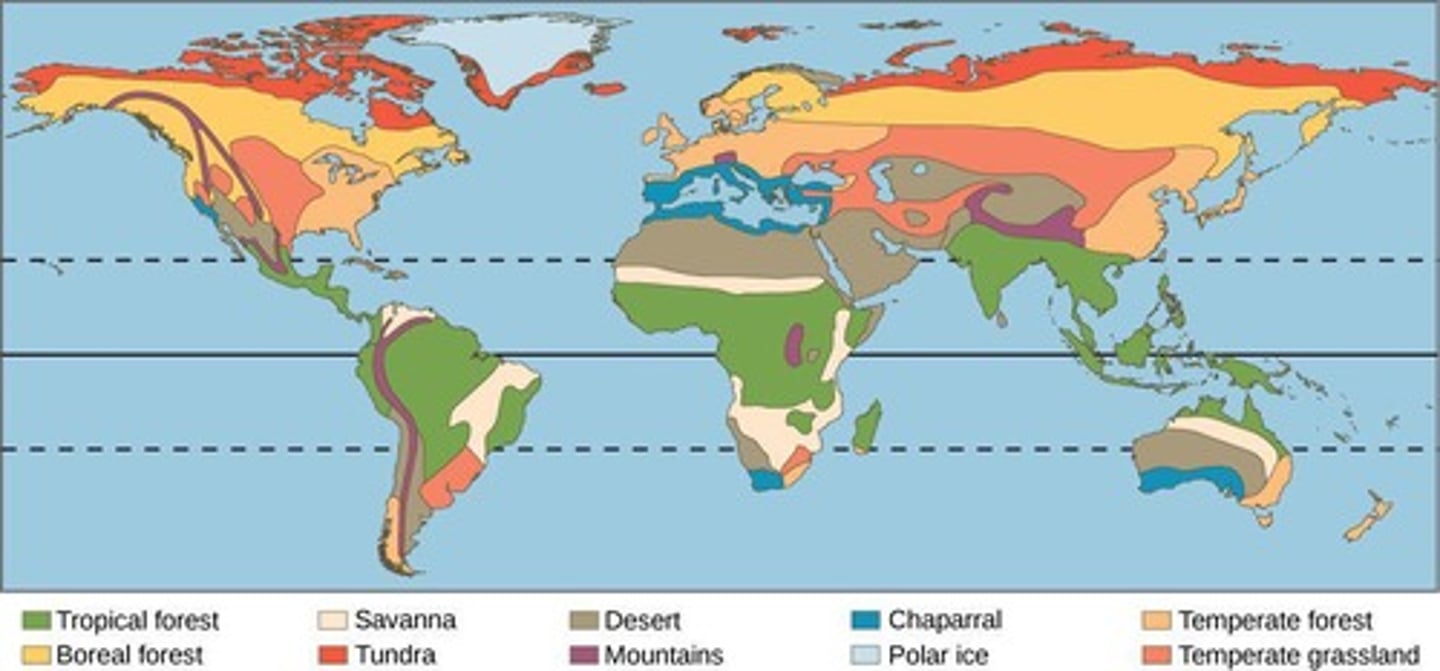
Biome
A region of Earth that experiences the same types of temperature and precipitation conditions, resulting in similar collections of plants and animals.
Trophic Cascade
A series of cause-and-effect events that occur after a change in an ecosystem.
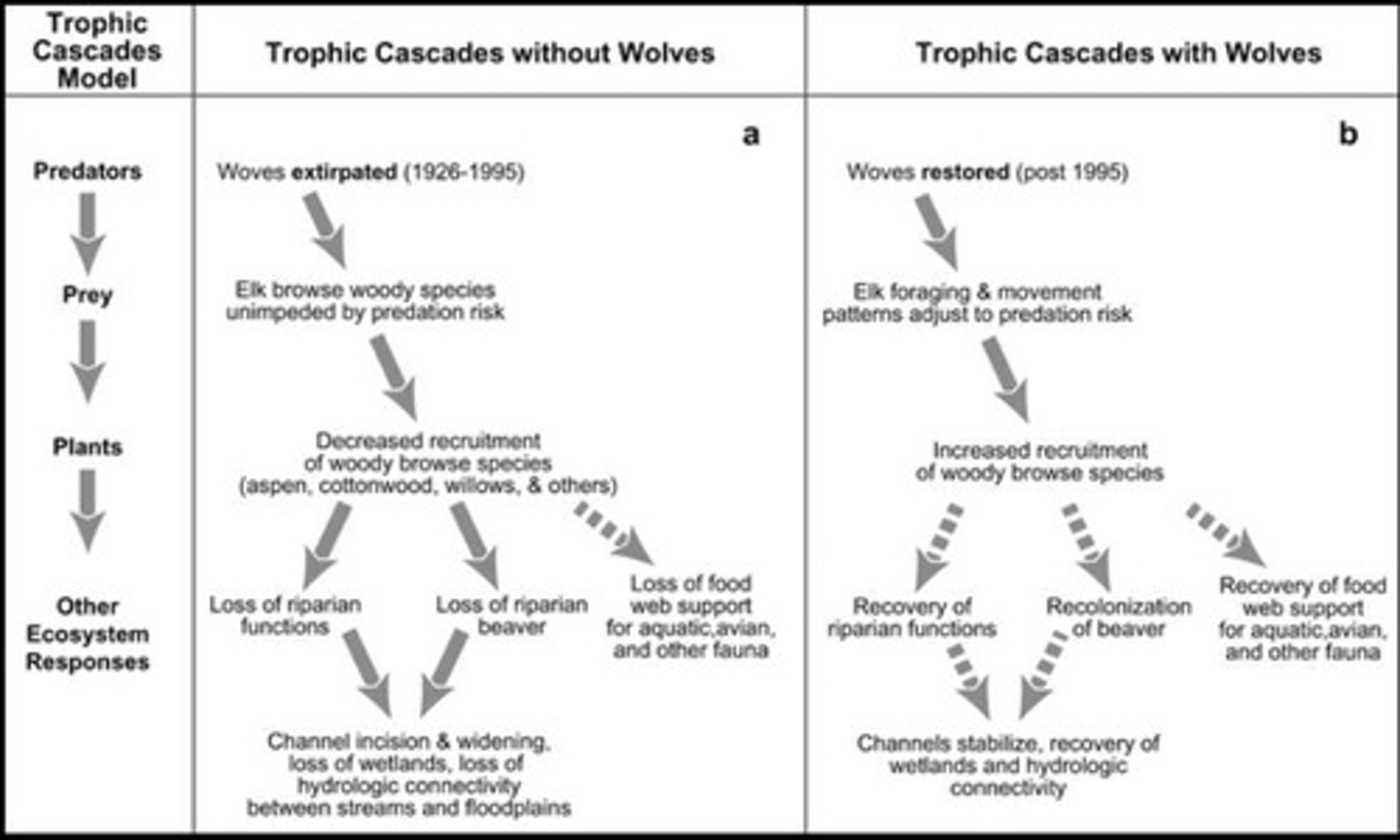
Keystone Species
A species on which the other species in an ecosystem largely depend, such that if the keystone species were removed, the ecosystem would change drastically.

Molecule
Groups of atoms connected by chemical bonds.
Chemical Bonds
Connections formed by atoms sharing electrons (covalent bonds) or by interactions between positive and negative charges (ionic bonds).
Chemical Reaction
Occurs when the bonds of molecules break and atoms are rearranged to make new molecules.
Reactants
The molecules that are taken apart in a chemical reaction.
Products
The molecules that are produced in a chemical reaction.
Endergonic Reactions
Chemical reactions that require energy.
Exergonic Reactions
Chemical reactions that release energy.
Hydrolysis
Involves breaking down large molecules into smaller pieces.
Cell Respiration
A chemical reaction used by living things, where oxygen is used to release energy from glucose.
ATP
Adenosine triphosphate, an energy carrier molecule produced in exergonic reactions and used in endergonic reactions.
ATP Production Equation
6O2 + C6H12O6 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy (36 ATP)
ATP Functions
Required for synthesizing large molecules, moving materials across cell membranes, and moving structures around in cells.
Aerobic Cell Respiration
Uses both glucose and oxygen, producing carbon dioxide and water as waste products.
Anaerobic Cell Respiration
Uses only glucose, producing ethanol or lactic acid as waste products.
Mitochondria
Organelles required for aerobic cell respiration.
Energy Conversion
Once energy is used, it is converted into heat and ultimately lost to the environment.
Recharging ATP
New energy can be used to 'recharge' the ATP molecules.
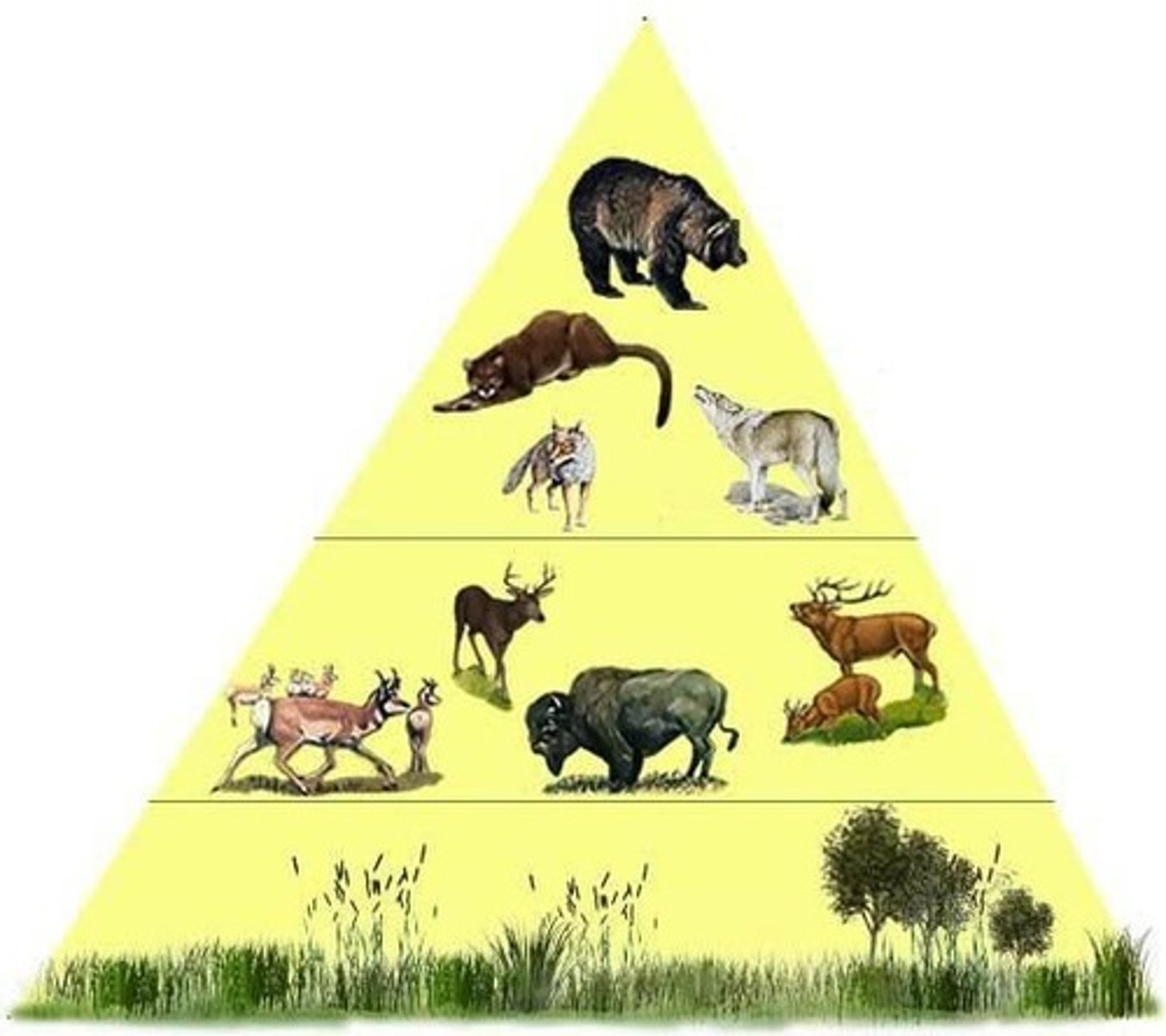
Food Chain
A linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another.
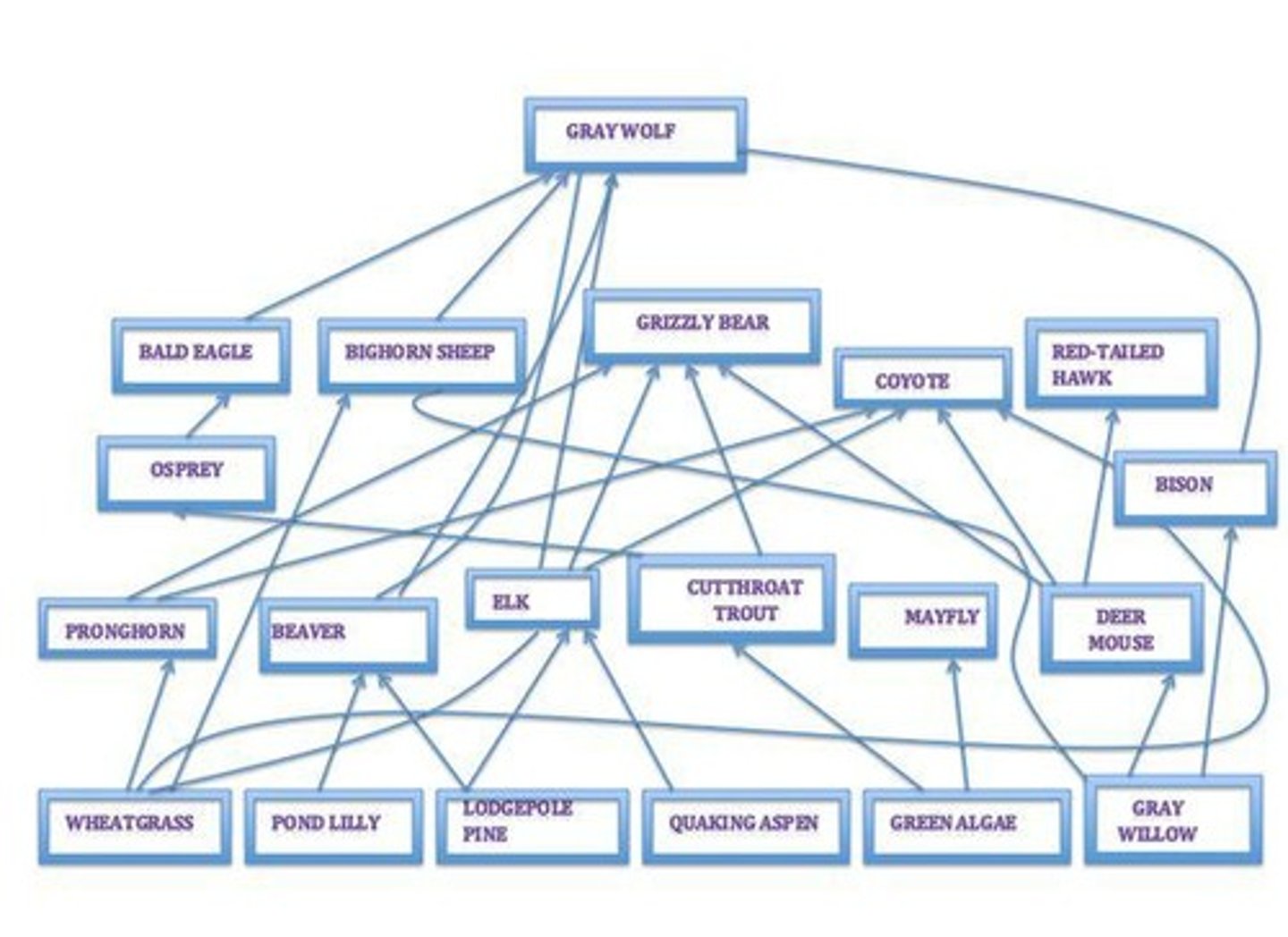
Food Web
A complex network of feeding relationships among various organisms in an ecosystem.
Biodiversity
The variety of life in the world or in a particular habitat or ecosystem.
Ecosystem Health
Maintained by biodiversity and species richness, which keeps the ecosystem healthy.
ATP Production in Anaerobic Respiration
Only 2 ATP are produced per glucose.
Aerobic Cell Respiration Inputs
Matter: Glucose, Oxygen.
Aerobic Cell Respiration Outputs
Matter: Carbon Dioxide, Water; Energy: 36 ATP.
Anaerobic Cell Respiration Inputs
Matter: Glucose.
Anaerobic Cell Respiration Outputs
Matter: Ethanol or Lactic Acid; Energy: 2 ATP.
Photosynthesis Reaction
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2.
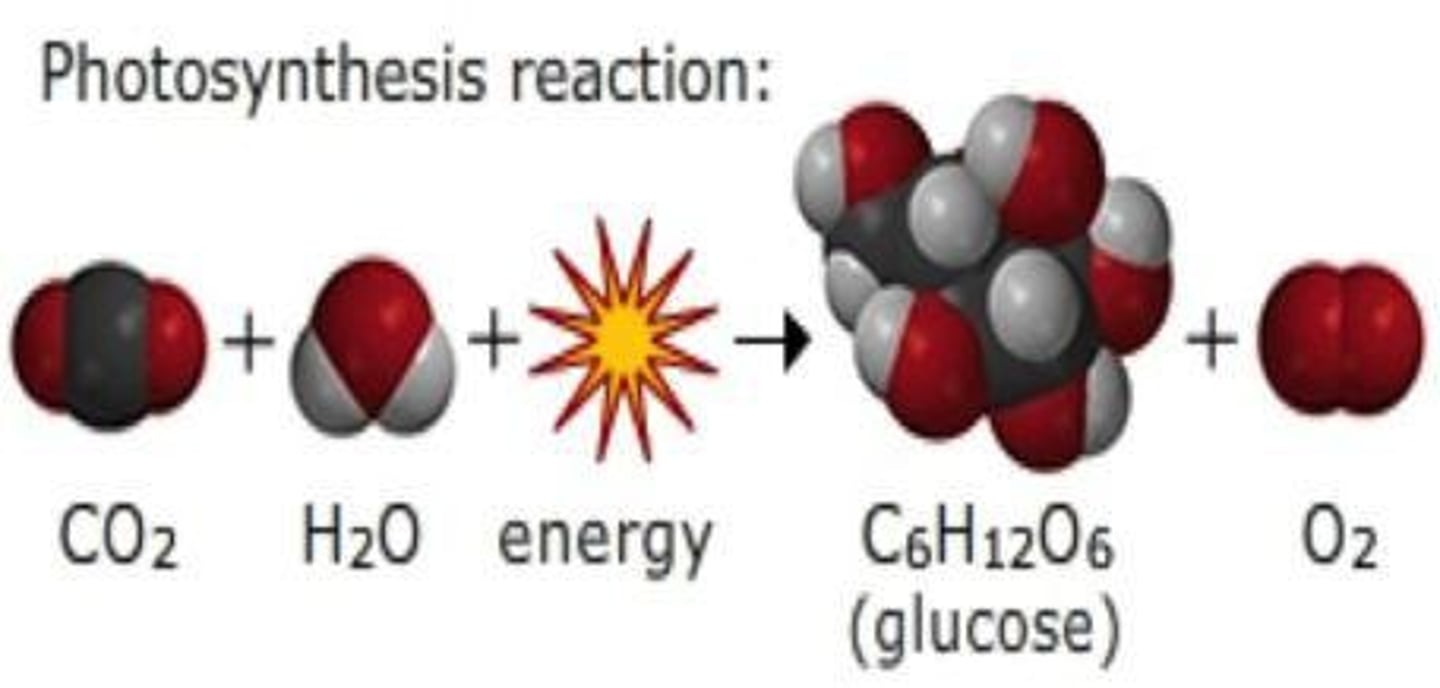
Photosynthesis Definition
The chemical reaction that some living things (plants and algae) use to capture and store energy from the sun.
Energy Source for Photosynthesis
The energy required for this reaction comes from sunlight.
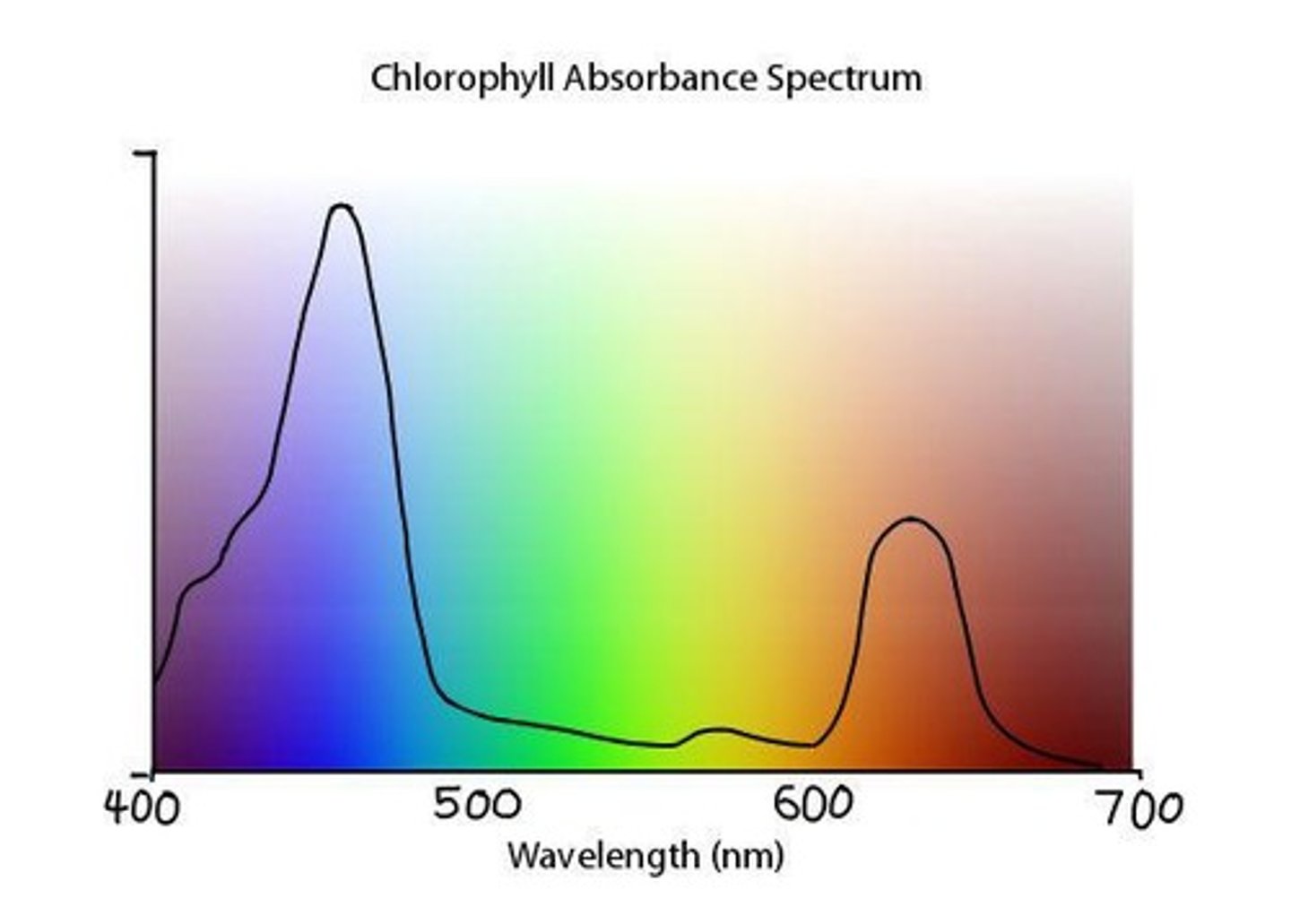
Chlorophyll Function
Absorbs red and blue-violet light and reflects green and yellow light.
Temperature Effect on Photosynthesis
Increased temperature increases the rate of photosynthesis up to a certain point.
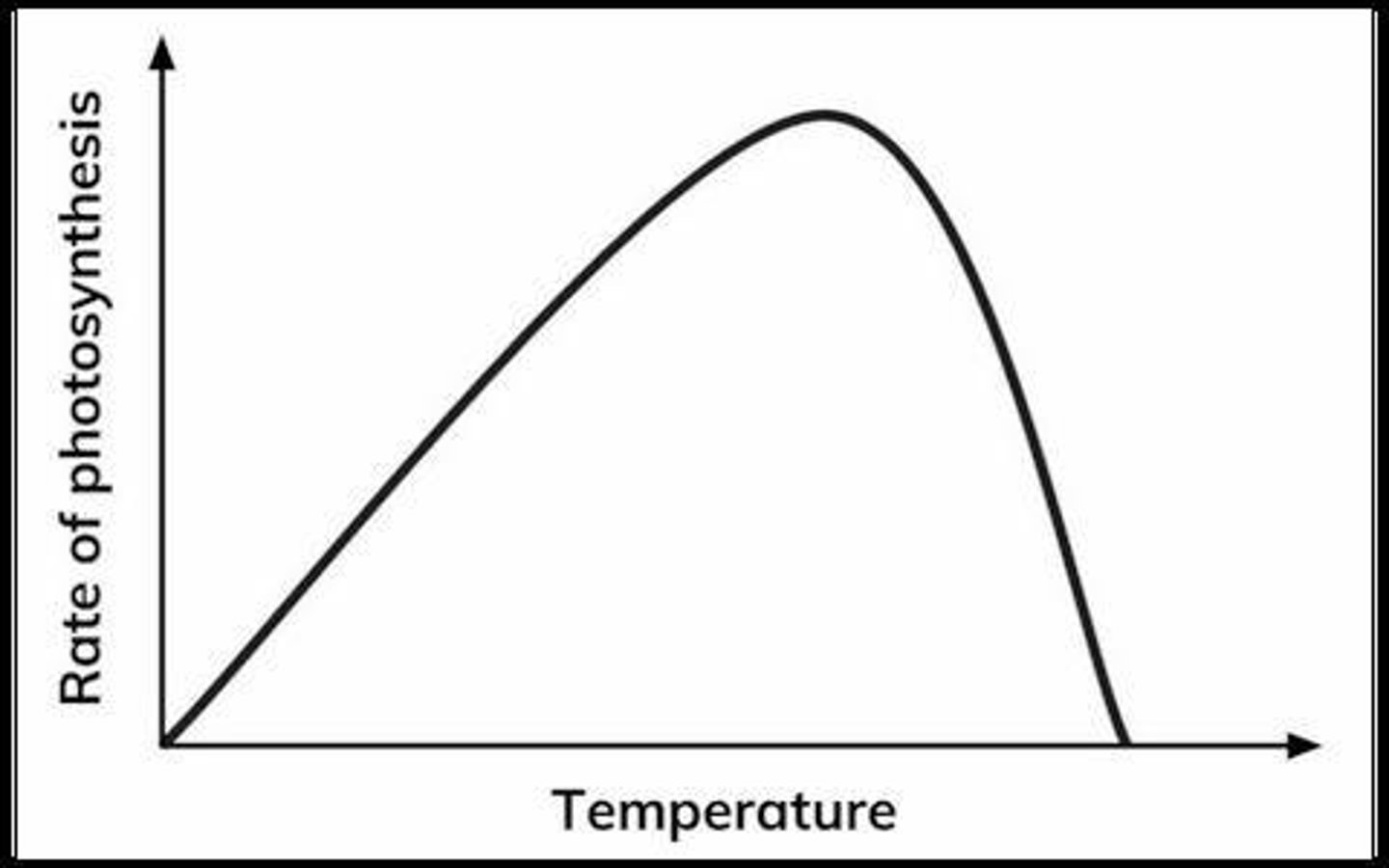
Optimum Temperature
Above the optimum temperature, the rate of photosynthesis drops off because the enzymes responsible for photosynthesis start to denature.
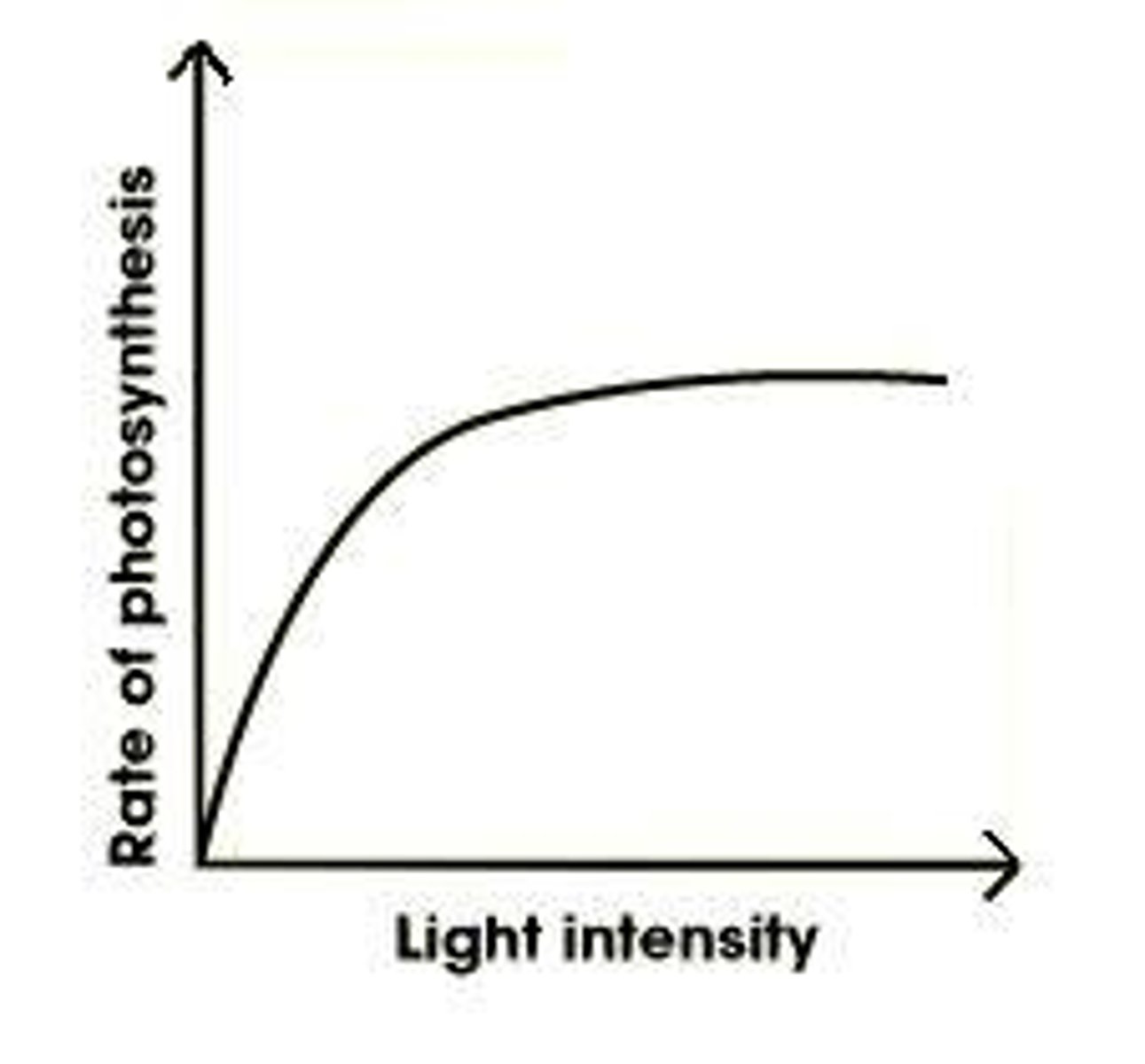
Light Intensity Effect on Photosynthesis
Both the amount and the wavelength of light can limit the amount of photosynthesis that occurs.
Carbon Dioxide Concentration Effect
In general, the more carbon dioxide there is, the more photosynthesis occurs.
Carbon Pools
Carbon atoms form the main structure of all organic molecules.
Carbon Fluxes
Processes that move carbon from pool to pool.
Carbon Cycle
A model of how carbon atoms are moved around within ecosystems.
Plant Biomass
Carbon is contained within the molecules of glucose, stored in roots or special storage organs.
Animal Biomass
Carbon is contained within the molecules of animals, including proteins, fats, and carbohydrates.
Atmospheric CO2
Carbon is stored in the atmosphere in the form of carbon dioxide, which is 0.04% CO2, or more than 400 ppm.
Dissolved Carbon
Carbon is stored in water as dissolved CO2 or as carbonic acid.
Dead Organic Material
Carbon is stored in soil, in peat, and in limestone rocks.
Fossil Fuels
Carbon is stored in coal, oil, and natural gas.
Coal formation
Coal is formed when peat becomes compressed over time under layers of sediment.
Oil and natural gas formation
Oil and natural gas are formed in mud beneath lakes and seas, and become trapped when the mud turns to rock.
Photosynthesis (carbon fixation)
Producers convert CO2 from the atmosphere or the water into glucose through the process of photosynthesis.
Diffusion
CO2 can move between the atmosphere and water through the process of diffusion.
Assimilation
When consumers eat producers or other consumers, the carbon contained within plant or animal biomass is assimilated into the organic molecules of the organisms on the next trophic level.
Decomposition
When organisms die and decay, the carbon in their biomass becomes dead organic material in the soil.
Fossil fuel formation
Over time and under the right conditions, dead organic material can become limestone, coal, oil, or natural gas trapped within layers of rock.
Combustion
When plant biomass is burned, the carbon is released to the atmosphere in the form of CO2.
Combustion of fossil fuels
When fossil fuels are burned to create energy, the carbon is also released to the atmosphere in the form of CO2.
Volcanoes
Volcanoes can return carbon stored in rocks or fossil fuels to the atmosphere.
Monomer
A molecule that can be bonded to other identical molecules to form a polymer.
Polymer
A large molecule made of similar subunits bonded together.
Classes of biomolecules
There are 4 classes of biomolecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids.
Amino Acids
The monomer of proteins.
Proteins
Proteins do most of the jobs within cells, including communication, movement, structures, chemical reactions, regulation.
Protein characteristics
Proteins contain C, H, O, N and sometimes P and/or S.
Protein uses
Proteins are used for communication, movement, structures, chemical reactions, and regulation within cells.
Protein structure
Amino acids link to form chains, chains fold into shapes that serve functions.
Protein
Biomolecule category that contains elements C, H, O, N, S, P and is made up of amino acids.
Carbohydrates
Biomolecule category that contains C, H, O and includes monosaccharides and polysaccharides.
Monosaccharide
The monomer of carbohydrates, also known as simple sugars, such as glucose.
Polysaccharide
The polymer of carbohydrates, also known as complex carbohydrates, such as starch or fiber.
Nucleic Acids
Biomolecule category that contains C, H, O, N, P and includes DNA and RNA.
Nucleotide
The monomer of nucleic acids, containing a nitrogenous base, a sugar, and a phosphate group.
Lipids
Biomolecule category that contains C, H, O and includes fatty acids, triglycerides, and phospholipids.
Fatty Acids
The monomer of lipids, which are long chains used for energy storage and insulation.
Triglycerides
A type of lipid polymer formed from glycerol and three fatty acids.
Phospholipids
A type of lipid that forms cell membranes, consisting of two fatty acids and a phosphate group.
Digestion Reaction
A reaction that breaks polymers down into monomers, releasing energy and is exergonic.
Synthesis Reaction
A reaction that connects monomers together to form polymers, requiring energy and is endergonic.
Metabolism
The total of all chemical reactions in the body, combining anabolism and catabolism.
Enzymes
Proteins that act as catalysts to speed up chemical reactions without being permanently changed.
Substrates
The reactants in enzyme-catalyzed reactions that bind to the enzyme's active site.
Active Site
The specific region on an enzyme where substrates bind to form the enzyme-substrate complex.
Enzyme-Substrate Complex
The intermediate formed when a substrate binds to an enzyme's active site.
Anabolism
The set of metabolic pathways that construct molecules from smaller units, requiring energy.
Catabolism
The set of metabolic pathways that break down molecules into smaller units, releasing energy.
C, H, O, N, S, P
Elements commonly found in biomolecules such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids.
1 C : 1 O
The ratio of carbon atoms to oxygen in carbohydrates.
Variable R Group
The part of an amino acid that varies among different amino acids, determining their properties.
Hydroxyl (OH) Groups
Functional groups present in carbohydrates that contribute to their solubility and reactivity.
Carboxylic Acid Group (COO-)
A functional group present in amino acids that contributes to their acidic properties.
Denaturation
Under certain conditions, enzymes may denature when the enzyme changes shape so the active site no longer fits the substrate.
Enzyme denaturation causes
Enzymes may denature under high temperatures because the heat energy disrupts the bonds holding the enzyme together.
Enzyme denaturation in pH
Enzymes may denature in high or low pH conditions because the H+ ions or the OH- ions disrupt the bonds holding the enzymes together.
DNA structure
DNA is a polymer made up of many nucleotide monomers bonded together to form a 'ladder' and twisted into a double helix.
DNA backbone
The sugar and phosphate of each nucleotide bond together to form a strong 'backbone' of alternating sugar and phosphate.
Complementary base pairs
The nucleotides form complementary base pairs according to Chargaff's rule: A always pairs with T, C always pairs with G.
Hydrogen bonds in DNA
The base pairs are held together with hydrogen bonds, which are easily formed and broken so the two halves of DNA may be split and re-formed easily.
Nucleic acid
Long molecules built from monomers called nucleotides.
Ribose
Molecular formula = C5H10O5; simple sugar that is found in RNA.
Deoxyribose
Molecular Formula - C5H10O4; a form of ribose sugar that has lost one hydroxyl group (OH) and is the sugar that makes up DNA.
DNA replication
The DNA molecule is 'unzipped' by the enzyme helicase; new nucleotides are added to the exposed nucleotides by the enzyme DNA polymerase, which follows the base pairing rules.
DNA ligase
An enzyme that binds DNA fragments together.