Biology Stage 1
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Cells
The basic unit of life that makes up all living organisms, consisting of cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane and containing genetic material.
Eukaryotic Organisms
Organisms whose cells have a nucleus enclosed within membranes, including animals, plants, fungi, and protists.
Prokaryotic Organisms
Organisms whose cells lack a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, including bacteria and archaea.
MRS GREN
Movement, Respiration, Sensitivity, Growth, Reproduction, Excretion, Nutrition
3 differences between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells are smaller and simpler, lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells are larger, more complex, and contain a nucleus and various organelles.
3 similarities between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells?
Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have cell membranes, contain genetic material (DNA), and carry out similar basic cellular processes such as metabolism and reproduction.
Mitosis
The process of cell division that results in two genetically identical daughter cells, essential for growth and repair.
Meiosis
The process of cell division that results in four genetically diverse daughter cells, essential for sexual reproduction.
The function of flagella
To provide motility to certain cells, allowing them to swim in liquid environments.
Autotrophs
Organisms that are able to make their own complex organic compounds from simple inorganic substances. They produce their own food through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, forming the base of food webs.
Heterotrophs
Organisms that are not able to make all of their own complex organic compounds from simple inorganic substances. They cannot produce their own food and rely on consuming other organisms or organic matter for energy.
Photosynthesis
The process by which plants convert sunlight into chemical energy, producing glucose and oxygen from carbon dioxide and water.
Cell Membrane
The thin, flexible barrier surrounding all cells, controlling the movement of substances in and out.
Phospholipid Head
Hydrophilic
Phospholipid Tail
Hydrophobic
Osmosis
The movement of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration.
Diffusion
The movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration until equilibrium is reached.
Equilibrium
A state in which opposing forces or activities are balanced, resulting in no net change in concentration.
Cell Theory
The fundamental concept in biology that states all living organisms are composed of cells, cells are the basic unit of life, and all cells arise from pre-existing cells.
Nucleus
The membrane-bound organelle in eukaryotic cells that contains the genetic material (DNA) and coordinates cellular activities such as growth, metabolism, and reproduction.
Mitochondria
The organelles known as the powerhouses of the cell, where ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is produced through cellular respiration.
Ribosomes
Cellular structures that synthesize proteins from amino acids, found in all living cells.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
A network of membranes involved in the synthesis of proteins and lipids, and important for intracellular transport.
Rough ER
A type of endoplasmic reticulum that has ribosomes attached to its surface, involved in protein synthesis and processing.
Smooth ER
A type of endoplasmic reticulum that lacks ribosomes on its surface, involved in lipid synthesis and detoxification processes.
Golgi Body
Modifies, Packages, and Transports Proteins
Lysosomes
Breaks down waste and unwanted materials.
Chloroplasts
Site of photosynthesis
Cell Wall
Provides structure and support
Vacuole
A membrane-bound organelle that stores nutrients, waste products, and helps maintain turgor pressure in plant cells.
Passive Transport
No energy required e.g. diffusion, and osmosis
Active Transport
Requires energy e.g. going against the concentration gradient
G1 Phase
The cell grows and carries out functions
S Phase
DNA Replication
G2 Phase
Preparation for mitosis (DNA is in a decondensed form called chromatin)
M Phase
Mitosis or Cell Division
Which organism type’s cells uses mitosis? Why?
Only eukaryotic cells use mitosis because they are more complex and have DNA stored in a nucleus

What phase of mitosis is this?
Interphase

What phase of mitosis is this?
Prophase
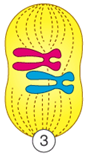
What phase of mitosis is this?
Metaphase

What phase of mitosis is this?
Anaphase
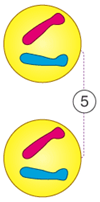
What phase of mitosis is this?
Telophase
Anaerobic Respiration
occurs only in the cytoplasm of cells and in the absence of oxygen. This process produces much smaller amounts of cellular energy (2 ATPs) than aerobic respiration (36 ATPs) due to the incomplete breakdown of glucose in the absence of oxygen. Like aerobic cell respiration, anaerobic respiration begins with a process called glycolysis in the cytoplasm. An anaerobic process of fermentation then follows
Aerobic Respiration
a process that occurs in cells where glucose is converted into cellular energy (ATP) in the presence of sufficient oxygen. This process produces a large amount of cellular energy (36 ATPs) as the presence of oxygen allows for a morecomplete breakdown of glucose. The by-products of this process are carbon dioxide and water