Cognitive Development Theories: Piaget and Vygotsky
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
Clinical Method
Flexible technique to study children's thinking.
Naturalistic Observation
Observing subjects in their natural environment.
Interactionist Perspective
View combining nature and nurture in development.
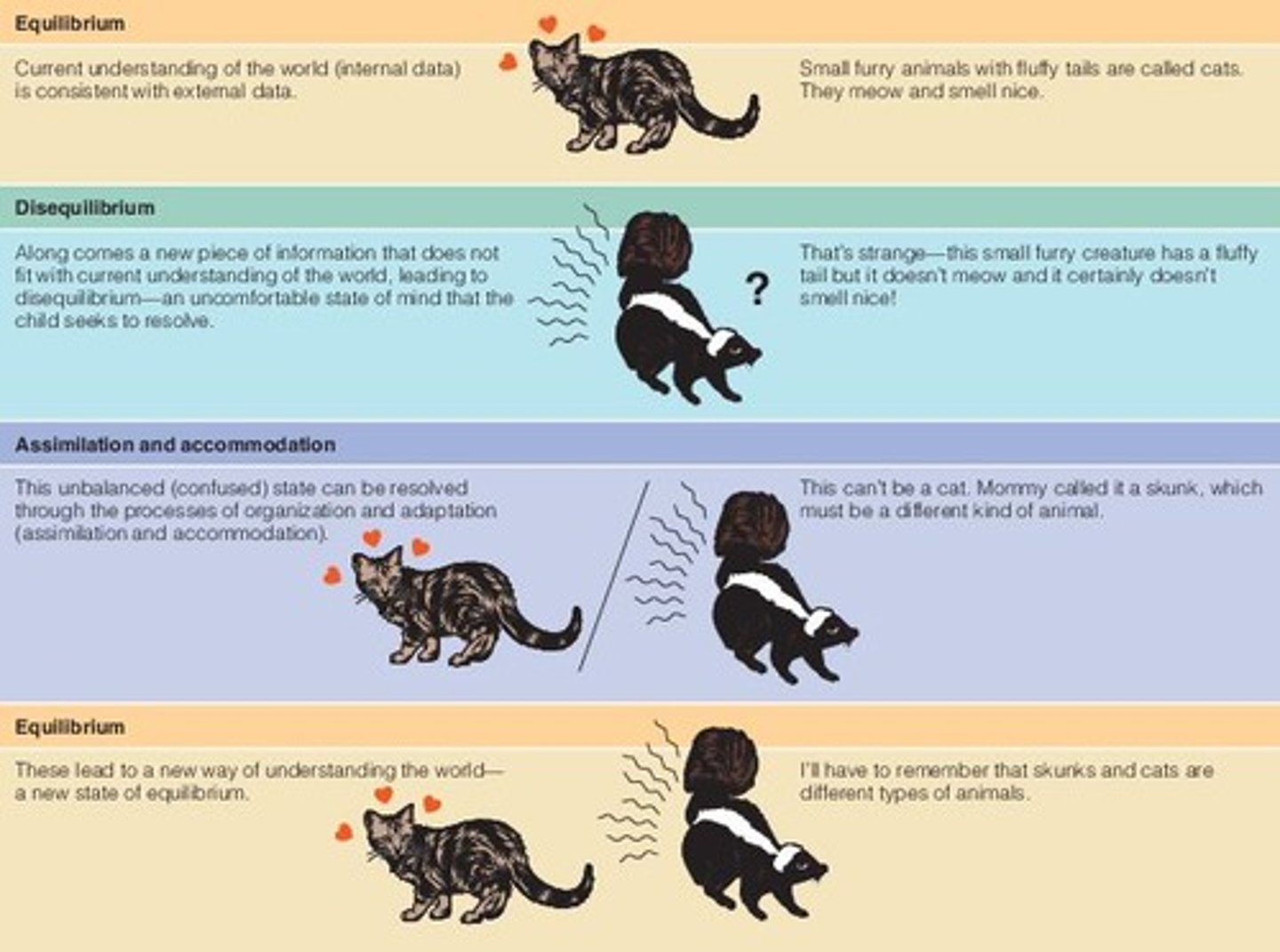
Schemes
Organized patterns of action or thought.
Adaptation
Adjusting to environmental demands through processes.
Assimilation
Integrating new experiences into existing schemes.
Accommodation
Modifying schemes to incorporate new experiences.
Cognitive Conflict
Discrepancy that stimulates cognitive development.
Sensorimotor Stage
First stage, birth to 2 years.
Preoperational Stage
Second stage, ages 2 to 7 years.
Concrete Operations Stage
Third stage, ages 7 to 11 years.
Formal Operations Stage
Final stage, ages 11 and beyond.
Neuroconstructivism
Knowledge constructed within existing neural frameworks.
Sociocultural Context
Cognition evolves through social interactions.
Zone of Proximal Development
Gap between independent and guided learning.
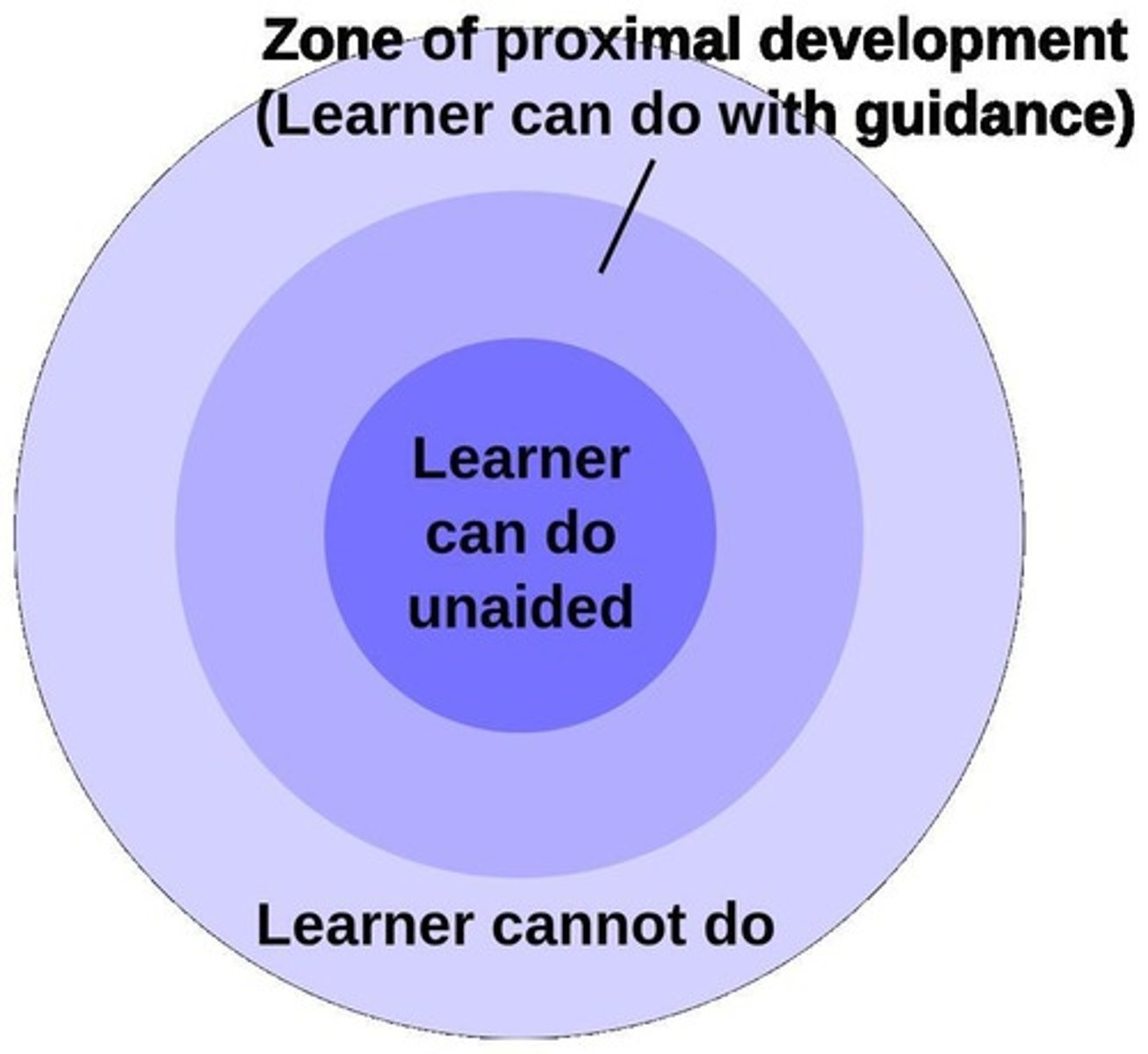
Guided Participation
Learning through participation with skilled partners.
Scaffolding
Support provided by more-skilled individuals.
Private Speech
Self-directed speech guiding thought and behavior.
Language Shapes Thought
Language influences cognitive processes and development.
Color Memory Study
Research on language's effect on color perception.
Cognitive Development
Process of acquiring knowledge and skills.
Critiques of Piaget
Underestimated young children's cognitive abilities.
Cognitive Development Stages
Four distinct phases of cognitive growth.

Cultural Mental Tools
Tools acquired through social interactions.
Active Development
Children construct knowledge through experiences.
Vygotsky's Theory Critique
Overemphasizes social interaction in knowledge acquisition.
Fischer's Dynamic Skill Framework
Behavior analysis requires context for accurate understanding.
Developmental Range
Individual abilities vary based on contextual factors.
Object Permanence
Understanding objects exist when out of sight.
A-not-B Error
Infants search last known location instead of new one.
Symbolic Capacity
Using symbols to represent objects or experiences.
Primary Circular Reactions
Infants repeat body-related actions from chance events.
Secondary Circular Reactions
Infants enjoy repeating actions for pleasure.
Coordination of Secondary Schemes
Combining actions to achieve simple goals.
Symbolic Thinking
Using words, images, gestures to represent ideas.
Centration
Focusing on one aspect of a problem.
Decentration
Focusing on multiple dimensions of a problem.
Seriation
Arranging items based on a measurable dimension.
Transitivity
Understanding relationships among elements in series.
Classification Skills
Grouping items based on various rules.
Formal-Operational Thought
Abstract reasoning and systematic problem-solving.
Hypothetical-Deductive Reasoning
Reasoning from general rules to specific outcomes.
Postformal Thought
Engaging in complex, context-dependent reasoning.
Relativistic Thinking
Knowledge varies based on context and perspective.
Dialectical Thinking
Reconciling paradoxes and inconsistencies in ideas.
Fluid Intelligence
Problem-solving and quick thinking abilities.
Crystallized Intelligence
Knowledge gained from experience and education.
Cognitive Aging
Decline in mental abilities with age.
Semantic Memory
Memory for facts and general knowledge.
Episodic Memory
Memory for personal experiences and events.
Processing Speed
Rate of cognitive processing and response.
Working Memory
Short-term retention and manipulation of information.
Emotion Regulation
Managing emotional responses effectively.
Processing speed theory
Hypothesis by Salthouse regarding cognitive performance.
Inhibition theory
Hypothesis by Hasher & Zacks regarding cognitive performance.
Encoding
Get information into the system.
Consolidation
Information is processed and organized in a form suitable for long-term storage, including fast-acting synaptic consolidation and slower-acting system consolidation.
Storage
Refers to holding information in a long-term memory store.
Retrieval
Process of getting information out when it is needed.
Information Processing Model of Memory
Emphasizes the basic mental processes involved in attention, perception, memory, and decision making.
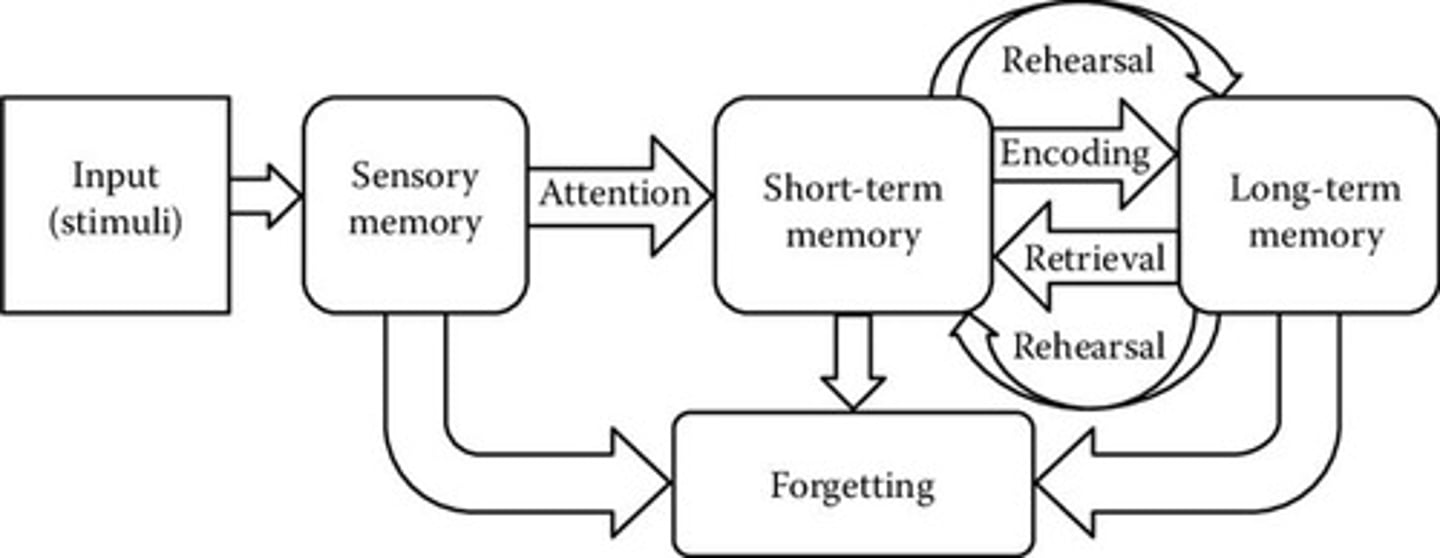
Sensory Memory
Includes Iconic Memory and Echoic Memory, both having very brief duration; if not attended, information fades quickly.
Baddeley's Working Memory Model
Modern view on the structure of working memory, estimated to hold 4 +/- 1 pieces of info.
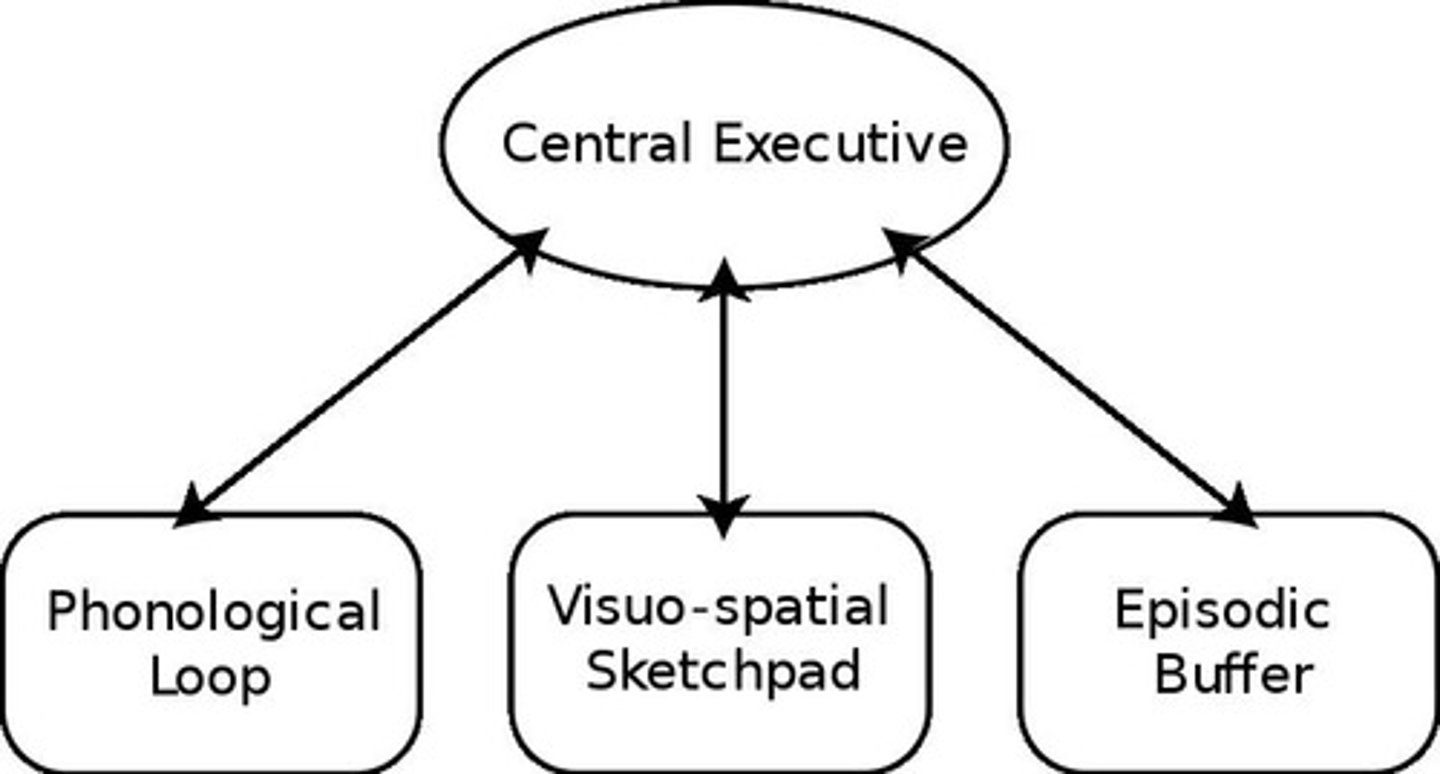
Focus of Attention
Most immediate state of working memory, holds 4 +/- 1 items.
Activated Long-Term Memory
Information that has recently been in the focus of attention.
Common WMC tasks
Includes Digit Span Forwards and Backwards, Complex Span tasks, and N-back task.
Hippocampus
Important for LTM memory formation and preparation of information for storage.
Subcortical structures important for memory
Includes Amygdala and Thalamus.
Cortical regions important for memory
Includes posterior portions of the parietal lobe, occipital lobe, prefrontal cortex, and medial temporal lobe structures.
Karl Lashley
Searched for the engram, concluding no single physical storage location existed in the brain.
Problem Solving
Use of the information-processing system to achieve a goal or arrive at a decision.
Habituation
Infer that an infant remembers something if they look at it for shorter periods of time than they did at initial exposure.
Operant Conditioning
Conjugate reinforcement shows infants can remember for varying durations based on age.
A-not-B task
An object search task used to assess memory in infants.
Semantic memory
Some evidence that by 3-4 months of age, babies have an understanding of basic categorization.
Episodic memory
Most learning over the first year is probably based more on reinforcement learning.
Childhood Amnesia
Many individuals have very few autobiographical memories of events that occurred during the first few years of life.
Memory Efficiency View
View that memory processes themselves improve throughout development.
Memory Strategies View
View that children learn strategic behaviors to improve memory throughout development.
Working Memory Capacity
Limited memory ability in children affects recall.
Fuzzy Trace Theory
Memory specificity reduces over time in children.
Self-Concept
Infants lack a coherent view of self.
Language Development
Language skills support memory encoding processes.
Simcock and Hayne (2002)
Study on regaining access to early memories.
Memory Strategies
Older children use more effective memory techniques.
Overlapping Waves Theory
Children use multiple strategies for problem-solving.
Elaboration
Advanced strategy mastered by adolescents for learning.
Metamemory
Awareness of memory processes improves during adolescence.
Expertise
Experts possess organized knowledge and strategies.
Adult Autobiographical Memory
Factors influencing recall include significance and emotion.
Reminiscence Bump
Unique memories occur between ages 16-25.
Memory Fluency
Efficient encoding during optimal neural maturation.
Memory and Aging
Elderly experience minor memory difficulties, especially recall.
Selective Optimization with Compensation
Older adults adapt strategies to cope with cognitive decline.
Memory Reconstruction
Early memories can be malleable and context-sensitive.
Availability vs Accessibility
Memory may exist but not be retrievable at times.
Contextual Factors
Influence the recall of earliest childhood memories.
TOT Phenomenon
Tip-of-the-tongue experience indicates memory availability.
Memory Attribution
Age of memories may shift with development.
Memory Consistency
Earliest memories reported can vary over time.
Socioeconomic Status (SES)
Influences the use of metacognitive strategies.