EL1 - Lecture 2 Description and classification of sounds
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
By Vzu Nguyen
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Classification
• In order to form consonants, the air-stream through the vocal organs must be obstructed in some way. Therefore, consonants can be classified according to: term-1
- voicing
- the place where the air-stream is obstructed (the ______ ___ ____________), and
- the way in which the air-stream is obstructed (the ______ ____ ____________).
place of articulation, manner of articulation
Which are the three criteria we use to classify consonants (please write them correct order)?
voicing, place of articulation, manner of articulation
According to manner of articulation
• Manner of articulation is the ______ in which the air-stream is obstructed or altered in the production of speech sounds.
• It describes the types of _____________ caused by the narrowing or closure of the articulators.
way, obstruction
classification according to place of articulation:
1. ______________:
E.g. /p/, /b/, /m/, /w/
2.______-________ :
E.g. /f/, /v/
3._____-_____/________ :
E.g. /θ/, /ð/
4. ______________:
E.g. /t/, /d/, /s/, /z/, /l/, /n/
5. ________-________/________-__________:
E.g. /ʃ/, /ʒ/, /tʃ/, /dʒ/, /r/
6. ___________:
E.g. /j/
7. _________:
E.g. /k/, /ɡ/, /ŋ/
8. __________:
E.g. /h/
bilabial, labio-dental, inter-dental, dental, alveolar, alveolo-palatal, palato-alveolar, palatal, velar, glottal
According to the manner of articulation
1. ______ (______ ______/________):
E.g. /p/, /t/, /k/, /b/, /d/, /g/
2. ______ (_______ ________):
E.g. /m/, /n/, /ŋ/
• Note: For every stop position in English, there is a nasal articulated in the same position. /p/ and /b/, /t/ and /d/, /k/ and /g/ vs. /m/, /n/, /ŋ/
3. _________ (____________):
E.g. /f/, /v/, /θ/, /ð/, /s/, /z/, /ʃ/, /ʒ/, /h/
• Notes: ______________ are continuant consonants which means that you can continue making them as long as you have enough air in your lungs.
4. _____________:
A stop is immediately followed by a homorganic fricative.
E.g. /tʃ/, /dʒ /
5. _______________ (____________ ______________):
a. __________: E.g. /l/
b. __________: E.g. /r/
c. _______ (_______-_________): E.g. /w/, /j/
stop (oral stop/plosive),
nasal (nasal stop),
fricative (spirant),
fricatives,
affricate,
approximant (frictionless continuant),
lateral,
retroflex,
glide (semi-vowel)
Definition
• Vowels are the sounds in the production of which none of the articulators come very close together so the passage of air-stream is relatively ___________________ and the air can get out __________.
• Vowels depend mainly on the_____________ ___ ____ __________ ___ ___ _________ . They are normally voiced.
unobstructed, freely, variations in the position of the tongue,
Consonants
• The sounds which are _______________ with some kind of ____________, or ___________, of the air stream.
• Those segments which occur at the edges of syllables, and are optional in the syllables. (Phụ âm thường xuất hiện ở đầu hoặc cuối âm tiết (như cat → /kæt/, stop → /stɒp/), và đôi khi có thể bị lược bỏ trong một số trường hợp, như trong tiếng Anh giao tiếp nhanh - hiện tượng nuốt/lướt âm trong tiếng Anh - elision).
articulated, stricture, closure
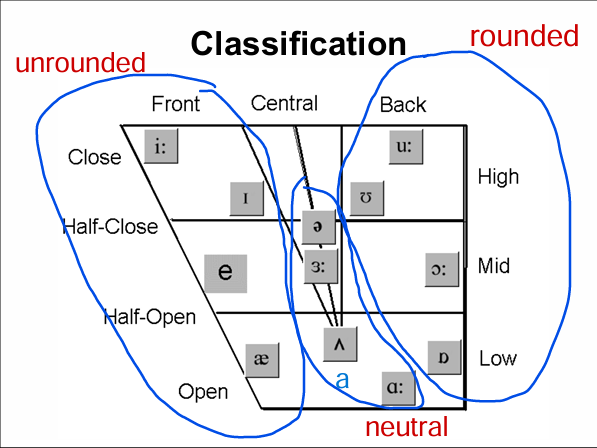
When classifying vowels (monophthongs), we will consider..........
short/long,
tongue height (high/low/mid),
part of the tongue raised (front/back/central),
degree of lip rounding (rounded/unrounded/neutral)
According to tongue height
1. ______ vowels: E.g.: /u:/, /i:/
2. ______ vowels: E.g.: /ɑː/, /æ/
3. ____ vowels: E.g.: /e/, /ɜː/
high, low, mid
According to the part of the tongue raised
1. _______ vowels: E.g. /i:/, /æ/
2. ________ vowels: E.g. /ʊ/, /ɒ/
3. _________ vowels: E.g. /ə/, /ʌ/
front, back, central
According to degree of lip rounding
1. _____________ vowels: E.g. /ʊ/, /ɒ/, /u:/, /ɔː/
2. _____________ vowels: E.g. /i:/, /ɪ/, /e/, /æ/
3. _____________ vowels: E.g. /ɜː/, /ə/, /ɑː/, /ʌ/
rounded, unrounded, neutral
Long and short vowels
• _______ vowels: E.g. /i:/, /u:/
• ________ vowels: E.g. /ɪ/, /ʊ/
• Long vowels tend to be longer than short vowels in similar contexts. The symbols consist of one single vowel plus a length mark made of two dots.
• They are different from short vowels not only in length but also in quality, resulting from differences in tongue shapes and lip positions.
long, short
From your memory, regenerate the classification charts of monophthongs and diphthongs
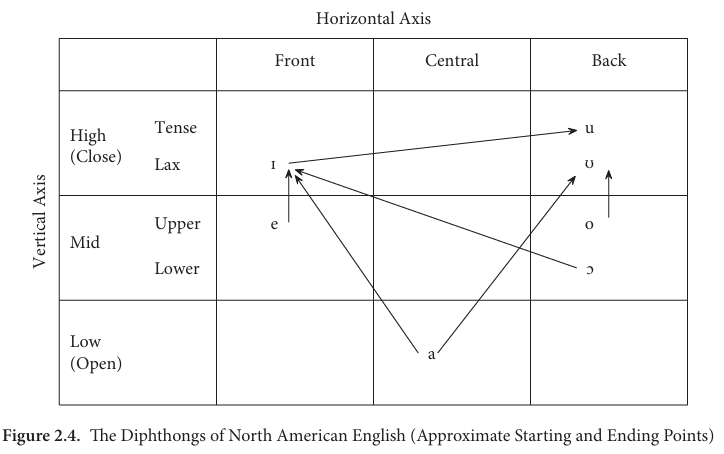
Diphthongs
• Definition:
- A diphthong is a _______ from one vowel to another, and the whole glide acts like one of the long simple vowels.
- In terms of length, diphthongs are like long vowels. E.g. /aɪ/, /eɪ/
glide
Diphthongs
• Classification:
- _____________ : ending in /ə/
- _______________
• Ending in /ɪ/
• Ending in /ʊ/
centring, closing
Describing diphthongs
• Describe the _________ from the first vowel to the second
glide