Inventory Management
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
SCM 2160
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
what is inventory
stock of items including materials, orders, information, and people that flow through or are used in a process to satisfy eventual demand
what do inventory management policies must be aligned with
aligned with competitive priorities → there is an “appropriate” amount of inventory
decisions are about balancing inventory costs with the pressures to increase inventory
what are inventory holding costs
variable costs associated with keeping inventory
$ per unit cost (or % of a unit cost)
Costs over a period of time (usually one year)
E.g., rent, heating, cooling, lighting, security, interest on loans, depreciation
what is capital cost
opportunity cost of investing in inventory relative to the expected return if invested elsewhere
what is storage and handling cost
includes costs associated with renting and staffing storage space, opportunity cost associated with the use of space for storage
what is taxes, insurance, and shrinkage cost
includes cost of insuring inventory, theft of inventory, spoilage and obsolescence
what are ordering costs
the costs associated with the act of placing an order, transaction costs
fixed cost per order, regardless of the number of units ordered
In a production setting, there is also set-up costs (fixed cost per production of a set quantity)
E.g., requisition and purchase ordering, transportation and shipping, receiving and storage
what are stockouts
what are inventory pressures
Inventory can support quick delivery, avoid stockouts
Higher volume orders may optimize ordering costs from suppliers
Increasing inventory by producing in large batch sizes may decrease set-up costs
Producing inventory may increase productivity and resource utilization
Increase efficiency of transportation resources and reduce less-than- truckload shipments
what is safety stock
buffer to protect against uncertainties in demand, lead time, processing time, quality and supply
what is decoupling
work-in-process inventory waiting for the next step (can accommodate different rates of production in system)
what is pipeline inventory
inventory moving from point-to-point in the system, including materials on their way from the suppliers
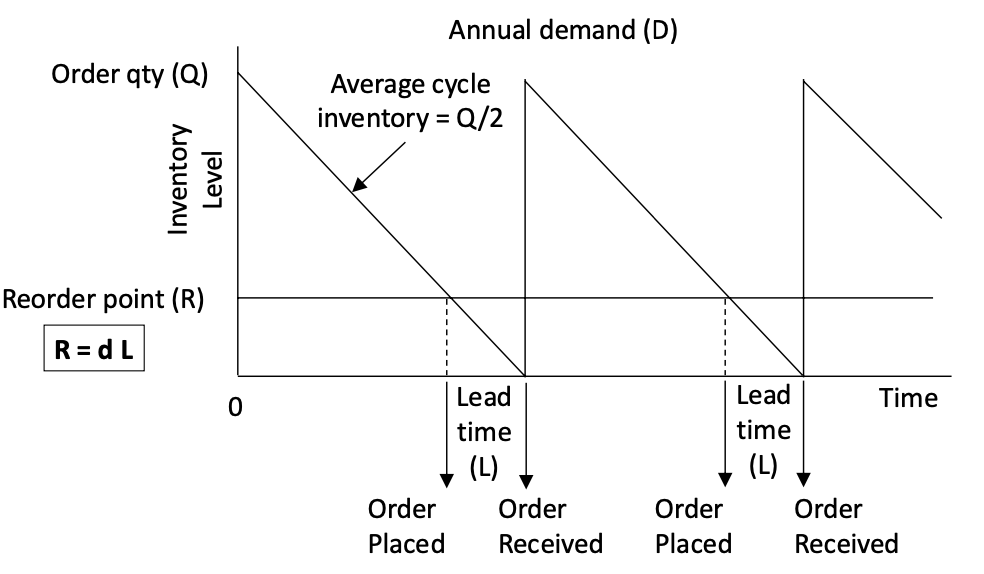
pipeline inventory (reorder point) = …

what is anticipation inventory
used to manage predictable variation in demand
what is cycle inventory
the portion of your total inventory that varies based on the size of an order or production batch (Q)
average cycle inventory: Q/2
what is economic order quantity (EOQ)
the value of Q that gives you the lowest total annual inventory costs
what are the assumptions of EOQ models
Demand is independent, known, and constant
Supply is certain and received all at once in a batch
Replenishment lead time is known and constant
Lead time: time between order placed and order received
Cost information is fixed and constant
No shortage and back orders
what is the equation for annual costs
annual holding cost + annual ordering (or setup) cost
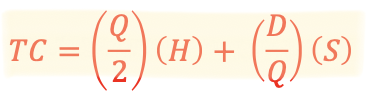
𝑇𝐶 = 𝑡𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑡 𝑝𝑒𝑟 𝑦𝑒𝑎𝑟
𝑄= 𝑜𝑟𝑑𝑒𝑟 𝑞𝑢𝑎𝑛𝑡𝑖𝑡𝑦 ,𝑙𝑜𝑡 𝑜𝑟 𝑏𝑎𝑡𝑐h 𝑠𝑖𝑧𝑒 𝑖𝑛 𝑢𝑛𝑖𝑡𝑠
𝐻= h𝑜𝑙𝑑𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑡 𝑝𝑒𝑟 𝑢𝑛𝑖𝑡 𝑝𝑒𝑟 𝑜𝑛𝑒 𝑦𝑒𝑎𝑟 𝑜𝑓 𝑡𝑒𝑛 % 𝑜𝑓 𝑡h𝑒 𝑖𝑡𝑒𝑚′𝑠 𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒
𝐷 = 𝑎𝑛𝑛𝑢𝑎𝑙 𝑑𝑒𝑚𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑖𝑛 𝑢𝑛𝑖𝑡𝑠 𝑝𝑒𝑟 𝑦𝑒𝑎𝑟
S = cost per order or set-up (in dollars per batch)
This equation can be used to compare the costs of different inventory policies
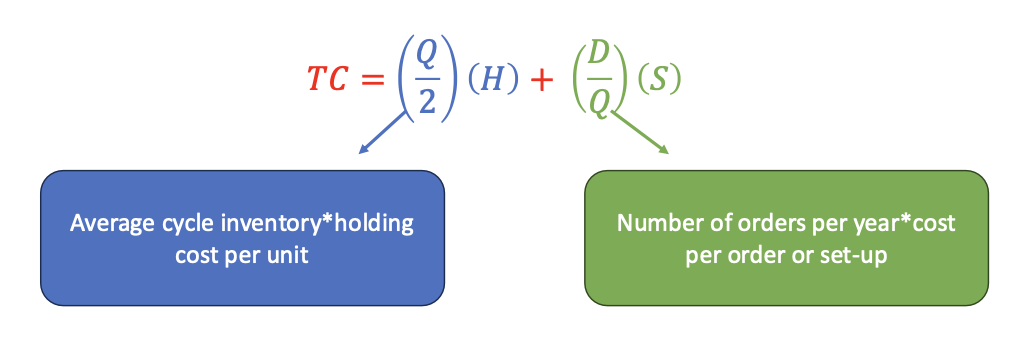
what are the two factors that affect how many order you place per year
demand and order size → total ordering costs
what does large quantity values minimize
minimize the number of orders

what does small quantity value minimize
minimize average cycle inventory and holding costs

what is independent demand
demand which is influenced by market conditions and is not related to inventory decisions for other items in stock
what are the different ways to determine when and how many to order
Q system (continuous review – fixed quantity)
P system (periodic review – fixed time-period)
ABC system
what is the Q system (continuous review)
Replenish decisions made in real-time based on inventory level
System triggers a fixed order quantity (Q) when inventory reaches a set reorder point (R)
Time between orders varies
what is the P system (periodic review)
Replenishment decisions made based on time between orders
Inventory review happens at fixed time intervals (periodically)
Order quantity (Q) varies, and is determined by current inventory level
what is most important decision in continuous review system
setting your reorder point
inventory will hit 0 exactly when you receive your next order
safety stock can change your reorder point
what is most important decision in periodic review system
selecting the time between orders and target inventory level
what is the ABC system
An inventory classification system in which a small percentage of items (A-level) account for most of the inventory value
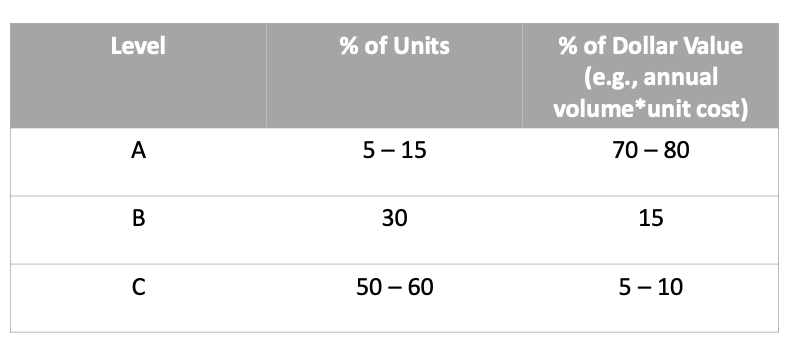
what are A-items in the ABC system
High priority
Tight control with regular review
Carefully determined Q, frequent deliveries, continuous review
Very accurate and detailed inventory records, update monthly
what are B-items in the ABC system
Moderate priority
Moderate control with regular attention
Order quantities or order points reviewed quarterly
Batch updating of inventory records
what are C-items in the ABC system
Low priority
Simple control
Large inventories, visual review
Simplified counting, annual review
what are the benefits of the Q system
May reduce total holding and ordering costs by tailoring reorder point
Fixed order sizes may support quantity discounts
Requires less safety stock
what are the benefits of the P system
Supports standardization of deliveries, scheduling of inventory assessment
Opportunities to combine orders for multiple products from same suppliers
Does not require computerized inventory management system