Introduction to Taxonomy and Phylogenetic Trees
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Taxonomy
Biology field classifying organisms by characteristics.

Domains
Three major categories of all life forms.
Eubacteria
True bacteria, including pathogens; prokaryotic.
Archaebacteria
Prokaryotes found in extreme environments.
Eukarya
Domain containing all eukaryotic organisms.
Phylogeny
Evolutionary history of a species.
Endosymbiosis
Prokaryote inside another, leading to eukaryotes.
Endosymbiotic Theory
Proposes coevolution led to eukaryotic speciation.
Common Ancestor
Shared ancestor from which species diverged.
Phylogenetic Tree
Diagram predicting evolutionary relationships among organisms.
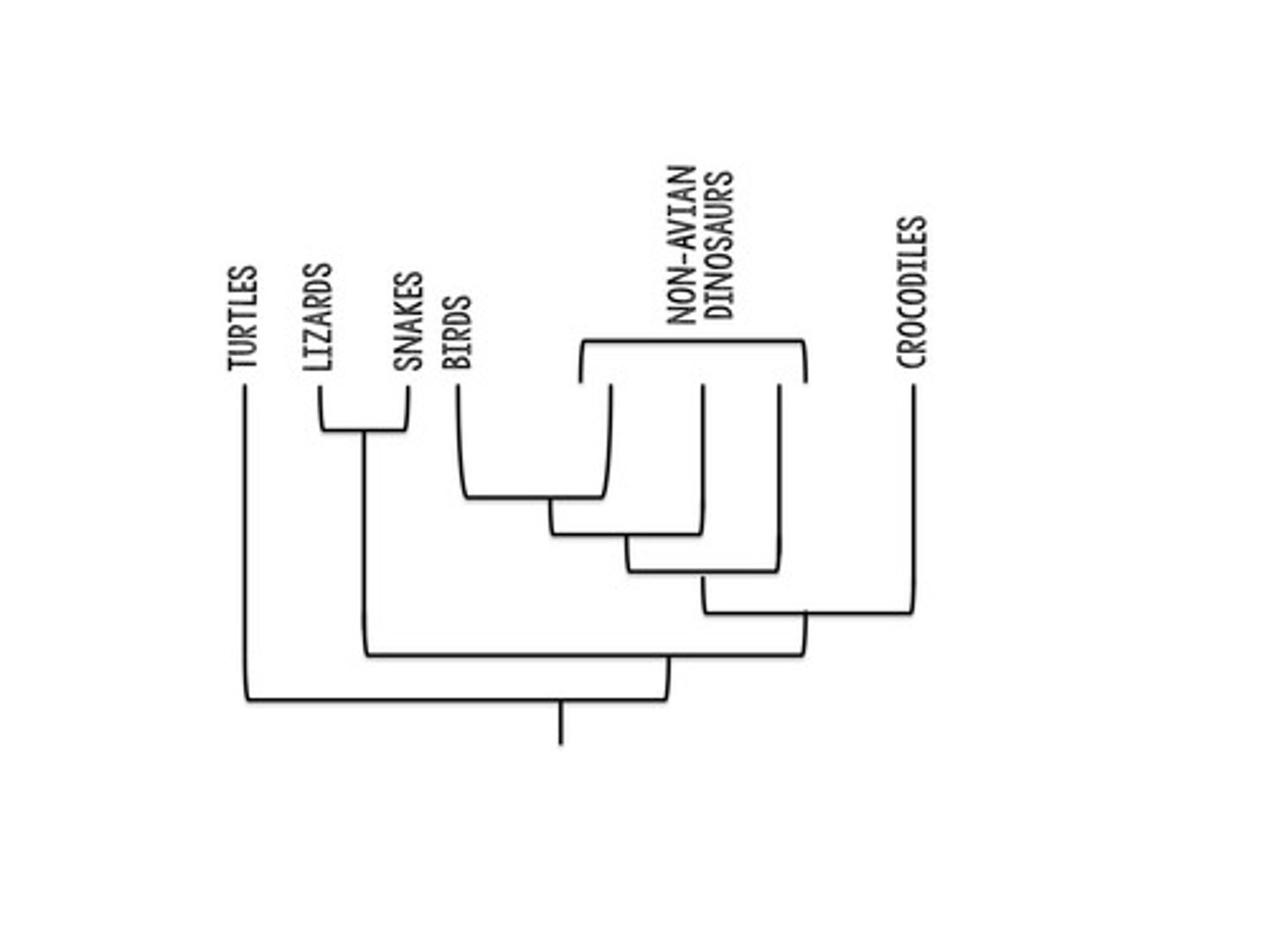
Branch Points
Indicate new species diverging from ancestors.
Maximum Parsimony
Simplest explanation used for tree creation.
Homologous Features
Traits from divergent evolution used for classification.
Speciation
Branching of a family tree into new species.
Extinction
Loss of a branch in a phylogenetic tree.
Morphology
Study of form and structure of organisms.
Genus Species
Binomial nomenclature format for naming organisms.
Carolus Linnaeus
Known as the Father of Taxonomy.
Italics in Naming
Genus capitalized, species in lowercase.
Phylogenetic Relationships
Connections based on shared inherited characteristics.
Reading Phylogenetic Trees
Start from root, move forward in time.