CELLS BIO SL Y1
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
🥑
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
3 rules of cell theory
composed of 1 or more cells, basic unit of structure and organization, come from pre - existing cells
electron microscopy
high resolution and magnification so can reveal ultrastructure in cells
freeze fracture microscopy
splits membranes along lipid bilayer allowing direct observation of membrane proteins
cryo EM
samples are frozen rapidly preserving them in a near - native state
fluorescent/immunofluorescent stains
uses antibodies attatched to fluorescent dyes which allows precise location
all cells have
plasma membrane, cytoplasm, DNA
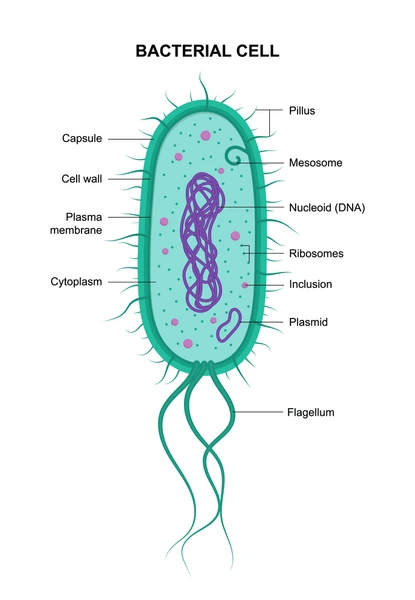
prokaryotes have
cell wall, plasma membrane, naked loop DNA, 70s ribosomes
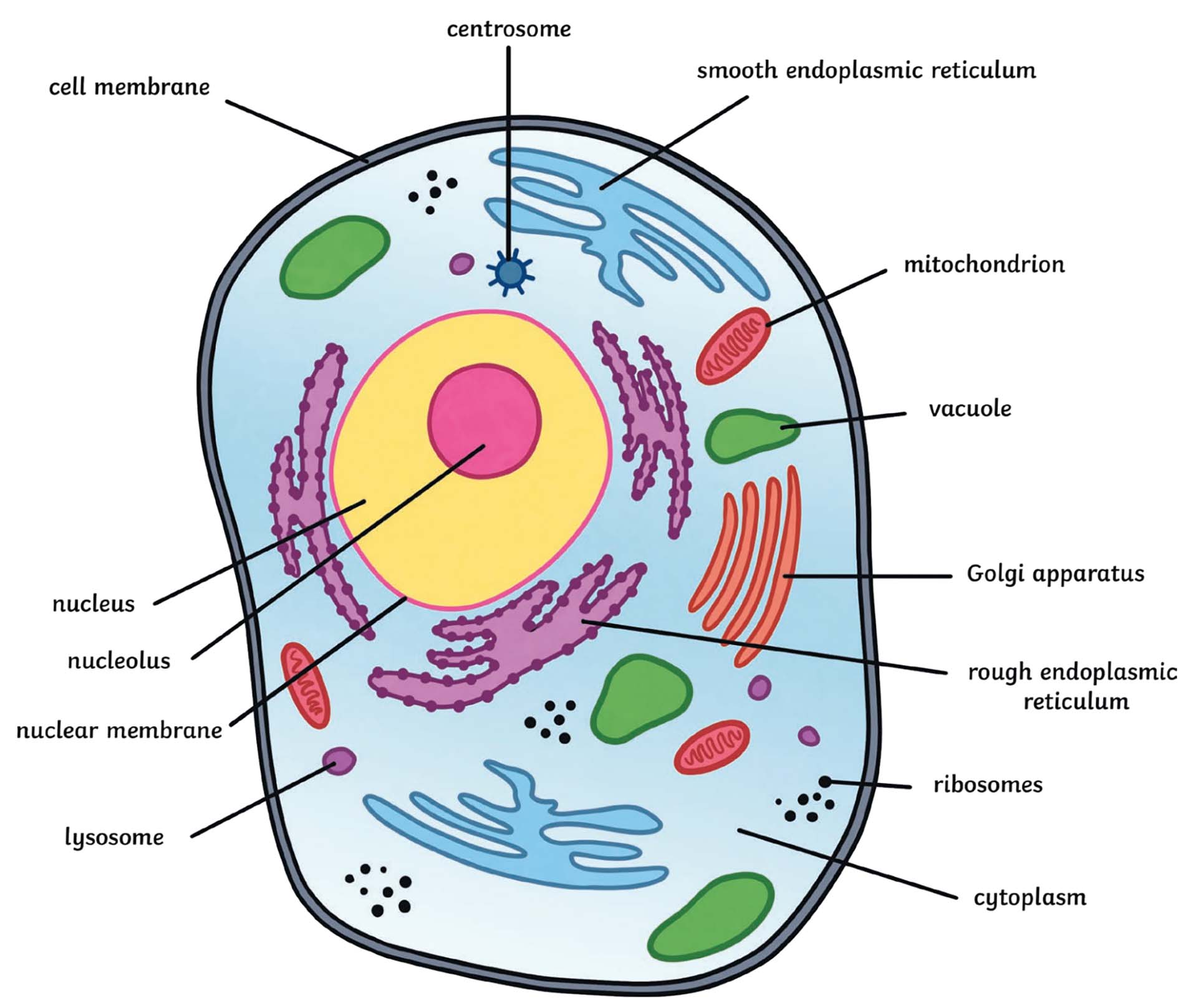
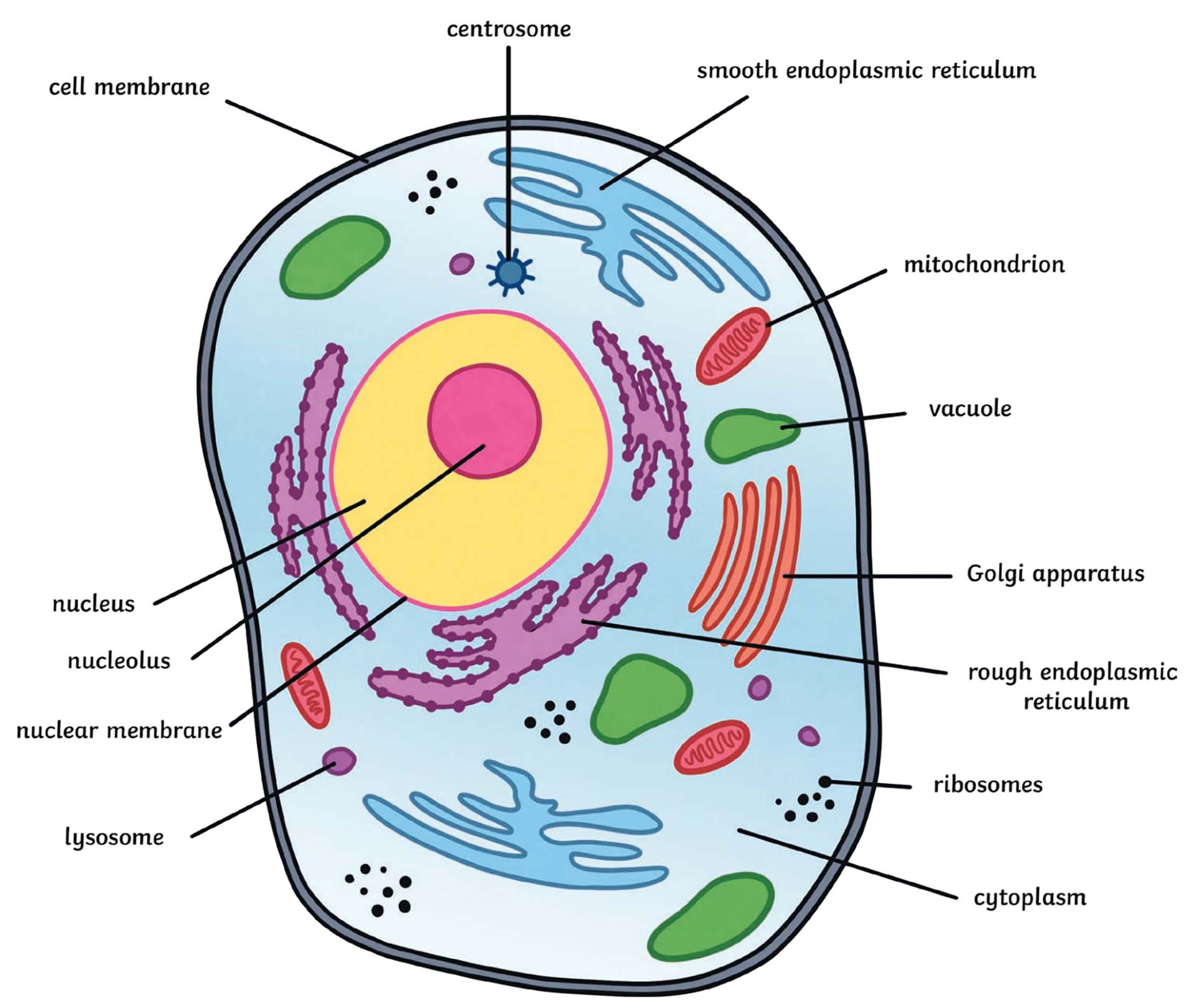
eukaryotes have
plasma membrane, compartamentalized cytoplasm, nucleus, membrane bound organelles, 80s ribosomes
8 functions of life
Homeostasis, metabolism, nutrition, movement, excretion, growth, response to stimuli, reproduce genetically similar offspring
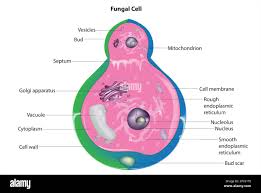
fungi has
no plastids, has chintin walls, large permanent vacuole, has centrioles and undulipodia in fungi with swimming male gametes
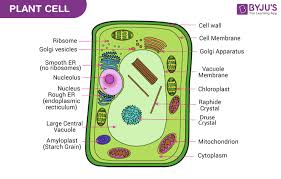
plant has
plastids like chloroplasts, cellulose walls, large permanent vacuole, has centrioles and undulipodia in fungi with swimming male gametes
animal has
no plastids, no wall, small temporary vacuole, has centrioles, has cillia and flagella
cell theory exceptions
aseptate fungal hyphae - many nuclei within cytoplasm, skeletal muscle fibres - multinucleated 4 protein, red blood cells - no nucleus, phloem sieve tube elements - lose nucleus at maturity