Enzymes and Metabolic Reactions Overview
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Metabolism
All chemical reactions within an organism's cells.
Chemical Reactions
Breaking and forming bonds during chemical changes.
Reactants
Substances changed during a chemical reaction.
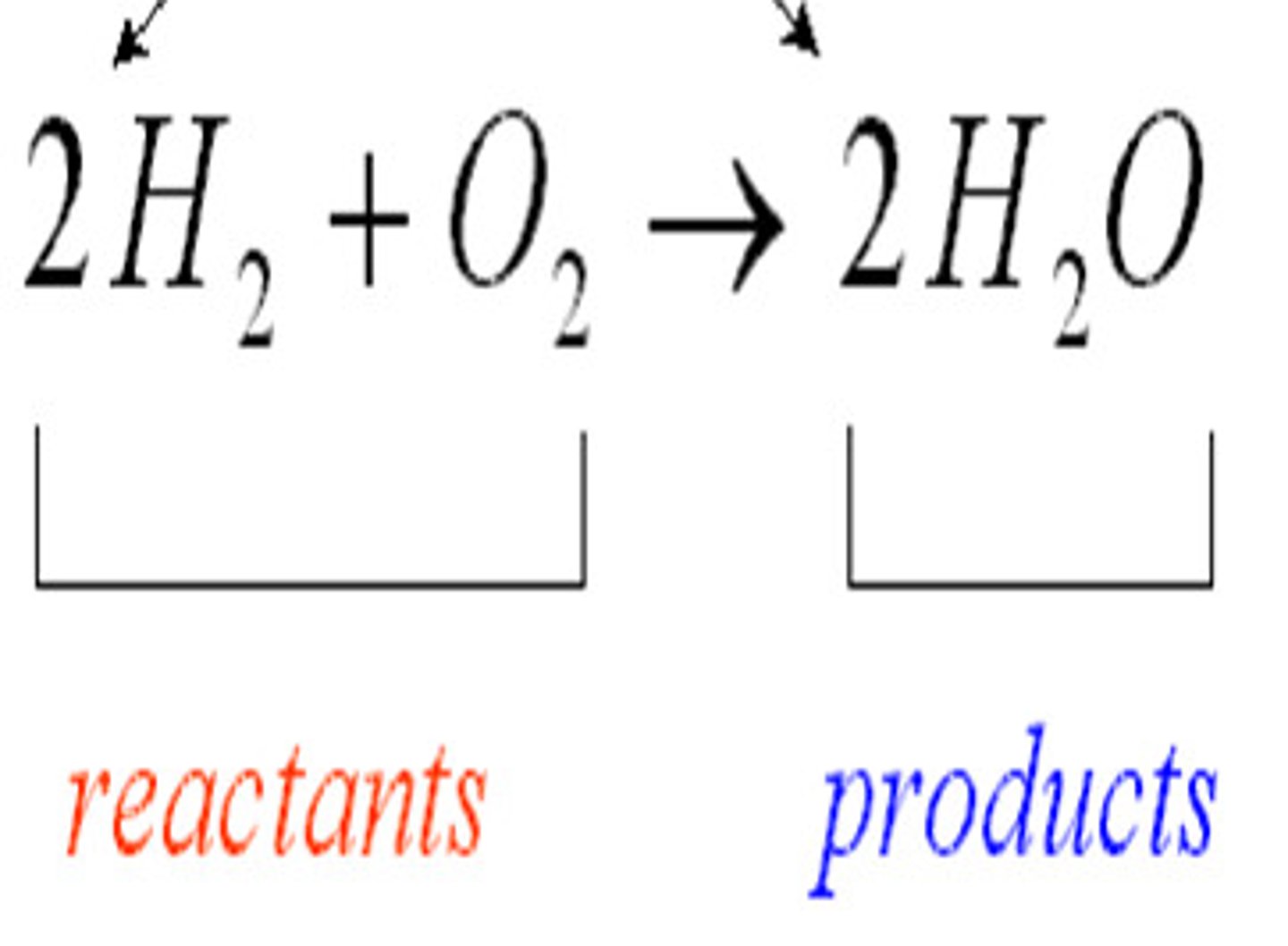
Products
Substances produced by a chemical reaction.
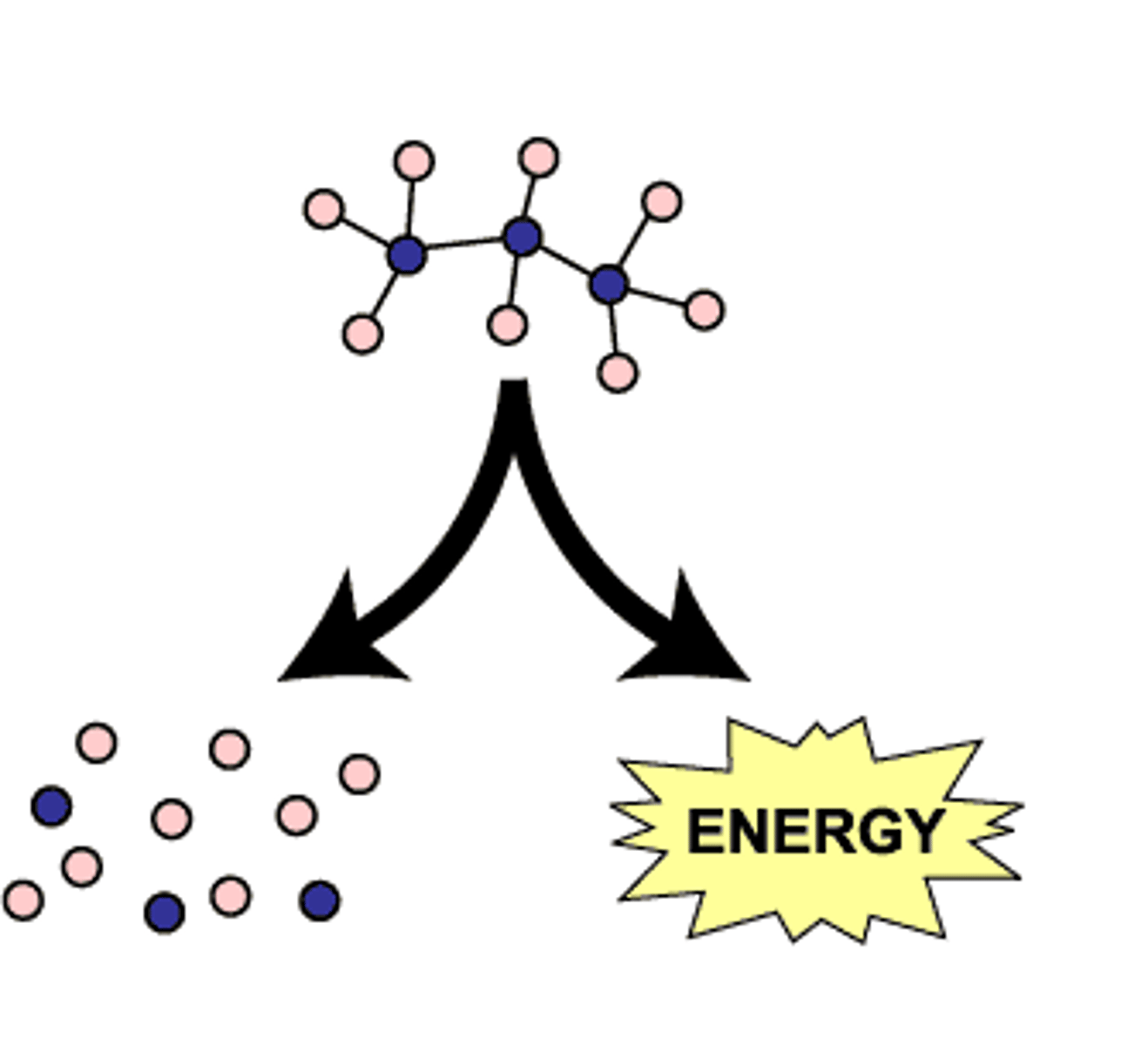
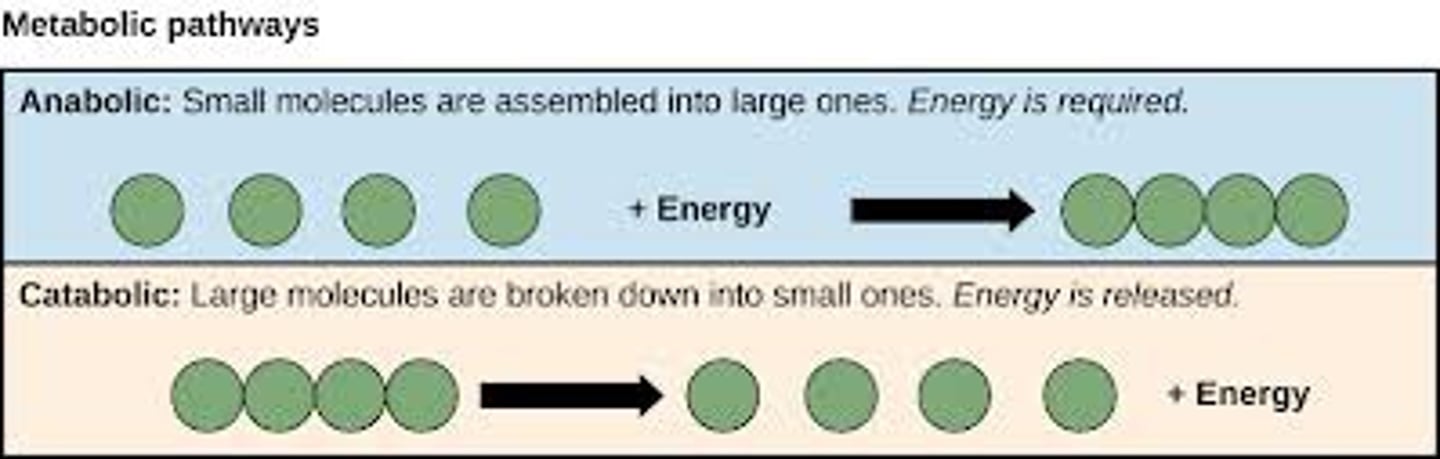
Catabolic Reactions
Break down larger molecules, releasing energy.
Anabolic Reactions
Build larger molecules from smaller molecules with less energy, consuming energy.
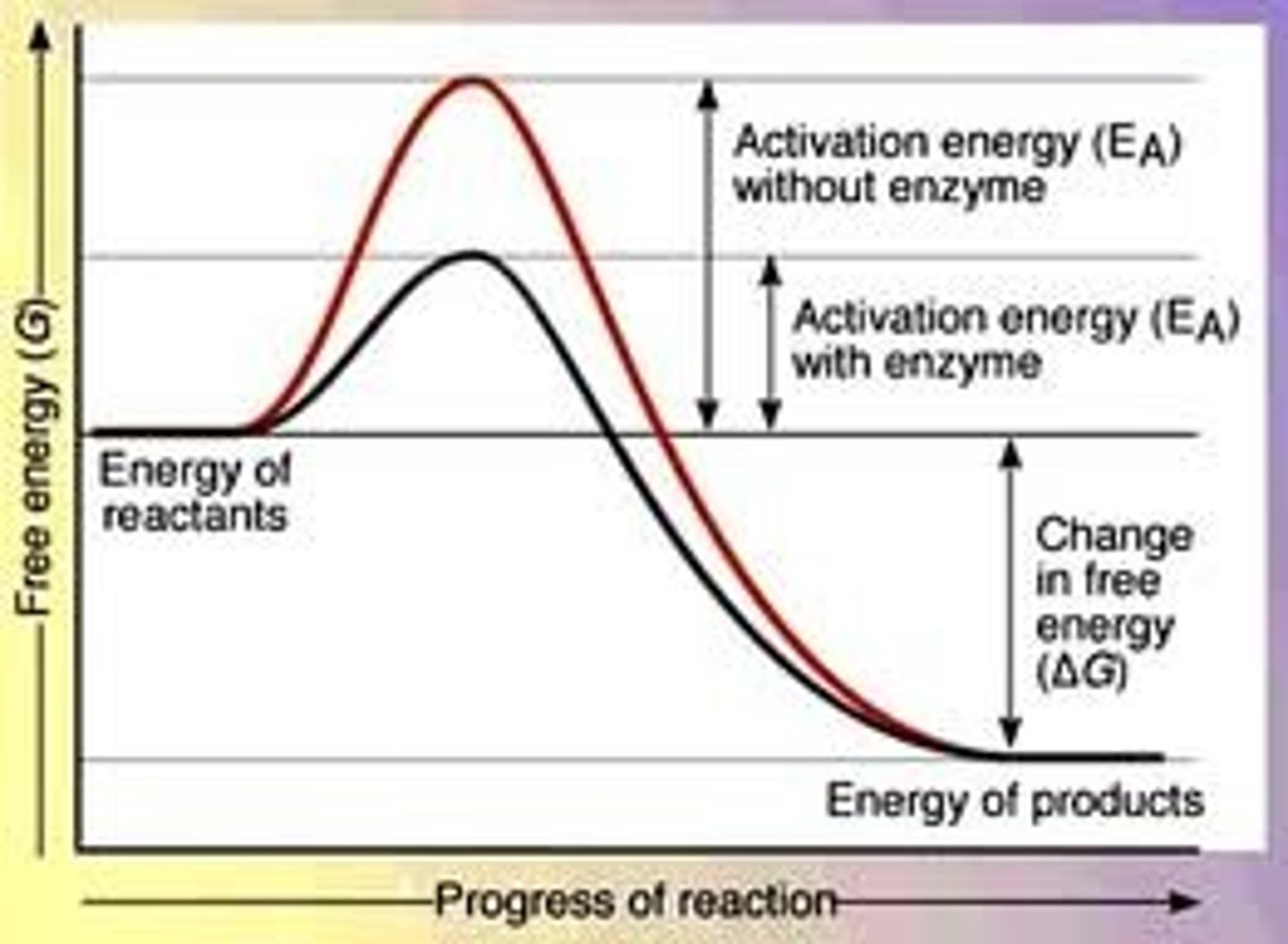
Activation Energy
Energy needed to start a chemical reaction.
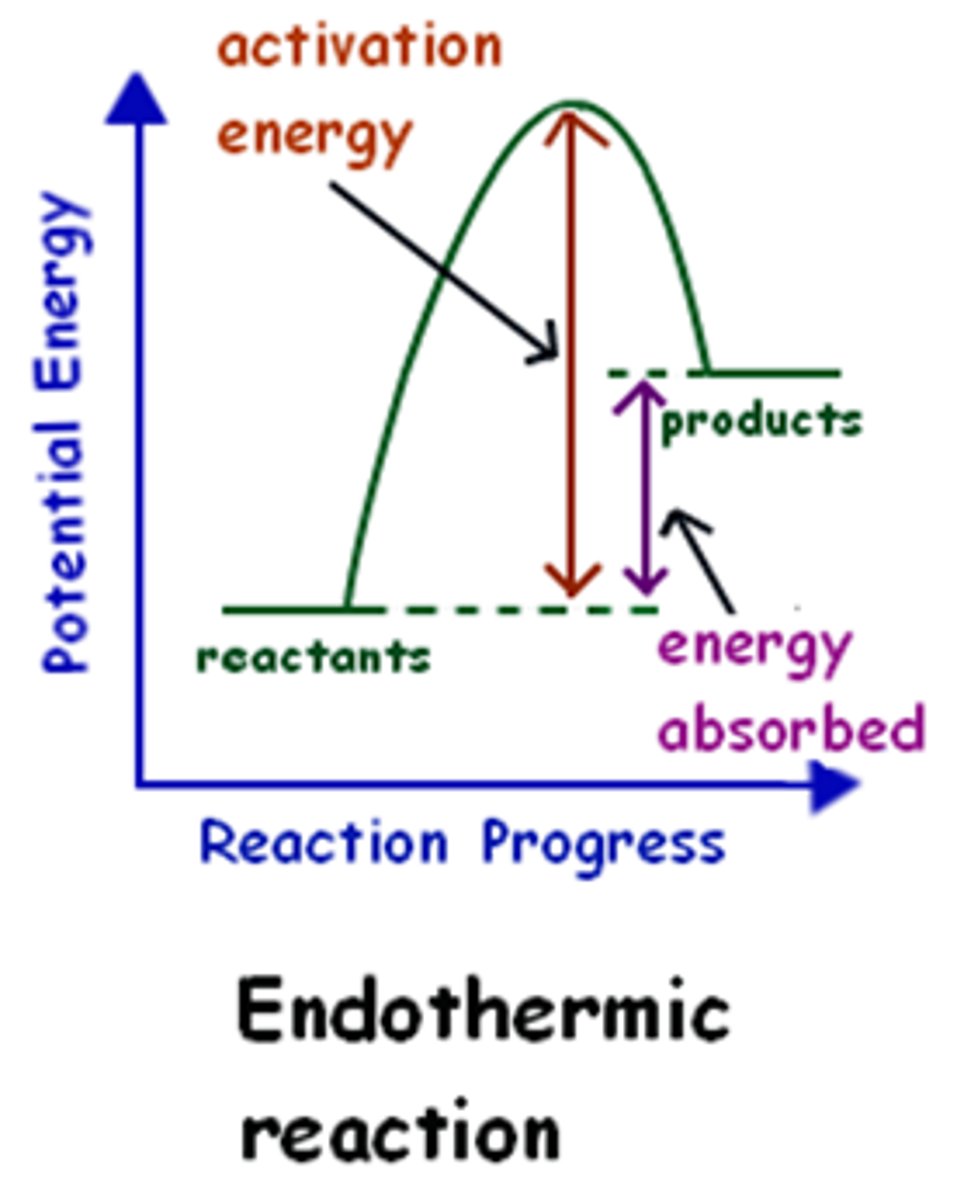
Endothermic Reaction
Absorbs energy, e.g., photosynthesis.
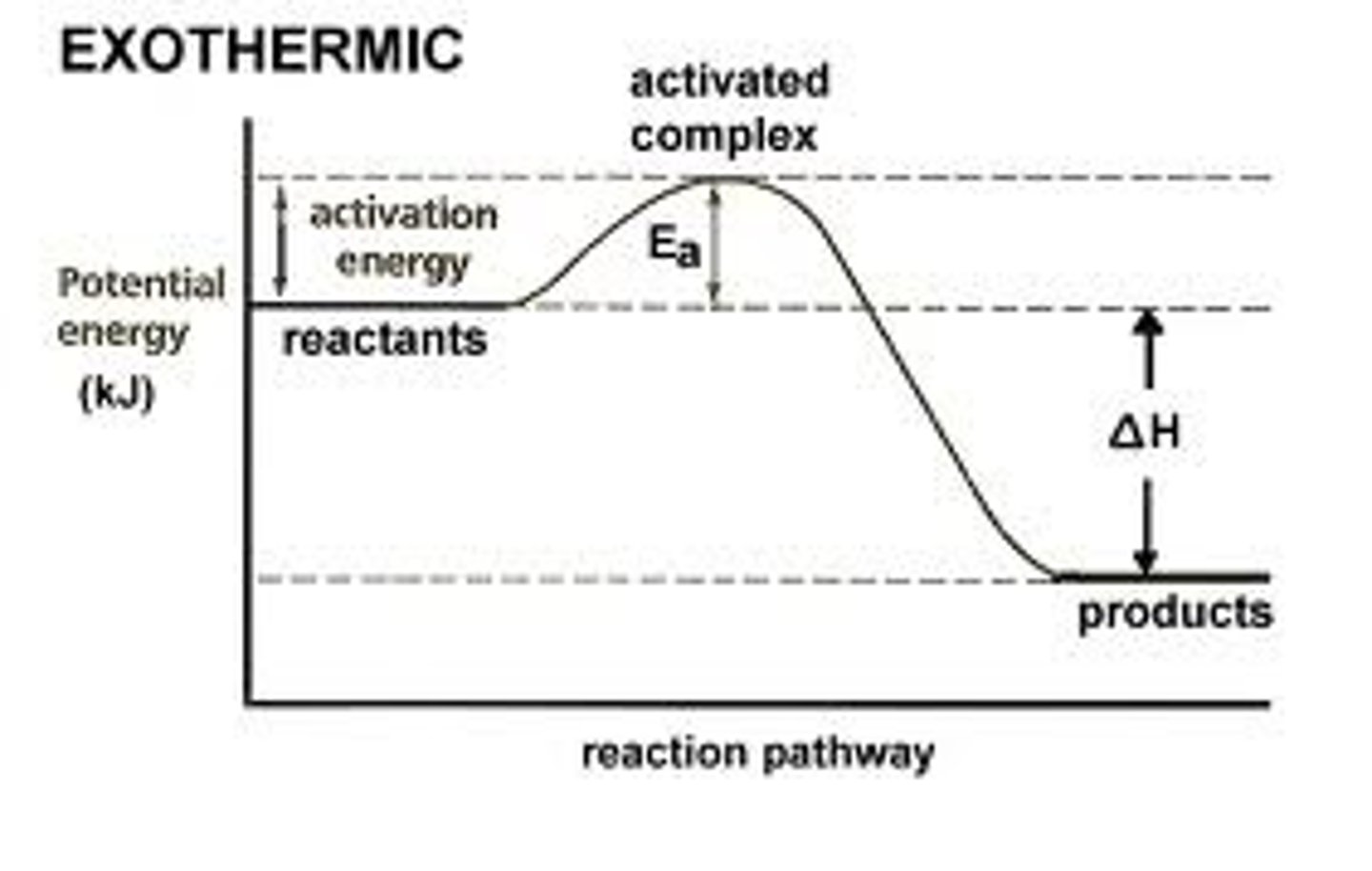
Exothermic Reaction
Releases energy, e.g., cellular respiration.
Photosynthesis
Converts CO2 and H2O into glucose using light.
Cellular Respiration
Converts glucose into ATP, releasing CO2 and H2O.
Enzymes
Proteins that speed up biochemical reactions.
Catalysts
Substances that accelerate reactions without alteration.
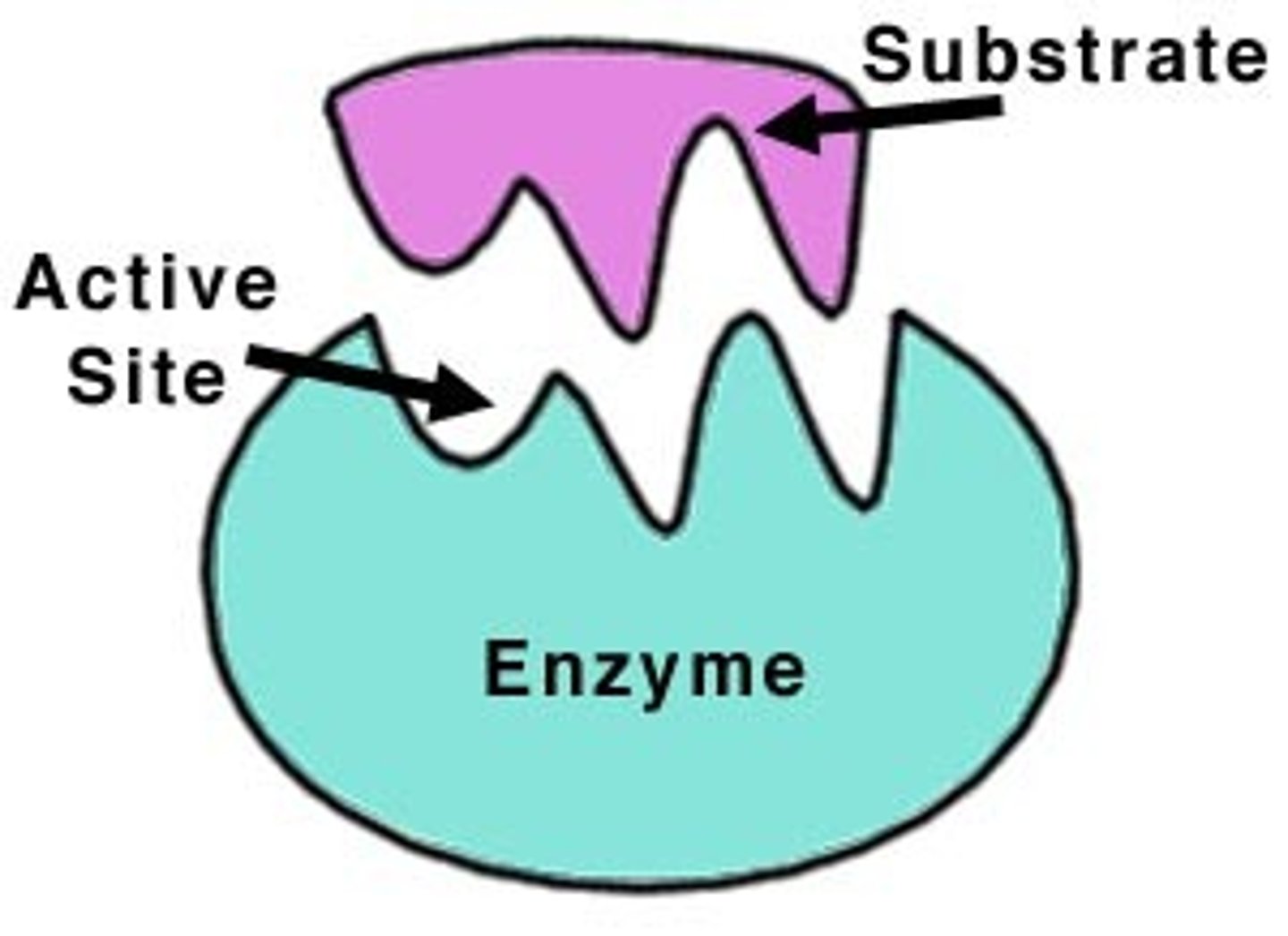
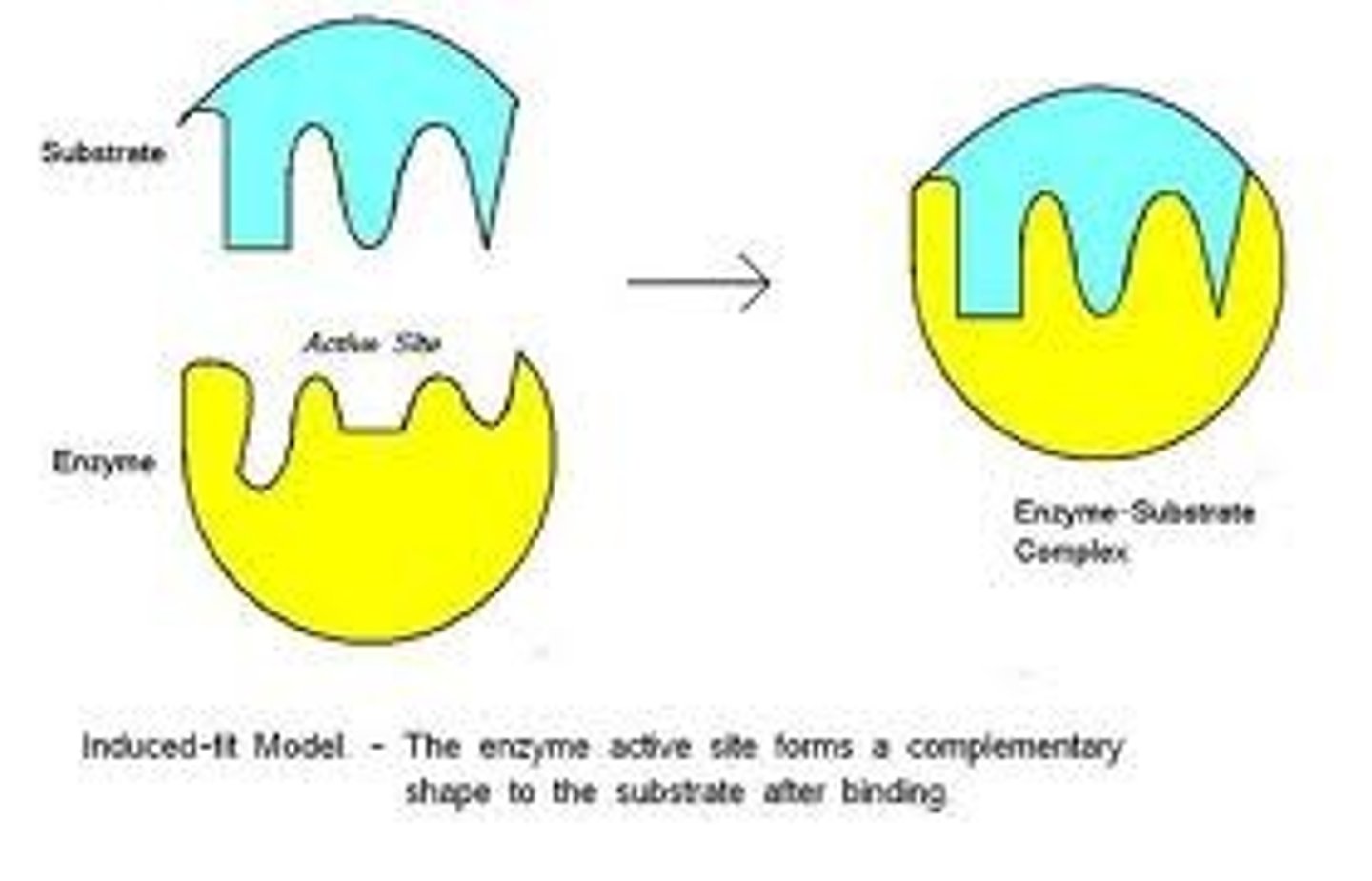
Active Site
Region on enzyme where substrates bind.
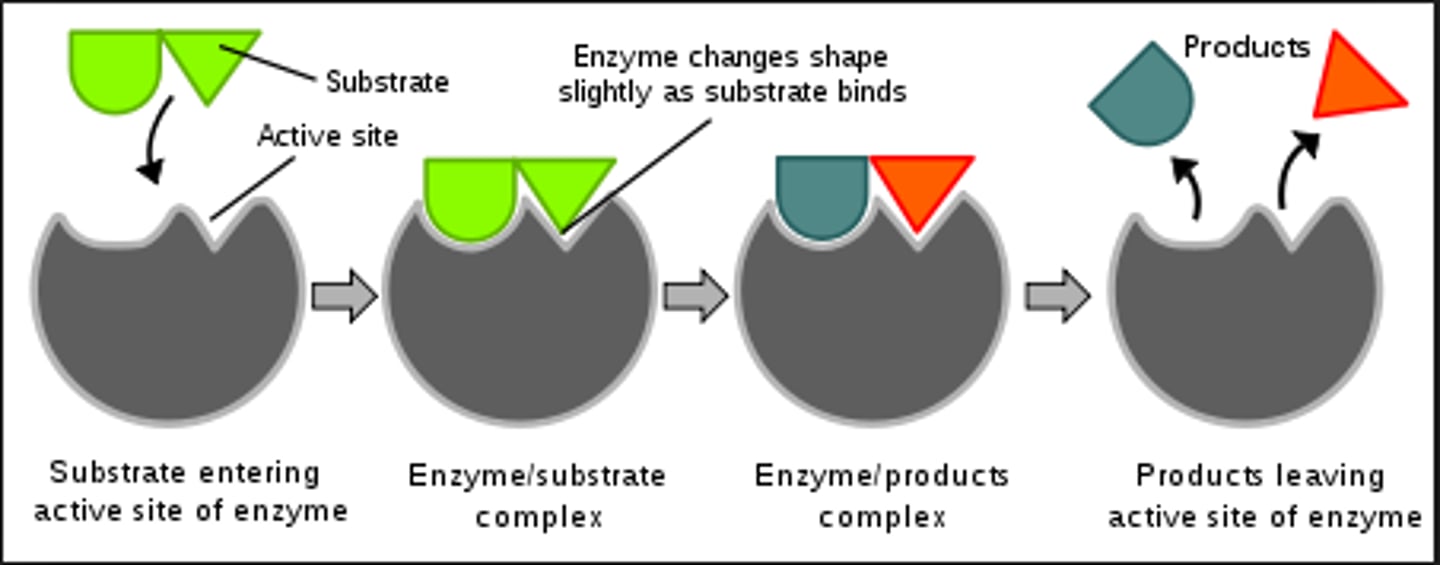
Induced Fit
Substrate binding alters enzyme shape for reaction.
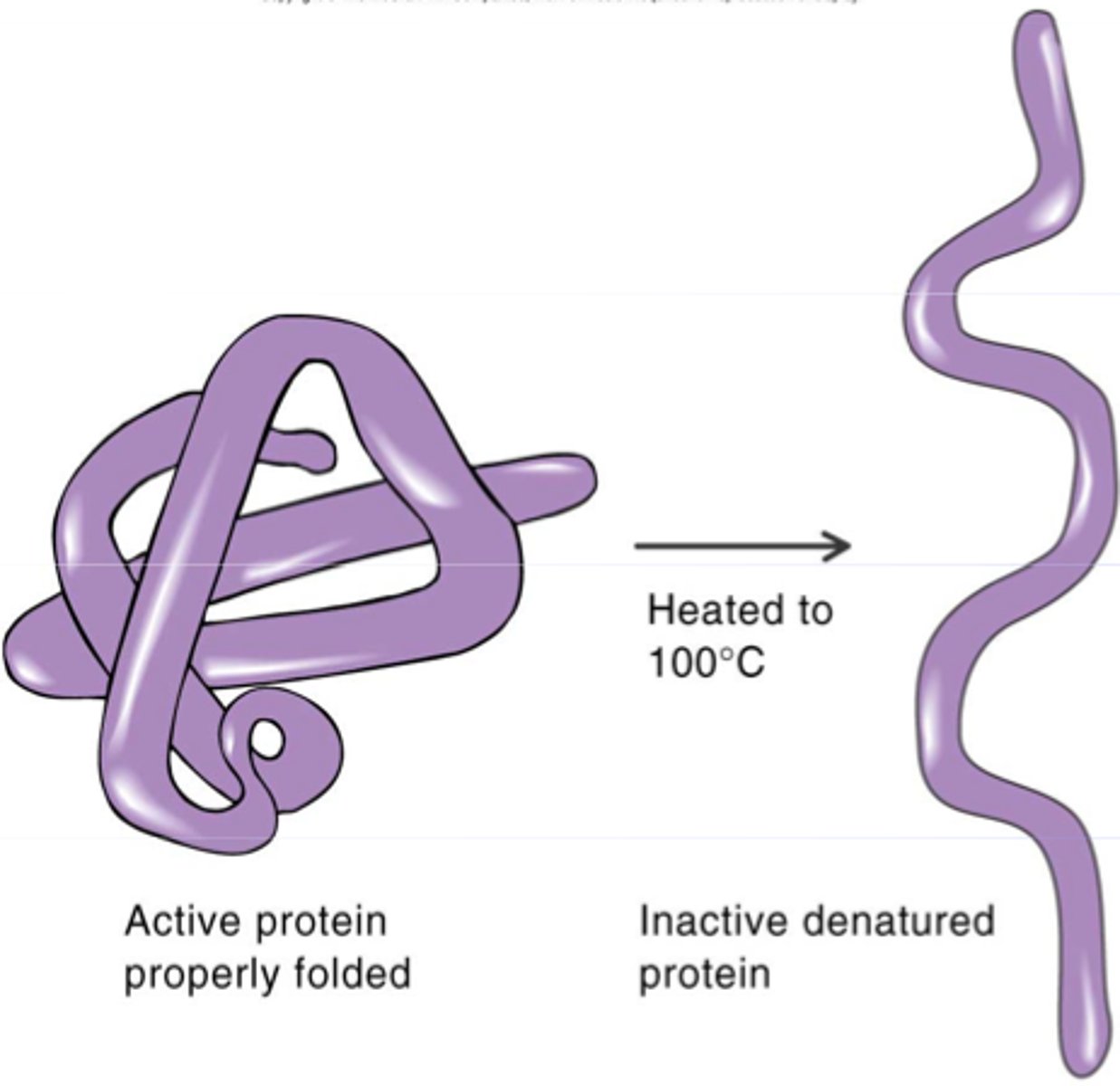
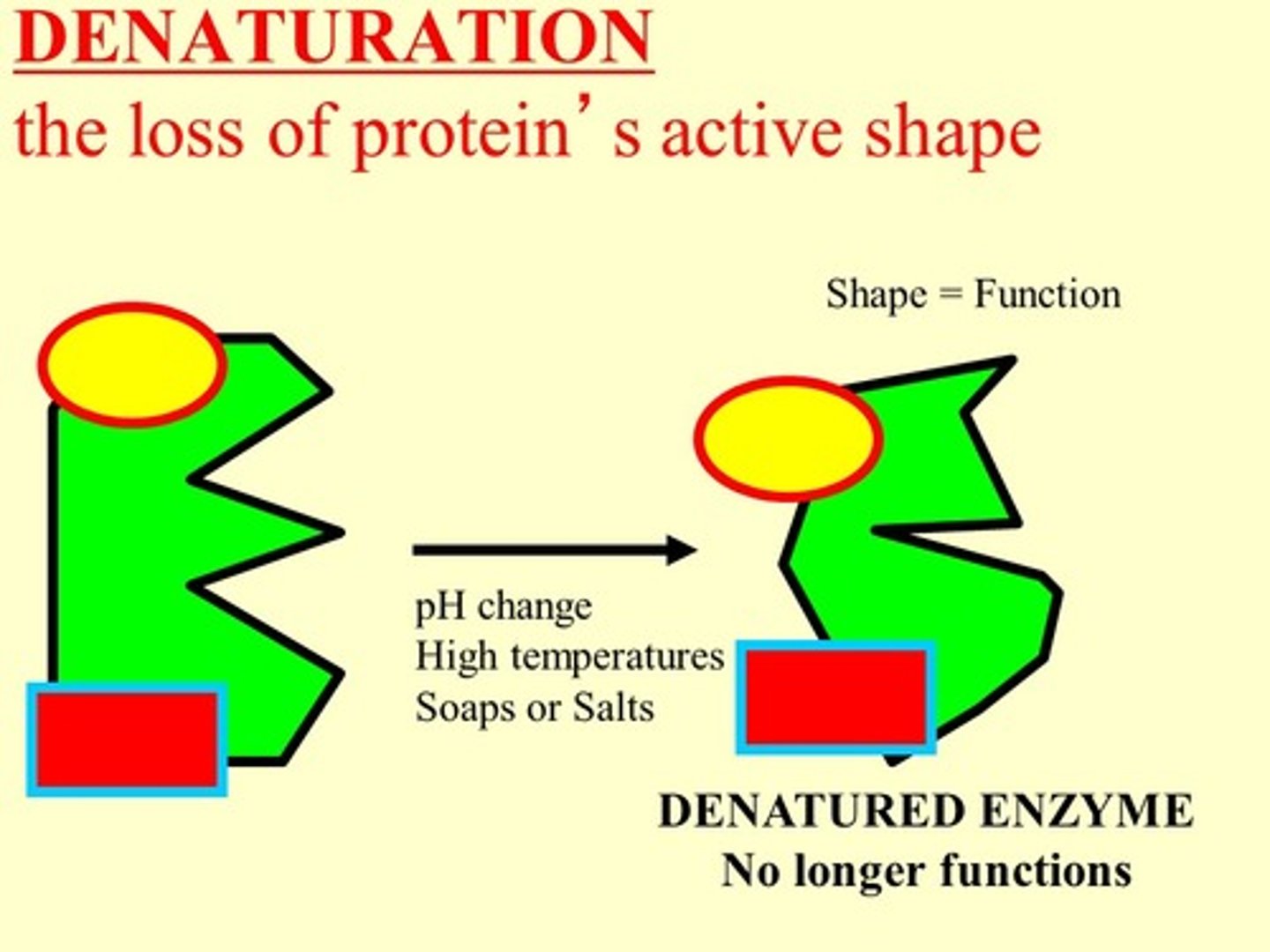
Denaturation
Loss of enzyme shape and function due to stress. It causes reduced activity.
Renaturation
Restoration of enzyme's original shape, not always possible.
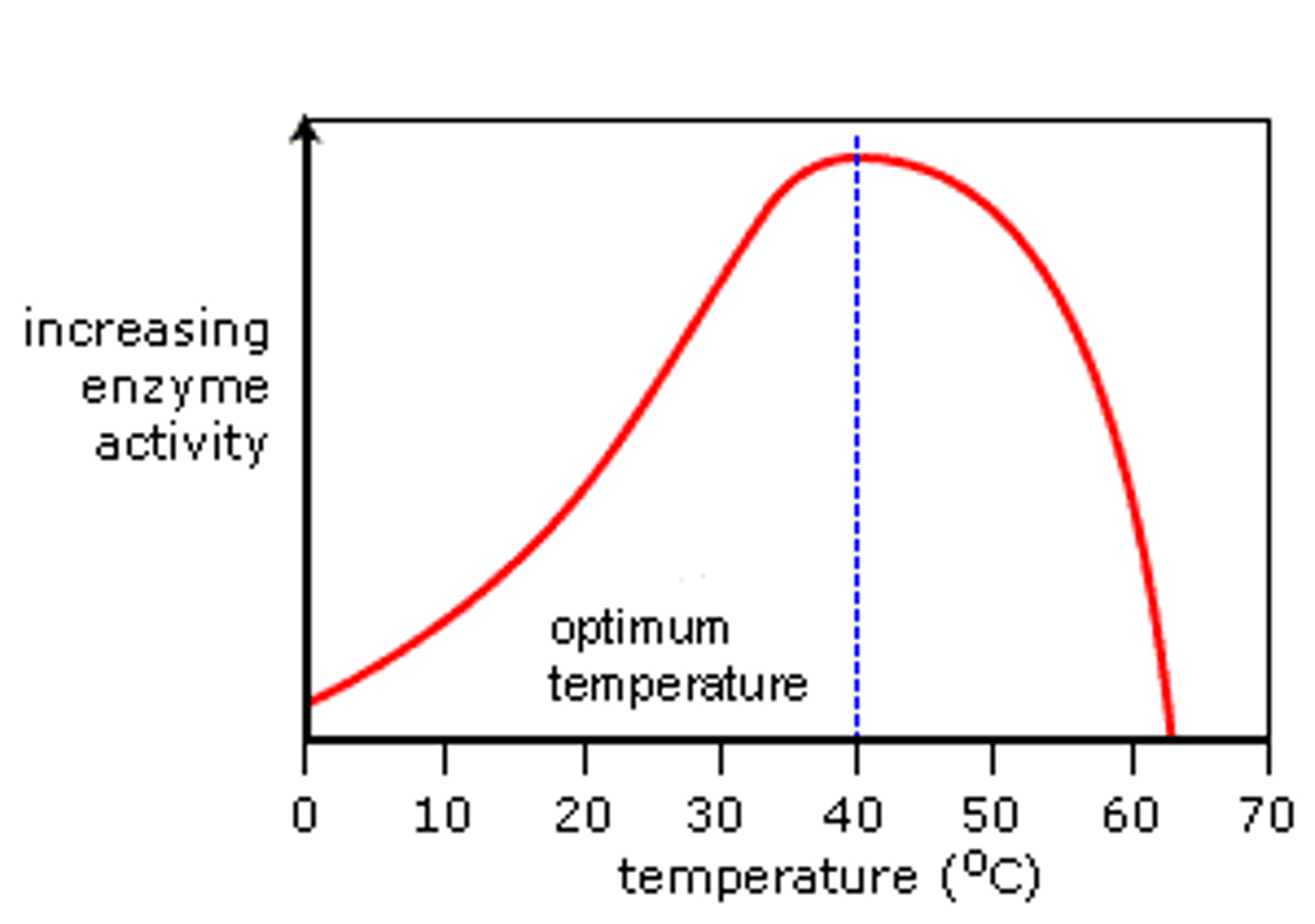
Temperature Effect
as the temperature increases kinetic energy increases, but if the temperature gets too high the protein denatures.
pH effect of the enzyme
Specific pH levels affect enzyme activity.
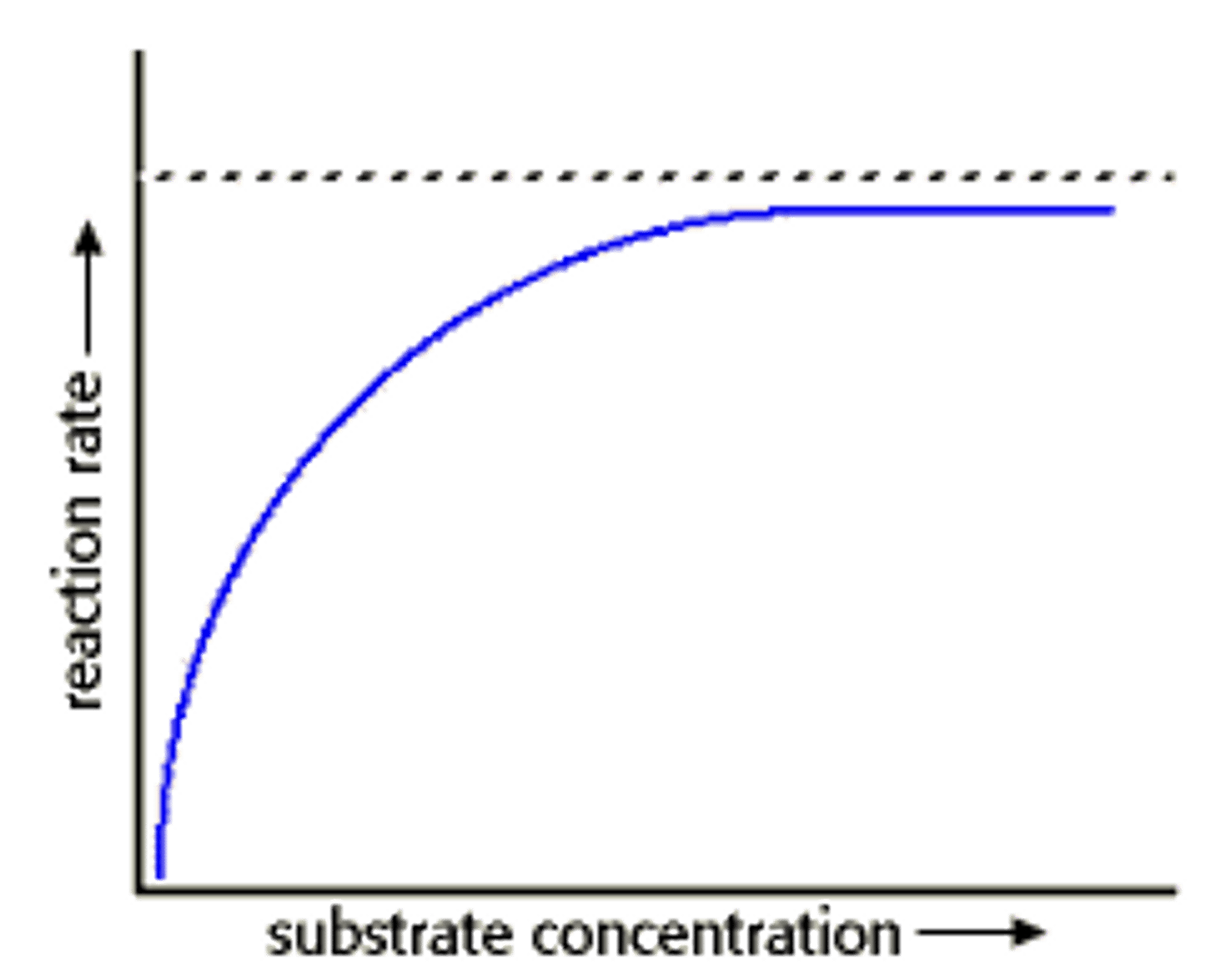
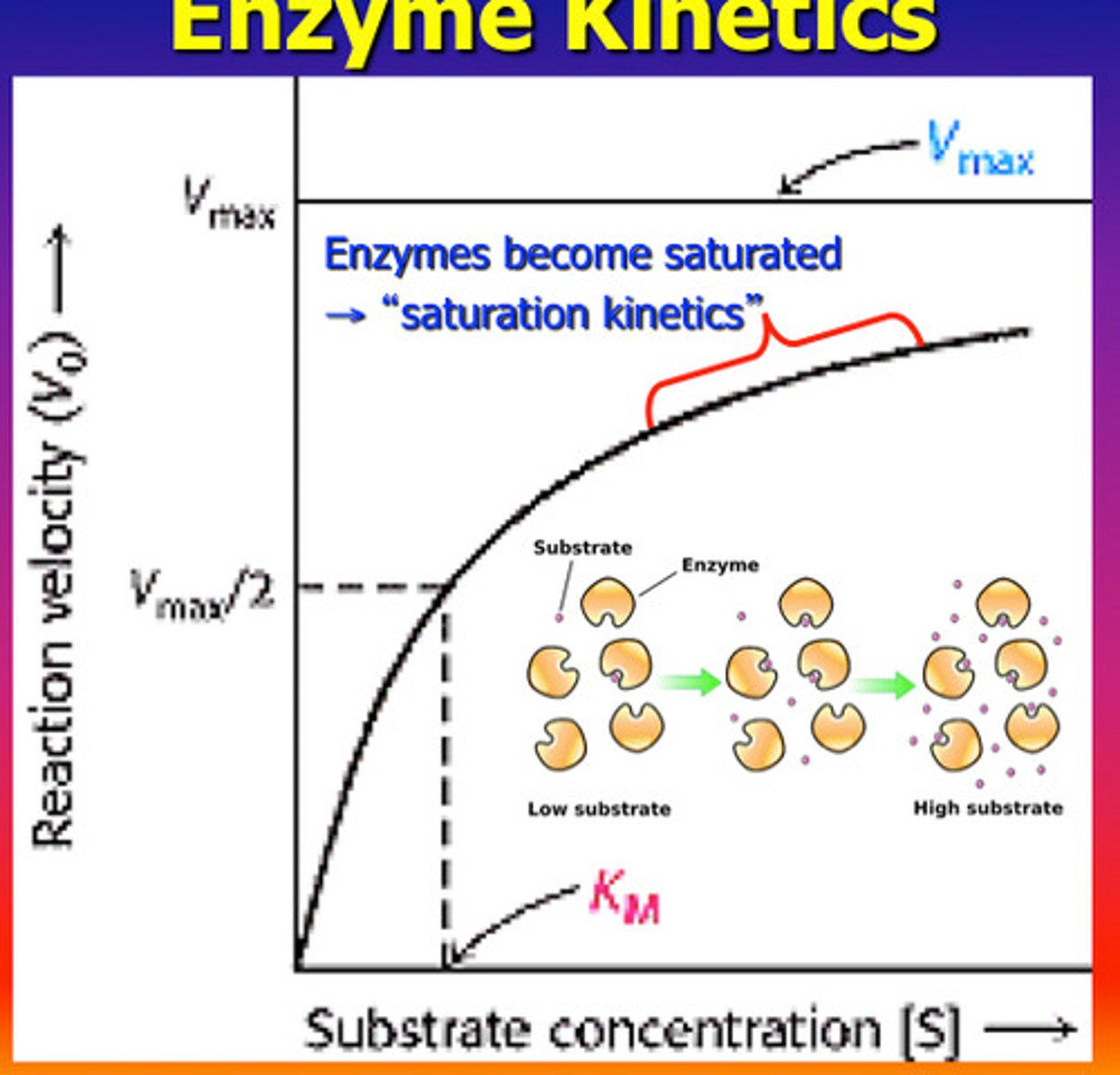
Substrate Concentration
Higher substrate levels increase reaction speed.
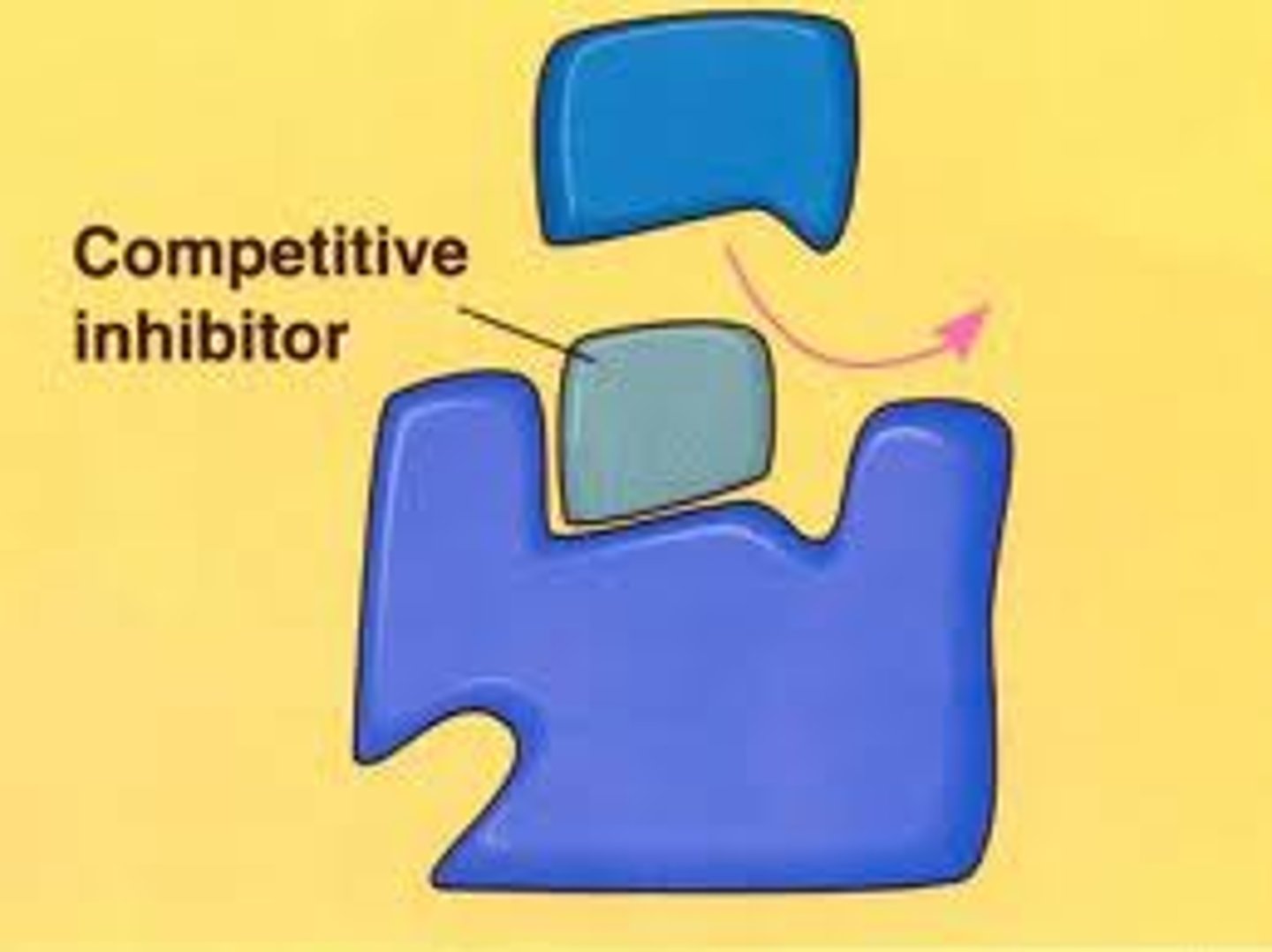
Competitive Inhibitor
Slows reaction by competing for active site.

Enzyme Saturation
when no matter how much substrate you add the enzyme is working at full capacity
Enzyme denaturation
When an enzyme loses it's shape and no longer fits the substrate, and does not function
activation energy
the minimum amount of energy required to start a chemical reaction