The periodic table
1/17
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What is an atom?
The smallest part of an element that can exist.
The chemical properties of each substance in the mixture is unchanged.
\
elemnts in the same group have the same number of electrons in their outer shell and this gives them similar properties.
* Hydrogen does not similarly react to the other metals in Group 1 (it does not react with water)
* hydrogen can form covalent bonds/ share electrons
* Hydrogen can form a negative ion /can gain an electron
* It can form an ion with A 1 plus charge
* It exists as a diatomic molecule; \[1 mark\]
* It forms covalent bonds/compounds; \[1 mark\]
* It is able to form H- ions; \[1 mark\]
* It has a low melting/boiling point; \[1 mark\]
* can conduct heat and electricity
* shiny
* malleable
* high density
* basic oxides
* does not conduct heat or electricity
* dull
* brittle
* low density
* acidic oxides
\
* Unreactive
* not easily form molecules because their atoms have stable arrangement of electrons
* Have 8 electrons in their outer shell, except for helium which has 2.
* very low melting and boiling points
\
\
* **boiling point increases with increasing relative atomic mass (**going down the group)
* as atoms get larger as you move down the group the intermolecular forces between the atoms increase, increasing the amount of energy needed to overcome this force.
What is group 1 and what are its properties.
Alkali metals.
forms alkaline solutions when they react with water. >ph 7
forms 1+ ions.
reactivity increases going down the group
outermost electrons get further away from the nucleus, so there are weak intermolecular forces of attraction between the outermost electron and the nucleus.
less energy is required to over come the force of attraction as it gets weaker, so the outer electron is lost more easily.
so, the alkali metals get more reactive as you descend the group.
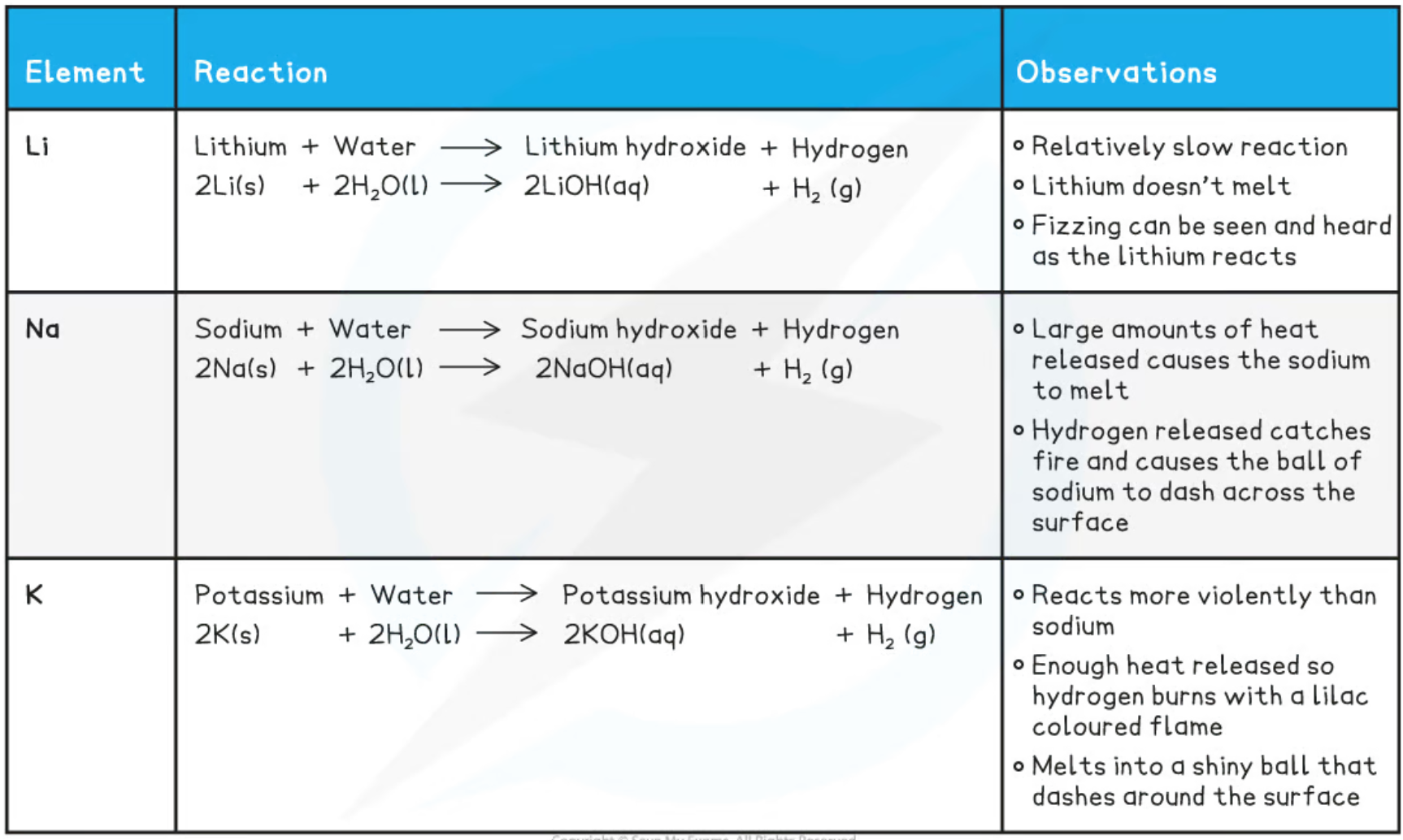
\n Describe the reactions of lithium (Li), sodium (Na) and Potassium(K) with oxygen.
4Li (s) + O 2(g) → 2Li2O (s)
4Na (s) + O2 (g) → 2Na2O (s)
4K (s) + O2 (g) → 2K2O (s)
The alkali metals react with oxygen in the air forming metal oxides, which is why the alkali metals tarnish when exposed to the air
The metal oxide produced is a dull coating that covers the surface of the metal
Describe the reactions of , lithium (Li), sodium, potassium with chlorine.
2Li (s) + Cl 2 (g) → 2LiCL(s)
2Na (s) + Cl2 (g) → 2NaCL (s)
2K (s) + Cl2 (g) → 2KCl (s)
All the group 1 metals react vigorously when heated with chlorine gas to form salts called metal chlorides
This reaction becomes more vigorous moving down the group, the same as with the reaction between the metals and water
* Non-metals
* consist of molecules made of pairs of atoms. (**diatomic)**
* forms 1- halide ions.
\
* the further down the group the higher the relative mass, melting point, and boiling point.
* due to increasing intermolecular forces as the atoms become larger, so more energy is required to overcome these forces
\
* Reactivity of group 7 non-metals **decreases** as you go down the group
* The number of shells of electrons increases
* but they need to gain one electron so
* an increased distance from the outer shell to the nucleus as you go down a group causes
* the forces of **attraction** between the nucleus and the outermost shell **decreases**