digestive system
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
purpose
breakdown and absorb food
take in food
digest food and water
break down a reabsorb
eliminate solid waste product
increase surface area by mechanical breakdown
chewing and mixing
convert to simple molecules via enzymes
large surface area of digestive tract with folds, projections
digestion
mechanical and chemical breakdown of food
resorption
absorption from intestinal epithelium to blood stream
one long muscular tube from mouth to anus
lumen is outside the body
monogastrics
simple non-ruminant mammalian
humans, pigs, mink
avian
simple non-ruminant
chickens, pigeons
foregut fermenter
ruminant
non-ruminant
hippo
hindgut fermenters
cecal fermenter
rabbit
caeco-colic fermenters
horses, elephants
oral cavity
fuction = parts
prehension
acquisition of food
lips, tongue, teeth, hands, split lip
teeth
helps decrease food size by grinding and cutting
types
incisors
biting off, cutting, front teeth
canines
tearing, sharp
premolars
grinding
molars
grinding
ruminants
rough dental pad instead of incisors
horses
sharp incisors to grab forage
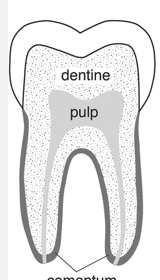
tooth anatomy
3 hard substances
enamel
outermost, white, very hard, calcium and phosphorus
cementum
middle, born, acts as the glue, connective tissues, bind tooth root to gum
dentin
yellow, calcified tissue, odontoblasts
pulp cavity
blood and nerve supply
crown
above gumline
socket
unique joint called gomphosis
brachydont
low crown
all carnivores
stop growing after eruption
pulp cavity in middle
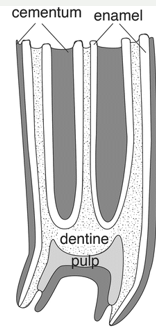
hypsodont
high crown
equine
continues to grow
pulp cavity does not extend above gumline
tongue
skeletal muscle in bundles
moves in three different directions
keratinized stratified squamous
papillae on dorsal surface
fungiform
taste buds
filiform
spikes, rough, traction for food
moist stratified squamous on ventral surface, no papillae
salivary glands
several pairs located on head and neck, under tongue
parotid, mandibular/submandibular, sublingual, zygomatic
contain amylase
starts chemical digestion of starches, contains buffer
mucous
thick, serous, or mixed
ducts empty saliva into oral cavity to lubricate food for chewing and swallowing
mastication
chewing
first mechanical breakdown
jaws, cheeks, tongue
salivary amylase
some chemical digestion of scratch to simple sugars
herbivores and omnivores
pharynx
a space, not an organ
swallowing
closes epiglottis over glottis to keep food and salvia out of larynx and trachea and sending it into esophagus
reflex triggered by food moving into pharynx
can be conscious
esophagus
muscular tube from pharynx to stomach
skeletal and or smooth muscles depending on species and area
lays flat, very muscular
will expand and layers wills trach
luman enclosed with folds
simple stomach = monogastric
abomasum of ruminant similar
enlarged area at end of esophagus just caudal to diaphragm
glandular types determine regions
gastric folds
rugae
esophageal region
Only significant in herbivores
No glands
Lined with keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Mixing, regurgitation
Ruminant forestomach and other foregut fermenter pouches = esophageal region
cardia region
Near heart and near esophageal junction, most cranial
Not glandular, but has some non-complicated mucous glands protection from acid
fundus region
body
deep gastric pits.glands
most of secretion
3 cells
3 cells
mucous cells
produce mucus
protection from acid
chief cells
produce inactive pepsinogen
proteolytic enzymes precursor
parietal cells
produce HCl
lowers pH of stomach to as low as 1.5
kills bacteria
drops to proper pH to turn inactive pepsinogen to active pepsin
breaks down protein
pylorus region
Pyloric sphincter joins stomach to small intestine
Dictates how much foodstuff enters the duodenum
Glands produce
mucous, HCl, pepsinogen, and G cells
gastrin
Stimulates HCl release when food present
herbivore specializations
foregut fermenters
Microbes ferment plant material prior to rest of GIT
Ruminants have 4 compartments
Camelids: 3 compartments
Kangaroo: pouches cranial to rest of stomach
rumen
large fermentation vat
left side of animal
papillae
symbiotic relationship with bacteria and protozoa
cellulase to degrade cellulose
microbes’ products absorbed
microbes digest in rest of GIT
reticulum
honeycomb stomach
Food moves back and forth
forms the bolus
“chewing the cud”
Most cranial, nearest to the heart
Esophageal opening dorsally
Continuation of rumen, liquid contents
Metal may get stuck here
hardware disease (reticulopericarditis)
omasum
Layers look like a book
Increased surface area
Layers of muscle and mucosa
Sorting, grinding filtering
Reabsorption of water
Regulates passage on by particle size
abomasum
True stomach
Secretes HCl and enzymes, similar to monogastric stomach
Right side
esophageal groove
Muscular ridged groove through reticulum, omasum to abomasum
Closes in young ruminant with action of suckling to become a tube
Milk to abomasum for digestion, not fermentation
Bypasses the rumen
duodenum
First part or SI, joins stomach
Pancreas lies in 1st loop and secretion enters along with bile from gallbladder and liver
Pancreatic and common bile ducts
Enzymatic digestion occurs here
Simple columnar epithelium
1 layer thick
Many submucosal and mucosal glands
digestive enzyme production
jejunum
Middle part
Largest and longest part
Longest villi
Simple columnar epithelium
Most final digestion and absorption of nutrients occurs here
Many mucosal and submucosal glands
ileum
Final part, joins to large intestine
Smallest part
Absorption of nutrients, little digestion
Shorter villi
Lymphatic nodules in mucosa and submucosa
Peyer’s patches
Increased goblet cells
mucous
surface area
Digestive and absorptive function made possible by the large surface area
Villi – small projections of the small intestinal mucosa
Each villus is lines with single layer of cells enterocytes
Absorption of nutrients take places across the surface of villi
Goblet cells
produce and secrete mucus
Protects the intestinal lining
provides lubrication
Microvilli
projections from each villi
Glycocalyx
filamentous fuzzy projections off of microvilli
Trap nutrients
large intestines
No true villi
Large folds and projections/pockets
Haustra
Fermentation by microbes
Absorbs water, water soluble things
Microbial products such as vitamins, VFAs
Parts:
cecum, colon, rectum, anus
cecum
Blind pouch where ileum and colon meet
Fermentation
Presence, size depends on species
None in mink, very large in horse and rabbits
Human appendix is extension off short cecum (vestigial)
Birds have 2
colon
Length depends on species
Carnivores: Short colon
Spiral colon in pigs, ruminants, camelids
Dorsal and ventral colons in horses
Ascending, transverse and descending in humans, some other mammals
Very short in mink
Rectum
Final part of large intestine
Primarily a holding area for undigested “waste” as feces
Some water absorption
Anus
2 layers: external and internal
Smooth and skeletal muscle sphincter
Changes to skeletal muscle for control of sphincter
Opening is reflex triggered by feces in the rectum, can also be by conscious control
herbivore specializations
hindgut fermenters
Microbes ferment plant material near end of GIT in large intestine (colon and cecum)
All animals do some hindgut fermentation, even carnivores
Cecal fermenters (rabbit)
Caeco-colonic fermenters (Horses, elephant)
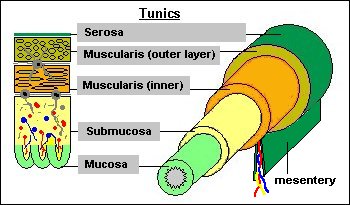
tubular digestive tract
tunica serosa
tunica muscularis
tunica submucosa
tunica mucosa
accessory organs
liver
gallbladder
pancreas
liver
just caudal to diaphragm
organized into lobes grossly, lobules microscopically
Produces bile (from hepatocytes)
Stores glucose as glycogen
Filters blood
Organized into lobes (lobules microscopically)
Lobules
hexagonal with 3 structures: portal triad
Hepatic portal vein, hepatic artery, bile duct
Canaliculi
very small bile ducts
blood flow in the liver
Portal system: bypasses general circulation
Blood comes to the liver from hepatic portal vein and hepatic artery
Hepatic portal vein:
from stomach and intestines, contains nutrients
Hepatic artery:
coming from celiac artery from aorta, contains oxygen
Hepatocytes process nutrients, “detoxify” blood as it runs through sinusoids
Bile is produced in liver by hepatocytes to aid in fat digestion
It runs through canaliculi to bile ducts in portal areas which join larger bile ducts until they run into the common bile duct to the duodenum
gallbladder
animals without
rats, camelids, horses
stores and concentrate bile from liver
cystic duct from gallbladder
joins common bile duct from liver to gallbladder and duodenum
lined with simple columnar
pancreas
2 roles
Endocrine
Islets of Langerhans
Lighter colored circular areas of cells
Produce insulin and glucagon for blood glucose utilization
Exocrine
Rest of pancreas (darker)
Produces digestive enzymes, mucus and bicarbonate through pancreatic duct into duodenum