Chapter 6 - Interpretation of an EKG Strip
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Incorrect Interpretation
A quick glance at a strip will often lead to an:
Step 1: Heart rate
Step 2: Heart rhythm
Step 3: P wave
Step 4: PR interval
Step 5: QRS complex
Five-Step Approach
Heart Rate
Five-Step Approach: Step 1
Heart Rhythm
Five-Step Approach: Step 2
P wave
Five-Step Approach: Step 3
PR interval
Five-Step Approach: Step 4
QRS complex
Five-Step Approach: Step 5
Five-Step Approach: Step 6
Counting the PQRST complexes conducted through the myocardium in 60 seconds
Heart Rate as the first step in the Five-Step approach is counting the number of electrical impulses by:
Counting the P waves
Counting the Atrial Rate on the EKG
Counting the number of QRS complexes noted
Counting the Ventricular rate on the EKG
Count the number of QRS complexes that occur within a 6-sec interval, and multiply by 10.
The Six Second Method:
Look at Q R S complex that falls on a heavy line on the strip, count number of large boxes between this R wave and the next R wave and divide this number by 300
The R-R interval Method:
Rhythm
Sequential beating of the heart as a result of the generation of electrical impulses:
Regular pattern
Intervals between R waves are regular
Irregular pattern
Intervals between R waves are not regular
0.06 sec or 1.5 small boxes
If the intervals vary by less than ___ seconds or ___ small boxes, we can consider the rhythm to be regular
Regularly irregular
Irregular rhythms that occur in a pattern
Occasionally irregular
Intervals of only one or two R to R are uneven
Irregularly irregular
R to R intervals exhibit no similarity
the atria depolarize
P wave is produced when:
Rounded and upright
The P wave should be:
S A node pacing or firing
P wave is the:
Sinus Rhythm
The P Wave pattern is referred to as a:
Step 1: Are P waves present?
Step 2: Are P waves occurring regularly?
Step 3: Is there one P wave present for each Q R S complex present and/or is there a Q R S for each P wave present?
Step 4: Are the P waves smooth, rounded, and upright in appearance, or are they inverted?
Step 5: Do all P waves look similar?
Five Questions to ask with the P Wave:
time interval from the onset of atrial contraction to onset of ventricular contraction
The PR interval measures:
from onset of P wave to the onset of the Q R S complex
The PR interval on the EKG appears from:
0.12-0.20 sec (3-5 small squares)
Normal PR interval:
1. Are P R intervals greater than 0.20 sec?
2. Are P R intervals less than 0.12 sec?
3. Are the P R intervals constant across the E K G strip?
P R Interval: Three Questions to Ask
Depolarization and contraction of the ventricles
The QRS complex represents:
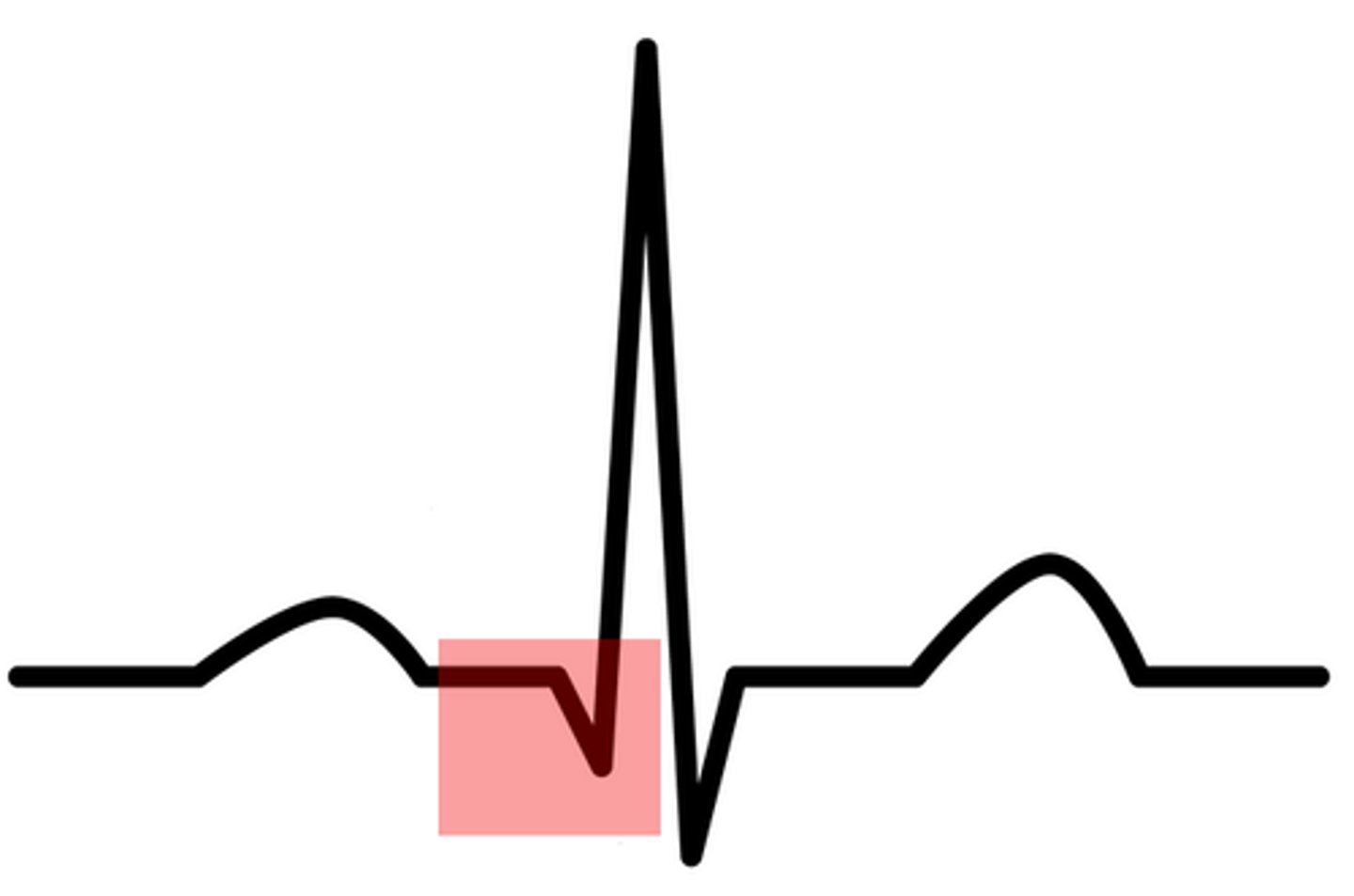
Q wave
First negative or downward deflection of this large complex
R wave (tallest waveform)
First upward or positive deflection following the P wave
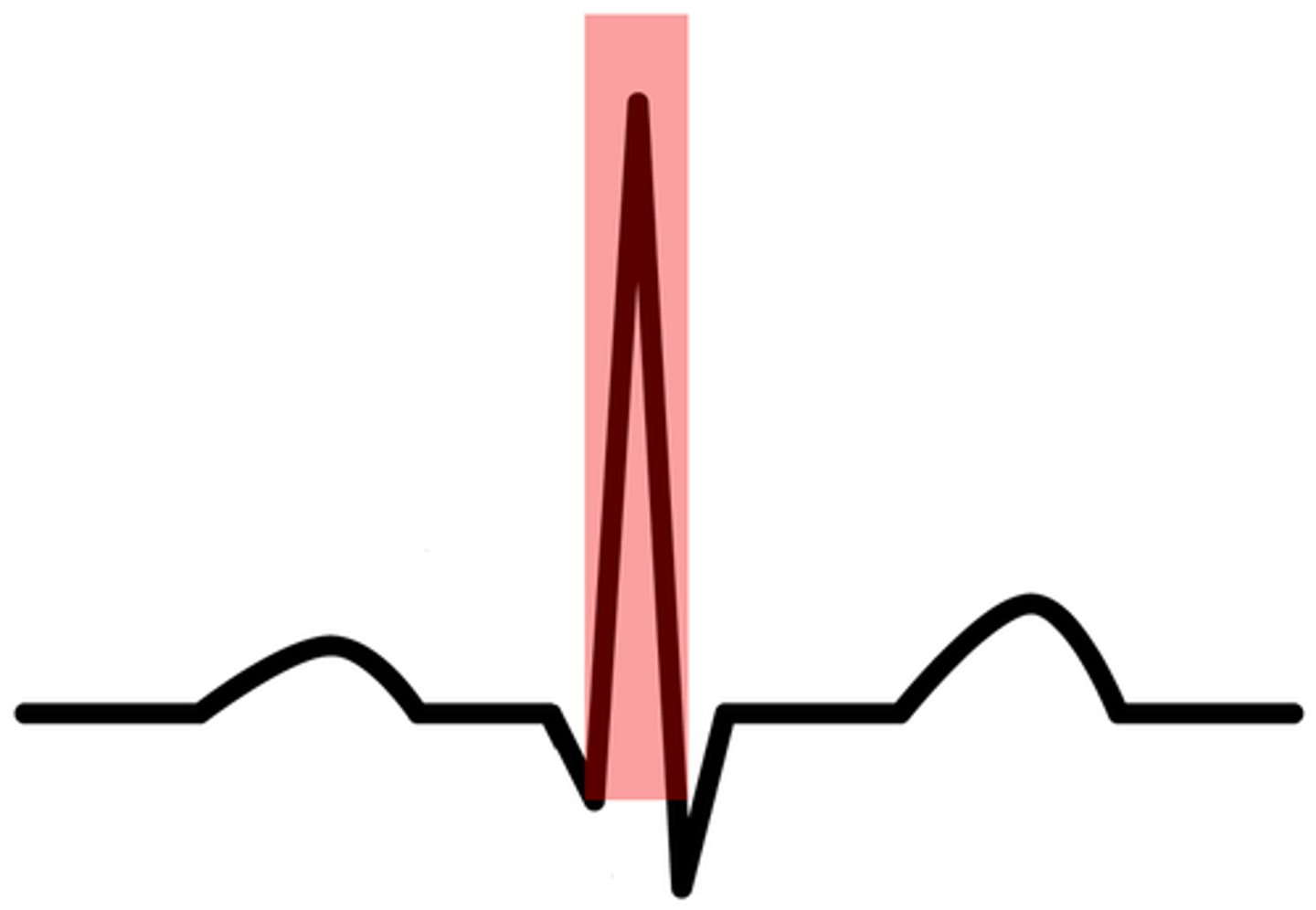
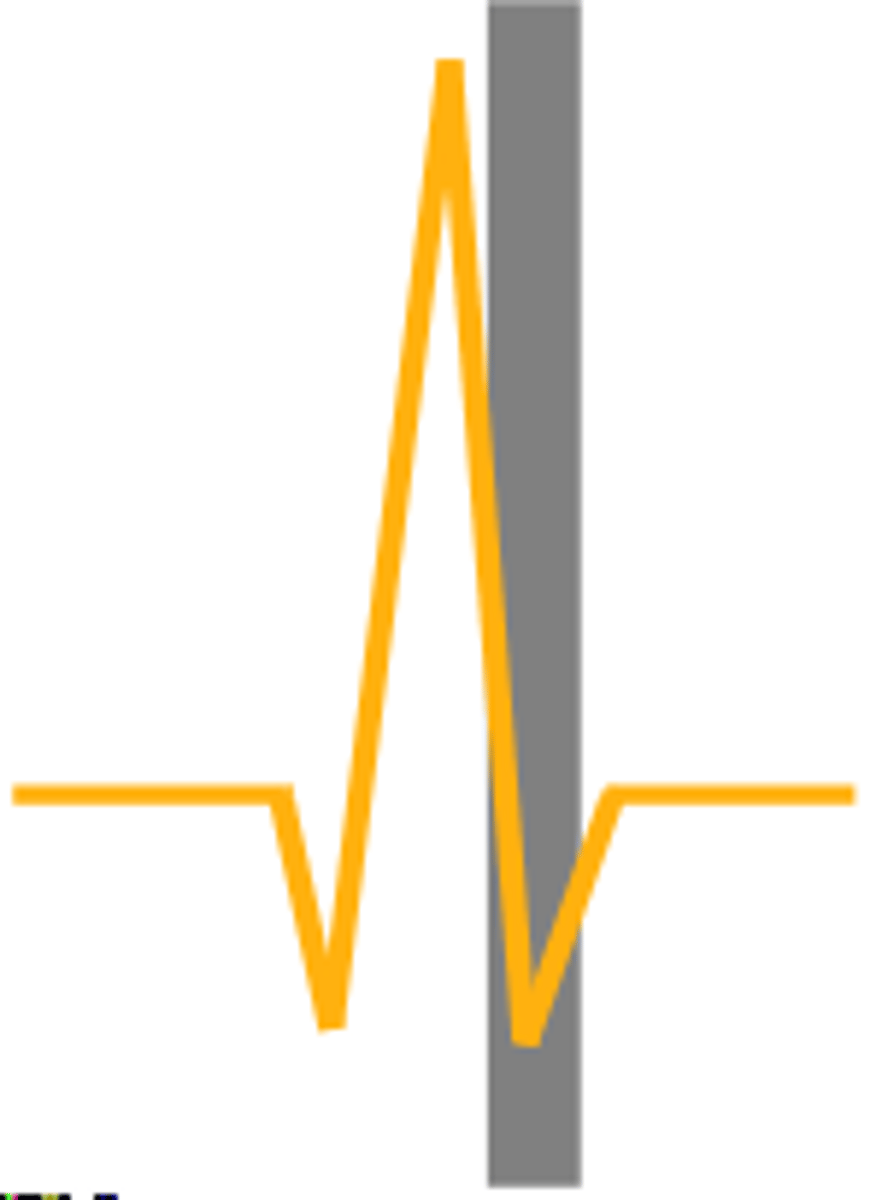
S Wave
The sharp, negative, or downward deflection that follows the R wave

1. Are Q R S intervals greater than 0.12 sec (wide)?
2. Are Q R S intervals less than 0.12 sec (narrow)?
3. Are the Q R S complexes similar in appearance across the E K G strip?
Q R S Complex: Three Questions to Ask
ST Segment
Begins with the end of the Q R S complex and ends with the onset of the T wave (consistent with isoelectric line)
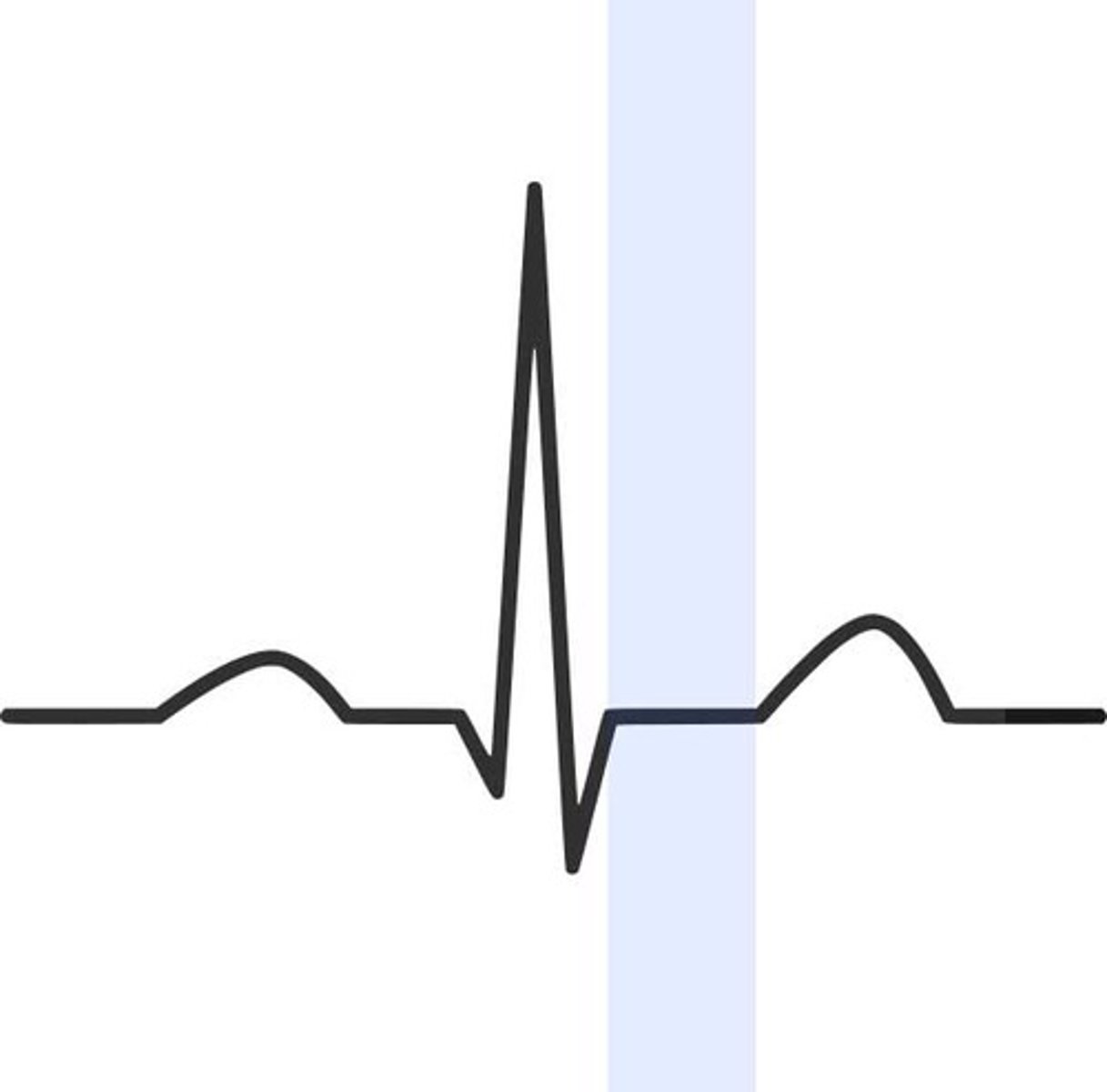
J-Point
Point at which the Q R S complex meets the S T segment
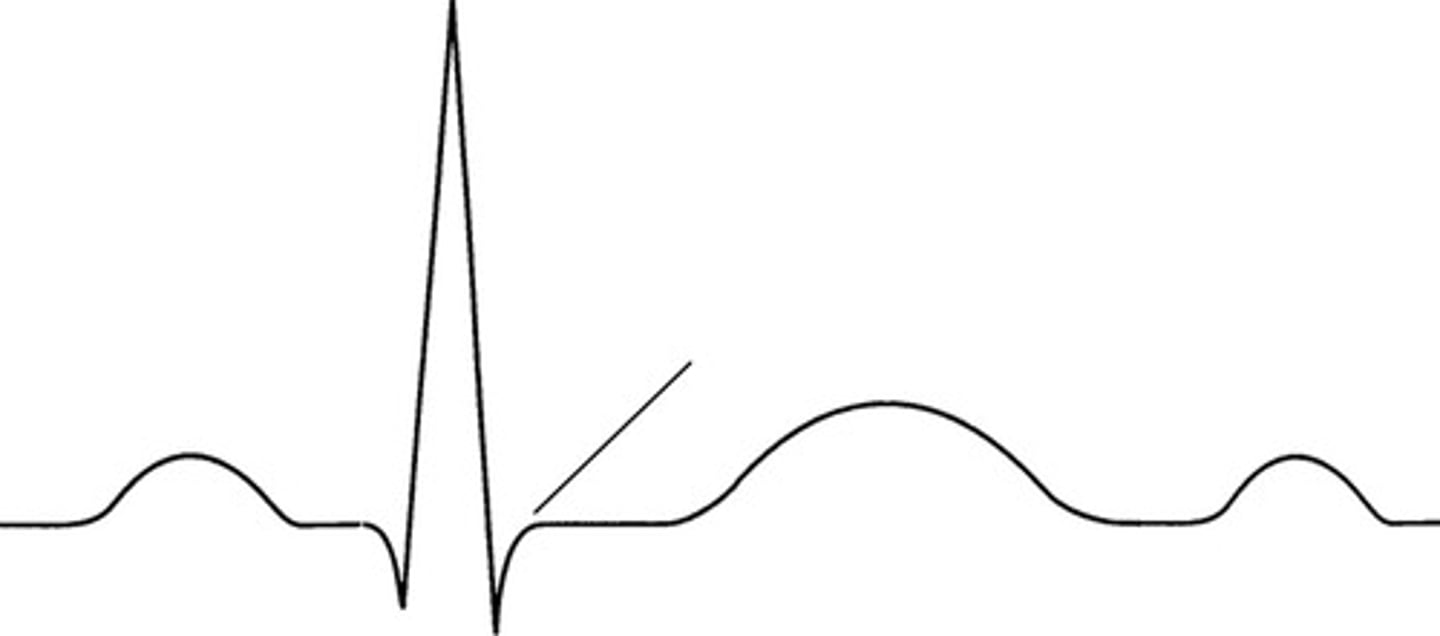
myocardial ischemia or injury may be indicated
If S T segment is elevated or depressed:
T Wave
the first upward or positive deflection following the Q R S complex
ventricular repolarization or relaxation
T Wave represents:
U wave
May appear after the T wave, usually not easily visible on EKG strips, appearing as a rounded or positive deflection, smaller than the T Wave
Hypokalemia or hyperthyroidism
A prominent U wave may represent:
Artifact
E K G waveforms from sources outside the heart
- Patient movement
- Loose or defective electrodes (fuzzy baseline)
- Improper grounding (60-cycle interference)
- Faulty E K G apparatus
Four causes of EKG artifact: